- Manuals
- Brands
- Isuzu Manuals
- Engine
- 4HK-1
- Manual
-
Bookmarks
Quick Links
Isuzu
4HK-1 and 6HK-1
ENGINE
FUEL SYSTEM
CE APPLICATIONS
Revised 8/29/06
Form Number 5137
1
Related Manuals for Isuzu 4HK-1
Summary of Contents for Isuzu 4HK-1
-
Page 1
Isuzu 4HK-1 and 6HK-1 ENGINE FUEL SYSTEM CE APPLICATIONS Revised 8/29/06 Form Number 5137… -
Page 2
Table Of Contents… -
Page 3
These engines also use an air to air aftercooling intake air system. The air to air intake system ports pressurized air flow between the turbocharger and the intake manifold through an air to air heat exchanger in front of the radiator. The 4HK-1 model has a displacement of 317 cubic inches (in ) or 5193 cubic centimeters (cc). -
Page 4
Isuzu 4HK-1 and 6HK-1 Engine Overview The electronic control system for the Isuzu 4HK-1 and 6HK-1 Engines use input information from a number of sensors and from the Excavator controller to determine the quantity and timing of the fuel delivery to the engine. -
Page 5
Isuzu 6HK1 Common Rail Engine Fuel System Common Fuel Temp Coolant Intake Air Boost Temp Barometric ENG Oil Engine Stop Rail Fuel PSI Sensor Temperature Temp. Sensor Sensor AMB PSI Switch Sensor Sensor Sensor Sensor Boost PSI Crankshaft Camshaft Sensor… -
Page 6
90° on the gear and one reference hole) on the camshaft gear flange surface on the 4HK-1 Engine. Seven through holes (six holes arranged equally every 60° on the gear and one reference hole) on the camshaft gear flange surface on the 6HK-1 Engine. -
Page 7
Isuzu 6HK1 Common Rail Engine Fuel System Common Fuel Temp Coolant Intake Air Boost Temp Barometric ENG Oil Engine Stop Rail Fuel PSI Sensor Temperature Temp. Sensor Sensor AMB PSI Switch Sensor Sensor Sensor Sensor Boost PSI Crankshaft Camshaft Sensor… -
Page 8
Isuzu 4HK-1 and 6HK-1 Engine Overview (continued) Inputs to 81 pin engine harness connector: • The 2 wire intake air temperature (IAT) sensor is installed on intake air tube and detects the temperature of intake air for optimum fuel injection control. -
Page 9
Isuzu 6HK1 Common Rail Engine Fuel System Common Fuel Temp Coolant Intake Air Boost Temp Barometric ENG Oil Engine Stop Rail Fuel PSI Sensor Temperature Temp. Sensor Sensor AMB PSI Switch Sensor Sensor Sensor Sensor Boost PSI Crankshaft Camshaft Sensor… -
Page 10
Isuzu 4HK-1 and 6HK-1 Engine Overview (continued) Inputs to 81 pin engine harness connector: (continued) • The CAN (Controller Area Network) Data Bus Connector transmits communication between the engine controller and the Excavator controller. This connector transmits throttle, idle up/down, work mode, breaker mode, tachometer, instrumentation and fault code information. -
Page 11
Isuzu 6HK1 Common Rail Engine Fuel System Common Fuel Temp Coolant Intake Air Boost Temp Barometric ENG Oil Engine Stop Rail Fuel PSI Sensor Temperature Temp. Sensor Sensor AMB PSI Switch Sensor Sensor Sensor Sensor Boost PSI Crankshaft Camshaft Sensor… -
Page 12
Isuzu 4HK-1 and 6HK-1 Engine Overview (continued) Outputs from 40 pin engine harness connector: (continued) • The injectors are controlled by the engine control module (ECM). The ECM sends a common power supply to injectors 1, 3 and 5. The ECM also sends a common power supply to injectors 2, 4 and 6. -
Page 13
Isuzu 6HK1 Common Rail Engine Fuel System Common Fuel Temp Coolant Intake Air Boost Temp Barometric ENG Oil Engine Stop Rail Fuel PSI Sensor Temperature Temp. Sensor Sensor AMB PSI Switch Sensor Sensor Sensor Sensor Boost PSI Crankshaft Camshaft Sensor… -
Page 14
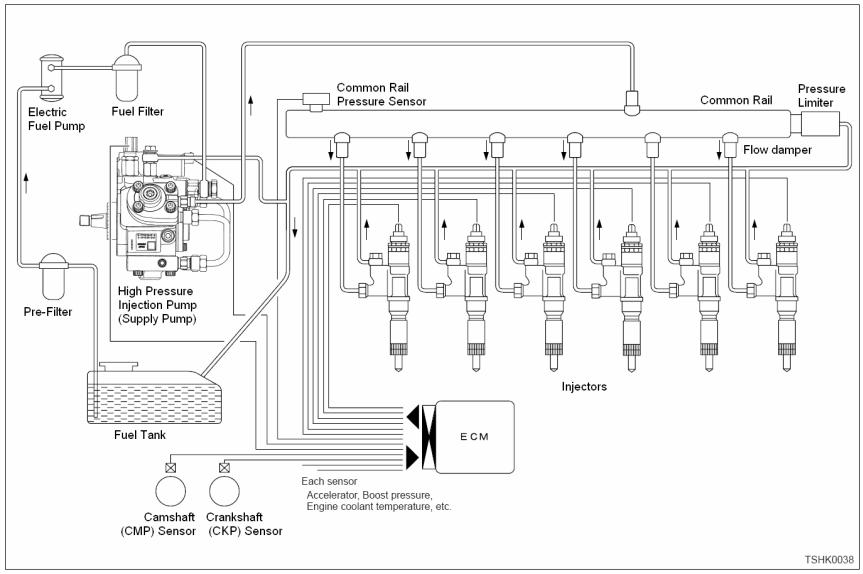
Isuzu 4HK-1 and 6HK-1 Engine Fuel Schematic Overview Fuel System Hydraulic Function Fuel comes from the tank and typically will go through a prefilter assembly. From the prefilter, the fuel then flows to an electric fuel pump, located in the hydraulic pump compartment. -
Page 16
Isuzu 4HK-1 and 6HK-1 Engine Fuel Schematic Overview The common rail system stores high pressure fuel between the supply pump and the injectors. The common rail also serves as an accumulator to dampen the fuel pulsations from the pump. Flow dampers are located at the outlet of the common rail to the lines to the injectors. -
Page 19
Isuzu 4HK-1 and 6HK-1 Engine Sensor Locations… -
Page 20
Exhaust gas Recirculation (EGR) System Exhaust Gas Recirculation system is abbreviated to EGR system. It recirculates part of exhaust gas into intake manifold to mix an inert gas with intake air. This leads to lower the combustion temperature to limit emissions of nitrogen oxide (NOx). It controls amount of EGR by opening/closing the EGR valve installed between exhaust manifold and intake manifold. -
Page 23: Engine Control System
Engine Control System 42 Installation of ECM Install the ECM in the reverse order of removal. EGR valve position learning is required after replacing the ECM. 1. Turn the key switch to “ON”. 2. Turn the key switch to “OFF”. 3.
-
Page 24
Engine Control System 56 Senser and actuator *Refer at last page.(About wiring diagrams) -
Page 25
57 Engine Control System Circuit diagram (Refer to “Wiring diagrams” for a way to read the diagram.) Main relay circuit TSWG0027… -
Page 26
Engine Control System 58 Starter for safety relay, glow circuit TSWG0068… -
Page 27
59 Engine Control System CAN, GND, DLC circuits TSHK0013… -
Page 28
Engine Control System 60 Injector circuit TSWG0031… -
Page 29
61 Engine Control System SCV circuit TSHK0016… -
Page 30
Engine Control System 62 CKP sensor, fuel temperature sensor, engine coolant temperature sensor, engine oil pressure sensor circuit TSHK0017… -
Page 31
63 Engine Control System Boost temperature sensor, boost pressure sensor circuit TSWG0034… -
Page 32
Engine Control System 64 CMP sensor, common rail pressure sensor, EGR circuit TSHK0018… -
Page 33
65 Engine Control System Memory clear switch, engine stop switch circuit TSWG0038… -
Page 34
This page Is Intentionally Left Blank. -
Page 35
67 Engine Control System TSHK0035… -
Page 36
Engine Control System 68 Terminal Terminal Number Number Boost pressure sensor GND CKP + Boost pressure sensor Vout CKP GND Boost pressure sensor Vcc E112 Terminal Number Terminal Number CMP shield Engine oil pressure sensor GND CMP GND Engine oil pressure sensor Vout CMP + Engine oil pressure sensor Vcc E113… -
Page 37
69 Engine Control System Terminal Terminal Number Number SCV−Lo CKP + SCV−Hi CKP GND Fuel temperature sensor + CKP shield ECT meter CMP + — CMP GND Overheating switch CMP shield ECT + Boost pressure sensor Vcc Terminal Engine oil pressure sensor Vcc Number Engine oil pressure sensor Vout EGR hall sensor U… -
Page 38
Engine Control System 70 Terminal Number — OS−INJ6 signal Injector power supply 2 Injector power supply 1 — OS−INJ4 signal OS−INJ2 signal — (Female connector on injector side) In cylinder head (Female connector on injector side) (Male connector on ECM side) (Male connector on ECM side) TSWG0041… -
Page 39
71 Engine Control System Connector list Connector Face Connector Face E-27 E-75 003-501 #1 injector (Silver) E-29 E-76 003-501 #2 injector (Silver) (Black) E-31 E-80 #3 injector (Silver) (Black) E-33 E-90 003-500 #4 injector (Silver) (Blue) E-35 E-93 #5 injector (Silver) (Gray) E-37 E-98… -
Page 40
Engine Control System 72 Connector Face Connector Face E-114 (Black) (Black) E-161 (Brown) (Gray) E-162 (Dark gray) (Gray) E-163 (Gray) (Black) E-164 (Black) FB-124 H-12 (Black) (Gray) FL-150 H-12 016-500 (Gray) 9 10 11 12 FL-269 H-20 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 020-500 003-502… -
Page 41
73 Engine Control System Connector Face Connector Face H-95 12 11 10 9 H-20 (ECM 16 15 14 13 side) 20 19 18 17 020-501 (Gray) H-95 (Injector side) (White) (Gray) H-95 (Injector side) (White) (Gray) H-94 (ECM side) (Gray) H-94 (ECM side) -
Page 42
This page Is Intentionally Left Blank. -
Page 43
103 Trouble Shooting — EXAMPLE From Service Manual Error Code: 0088 Common rail pressure is abnormally high (1st or 2nd stage). TSHK0041 Name 1. Common rail 5. Fuel tank 2. Fuel filter 6. Supply pump 3. Electromagnetic Pump 7. Injector 4. -
Page 44: Trouble Shooting 104
Trouble Shooting 104 Engine control module (ECM) CMP sensor EGR position EGR position EGR position Common rail pressure signal sensor signal sensor signal sensor signal sensor signal 99 E-56 98 E-56 E-56 E-56 E-56 E-56 E-56 E-56 E-56 E-56 E-56 E-56 E-56 H-20…
-
Page 45
105 Trouble Shooting — EXAMPLE From Service Manual Error Code set condition Back-up mode 1st step • L mode fixed. • Rail pressure is more than 185MPa for 5 seconds • Limited injection amount 3 (multi-injection stopped) or more. • Target RP upper limit (80MPa) •… -
Page 46: Trouble Shooting 106
Trouble Shooting 106 Step Action Value Check the fuel return pipe between the supply pump and the fuel tank for breakage, twist, etc. Check for clogging or twisting in the vent hose of the fuel tank. — Check for foreign matter in the fuel tank. If the trouble is detected, repair as required.
-
Page 47
107 Trouble Shooting — EXAMPLE From Service Manual About common rail pressure sensor TSWG0055 Name 1. Sensor ground 2. Sensor signal 3. Sensor power supply Characteristics of common rail pressure sensor (MPa) TSWG0201… -
Page 48
5. 380002726 EMPS/EST ECM Cable 6. 380002728 EMPS/EST RS232 Null Modem Cable Start the Engine Download Tool — Isuzu EMPS The Additional Tools screen provides a button linking the Electronic Service Tool to: • Engine Diagnostic Tool — Isuzu EMPS… -
Page 49: Process Menu
Preliminary ELECTRONIC SERVICE TOOL (EST) Engine Module Programming System (EMPS) — Summary Selecting an EMPS Process Process Menu Select an EMPS operation from the Process Menu Process Menu. • ECM Reflash — Select when the ECM control program is suspected to have ECM Reflash damaged/corrupted files.
-
Page 50
This page Is Intentionally Left Blank.
This manual is also suitable for:
6hk-1
-
Contents
-
Table of Contents
-
Bookmarks
Quick Links
URL:http://www.hitachi-c-m.com
PRINTED IN JAPAN (K) 2015, 06
PART NO.
EWDCY-EN-00
Engine Manual
Workshop Manual
4HK1
GB3
EXHAUST EMISSION
STANDARDS
Service Manual consists of the following sections.
Technical Manual (Operational Principle)
Technical Manual (Troubleshooting)
Workshop Manual
Engine Manual
Related Manuals for Hitachi 4HK1
Summary of Contents for Hitachi 4HK1
-
Page 1
PART NO. EWDCY-EN-00 Engine Manual Workshop Manual 4HK1 EXHAUST EMISSION STANDARDS URL:http://www.hitachi-c-m.com Service Manual consists of the following sections. Technical Manual (Operational Principle) Technical Manual (Troubleshooting) Workshop Manual PRINTED IN JAPAN (K) 2015, 06 Engine Manual… -
Page 2
Find manuals at https://best-manuals.com Find manuals at https://best-manuals.com… -
Page 3
FOREWORD FOREWORD This manual describes the service procedures for the 4HK1 diesel engine (GB 3). The contents of this manual are current at the date of issue, but may differ slightly from your engine due to specification changes This manual describes the service procedures for the 4HK1 diesel engine (GB 3). or other modifications made thereafter. The contents of this manual are current at the date of issue, but may differ slightly from your engine due to specification changes or other modifications made thereafter. The engine specification and description, which is not installed in the machine, may be explained on this manual. This manual consists of the following sub-sections. This manual consists of the following sub-sections. Publication No. Publication Name Sub-sections IDE-2820 ENGINE Introduction Publication No. Publication Name Sub-sections Service Information Guide IDE-2820 ENGINE Introduction Maintenance Information… -
Page 4
Find manuals at https://best-manuals.com Find manuals at https://best-manuals.com… -
Page 5
Introduction (All) 0-1 Introduction Introduction (All) Table of Contents Introduction…………….0-2 safety information…………0-2 Find manuals at https://best-manuals.com Find manuals at https://best-manuals.com… -
Page 6
0-2 Introduction (All) Introduction safety information while paying sufficient attention to the handling precautions. Repair work safety information Furthermore, for work besides this, carry out work while wearing safety clothes and equipment. When the engine is unloaded from the machine, use the engine stand. -
Page 7: Table Of Contents
Service Information Guide (All) 14A-1 Description General Information Service Information Guide (All) Table of Contents Contents included in service information…..14A-2 Plastic gauge…………..14A-4 Recommended liquid gasket………14A-6 Thread locking adhesive agent……..14A-8 Term…………….14A-9 Abbreviations ………….14A-10 Standard bolts…………..14A-13 Find manuals at https://best-manuals.com Find manuals at https://best-manuals.com…
-
Page 8: Contents Included In Service Information
14A-2 Service Information Guide (All) Contents included in service information Contents included in service information Connection Includes the connection procedures for wiring, piping, Removal etc. Includes the removal procedure when repairing parts, devices, etc. Writing Includes the writing procedure necessary when replacing Installation the ECM or supply pump.
-
Page 9
Service Information Guide (All) 14A-3 1. Forward 9. Gas or warm air 2. Upward 10. Mixing of outside air and gas or mixing of cold 3. Operating section or operating direction air and warm air 4. Detail of a particular part 11. -
Page 10: Plastic Gauge
14A-4 Service Information Guide (All) Plastic gauge Using the plasti-gauge Type Measurable range : 0.025 to 0.076 mm { 0.00098 PG-1 (Green) to 0.00299 in } : 0.051 to 0.152 mm { 0.00201 PR-1 (Red) to 0.00598 in } : 0.102 to 0.229 mm { 0.00402 PB-1 (Blue) to 0.00902 in } Method for measuring clearance between the connecting…
-
Page 11
Service Information Guide (All) 14A-5… -
Page 12: Recommended Liquid Gasket
14A-6 Service Information Guide (All) Recommended liquid gasket Using the thread liquid gasket Type Product name Manufacturer Location of use (Reference) Silicon type ThreeBond 1207B ThreeBond Engine oil seal retainer (Room- ThreeBond 1207C ThreeBond Engine oil pan temperature ThreeBond 1215 ThreeBond Timing gear case vulcanized)
-
Page 13
Service Information Guide (All) 14A-7 Caution: ・ If the workshop manual specifies an application method, follow that method. -
Page 14: Thread Locking Adhesive Agent
14A-8 Service Information Guide (All) Thread locking adhesive agent Using the thread locking adhesive agent Type Color Loctite 242 Blue Loctite 262 Loctite 271 Caution: ・ Thoroughly remove grime, moisture, oil, and grease from the bolts, bolt holes, and screw thread portion of the nuts to which thread locking adhesive agent will be applied.
-
Page 15: Term
Service Information Guide (All) 14A-9 Term Term Nominal dimension Refers to standard values during production. Specified value Refers to specified values for inspection, adjustment, assembly, and installation. Limit Refers to maximum or minimum values that should not be exceeded during maintenance. Parts exceeding these values must be repaired or replaced.
-
Page 16: Abbreviations
14A-10 Service Information Guide (All) Abbreviations Abbreviations Abbreviation Description A- E Analog/Digital ABDC After bottom dead center Alternating current Accessory Alternating current generator Actuator American Petroleum Institute Assembly ATDC After top dead center Automatic transmission fluid Battery + terminal Battery BBDC Before bottom dead center Bracket…
-
Page 17
Service Information Guide (All) 14A-11 Abbreviation Description F — N Feedback Fuel cut Fusible link Fusible link wire Front Fuel temperature Forward Generator Ground Hydrocarbon HO2S Superheat O2 sensor Idle air control Intake air temperature Integrated circuit ID Plate Name plate IDSS ISUZU Diagnostic Service System Intake manifold temperature… -
Page 18
14A-12 Service Information Guide (All) Abbreviation Description O — W O2 sensor On-board diagnosis Original equipment manufacturer Option Oil temperature Pilot light Pump control valve / Positive crankcase ventilation Proportion-integration Particulate matter Power take-off Pulse width modulation wave Quick on start system Quick warming up system Right side Relay… -
Page 19: Standard Bolts
Service Information Guide (All) 14A-13 Standard bolts List of standard bolt and nut tightening torques Note: ・ Those indicated with an asterisk (*) are used The tightening torque values in the following table apply for the internal threaded portion of soft to locations where no tightening torque is specified.
-
Page 20
14A-14 Service Information Guide (All) Strength category Bolt head shape Hex bolt Flange bolt Hex bolt Flange bolt M18 — M24 : 151.0 to 225.6 N・m : 195.2 to 293.2 N・m M18 x 1.5 { 15.4 to 23.0 kgf・m / ―… -
Page 21
Service Information Guide (All) 14A-15 Strength category Bolt head shape Hex bolt Flange bolt Hex bolt Flange bolt M6 — M16 : 5.6 to 11.2 N・m { 0.6 : 6.6 to 12.2 N・m { 0.7 M6 x 1 to 1.1 kgf・m / 50 to 99 to 1.2 kgf・m / 58 to 108 ―… -
Page 22
14A-16 Service Information Guide (All) Strength category Bolt head shape Hex bolt Flange bolt Hex bolt Flange bolt M18 — M24 : 222.5 to 334.3 N・m : 229.5 to 345.2 N・m M18 x 1.5 { 22.7 to 34.1 kgf・m / ―… -
Page 23
Service Information Guide (All) 14A-17 1. Hex bolt (4.8, 4T) 10. Hex bolt (Non-thermally refined 8.8) 2. Hex bolt (4.8, 4T) 11. Flange bolt (8.8) 3. Flange bolt (4.8, 4T) 12. Flange bolt (8.8) 4. Flange bolt (4.8, 4T) 13. Hex bolt (9.8, 9T) 5. -
Page 24
14A-18 Service Information Guide (All) Connector (Brass tapered screws) Screw size PT(R)1/8 PT(R)1/4 PT(R)3/8 PT(R)1/12 : 2.0 to 14.7 N・m : 4.9 to 15.7 N・m : 9.8 to 16.7 N・m : 9.8 to 17.7 N・m ― { 0.20 to 1.50 kgf・m / { 0.5 to 1.6 kgf・m / 43 { 1.0 to 1.7 kgf・m / 87 { 1.0 to 1.8 kgf・m / 87… -
Page 25
Mechanical (4HK1) 1B-1 Engine Mechanical (4HK1) Table of Contents Cylinder head cover…………1B-2 installation……………1B-256 removal……………1B-2 Flywheel…………..1B-262 installation…………..1B-3 removal…………..1B-262 Cylinder head assembly………..1B-4 inspection…………..1B-264 removal……………1B-4 installation……………1B-265 disassembly……………1B-13 Crankshaft front oil seal……….1B-267 inspection…………..1B-19 removal…………..1B-267 reassembly…………..1B-25 installation……………1B-269 installation…………..1B-34 Crankshaft rear oil seal……….1B-272 Idle gear……………..1B-49 removal…………..1B-272 removal…………..1B-49… -
Page 26: Cylinder Head Cover
1B-2 Mechanical (4HK1) Cylinder head cover removal Ventilation hose disconnect Remove the air leak pipe from the EGR cooler and bracket. Note: ・ The existence or nonexistence of the equipment varies depending on the machine manufacturer. Remove the bracket from the cylinder head cover.
-
Page 27: Installation
Mechanical (4HK1) 1B-3 installation Connect the oil level gauge guide tube to the cylinder head cover. Cylinder head cover installation tightening torque: 19 N・m { 1.9 kgf・m / 14 lb・ft } Align the head cover gasket to the cylinder head Install the bracket to the cylinder head cover.
-
Page 28: Cylinder Head Assembly
1B-4 Mechanical (4HK1) Cylinder head assembly removal Turbocharger assembly removal Remove the exhaust pipe from the turbocharger Battery ground cable disconnect assembly. Disconnect the battery ground cable from the battery. Remove the air cleaner duct from the air cleaner Caution:…
-
Page 29
Mechanical (4HK1) 1B-5 Disconnect the water return pipe from the 13. Remove the turbocharger assembly from the exhaust turbocharger assembly. manifold. Remove the water return pipe from the water pump. Note: ・ The turbocharger specification varies Note: depending on the machine manufacturer. -
Page 30
1B-6 Mechanical (4HK1) Caution: Disconnect the harness connector from the EGR valve. ・ After removing the EGR pipe, seal to prevent intrusions of foreign material. Remove the EGR valve from EGR pipe C. Caution: ・ After removing the EGR valve, seal to prevent intrusions of foreign material. -
Page 31: Inlet Cover
Mechanical (4HK1) 1B-7 3. Fan guide bracket 2. Gasket 3. Inlet pipe Disconnect the radiator upper hose from the water 4. Boost pressure/boost temperature sensor outlet pipe. 10. Oil level gauge guide tube removal Remove the EGR cooler water pipe from the engine assembly.
-
Page 32
1B-8 Mechanical (4HK1) Remove the fuel pipe from the fuel supply pump and the common rail assembly. Note: ・ Remove the clip. Caution: ・ Do not reuse the gasket. 14. Fuel leak off pipe assembly removal Disconnect the fuel leak-off pipe from the cylinder head assembly. -
Page 33
Mechanical (4HK1) 1B-9 Disconnect the injector harness from the injector. Caution: ・ Be careful not to damage the injector side stud bolts. Remove the injector harness from the cylinder head assembly. Note: ・ Remove the bracket tightening bolts and then remove the injector harness together with the bracket. -
Page 34
1B-10 Mechanical (4HK1) SST: 5-8840-0019-0 — sliding hammer 1. Injector 2. Injector sleeve Caution: ・ Store each ID code plate on the injector head with the cylinder number tag attached to avoid a mix-up. ・ Be extremely careful not to damage the injector nozzle. -
Page 35
Mechanical (4HK1) 1B-11 Remove the camshaft bearing from the cylinder head assembly. Note: ・ Temporarily assemble the removed caps and bearings in the original position to avoid a mix- up after the bearings have been inspected. Remove the rocker arm shaft from the cylinder head assembly. -
Page 36: Cylinder Block
1B-12 Mechanical (4HK1) 22. Cylinder head assembly removal Remove the cylinder head assembly from the cylinder block. Note: ・ Loosening order of the head bolts Caution: ・ Since the idle gear C protrudes from the bottom surface of the cylinder head, be careful not to damage the gear.
-
Page 37
Mechanical (4HK1) 1B-13 disassembly Engine hanger bracket removal Remove the front engine hanger bracket from the cylinder head assembly. Remove the rear engine hanger bracket from the cylinder head assembly. 1. EGR cooler bracket 2. Bracket Inlet cover removal Remove EGR pipe C from the case. -
Page 38
1B-14 Mechanical (4HK1) Caution: 1. Distance tube 2. Washer ・ Do not forget to remove the bolts indicated by 3. Exhaust manifold the arrow in the diagram. Remove the gasket from the cylinder head assembly. Thermostat removal Remove the fan guide bracket from the water outlet pipe. -
Page 39
Mechanical (4HK1) 1B-15 1. Overheat switch Remove the idle gear C from the cylinder head 2. Engine coolant temperature sensor assembly. CMP sensor removal Remove the CMP sensor from the cylinder head assembly. 1. Idle gear C 2. Idle gear shaft 10. -
Page 40
1B-16 Mechanical (4HK1) SST: 8-9439-6862-0 — pivot ASM 13. Valve stem oil seal removal Remove the valve stem oil seal from the valve guide using the pliers. Caution: ・ Do not reuse the valve stem oil seal. Remove the valve spring seat from the cylinder head assembly. -
Page 41
This as a preview PDF file from best-manuals.com Download full PDF manual at best-manuals.com…
- Brands:
Isuzu - File Size:
3.2MB - Total Pages:
121 - File Type:
PDF
INTRODUCTION & ENGINE MECHANICAL FEATURES
The 2005 model year NPR/NQR truck, the 4HK1-TC inline 4 cylinder engine replaces the 4HE1-TC engine for advanced exhaust emission countries. The 4HK1-TC engine has been newly developed on the basis of previous 4HE1-TC engine, with additional features including the employment of four valve mechanism per a cylinder that are operated via a single camshaft, common rail fuel injection system, water-cooled exhaust gas re-circulation (EGR) system, and the change of combustion chamber form. The larger engine displacement and the common rail fuel injection system have resulted in an increase both in maximum output and torque, and met Euro 3 emission regulation standard. Most conspicuous items are listed below.
- Multi fuel injection type high-pressure common rail system and is made with Denso.
- Single overhead camshaft (OHC) with 4 valves per a cylinder.
- Electrical control EGR valve, water-cooled EGRcooler.
- Turbocharger with intercooler.
The base transmission is MYY for 4HK1-TCN low output engine, MZZ for 4HK1-TCS high output engine. The Smoother system is available for only MYY transmission.
GEAR TRAIN
To rotate the fuel supply pump with engine speed, idle gear has changed with three steps. The crankshaft gear (42 teeth) corresponds with the large diameter of idle gear A (72 teeth). The fuel supply pump gear (35 teeth) corresponds with the middle diameter of idle gear A (60 teeth). The idle gear B (61 teeth) corresponds with the small diameter of idle gear A (30 teeth).
Valve Train
To improve exhaust emission and engine output performance, four valve mechanism is newly adopted for 4HK1-TC engine. Note that the adjustment method of valve clearance has been changed from 4HK1-TC engine as following steps:
- Rotate the crankshaft to make the No.1 cylinder meet the compression top dead center (TDC). There are 2 marks stamped on the crank pulley. The mark (1) is used to bring the engine No.1 or No. 4 cylinder to TDC. The mark (2) is irrelevant. Do not use the mark (2).
- Loosen fully each adjusting screw (8) & (2) of the bridge and the rocker arm.
- Insert a 0.4mm (0.016in) thickness gauge between the tip of the rocker arm and bridge cap (5), and adjust the clearance with the adjusting screw (3) on the rocker arm, and then fix it with a lock nut (4).
- With a thickness gauge kept inserted, check that the adjusting screw (6) contacts the valve shaft end and the movement of the thickness gauge has become tight when the adjusting screw (6) on the bridge is tightened lightly.
- Check the valve shaft end on the opposite side floats or it contacts obliquely. In case of a floating or oblique contact, loosen a little the adjusting screw (6) on the bridge side and adjust so that the valve shaft ends on both sides get in contact properly. Bridge (8) & valve shaft end clearance less than 0.1 mm (0.004in).
- After the adjustment so that the end of the valves on both sides touch properly, tighten up the lock nut (7) on the bridge (8).
CYLINDER HEAD COVER & HEAD COVER CASE
Along with the employment of a common rail type fuel injection system, the head cover is split and housed in a newly introduced head cover case attached with an intermediate connector for the injector. The head cover case is so designed that it is secured individually to the cylinder head with four bolts, and further it is tightened together with the head cover with nine bolts. Accordingly, the head cover is removable individually regardless of the injector harness, thus enabling easy inspection and service including the valve clearance adjustment.
ENGINE CONTROL MODULE (ECM)
The engine control module (ECM) is located at inside of engine-side cover on the left via mounting bracket and is beside the engine. The ECM is made by Transtron. The ECM mainly controls the following:
- Fuel injection control
- Fuel timing control
- Exhaust gas recirculation (EGR) system control
- Preheating system control
- Exhaust brake control
- Power take off (PTO) control
- On-board diagnostics for engine control
The ECM constantly observes the information from various sensors. The ECM controls the systems that affect vehicle performance. The ECM performs the diagnostic function of the system. The ECM can recognize operational problems, alert the driver through the malfunction indicator lamp (MIL), and store diagnostic trouble code (DTC). DTC identify the system faults to aid the technician in making repair.
This diagnostic applies to internal microprocessor integrity conditions within the ECM. The electronically erasable programmable read only memory (EEPROM) memorize learning data and injector ID code data for engine control and communication with other control module.
Symbol “!” warns you of an electric shock hazard. To avoid shock and possible serious injury, DO NOT touch the terminals. When disconnecting the harness connector, always turn OFF the ignition switch or disconnect the battery cable.
Download or Read Online Isuzu 4HK-1 Engine Service Manual
Save PDF/Read Online

Isuzu
4HK-1 and 6HK-1
ENGINE
FUEL SYSTEM
CE APPLICATIONS
|
Revised 8/29/06 |
Form Number 5137 |
1
Isuzu 4HK-1 and 6HK-1 Engine Overview
The Tier III CX330 Excavators are equipped with an Isuzu 6HK-1 model common rail fuel system Engine. The Isuzu 4HK-1 model will be used in at least one other
Excavator model. These engines have 4 valves per cylinder, operated by a single overhead cam to optimize air flow, fuel economy and emissions. The injector is now located at the center of the piston under the valve cover. The fuel system is now totally electronically controlled. These engines use an water cooled Exhaust Gas Recirculation, (EGR) system, which allows a controlled amount of exhaust gas to return back to the intake. This EGR system is used to reduce the emissions level of the engine. These engines also use an air to air aftercooling intake air system. The air to air intake system ports pressurized air flow between the turbocharger and the intake manifold through an air to air heat exchanger in front of the radiator. The 4HK-1 model has a displacement of 317 cubic inches (in3) or 5193 cubic centimeters (cc). The 6HK-1 model has a displacement of 475 cubic inches (in3) or 7790cubic centimeters (cc).
The ECM calculates the basic injection amount based on the signals from throttle position sensor, boost pressure sensor, crank position sensor, cam position sensor, etc.
It regulates the opening/closing period of common rail pressure control valve and the electric activation of each injector according to the common rail pressure, engine coolant temperature, etc. at this time, to correct the optimum injection timing and injection amount.
At engine start (after the key switch is turned to the START position to start the engine, and until the return of the key switch to the ON position), the fuel injection quantity is controlled based on information from the start signal, engine speed, and engine coolant temperature. At low temperature, the fuel injection quantity increases. When the engine starts completely, this boosted quantity mode at starting is cancelled and normal running mode is restored.
The ECM calculates the current altitude based on the barometric pressure sensor signal. It corrects the fuel flow according to the altitude etc. at this time.
The Excavator machine controller communicates with the engine controller (ECM) via the CAN Data Bus system to control engine speed, return to idle command, activate the work modes and also to set the engine speed required for the breaker mode.
Engine Performance Needs
1.Air
2.Compression
3.Fuel
3
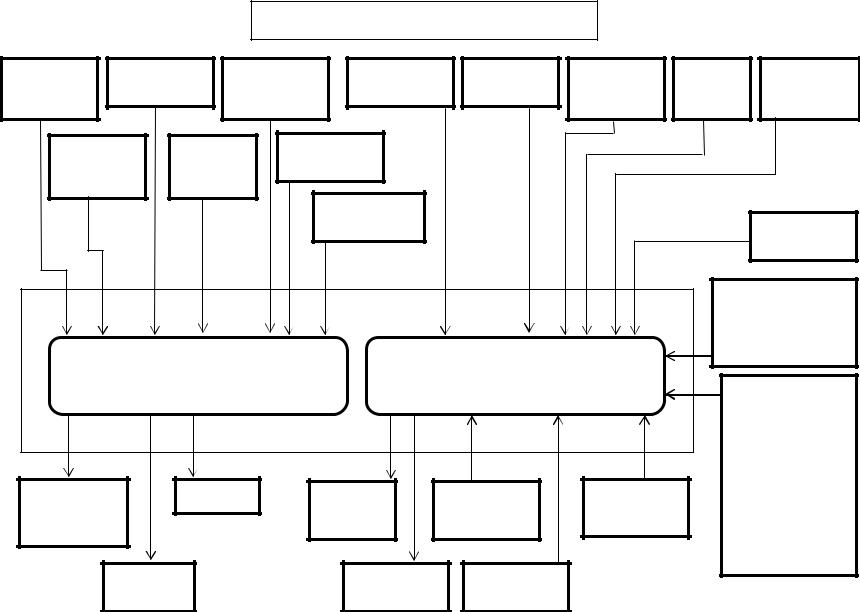
Isuzu 4HK-1 and 6HK-1 Engine Overview
The electronic control system for the Isuzu 4HK-1 and 6HK-1 Engines use input information from a number of sensors and from the Excavator controller to determine the quantity and timing of the fuel delivery to the engine.
The engine control module (ECM), is located on the inside rear of the cab. The ECM has two connectors, one an 81 pin and one 40 pin, for inputs and outputs. The engine control module requires downloading of control software to give it the ability to control all functions.
Inputs to 40 pin engine harness connector:
•The common rail fuel pressure sensor has 3 wires and is located on the common rail. This sensor detects the fuel pressure in the common rail, converts the pressure into a voltage signal, and sends the signal to the ECM. Higher common rail pressure provides higher fuel pressure sensor voltage while lower pressure provides lower fuel pressure sensor voltage.
•The 2 wire variable resistor fuel temperature sensor is installed on the fuel supply pump. The fuel temperature sensor measures the temperature of the drain fuel from the pump. When the fuel temperature sensor is cold, the sensor resistance is high.
When the fuel temperature increases, the sensor resistance decreases. With high sensor resistance, the ECM detects a high voltage on the signal circuit. With lower sensor resistance, the ECM detects a lower voltage on the signal circuit.
|
Fuel Temp. |
Fuel Temp. |
Ohms |
Fuel Temp. |
Fuel |
Ohms Ω |
|
|
(°C) |
(°F) |
Ω |
(°C) |
Temp. (°F) |
||
|
140 |
284 |
75 |
40 |
104 |
1,150 |
|
|
120 |
248 |
111 |
20 |
68 |
2,450 |
|
|
100 |
212 |
184 |
0 |
32 |
5,740 |
|
|
80 |
176 |
318 |
-20 |
-4 |
15,000 |
|
|
60 |
140 |
584 |
-40 |
-40 |
45,770 |
•The 2 wire engine coolant temperature sensor is located on the thermostat housing at the right front corner of the engine. The coolant sensor’s temperature detection component uses a thermistor. A 5 volt reference voltage is applied at all times to the sensor from the ECM. The ECM detects a voltage change due to a resistance value change in the sensor caused by the coolant temperature change.
|
Coolant |
Coolant |
Ohms |
Coolant |
Coolant |
Ohms Ω |
|
Temp. (°C) |
Temp. (°F) |
Ω |
Temp. (°C) |
Temp. (°F) |
|
|
140 |
284 |
76 |
40 |
104 |
1,161 |
|
120 |
248 |
118 |
20 |
68 |
2,500 |
|
100 |
212 |
190 |
0 |
32 |
5,773 |
|
80 |
176 |
325 |
-20 |
-4 |
15,216 |
|
60 |
140 |
591 |
-40 |
-40 |
47,365 |
4
Isuzu 6HK1 Common Rail Engine Fuel System
|
Common |
Fuel Temp |
Coolant |
Intake Air |
Boost Temp |
Barometric |
ENG Oil |
Engine Stop |
|||
|
Rail Fuel PSI |
Sensor |
Temperature |
Temp. Sensor |
Sensor |
AMB PSI |
PSI |
Switch |
|||
|
Sensor |
Sensor |
Sensor |
Sensor |
|||||||
|
Crankshaft |
Camshaft |
Boost PSI |
||||||||
|
Position |
Position |
Sensor |
||||||||
|
Sensor |
Sensor |
EGR Position |
||||||||
|
Sensor |
Start Signal |
|||||||||
|
(Fuel Boost) |
||||||||||
|
Power Supply |
||||||||||
|
1 Ignition Wire |
||||||||||
|
2 Positive Wires |
||||||||||
|
Engine Harness 40 Pin |
Engine Harness 81 Pin |
6 Ground Wires |
||||||||
|
Connector A1 |
||||||||||
|
Connector A0 |
CAN Data Bus |
|||||||||
|
Engine Control Module |
||||||||||
|
Connector |
||||||||||
|
Throttle, |
||||||||||
|
Idle Up/Down, |
||||||||||
|
Pump PSI |
Injectors |
Main ECM |
Diagnostic |
Memory Clear |
Work Modes, |
|||||
|
Breaker Mode, |
||||||||||
|
Control Valve |
Power |
Switch X24 |
Switch X23 |
|||||||
|
Tach, |
||||||||||
|
(SCV) |
Relay |
|||||||||
|
(Instrumentation |
||||||||||
|
EGR DC |
Glow |
Data Link |
& Faults) |
|||||||
|
Motor |
Relay |
Diag Conn X4 |
||||||||
|
5 |
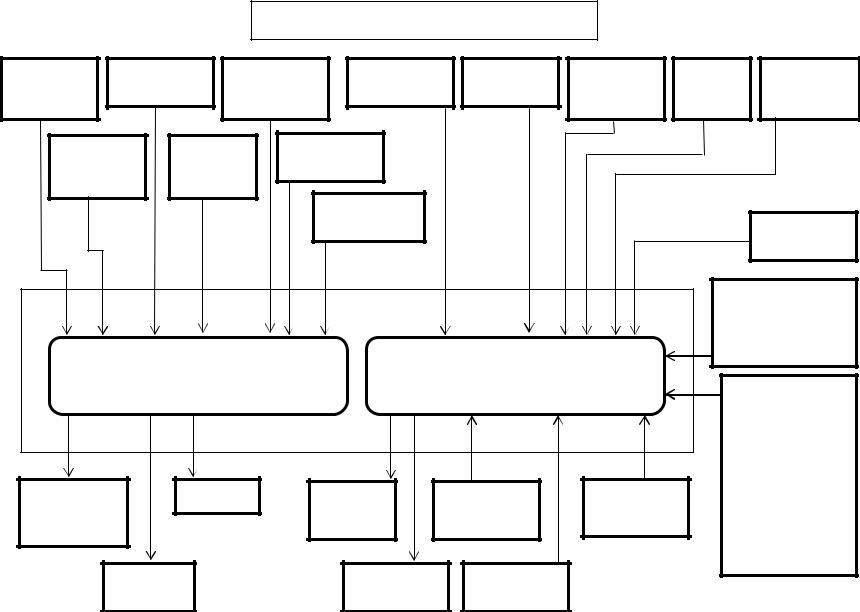
Isuzu 4HK-1 and 6HK-1 Engine Overview (continued)
Inputs to 40 pin engine harness connector(continued):
•The 2 wire crankshaft position sensor (CKP) is located on the flywheel housing at the left rear corner of the engine. The CKP sensor detects 45 projections equally spaced every 7.5° around the flywheel periphery. There is also a space (equal to 3 projections) to act as a top dead center (TDC) reference signal for the engine control module (ECM). With these 45 pulses and the TDC reference signal, the ECM calculates the engine speed and exact position of the crankshaft.
•The 2 wire camshaft position sensor (CMP) is located on the cylinder head at the rear of the camshaft gear. The camshaft position sensor detects a total of the number of the cylinders in the engine plus an extra one. The extra hole indicates the top dead center position of number 1 cylinder. Five through holes (four holes arranged equally every 90° on the gear and one reference hole) on the camshaft gear flange surface on the 4HK-1 Engine. Seven through holes (six holes arranged equally every 60° on the gear and one reference hole) on the camshaft gear flange surface on the 6HK-1 Engine. The camshaft position sensor indicates the rotational position of the camshaft to the ECM. The CMP signal input, determines the crank angle and the ECM can use it to control fuel injection and calculate the engine speed. The crankshaft position sensor (CKP) typically controls these functions, however it is done by CMP sensor if the CKP sensor is faulty.
Diagnostic aid
If there is relevant Error Code to the crankshaft (CKP) sensor and Camshaft (CMP) sensor, the engine will not start until memory clear is performed.
If an intermittent trouble is suspected, the following may be the cause:
•Improper connection of harness connector
•Defective harness routing
•Worn harness cover
•Wire disconnection inside harness cover
•The 3 wire boost pressure sensor is located in the piping to the intake manifold of the engine. The sensor converts the boost pressure into the voltage signal and sends it to engine control module (ECM). The ECM should detect a higher signal voltage at a high boost pressure.
•The 4 wire Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) position sensor is installed in EGR valve and detects the valve lift amount of EGR.
Note:
Do not disassemble the EGR position sensor. If it is faulty, replace it as EGR valve assembly.
6
Isuzu 6HK1 Common Rail Engine Fuel System
|
Common |
Fuel Temp |
Coolant |
Intake Air |
Boost Temp |
Barometric |
ENG Oil |
Engine Stop |
|||
|
Rail Fuel PSI |
Sensor |
Temperature |
Temp. Sensor |
Sensor |
AMB PSI |
PSI |
Switch |
|||
|
Sensor |
Sensor |
Sensor |
Sensor |
|||||||
|
Crankshaft |
Camshaft |
Boost PSI |
||||||||
|
Position |
Position |
Sensor |
||||||||
|
Sensor |
Sensor |
EGR Position |
||||||||
|
Sensor |
Start Signal |
|||||||||
|
(Fuel Boost) |
||||||||||
|
Power Supply |
||||||||||
|
1 Ignition Wire |
||||||||||
|
2 Positive Wires |
||||||||||
|
Engine Harness 40 Pin |
Engine Harness 81 Pin |
6 Ground Wires |
||||||||
|
Connector A1 |
||||||||||
|
Connector A0 |
CAN Data Bus |
|||||||||
|
Engine Control Module |
||||||||||
|
Connector |
||||||||||
|
Throttle, |
||||||||||
|
Idle Up/Down, |
||||||||||
|
Pump PSI |
Injectors |
Main ECM |
Diagnostic |
Memory Clear |
Work Modes, |
|||||
|
Breaker Mode, |
||||||||||
|
Control Valve |
Power |
Switch X24 |
Switch X23 |
|||||||
|
Tach, |
||||||||||
|
(SCV) |
Relay |
|||||||||
|
(Instrumentation |
||||||||||
|
EGR DC |
Glow |
Data Link |
& Faults) |
|||||||
|
Motor |
Relay |
Diag Conn X4 |
||||||||
|
7 |
Isuzu 4HK-1 and 6HK-1 Engine Overview (continued)
Inputs to 81 pin engine harness connector:
•The 2 wire intake air temperature (IAT) sensor is installed on intake air tube and detects the temperature of intake air for optimum fuel injection control.
•The 2 wire boost temperature sensor is installed onto the EGR valve on the upstream side of intake manifold. The sensor is a thermistor type. The resistance in the sensor changes as the temperature changes. When the intake temperature sensor is cold, the sensor resistance is high. When the intake temperature increases, the sensor resistance decreases. With high sensor resistance, the ECM detects a high voltage on the signal circuit. With lower sensor resistance, the ECM detects a lower voltage on the signal circuit.
•The 3 wire barometric pressure sensor is installed on the machine and converts the ambient barometric pressure into a voltage signal. The ECM calculates barometric pressure by this voltage signal and corrects the fuel injection amount (high-altitude correction) as the machine works at a higher elevation.
•The 3 wire engine oil pressure sensor is located on the left side of the engine just below and forward of the high pressure injection pump.
•An engine emergency stop signal is sent from the machine controller to the engine controller. The machine controller receives an engine stop signal from the stop switch located in the instrument cluster.
•As the engine is started (after the key switch is turned to the START position to start the engine, and until the return of the key switch to the ON position), optimum fuel injection quantity is delivered based on information from the starter switch signal, engine speed, and the engine coolant temperature sensor (ECT). At low temperature, the fuel injection quantity increases. As the engine starts completely, this boosted quantity mode at starting is cancelled and normal running mode is restored.
•Power Supply – Ignition power is sent to the engine control module (ECM) any time that the key switch is in the run position. When the ignition signal is present, the ECM activates the main relay. Once the Main Relay (K33 on machine schematic) is activated, battery power is fed to the ECM through the relay normally open (NO) contact to pins number 2 and 6. When the key switch is turned to the off position, the ECM continues to hold the main relay activated for a period of time to allow the ECM to power down safely. This delay is about 10 seconds. The ECM has six ground connections in total.
8
Isuzu 6HK1 Common Rail Engine Fuel System
|
Common |
Fuel Temp |
Coolant |
Intake Air |
Boost Temp |
Barometric |
ENG Oil |
Engine Stop |
|||
|
Rail Fuel PSI |
Sensor |
Temperature |
Temp. Sensor |
Sensor |
AMB PSI |
PSI |
Switch |
|||
|
Sensor |
Sensor |
Sensor |
Sensor |
|||||||
|
Crankshaft |
Camshaft |
Boost PSI |
||||||||
|
Position |
Position |
Sensor |
||||||||
|
Sensor |
Sensor |
EGR Position |
||||||||
|
Sensor |
Start Signal |
|||||||||
|
(Fuel Boost) |
||||||||||
|
Power Supply |
||||||||||
|
1 Ignition Wire |
||||||||||
|
2 Positive Wires |
||||||||||
|
Engine Harness 40 Pin |
Engine Harness 81 Pin |
6 Ground Wires |
||||||||
|
Connector A1 |
||||||||||
|
Connector A0 |
CAN Data Bus |
|||||||||
|
Engine Control Module |
||||||||||
|
Connector |
||||||||||
|
Throttle, |
||||||||||
|
Idle Up/Down, |
||||||||||
|
Pump PSI |
Injectors |
Main ECM |
Diagnostic |
Memory Clear |
Work Modes, |
|||||
|
Breaker Mode, |
||||||||||
|
Control Valve |
Power |
Switch X24 |
Switch X23 |
|||||||
|
Tach, |
||||||||||
|
(SCV) |
Relay |
|||||||||
|
(Instrumentation |
||||||||||
|
EGR DC |
Glow |
Data Link |
& Faults) |
|||||||
|
Motor |
Relay |
Diag Conn X4 |
||||||||
|
9 |
Isuzu 4HK-1 and 6HK-1 Engine Overview (continued)
Inputs to 81 pin engine harness connector: (continued)
•The CAN (Controller Area Network) Data Bus Connector transmits communication between the engine controller and the Excavator controller. This connector transmits throttle, idle up/down, work mode, breaker mode, tachometer, instrumentation and fault code information.
•The memory clear (X23), diagnostic switch (X24) and data link (X4) connectors are not used with the Case Electronic Service Tool (EST) diagnostic system. They are required when using the Tech 2 Diagnostic Tool.
Outputs from 81 pin engine harness connector:
•When the ignition signal is present from the keyswitch, the ECM activates the main relay. Once the Main Relay (K33 on machine schematic) is activated, battery power is fed to the ECM through the relay normally open (NO) contacts to pins number 2 and 6. When the key switch is turned to the off position, the ECM continues to hold the main relay activated for a period of time to allow the ECM to power down safely. This delay is about 10 seconds.
•The glow control relay system consists of the ECM, glow relay, glow plug. When the key switch is turned ON with low engine coolant temperatures, the ECM determines the glow time and operates the glow relay (K2). After a certain time has elapsed, the ECM will turn the glow relay to “OFF”. Also, after-glow function allows to stabilize idling immediately after starting.
Outputs from 40 pin engine harness connector:
•The engine driven high pressure injection pump pressurizes fuel to feed to the common rail. The injection pump has a suction control valve (SCV), and a fuel temperature (FT) sensor. The suction control valve (SCV) is installed onto high pressure pump section and controls supply of fuel (discharge amount) to common rail. The engine control module (ECM) regulates period of electrical activation time of the SCV to regulate the fuel discharge amount.
Do not replace the SCV. If it is faulty, replace it as supply pump ASM.
•The exhaust gas recirculation (EGR) system recirculates a part of the exhaust gas to the engine intake to reduce the combustion temperature inside the cylinders to reduce NOx (nitrogen oxides) in the exhaust gas. The EGR valve opening is calculated according to the engine coolant temperature (ECT), the engine speed, and the target fuel injection quantity. The EGR motor is the brushless DC motor, and is driven by three phases. The ECM drives the EGR motor through the EGR motor drive circuits U, V, and W. The motor rotates with a combination of the threephase signals. The ECM sets the Error Code when the EGR motor drive duty is high and the difference between the target EGR position and actual EGR position is large.
10
Isuzu 6HK1 Common Rail Engine Fuel System
|
Common |
Fuel Temp |
Coolant |
Intake Air |
Boost Temp |
Barometric |
ENG Oil |
Engine Stop |
|||
|
Rail Fuel PSI |
Sensor |
Temperature |
Temp. Sensor |
Sensor |
AMB PSI |
PSI |
Switch |
|||
|
Sensor |
Sensor |
Sensor |
Sensor |
|||||||
|
Crankshaft |
Camshaft |
Boost PSI |
||||||||
|
Position |
Position |
Sensor |
||||||||
|
Sensor |
Sensor |
EGR Position |
||||||||
|
Sensor |
Start Signal |
|||||||||
|
(Fuel Boost) |
||||||||||
|
Power Supply |
||||||||||
|
1 Ignition Wire |
||||||||||
|
2 Positive Wires |
||||||||||
|
Engine Harness 40 Pin |
Engine Harness 81 Pin |
6 Ground Wires |
||||||||
|
Connector A1 |
||||||||||
|
Connector A0 |
CAN Data Bus |
|||||||||
|
Engine Control Module |
||||||||||
|
Connector |
||||||||||
|
Throttle, |
||||||||||
|
Idle Up/Down, |
||||||||||
|
Pump PSI |
Injectors |
Main ECM |
Diagnostic |
Memory Clear |
Work Modes, |
|||||
|
Breaker Mode, |
||||||||||
|
Control Valve |
Power |
Switch X24 |
Switch X23 |
|||||||
|
Tach, |
||||||||||
|
(SCV) |
Relay |
|||||||||
|
(Instrumentation |
||||||||||
|
EGR DC |
Glow |
Data Link |
& Faults) |
|||||||
|
Motor |
Relay |
Diag Conn X4 |
||||||||
|
11 |
Isuzu 4HK-1 and 6HK-1 Engine Overview (continued)
Outputs from 40 pin engine harness connector: (continued)
•The injectors are controlled by the engine control module (ECM). The ECM sends a common power supply to injectors 1, 3 and 5. The ECM also sends a common power supply to injectors 2, 4 and 6. The ECM fires the injectors by controlling the ground of the individual injectors. The ECM calculates the basic injection amount and timing based on the signals from throttle position sensor, boost pressure sensor, crankshaft (CKP) sensor, camshaft (CMP) sensor, etc. The timing of the injection is controlled by when the injector activates. The fuel quantity delivered is based upon the amount of time that the injector is open and also the pressure supplied by the common rail. To improve combustion in cylinders, the system injects a little fuel (preinjection or pilot injection) and ignites it at the beginning of the cycle. A second injection (main injection) delivers the fuel required deliver the horsepower needed.
12
Isuzu 6HK1 Common Rail Engine Fuel System
|
Common |
Fuel Temp |
Coolant |
Intake Air |
Boost Temp |
Barometric |
ENG Oil |
Engine Stop |
|||
|
Rail Fuel PSI |
Sensor |
Temperature |
Temp. Sensor |
Sensor |
AMB PSI |
PSI |
Switch |
|||
|
Sensor |
Sensor |
Sensor |
Sensor |
|||||||
|
Crankshaft |
Camshaft |
Boost PSI |
||||||||
|
Position |
Position |
Sensor |
||||||||
|
Sensor |
Sensor |
EGR Position |
||||||||
|
Sensor |
Start Signal |
|||||||||
|
(Fuel Boost) |
||||||||||
|
Power Supply |
||||||||||
|
1 Ignition Wire |
||||||||||
|
2 Positive Wires |
||||||||||
|
Engine Harness 40 Pin |
Engine Harness 81 Pin |
6 Ground Wires |
||||||||
|
Connector A1 |
||||||||||
|
Connector A0 |
CAN Data Bus |
|||||||||
|
Engine Control Module |
||||||||||
|
Connector |
||||||||||
|
Throttle, |
||||||||||
|
Idle Up/Down, |
||||||||||
|
Pump PSI |
Injectors |
Main ECM |
Diagnostic |
Memory Clear |
Work Modes, |
|||||
|
Breaker Mode, |
||||||||||
|
Control Valve |
Power |
Switch X24 |
Switch X23 |
|||||||
|
Tach, |
||||||||||
|
(SCV) |
Relay |
|||||||||
|
(Instrumentation |
||||||||||
|
EGR DC |
Glow |
Data Link |
& Faults) |
|||||||
|
Motor |
Relay |
Diag Conn X4 |
||||||||
|
13 |
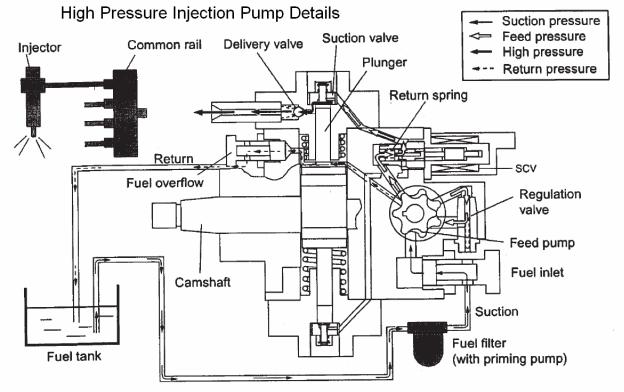
Isuzu 4HK-1 and 6HK-1 Engine Fuel Schematic Overview
Fuel System Hydraulic Function
Fuel comes from the tank and typically will go through a prefilter assembly. From the prefilter, the fuel then flows to an electric fuel pump, located in the hydraulic pump compartment. The 24 volt electric fuel pump is powered directly by the battery relay, through the 65 amp fuse (F23) and the 10 amp electrical fuel pump fuse (F8) in the fuse box. The electric fuel pump then sends the fuel through the fuel filter also located hydraulic pump compartment to the inlet port of the high pressure injection pump.
The high pressure injection pump is mounted at the left rear of the engine. This pump needs to be timed to the engine. To install the pump, bring the engine to TDC and then align the mark on the pump drive gear to the mark on the front face of the high pressure pump. Once these conditions are met, install the injection pump. The high pressure injection pump has a shaft driven gerotor feed (charge) pump which provides fuel to the pump pressure control valve (Suction Control Valve SCV). The gerotor pump outlet pressure is controlled by the regulation valve to provide a constant pressure at the inlet of the high pressure pumping pistons. The high pressurepump PSI regulator (SCV), located in the injection pump, controls the flow output of the high pressure pump. The high pressure pump supplies the quantity of fuel to the common rail required to maintain the pressure dictated by the engine control unit (ECM). This assures that only the required amount of fuel is pressurized, improving energy efficiency and limiting heating of fuel in the system. The common rail pressure will range from 3625 to 29,000 PSI (25 to 200 MPa). Excess flow from the feed pump and internal leakage from the injection pump returns to the tank. The fuel temperature sensor (FT) monitors the temperature of this fuel.
14
15
Introduction
Hitachi Construction Machinery Co., Ltd
This Manual describes the structure and the troubleshooting of electronic control fuel injection system (common rail type) in 4HK1 and 6HK1 industrial engines.Use this manual sufficiently to perform service work properly and quickly.
General Contents
Control System Electronic control fuel injection system (Common rail type)
Engine Manual (1/2)
Disassemble and Assemble Engine General Information
Engine Mechanical (4HK1、6HK1)
Cooling System
Fuel System
Engine Electrical
Exhaust System and Turbocharger
General Information
GENERAL INFORMATIONGeneral Information
ContentsGeneral Information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 0A-2
Service Precautions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 0A-2Reading the model . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 0A-6General information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 0A-7
0A-2 General Information
General Information 0A-1
0A-2 General Information
General InformationService PrecautionsIn order to carry out work safely
1. Always use an engine stand when taking theengine down from the vehicle. Do not place the engine directly onto the ground,or place in a manner that interferes with the oilpan.
2. If you are working together with others, always payattention to each other’s safety.
3. If you are repairing any part of the electricalsystem, always remove the minus side cable fromthe battery terminal before starting work. If you areremoving the battery cover, always remove thecover in a place that is away from sources of fire/heat.
4. Do not perform painting work or leave the enginerunning for long periods of time in an enclosed orbadly ventilated indoor workshop.
5. Always use the correct specialized tool indicated inthe instructions. Using the incorrect tool maycause damage to the parts or injury to the personusing the tool.
6. All regular tools, gauges and special tools shouldbe regularly inspected, and prepared beforestarting work. Do not use bent spanners, hammerswith damaged edges, chipped chisels, or any otherfaulty or damaged tools.
7. Always pay close attention to safety and handlingrequirements when using grinders, cranes,welders, and other such equipment. Moreover, always wear the correct protectivegarments and use the necessary safety tools forthe job in hand.
WSHK0190
General Information 0A-3
8. Always check that there are no fuel leaks whenperforming maintenance work on the fuel system.(It may cause a fire.)
9. Pay close attention to the risk of ignition if you arehandling parts that carry a high voltage.Furthermore, any oil or grease spilt onto rubberparts must be wiped off immediately, as it willcause deterioration of the rubber.
Replacement parts and part numbers. 1. Always replace packing, oil seals, o-rings, caulking
lock nuts, folding lock plates, split pins and othersuch parts with brand new parts.
2. The parts numbers contained in this manual maynot represent the supply condition of the parts, andthe part numbers may be changed due torevisions. Therefore, parts should always bechecked against a parts catalogue before use.
Liquid gasket1. Each time you disassemble parts that use liquid
gasket, completely remove the old gasket residuefrom each of the parts and matching sections usinga scraper, then clean each of the parts tocompletely remove oil, water, and dirt etc. from thevarious surfaces. Using the specified type of liquidgasket, apply new liquid gasket to each of thesurfaces before reassembling the parts.
2. In order to make it easier to clean liquid gasketsurfaces, apply gasket remover liquid (Pando-391D made by Three Bond Co., Ltd.) and leavethe part to stand for approximately 10 minutes,after which the old liquid gasket residue will beeasier to remove.However, this should not be used on resincomponents or painted components.
3. Please take care not to apply too much or too littleliquid gasket. Also, you should always re-apply the liquid gasketupon itself when you start and finish application.
4. Make sure that there are no gaps when re-installing the liquid gasket parts to each other. Ifthere are gaps between the two parts, re-apply theliquid gasket. Some parts, especially the oil pan,use the same size studs as a guide to eliminate theneed for knock pin positioning etc.
5. Re-install these parts within 7 minutes of applyingthe liquid gasket.
WSHK0191 WSHK0192
0A-4 General Information
If more than 7 minutes passes, remove theprevious liquid gasket and re-apply it.
6. Please wait for at least 30 minutes since the lastpart is installed before starting the engine.
Liquid gasket
• Always use the liquid gasket products listed above,or a liquid gasket identical to the ones listed above.
• Use the correct quantity of liquid gasket. Alwaysfollow the handling instructions for each product.
Application procedure1. Wipe the contact surfaces clean of all water,
grease or oil. The contact surfaces should be dry. 2. Apply a regular bead width of liquid gasket to one
of the contact surfaces. Make sure that the beaddoes not break at this point.
Notes: If there are special regulations concerning theapplication procedure in the repair document, pleasefollow those regulations.
Work procedure1. Wipe the joint surfaces of the bolt, bolt hole, and
screw thread section clean of water, grease, andoil. The contact surfaces should be dry.
2. Apply Loctite to the top 1/3 of the screw. 3. Tighten the bolt to the correct tightening torque.
Important: After tightening the bolt, do not apply excessive torqueor try to rotate the bolt until at least one hour haspassed, and the Loctite has hardened.
Procedure for using the Plastigauge
Example: Procedure for measuring the clearancebetween the connecting rod bearing and crank pin.
• Clean the connecting rod and bearing, and installthe bearing to the rod.
• Cut the plastigauge to the same width as the crankpin, and while avoiding the oil pore of the crank pinlay the gauge parallel to the pin.
Seal section Product name Manufacturer’s name
Between cylinder block and – Flywheel housing 1207B Three Bond
Between cylinder block and – Flywheel housing and –Crankcase 1207B Three Bond
Between cylinder block and – Crank case 1207B Three Bond
Between cylinder block and – Front cover 1207B Three Bond
Cylinder block, head plug nipple, unit, switches 262 Loctite
Type Measurable range mm (in)
PG-1 (Green) 0.025 – 0.076 (0.001 – 0.003)
PR-1 (Red) 0.051 – 0.152 (0.002 – 0.006)
PB-1 (Blue) 0.102 – 0.229 (0.004 – 0.009)
General Information 0A-5
• Line up the marks on the connecting rod and capand install the crank pin, apply molybdenumdisulfide to the thread section and bearing surfaceof the fastening bolt, and rotate both cap and boltto the correct torque.
Important: Do not move the connecting rod while using theplastigauge.
• Gently remove the cap and connecting rod, andmeasure the crushed width of the plastigauge(clearance between rod and pin) using the scaleprinted on the bag.
Example: Measuring the clearance between the crankbearing and crank journal
• Clean the clamp face of the cylinder block andcrankcase bearing, and also the bearing, andinstall the cylinder block to the crankcase.
• Gently rest the crankshaft on the cylinder block,and rotate it approximately 30 degree to stabilize it.
• Cut the plastigauge to the same size as the journalwidth, and while avoiding the oil pore of the journallay the gauge parallel to the journal.
• Gently rest the crank case on the cylinder block,apply molybdenum disulfide to the thread sectionand bearing surface of the fastening bolt, andtighten in sequence to the correct torque.
Important: Do not rotate the crankshaft while using theplastigauge.
• Gently remove the crankcase, and measure thecrushed width of the plastigauge (clearancebetween bearing and journal) using the scaleprinted on the bag.
0A-6 General Information
Reading the modelEngine number stamping position4HK1
WSHK0185
General Information 0A-7
6HK1
General informationTerminology, description of abbreviations Terminology definitions
WSHK0186
Term Explanation
Maintenance standard The generic name for reference values required for maintenance, such as nominaldimension, selection of a reference point, and limit.
Nominal dimension Shows the standard value at the point of manufacture that does not include thecommon difference.
Selection of a reference point Shows the standard value after assembling, repairing, or adjusting.
Limit When this value (dimensions) is reached, it shows that the part has reached its fulllimit and must be replaced or repaired.
Front ⋅ rear, left ⋅ right, upper ⋅ lower
These show each orientations of parts installed to the vehicle when looking fromthe vehicle’s forward direction.
Unit Units written to SI conventions (mainly torque, pressure, force)[Example] Length: mm, Torque: N⋅m kgf⋅m
Warning Items that carry the warning mark pose a danger to life or threat of serious injury ifnot strictly observed.
Caution Items that carry the caution mark may cause injury or lead to accidents if not strictlyobserved.
Important Items that carry the important mark may cause the vehicle to break down, or mayprevent the guaranteed normal operation of the system or related parts if not strictlyobserved.
0A-8 General Information
Description of abbreviations
Notes Items that should receive special mention within a work procedure.
Term Explanation
Abbreviation Description
AC Alternating CurrentAlternating Current
ACC AccessoryAccessory
ACG Alternating Current GeneratorAlternating current generator
API American Petrol InstituteAmerican Petroleum Institute
ASM (Assy) AssemblyAssembly
ATDC After Top Dead CenterAfter Top Dead Center
BAT, BATT BatteryBattery
BRG, Brg BearingBearing
BKT, BRKT BracketBracket
BTDC Before Top Dead CenterBefore Top Dead Center
CO Carbon OxideCarbon Monoxide
CONN ConnectorConnector
CPU Central Processing UnitCentral processing unit
C/U Control UnitControl unit
DC Direct CurrentDirect current
DI Direct InjectionDirect injection
ECU Engine Control Unit / Electronic ControlUnitEngine control unit / control unit
ECM Engine Control ModuleEngine control module
EGR Exhaust Gas RecirculationExhaust gas recirculation
Exh, EXH ExhaustExhaust
Ft, FRT FrontFront
FWD ForwardForward
F/C Fuel CutFuel Cut
GND GroundEarth
IC Integrated CircuitIntegrated circuit
ID Plate Identification plateIdentification plate, ID plate
IN Intake, IntakeIntake
ISO International Organization forStandardizationInternational Organization forStandardization
I/PUMP Injection PumpInjection Pump
JIS Japanese Industrial StandardJapanese Industrial Standard
L/H, LH Left HandLeft hand side
M/V Magnetic ValveMagnetic valve
NOx Nitrogen OxideNitrogen Oxide
N-TDC Number — Top Dead CenterTop dead center rotational frequency
OPT OptionOption
P Pole(S)Pole
PCV Pump Control Valve/ PositiveCrankcase VentilationPump control valve/ Positive crankcaseventilation
PM Particulate MatterParticulate matter
PS Pre-StrokePre-stroke
PTO Power Take OffPower take off
QOS Quick On SystemRapid preheating system
Rr, RR RearRear
Abbreviation Description
General Information 0A-9
SI (International System of Units)With regards the conversion to SI (InternationalSystem of Units)The introduction of the SI systems aims tointernationally unify the metric system and the variousunits used by different countries (traditional weightsand measures, the foot pound method etc.), and tocurb the confusion that occurs between the differentunits (conversion calculations etc.). The new calculating method which adopted SI unitswas completely adopted in Japan in 1992, and isstandardized by JIS-Z-8203. All of the units in this manual are written in line with theInternational System of Units SI units, and conventionalunits are written in brackets.
SIFrench) Abbreviated name of Le Systeme Internationald’Unites
Connection between main SI units and conventional units
*1 Published service data may conveniently use kg forforce and mass (weight) instead of kgf. *2 Some conversion results may be rounded off to 1 or2 decimal places. Converting expressions of quantityWhen converting, prefixes such as k (kilo) or m (mili)are used.
• 200 kgf/cm2 = 19,620 kPa = 19.6 MPa• 40 mmHg = 5,332 Pa = 5.3 kPa
Conversion formulaLength
• km × 0.6214 = mile• m × 3.281 = ft• mm × 0.03937 = in
Pressure• kPa × 0.0101972 = kg/cm2
• kPa × 0.145038 = psi• MPa × 10.197162 = kg/cm2
• MPa × 145.03774 = psiTightening torque
• N⋅m × 0.101972 = kg⋅m• N⋅m × 0.737562 = lb ft
Speed• kg/h × 0.6214 = MPH
Temperature• °C × 1.8 + 32 = °F
R/H, RH Right HandRight hand side
R/L RelayRelay
STD StandardStandard
SW SwitchSwitch
TICS Timing & Injection rate Control SystemA type of injection system
VGS Turbo Variable Geometry turbochargerSystemAdjustable turbo, VGS turbo
W/L Warning LampWarning lamp
Abbreviation Description
SI Conventional Unit Item, unit conversion
Length m m Same as the conventional unit
Weight (Mass) kg kg Same as the conventional unit
Force N * kg, kgf 1 kgf = 9.80665 N
Torque N⋅m * kg⋅m, gf⋅m 1 kgf⋅m = 9.80665 N⋅m
Pressure Pa *kg/cm2, mmHg 1 kgf/cm2 = 9.80665 kPa, 1 mmHg = 133.3 Pa
Dynamic force, horsepower W PS 1 PS = 0.74 kW
Capacity, air volume displacement m3 Litle, L, cc 1 Litle = 1 dm3, 1 cc = 1mLitle = 1cm3
Fuel consumption g/(kW⋅h) g/(PS⋅h) 1 g/(PS⋅h) = 1.360 g/(kW⋅h)
M Mega 106 1,000,000
k Kilo 103 1,000
h Hecto 102 100
d Deci 10-1 0.1
c Centi 10-2 0.01
m Milli 10-3 0.001
µ Micro 10-6 0.000001
0A-10 General Information
Table of tightening torqueThe tightening torque values in the table below apply toall situations unless a special tightening torque isspecified. bolts, nuts
The * mark indicates where soft materials have been used for internal thread sections, such as castings.
N⋅m kgf⋅m
Strengthclassification
4.84T 7T
Bolt headsection shape Hexagon head bolt Flange bolt Hexagon head bolt Flange bolt
* M10 × 1.5 19.6 ~ 33.3 2.0 ~ 3.4 22.3 ~ 37.2 2.3 ~ 3.8 27.5 ~ 45.1 2.8 ~ 4.6 30.3 ~ 50.4 3.1 ~ 5.1
M12 × 1.25 49.0 ~ 73.5 5.0 ~ 7.5 54.9 ~ 82.3 5.6 ~ 8.4 60.8 ~ 91.2 6.2 ~ 9.3 68.1 ~ 102.1 6.9 ~ 10.4
* M12 × 1.75 45.1 ~ 68.6 4.6 ~ 7.0 51.0 ~ 76.5 5.2 ~ 7.8 56.9 ~ 84.3 5.8 ~ 8.6 62.7 ~ 94.0 6.4 ~ 9.6
M14 × 1.5 76.5 ~ 114.7 7.8 ~ 11.7
83.0 ~ 124.5 8.5 ~ 12.7
93.2 ~ 139.3 9.5 ~ 14.2
100.8 ~ 151.1 10.3 ~ 15.4
* M14 × 2 71.6 ~ 106.9 7.3 ~ 10.9
77.2 ~ 115.8 7.9 ~ 11.8
88.3 ~ 131.4 9.0 ~ 13.4
94.9 ~ 142.3 9.7 ~ 14.5
M16 × 1.5 104.0 ~ 157.0 10.6 ~ 16.0
115.6 ~ 173.3 11.8 ~ 17.7
135.3 ~ 204.0 13.8 ~ 20.8
150.1 ~ 225.2 15.3 ~ 23.0
* M16 × 2 100.0 ~ 149.1 10.2 ~ 15.2
109.4 ~ 164.2 11.2 ~ 16.7
129.4 ~ 194.2 13.2 ~ 19.8
142.5 ~ 213.8 14.5 ~ 21.8
M18 × 1.5 151.0 ~ 225.6 15.4 ~ 23.0 — 195.2 ~ 293.2 19.9 ~
29.9 —
* M18 × 2.5 151.0 ~ 225.6 15.4 ~ 23.0 — 196.1 ~ 294.2 20.0 ~
30.0 —
M20 × 1.5 206.0 – 310.0 21.0 ~ 31.6 — 269.7 ~ 405.0 27.5 ~
41.3 —
* M20 × 2.5 190.2 ~ 286.4 19.4 – 29.2 — 249.1 ~ 374.6 25.4 ~
38.2 —
M22 × 1.5 251.1 – 413.8 25.6 ~ 42.2 — 362.8 ~ 544.3 37.0 ~
55.5 —
* M22 × 2.5 217.7 ~ 327.5 22.2 ~ 33.4 — 338.3 ~ 507.0 34.5 ~
51.7 —
M24 × 2 358.9 ~ 539.4 36.6 ~ 55.0 — 430.5 ~ 711.0 43.9 ~
72.5 —
* M24 × 3 338.3 ~ 507.0 34.5 ~ 51.7 — 406.0 ~ 608.0 41.4 ~
62.0 —
General Information 0A-11
The * mark indicates where soft materials have been used for internal thread sections, such as castings.
N⋅m kgf⋅m
Strength classification 8.8 9.89T
Bolt head sectionshape Hexagon head bolt Flange bolt Hexagon head bolt Flange bolt
M6 × 1 5.6 ~ 11.2 0.6 ~ 1.1
6.6 ~ 12.2 0.6 ~ 1.2 — —
M8 × 1.25 13.4 ~ 25.7 1.4 ~ 2.6
15.3 ~ 28.4 1.6 ~ 2.9
16.7 ~ 30.4 1.7 ~ 3.1
18.1 ~ 33.6 1.9 ~ 3.4
M10 × 1.25 31.3 ~ 52.5 3.2 ~ 5.4
35.4 ~ 58.9 3.6 ~ 6.1
37.3 ~ 62.8 3.8 ~ 6.4
42.3 ~ 70.5 4.3 ~ 7.2
* M10 × 1.5 31.3 ~ 51.4 3.2 ~ 5.2
34.5 ~ 57.5 3.5 ~ 5.8
36.3 ~ 59.8 3.7 ~ 6.1
40.1 ~ 66.9 4.1 ~ 6.8
M12 × 1.25 69.3 ~ 104.0 7.1 ~ 10.6
77.7 ~ 116.5 7.9 ~ 11.9
75.5 ~ 113.8 7.7 ~ 11.6
85.0 ~ 127.5 8.7 ~ 13.0
* M12 × 1.75 64.8 ~ 96.1 6.6 ~ 9.8
71.4 ~ 107.2 7.3 ~ 10.9
71.6 ~ 106.9 7.3 ~ 10.9
79.5 ~ 119.2 8.1 ~ 12.2
M14 × 1.5 106.2 ~ 158.8 10.8 ~ 16.2
114.9 ~ 172.3 11.7 ~ 17.6
113.8 ~ 170.6 11.6 ~ 17.4
123.4 ~ 185.1 12.6 ~ 18.9
* M14 × 2 100.6 ~ 149.8 10.3 ~ 15.3
108.2 ~ 162.2 11.1 ~ 16.6
106.9 ~ 160.0 10.9 ~ 16.3
115.5 ~ 173.3 11.8 ~ 17.7
M16 × 1.5 154.3 ~ 232.5 15.7 ~ 23.7
171.1 ~ 256.7 17.4 ~ 26.2
160.0 ~ 240.3 16.3 ~ 24.5
176.9 ~ 265.3 18.0 ~ 27.1
* M16 × 2 147.6 ~ 221.4 15.0 ~ 22.6
162.5 ~ 243.8 16.6 ~ 24.9
153.0 ~ 229.5 15.6 ~ 23.4
168.5 ~ 252.7 17.2 ~ 25.8
M18 × 1.5 222.5 ~ 334.3 22.7 ~ 34.1 — 229.5 ~ 345.2 23.4
~ 35.2 —
* M18 × 2.5 223.6 ~ 335.4 22.8 ~ 34.2 — 230.5 ~ 346.2 23.6
~ 35.3 —
M20 × 1.5 307.4 ~ 461.7 31.4 ~ 47.1 — 316.8 ~ 475.6 32.3
~ 48.5 —
* M20 × 2.5 284.0 ~ 472.1 29.0 ~ 43.5 — 293.2 ~ 440.3 29.2
~ 44.9 —
M22 × 1.5 413.6 ~ 620.5 42.2 ~ 63.3 — 424.6 ~ 636.5 43.3
~ 64.9 —
* M22 × 2.5 385.7 ~ 578.0 39.3 ~ 58.9 — 394.2 ~ 592.3 40.0
~ 60.4 —
M24 × 2 490.8 ~ 810.5 50.0 ~ 82.7 — 554.1 ~ 830.6 56.5
~ 84.7 —
* M24 × 3 462.8 ~ 693.1 47.2 ~ 70.7 — 520.7 ~ 781.6 53.1
~ 79.7 —
0A-12 General Information
Designations for bolt heads
Legend1. Hexagon head bolt(4.8, 4T)2. Hexagon head bolt(4.8, 4T)3. Flange bolt(4.8, 4T)4. Flange bolt(4.8, 4T)5. Hexagon head bolt(7T)6. Flange bolt(7T)7. Hexagon head bolt (refined 8.8)8. Hexagon head bolt (refined 8.8)
9. Hexagon head bolt(Un-refined 8.8)10. Hexagon head bolt(Un-refined 8.8)11. Flange bolt(8.8)12. Flange bolt(8.8)13. Hexagon head bolt(9.8, 9T)14. Hexagon head bolt(9.8, 9T)15. Flange bolt(9.8, 9T)16. Flange bolt(9.8, 9T)
Flare nut
Pipe diameter tightening torque(for medium and large
size vehicles)
Flare nut 2 side width (mm)
Old New
Flare nut tightening torque (service standard value) N⋅m kgf⋅m
φ4.76 mm 12.8 ~ 18.6 1.3 ~ 1.9 14 14
φ6.35 mm 23.5 ~ 49 2.4 ~ 5.0 17 17
φ8.0 mm 23.5 ~ 49 2.4 ~ 5.0 19 17
φ10.0 mm 44.1 ~ 93.2 4.5 ~ 9.5 22 19
φ12.0 mm 58.8 ~ 137.3 6.0 ~ 14.0 27 24
φ15.0 mm 78.5 ~ 156.9 8.0 ~ 16.0 30 30
General Information 0A-13
Taper screw from connectors (brass)
Special Tool Classification
A; Essential toolServicing operation cannot be done with any other tools than the essential tool.
B; Recommended toolServicing work can be done with a general-purpose tool commercially available.However, it is advisable to use the recommended tool as much as possible for a reduced work time and an improvedsafety in work operations.
C; Available tool Although it takes a more working time, servicing operations can be made with a tool commercially available assubstitute for the available tool.
N⋅m kgf⋅m
Screw size PT(R) 1/8 PT(R) 1/4 PT(R) 3/8 PT(R) 1/12
— 2.0 ~ 14.7(0.2 ~ 1.5)
4.9 ~ 15.7(0.5 ~ 1.6)
9.8 ~ 16.7(1.0 ~ 1.7)
9.8 ~ 17.7(1.0 ~ 1.8)
0A-14 General Information
ENGINE MECHANICAL (4HK1, 6HK1)
ENGINEENGINE MECHANICAL (4HK1, 6HK1)
TABLE OF CONTENTSDIESEL ENGINE (4HK1, 6HK1) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1A-3
Precautions on Service Work. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1A-3Main Data and Specifications. . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1A-11
Cylinder Head Cover. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1A-14Components. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1A-14Removal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1A-15Installation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1A-16Torque Specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1A-18
Inlet Cover. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1A-20Components. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1A-20Removal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1A-21Installation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1A-22Torque Specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1A-24
Turbocharger and Exhaust Manifold . . . . . . . . . . 1A-25Components. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1A-25Removal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1A-26Inspection. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1A-27Installation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1A-28Torque Specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1A-31
Timing Gear Train . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1A-34Components. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1A-34Removal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1A-35Inspection. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1A-37Installation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1A-39Torque Specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1A-50Special Tool . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1A-51
Rocker Arm Shaft ASM . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1A-52Components. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1A-52Removal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1A-52Disassembly. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1A-53Reassembly . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1A-55Installation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1A-56Torque Specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1A-58
Camshaft ASM . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1A-59Components. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1A-59Removal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1A-60Disassembly. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1A-61Reassembly . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1A-63Fixing torque . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1A-65Special Tool . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1A-65Installation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1A-66Torque Specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1A-68
Valve Stem Seal, Valve Spring . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1A-69Components. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1A-69Removal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1A-69Inspection. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1A-70Installation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1A-71Special Tool . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1A-73
Cylinder Head . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1A-74Components. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1A-74Removal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1A-74Disassembly. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1A-78
Inspection. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1A-81Reassembly . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1A-87Installation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1A-94Torque Specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1A-101Special Tool . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1A-101
Piston, Connecting Rod . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1A-103Components . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1A-103Removal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1A-103Disassembly. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1A-104Reassembly . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1A-110Installation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1A-112Torque Specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1A-114Special Tool . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1A-114
Flywheel . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1A-115Components . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1A-115Removal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1A-115Inspection. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1A-117Installation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1A-117Torque Specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1A-119Special Tool . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1A-119
Front Cover . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1A-120Components . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1A-120Removal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1A-121Installation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1A-122Torque Specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1A-124
Crankshaft Front Oil Seal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1A-126Components . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1A-126Removal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1A-126Installation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1A-128Torque Specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1A-133Special Tool . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1A-133
Crankshaft Rear Oil Seal. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1A-134Components . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1A-134Removal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1A-134Installation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1A-135Special Tool . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1A-138
Crankshaft . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1A-139Components . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1A-139Removal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1A-139Disassembly. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1A-141Reassembly . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1A-141Inspection. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1A-141Installation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1A-146Torque Specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1A-150Special Tool . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1A-150
Cylinder Block . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1A-152Components . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1A-152Removal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1A-152Inspection. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1A-153Installation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1A-154
Lubrication System . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1A-157Precautions on Service Work . . . . . . . . . . . . .1A-157
ENGINE MECHANICAL (4HK1, 6HK1)
Function Check . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1A-158Special Tool . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1A-159
Oil Port Cover ASM. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1A-160Components. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1A-160Removal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1A-160Installation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1A-160
Oil Cooler . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1A-162Components. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1A-162Removal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1A-163Disassembly. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1A-164Reassembly . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1A-164Installation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1A-165
Oil Pan . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1A-168Components. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1A-168Removal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1A-168Installation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1A-169
Oil Pump . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1A-171Components. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1A-171Removal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1A-171Disassembly. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1A-172Reassembly . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1A-172Inspection. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1A-173Installation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1A-174
Oil Pressure Switch. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1A-178Inspection. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1A-178
ENGINE MECHANICAL (4HK1, 6HK1) 1A-3
DIESEL ENGINE (4HK1, 6HK1)Precautions on Service WorkMatters that require attention in terms ofmaintenanceTo prevent damage to the engine and ensure reliabilityof its performance, pay attention to the following inmaintaining the engine: When taking down the engineon the ground, do not make the bearing surface of theoil pan touch directly the ground. Use a wood frame, forexample, to support the engine with the engine foot andthe flywheel housing.
Because there is only a small clearance between theoil pan and the oil pump strainer, it can damage theoil pan and the oil strainer.• When the air duct or air cleaner is removed, cover
the air intake opening to prevent foreign matterfrom getting into the cylinder. If it gets into it, it canconsiderably damage the cylinder and others whilethe engine is operating.
• When maintaining the engine, never fail to removethe battery ground cable. If not, it may damage thewire harness or electrical parts. If you needelectricity on for the purpose of inspection, forinstance, watch out for short circuits and others.
• Apply engine oil to the sliding contact surfaces ofthe engine before reassembling it. This ensuresadequate lubrication when the engine is firststarted.
• When valve train parts, pistons, piston rings,connecting rods, connecting rod bearings orcrankshaft journal bearings are removed, put themin order and keep them.
• When installing them, put them back to the samelocation as they were removed.
• Gaskets, oil seals, O-rings, etc. must be replacedwith new ones when the engine is reassembled.
• As for parts where a liquid gasket is used, removean old liquid gasket completely and clean it upthoroughly so that no oil, water or dust may beclung to them. Then, apply the designated liquidgasket to each place anew before assembly.
• Surfaces covered with liquid gasket must beassembled within 7 minutes of gasket application.If more than 7 minutes have elapsed, remove theexisting liquid gasket and apply new liquid gasket.
• When assembling or installing parts, fasten themwith the specified tightening torque so that theymay be installed properly.
Matters that require attention in specifically dealingwith this engine.Holes or clearances in the fuel system, which serve asa passage of fuel, including the inside of the injector,are made with extreme precision. For this reason, theyare highly sensitive to foreign matter and if it gets in, itcan lead to an accident on the road, for instance; thus,make sure that foreign matter will be prevented fromgetting in.When servicing the fuel system, every precaution mustbe taken to prevent the entry of foreign material into thesystem.
• Before beginning the service procedure, wash thefuel line and the surrounding area.
• Perform the service procedures with clean hands.Do not wear work gloves.
• Immediately after removing the fuel hose and/orfuel pipe, carefully tape vinyl bags over theexposed ends of the hose or pipe.
• Always replace the high-pressure pipe in fuelsystem with new one if it has been removed.Reuse of it causes damage the seal surface,resulting in fuel leakage.
• If parts are to be replaced (fuel hose, fuel pipe,etc.) do not open the new part packaging untilinstallation.
Work procedure• The fuel opening must be quickly sealed when
removing the fuel pipe, injection pipe, fuel injector,fuel supply pump, and common rail.
• The eyebolts and gasket must be stored in a cleanparts box with a lid to prevent adhesion of foreignmatter.
• Fuel leakage could cause fires. Therefore, afterfinishing the work, wipe off the fuel that has leakedout and make sure there is no fuel leakage afterstarting the engine.
1A-4 ENGINE MECHANICAL (4HK1, 6HK1)
How to read the model4HK1
Name1. Cast The Engine Model 2. Stamp An Engine Number
ENGINE MECHANICAL (4HK1, 6HK1) 1A-5
6HK1
Name1. Stamp An Engine Number
Explanations on functions and operation
Electronic engine controlWith the control unit, the range from injection to airintake/exhaust, including fuel injection quantity,injection timing, intake air restriction, EGR, and idlingrpm, is controlled.
Cylinder blockThe cylinder block is cast-iron with the center distanceof each bore being equal and is of the highly rigid,symmetrical structure with the crankshaft center beingthe center. The bearing cap is of the ladder framestructure and tightened up under the plastic rangerotation angle method.
Cylinder linerThe cylinder liner is selected to match an internaldiameter of a bore of the cylinder block and built, whichis imprinted on the left side of the cylinder.
PistonThe piston is aluminum-alloy and an autothermaticpiston with a strut cast, while the combustion chamberis a round reentrant type.
Cylinder headThe cylinder head is cast-iron and there are 4 valvesper cylinder. The angular tightening method of thecylinder head bolt further increases reliability anddurability.
WSHK0001
1
1A-6 ENGINE MECHANICAL (4HK1, 6HK1)
CrankshaftTuftriding is given, while on the No. 1 balance weightimprinted is the grade of each journal diameter.
EGR systemBased upon data, including water temperature, enginespeeds or engine loads, it is controlled via EngineControl Module (ECM) to purify exhaust by recyclingpart of it. Its main components include an EGR valve, an EGRcooler and various sensors.
Connecting rod cap boltThe angular tightening method of the connecting rodcap bolt further increases reliability and durability.
Common rail-type electronic control injectionsystemThe common rail-type electronic control injectionsystem is composed of a fuel supply pump that sets thetarget pressure of high-pressure fuel and supply it, acommon rail that measures such high-pressure fueland a fuel injector that turns it into a fine spray andinjects it. Each is controlled via ECM based uponvarious signals, while injection timing or fuel injectionquantity is controlled under every possible drivingcondition.
Fuel injectorThe fuel injector is a 7-hole nozzle that adjusts fuelinjection quantity or injection timing by opening orclosing an electromagnetic valve on the head of thefuel injector.ECM corrects the dispersion of fuel injection quantitybetween fuel injectors according to ID code data inmemory. At the replacement of fuel injectors, ID codedata should be stored in ECM.
Fuel filter with sedimenterIt is a fuel filter with sedimenter that gets rid of water bymaking use of the difference in specific gravity betweenlight oil and water, which comes with an indicator thatnotifies you that it is filled with water.
Preheating systemThe preheating system consists the ECM, the glowrelay, glow plugs and the glow indicator lamp. Thepreheating system is operated when the engine coolanttemperature is low, and make the engine easy to start.
Lubrication systemIt is an oil filter with full-flow bypass, which uses awater-cool oil cooler and oil jet to cool the piston.
Function checkInspection/adjustment of valve clearance
1. Inspection of valve clearance• Remove the cylinder head cover.• Remove the fuel injector harness ASM.• Loosen the terminal nuts alternately to remove.• Remove the leak off pipe.
• Rotate the crankshaft to make the No.1 cylindermeet the compression top dead center (TDC).
4HK1
6HK1
• Insert a 0.4 mm (0.016 in) thickness gauge into aclearance between the rocker arm and the bridgeto check it and adjust it if needed.
Caution:Adjust while being cold.
2. Adjustment of valve clearance
Caution:Adjust valve clearance carefully so that the bridge maybecome level (hit the end of the 2 valve axes).
Valve clearance mm (in)Intake valve 0.4 (0.016)Exhaust valve 0.4 (0.016)
ENGINE MECHANICAL (4HK1, 6HK1) 1A-7
a. Completely loosen all of the bridge and rockerarm adjusting nuts and adjusting screws(4HK1: 8 nuts and 8 screws, 6HK1: 12 nuts and12 screws).
b. Place a 0.4 mm (0.016 in) thickness gaugebetween the No. 1 cylinder rocker arm end andthe bridge cap.
c. Tighten the rocker arm adjusting screw until thethickness gauge is snug (not tight) between therocker arm end and the bridge cap.
d. Tighten the rocker arm lock nut.e. Tighten the bridge adjusting screw until the
bridge contacts the valve head.f. Tighten the bridge lock nut.g. Check that the thickness gauge is still held
snugly between the rocker arm end and thebridge cap. If it is too tight, slightly loosen thebridge adjusting screw and lock nut to restoresnugness.
h. Remove the thickness gauge.i. Repeat the above procedure for the remaining
cylinders.
Name1. Rocker Arm2. Bridge Cap3. Bridge
• With a thickness gauge kept inserted, tightenan adjusting screw of the bridge lightly andmake sure that the tip of the adjusting screwtouches the end of valve axis and themovement of the thickness gauge has becometight.
• Then, check if the end of the valve axis on theopposite side is unstable or hits diagonally. Ifso, loosen the bridge adjusting screw a little sothat the end of the valves on both sides maytouch properly.Valve bridge clearance: ± 0.1 mm (0.0039 in) orless
• After making an adjustment so that the end ofthe valves on both sides may touch properly,tighten up an adjusting screw nut of the bridgewith a flathead screwdriver so that the bridgeadjusting screw may not rotate.
Caution:If the adjusting screw of the bridge is poorly adjusted,the bridge would tilt and be pushed down and seized,which may damage the bridge guide, for example.Thus, adjust it accurately.Tightening torque: 22 N⋅m (2.2 kg⋅m/16 lb ft)
Tightening torque: 22 N⋅m (2.2 kg⋅m/16 lb ft)
Tightening torque:Rocker arm adjustmentscrew nut
22 N⋅m (2.2 kg⋅m/16 lb ft)
Bridge adjustment screwnut
22 N⋅m (2.2 kg⋅m/16 lb ft)
1A-8 ENGINE MECHANICAL (4HK1, 6HK1)
Adjustment table (4HK1)
Adjustment table (6HK1)
• If the No. 1 cylinder is the compression TDC,adjust a valve clearance with mark given onthe table and if the No. 4 (4HK1) or No. 6(6HK1) cylinder is the compression TDC, thatwith × mark.
4HK1
6HK1
Cylinder No. 1 2 3 4
Valve arrangement IN EX IN EX IN EX IN EX
No. 1 cylinderCompression top dead center position
No. 4 cylinderCompression top dead center position
× × × ×
Cylinder No. 1 2 3 4 5 6
Valve arrangement IN EX IN EX IN EX IN EX IN EX IN EX
No. 1 cylinderCompression top dead center position
No. 6 cylinderCompression top dead center position
× × × × × ×
WSHK0002
ENGINE MECHANICAL (4HK1, 6HK1) 1A-9
• Attach the harness ASM to the fuel injector.Tighten the harness bracket with thedesignated torque.
Tightening torque: 48 N⋅m (4.9 kg⋅m/35 lb ft)• Install the terminal nuts on the fuel injector.
Tightening torque: 2 N⋅m (0.2 kg⋅m/18 lb in)
Note:• Tighten the terminal nuts alternately in order to
prevent imbalance in tightening because they areunified.
• Do not tighten the nuts too tightly because it leadsto damage to the terminal stud.• Install the cylinder head cover.
Refer to the “Cylinder Head Cover”.
Compression pressure inspection• Warm-up the engine.• Remove a negative terminal of the battery and
remove all the glow plugs.• Remove the harness connector for the fuel injector
built on the lower head cover (no fuel will beinjected).
Caution:When the harness connector is removed, ECM judgesthat it broke down and DTC is recorded. Uponcompletion of measurement, never fail to clear memoryof ECM.(For how to clear memory of ECM, refer to the EngineControl System Section)
4HK1
Name1. Fuel Injector Harness Connector
6HK1
Name1. Fuel Injection Harness Connector
• Install the negative terminal of the battery.• Turn on the starter to emit foreign matter within the
cylinders.• Install an adapter and a gauge of a compression
gauge of the special tool.
WSHK0003
WSHK0004
1
1A-10 ENGINE MECHANICAL (4HK1, 6HK1)
Compression gauge: 5-8840-2675-0 (J-26999-12)Compression gauge adapter4HK1: EN-467226HK1: 5-8840-2622-0
• Turn on the starter to inspect compressionpressure.
4HK1
6HK1
• Measure each cylinder one by one.
Caution:To keep engine speed at 200 rpm or more, use fullycharged batteries.
• Remove a compression gauge of the special tool.• Remove a negative terminal of the batteries.• Install a harness connector for the fuel injector built
on the lower head cover.• Install all the glow plugs.
• Install the negative terminal of the battery.
Compression pressure MPa (psi) / 200 rpm
Standard 2.84 – 3.24 (412 – 469)
Limit 1.96 (284)
Differences among the cylinders 294 kPa (43)
Compression pressure MPa (psi) / 200 rpm
Standard 3.24 (469)
Limit 2.26 (327)
Differences among the cylinders 294 kPa (43)
Tightening torque: 20 N⋅m (2.0 kg⋅m/15 lb ft)
ENGINE MECHANICAL (4HK1, 6HK1) 1A-11
Main Data and Specifications
Item Engine model 4HK1
Type Diesel/4-cycle/water cooled-type, inline four-cylinder OHC
Combustion chamber form Direct injection type
Cylinder liner type Dry type
Number of cylinders — cylinder bore × strokes
mm (in) 4-115 (4.53) × 125 (4.92)
Displacement cc (cu.in) 5193 (317)
Compression ratio 17.5
Compression pressure MPa (psi)/rpm 3.23 (468)/200
Idle speed rpm 800
Valve clearance Intake 0.4 (0.016) (cold)
mm (in) Exhaust 0.4 (0.016) (cold)
Ignition type Compressed ignition
Injection order 1 — 3 — 4 — 2
Lubricating system
Lubricating type Pressure type
Oil pump type Gear type
Volume of lubricating oil L (qts) 13.0 (13.7) — 20.5 (21.7)
Oil filter type Full flow filter (cartridge type)
Oil cooling type Built-in, water-cooling
Cooling system
Cooling type Water cooling type
Radiator type Corrugated fin (pressure type)
Water pump type Centrifugal, belt type
Thermostat type 2 wax-type units
Thermostat valve-opening temperature °C (°F) 85 (185)
Volume of coolant L (qts) 14 (14.8) (incl. radiator)
Fuel system
Injection pump type Electronic control common rail type
Governor type Electronic type
Timer type Electronic type
Injection nozzle type Multi-hole type7-hole and φ 0.16 mm (0.0063 in) inside diameter
Charging system
Generator type AC type
Power output V/A 24 — 50
Regulator type IC
1A-12 ENGINE MECHANICAL (4HK1, 6HK1)
Starting system
Starter type Reduction type
Power output V-kw 24 — 5.0
Preheat system type Glow plug
Glow plug standard voltage/electric current V/A 23 — 3.5
Item Engine model 6HK1
Type Diesel/4-cycle/water cooled-type, inline four-cylinder OHC
Combustion chamber form Direct injection type
Cylinder liner type Dry type
Number of cylinders — cylinder bore × strokes
mm (in) 6-115 (4.53) × 125 (4.92)
Displacement cc (cu.in) 7790 (475)
Compression ratio 17.5
Compression pressure MPa (psi)/rpm 3.04 (441)/200
Idle speed rpm For Hitachi products: 800, For JCB and Sumitomo products: 900
Valve clearance Intake 0.4 (0.016) (cold)
mm (in) Exhaust 0.4 (0.016) (cold)
Ignition type Compressed ignition
Injection order 1 — 5 — 3 — 6 — 2 — 4
Lubricating system
Lubricating type Pressure type
Oil pump type Gear type
Volume of lubricating oil L (qts) 28 (29.6) — 38 (40.2)
Oil filter type Full flow filter (cartridge type)
Oil cooling type Built-in, water-cooling
Cooling system
Cooling type Water cooling type
Radiator type Corrugated fin (pressure type)
Water pump type Centrifugal, belt type
Thermostat type 2 wax-type units
Thermostat valve-opening temperature °C (°F) 82 (180)
Volume of coolant L (qts) 14.5 (15.3)
Fuel system
Injection pump type Electronic control common rail type
Governor type Electronic type
Timer type Electronic type
Item Engine model 4HK1
ENGINE MECHANICAL (4HK1, 6HK1) 1A-13
Special tool
Injection nozzle type Multi-hole type7-hole and φ0.16 mm (0.0063 in) inside diameter
Charging system
Generator type AC type
Power output V/A 24 — 90/50
Regulator type IC
Starting system
Starter type Reduction type
Power output V-kw 24 — 5.0
Preheat system type Glow plug
Glow plug standard voltage/electric current V/A 23 — 3.5
Item Engine model 6HK1
Illustration Tool Number/Description
5-8840-26750-0J-26999-12
Compression gauge
EN-46722Compression gauge
adapter(4HK1)
5-8840-2622-0Compression gauge
adapter(6HK1)
1A-14 ENGINE MECHANICAL (4HK1, 6HK1)
Cylinder Head CoverComponents4HK1
Name1. Head Cover2. Gasket
3. Head Cover Case4. Gasket
ENGINE MECHANICAL (4HK1, 6HK1) 1A-15
6HK1
Name1. Head Cover2. Gasket
3. Head Cover Case4. Gasket
Removal1. Remove the head cover.2. Remove the gasket.
WSHK0005
1
2
3
4
1A-16 ENGINE MECHANICAL (4HK1, 6HK1)
4HK1
Name1. Head Cover
6HK1
Name1. Head Cover
3. Remove the fuel injector harness connector.4. Remove the head cover case.5. Remove the gasket.
4HK1
Name1. Head Cover Case2. Fuel Injector Harness Connector
6HK1
Name1. Head Cover Case2. Fuel Injector Harness Connector
Installation1. Install the gasket on the lower cover.2. Install the head cover case.
3. Install the fuel injector harness connector.
WSHK0006
1
Tightening torque: 4HK1: 18 N⋅m (1.8 kg⋅m/13 lb ft), 6HK1: 13 N⋅m (1.3 kg⋅m/9.6 lb ft)
WSHK0007
2
1
ENGINE MECHANICAL (4HK1, 6HK1) 1A-17
Caution:Push it in thoroughly until the claws of the lock raise.4HK1
Name1. Head Cover Case2. Fuel Injector Harness Connector
6HK1
Name1. Head Cover Case2. Fuel Injector Harness Connector
4. Install the gasket on the head cover.5. Install the head cover and tighten up according to
the orders given on the figure.
4HK1
6HK1
Tightening torque: 4HK1: 18 N⋅m (1.8 kg⋅m/13 lb ft), 6HK1: 13 N⋅m (1.3 kg⋅m/9.6 lb ft)
WSHK0007
2
1
WSHK0008
1A-18 ENGINE MECHANICAL (4HK1, 6HK1)
Torque Specifications4HK1
ENGINE MECHANICAL (4HK1, 6HK1) 1A-19
6HK1
WSHK0009
N mkg m/lb ft
13 1.3 / 9.6
13 1.3 / 9.6
1A-20 ENGINE MECHANICAL (4HK1, 6HK1)
Inlet CoverComponents4HK1
Name1. Case ASM2. Inlet Cover3. Inlet Pipe Gasket
4. Inlet Pipe5. Reed Valve
ENGINE MECHANICAL (4HK1, 6HK1) 1A-21
6HK1
Name1. Case ASM2. Inlet Cover3. Inlet Pipe Gasket
4. Inlet Pipe5. Reed Valve4. Bolt
Removal1. Remove the common rail.
Refer to the “Common Rail” in the fuel systemsection.
2. Remove the inlet pipe.3. Remove the case ASM.• Remove the reed valve from the case ASM.• Inspect the valve whether the carbon has not come
in contact around the valve.
4HK1
WSHK0177
4
1
6
5
3
2
1A-22 ENGINE MECHANICAL (4HK1, 6HK1)
6HK1
4. Remove the boost pressure sensor and bracket.
Name1. Boost Pressure Sensor2. Bracket
5. Remove the inlet cover.• On the place where the case ASM is to be installed
inside the inlet cover (arrowed) is a bolt. Be carefulnot to forget to remove it.
• Peel the liquid gasket off carefully.
* 4HK1 is shown for illustration.
Installation1. Install the inlet cover.• Apply the liquid gasket (ThreeBond 1207C or
equivalent) by using a bead diameter of 2.5 – 5.5mm (0.1 – 0.2 in) along a groove of the inlet cover.
• Install within seven minutes after applying liquidgasket.
Caution:• Be careful not to forget to fasten the bolt indicated
with an arrow.• Tighten up the stud part together with the common
rail.
* 4HK1 is shown for illustration.
WSHK0236
2
1
Tightening torque: 22 N⋅m (2.2 kg⋅m/16 lb ft)
ENGINE MECHANICAL (4HK1, 6HK1) 1A-23
2. Install the boost pressure sensor and bracket.Apply Loctite to the bolt shown on the illustrationand install it.
Name1. Boost Pressure Sensor2. Bracket
3. Install the reed valve to the case ASM• Apply the liquid gasket (Loctite 262) on the
mounting bolt and tighten it to the specified torque.
4. Install the case ASM.• Apply the liquid gasket and mount within 7
minutes.
4HK1
Name1. Case ASM2. Reed Valve3. Bolt
6HK1
Name1. Case ASM2. Reed Valve3. Bolt
5. Install the gasket on the inlet pipe and tighten upwith the specified torque.
6. Install the common rail.Refer to the “Common Rail” in the fuel systemsection.
Tightening torque: 21.6 N⋅m (2.2 kg⋅m/16 lb ft)
Tightening torque: 9.8 N⋅m (1.0 kg⋅m/7.2 lb ft)
Tightening torque: 24 N⋅m (2.4 kg⋅m/18 lb ft)
WSHK0236
2
1
Tightening torque: 24 N⋅m (2.4 kg⋅m/18 lb ft)
WSHK0179
3
2
1
1A-24 ENGINE MECHANICAL (4HK1, 6HK1)
Torque Specifications4HK1
6HK1
WSHK0063
20 (2 / 15) 39 (3 / 29)
24.5 (2.5 / 18)
N m(kg m/lb ft)
ENGINE MECHANICAL (4HK1, 6HK1) 1A-25
Turbocharger and Exhaust ManifoldComponents4HK1
Name1. Oil Feed Pipe2. Water Return Pipe3. Exhaust Manifold4. Water Feed Pipe
5. Turbo Charger ASM6. Exhaust Adapter7. Oil Return Pipe
1A-26 ENGINE MECHANICAL (4HK1, 6HK1)
6HK1
Name1. Oil Feed Pipe2. Exhaust Manifold3. Turbo Charger ASM
4. Exhaust Adapter5. Oil Return Pipe
Removal1. Loosen the radiator drain cock to drain coolant.
(4HK1 only)2. Remove the air intake duct from the turbocharger
and the air cleaner.3. Remove the charge air pipe from the turbocharger
and the charge air cooler.4. Disconnect the exhaust pipe.5. Remove the EGR pipe.6. Remove the oil feed pipe.7. Remove the oil return pipe.8. Remove the water feed pipe. (4HK1 only)
WSHK0012
2
5
4 3
1
ENGINE MECHANICAL (4HK1, 6HK1) 1A-27
• Remove the water return pipe. (4HK1 only)
Name1. Water Return Pipe
9. Remove the heat protector on the turbocharger.10. Remove the exhaust adapter bolts.11. Remove the four turbocharger clamping nuts.12. Remove the turbocharger from the exhaust
manifold.13. Remove the exhaust manifold.4HK1
Name1. Exhaust Manifold2. Turbocharger3. Exhaust Adapter
6HK1
Name1. Exhaust Manifold2. Turbocharger3. Exhaust Adapter
Inspection• Inspection of exhaust manifold
Inspect the plane surface of the plane on which themanifold and the cylinder head are to be installed.
Caution:If the plane surface exceeds the limit, replace it.
* 4HK1 is shown for illustration.
Manifold installation plane surface mm (in)
Standard 0.3 (0.01) or less
Limit 0.5 (0.02)
WSHK0013
1 3 2
1A-28 ENGINE MECHANICAL (4HK1, 6HK1)
• Check a crack in the exhaust manifold visually.Carefully inspect the turbocharger for abrasion and/orexcessive wear. Make any necessary adjustments,repairs, and/or part replacements.Inspecting the turbocharger is refered to the “Turbochager” in the exhaust system section.
Installation1. Put the gasket in to install the exhaust manifold.• 4HK1: Tighten up with the 2 nuts and 6 bolts
according to the order given on the figure.
• 6HK1: Tighten up with the 12 nuts according to theorder given on the figure.
Caution:Do not tighten up too much because it hampersexpansion and contraction due to the heat from themanifold.4HK1
6HK1
2. Install the gasket and turbocharger to the exhaustmanifold. Tighten the nuts to the specified torque.
Tightening torque: 52 N⋅m (5.3 kg⋅m/38 lb ft)3. Tighten the adapter bolts (exhaust manifold side)
to the specified torque.
Tightening torque: 32.4 N⋅m (3.3 kg⋅m/24 lb ft)4HK1
Name1. Exhaust Manifold2. Turbocharger3. Exhaust Adapter
Tightening torque: 34 N⋅m (3.5 kg⋅m/25 lb ft)
Tightening torque: 55 N⋅m (5.6 kg⋅m/41 lb ft)34 N⋅m (3.5 kg⋅m/25 lb ft) for (7)only
WSHK0014
ENGINE MECHANICAL (4HK1, 6HK1) 1A-29
6HK1
Name1. Exhaust Manifold2. Turbocharger3. Exhaust Adapter
4. Install the water feed pipe to the turbocharger.(4HK1 only)
• Tighten the joint bolts to the specified torque.
Tightening torque: 41 N⋅m (4.2 kg⋅m/30 lb ft)• Install the pipe bracket and tighten the bolts to the
specified torque.
Tightening torque: 24 N⋅m (2.4 kg⋅m/18 lb ft)4HK1
Name1. Water Feed Pipe
5. Install the water return pipe. Tighten the joint boltsto the specified torque. (4HK1 only)
Tightening torque: 41 N⋅m (4.2 kg⋅m/30 lb ft)6. Install the water return pipe bracket. Tighten the
bolts to the specified torque. (4HK1 only)
Tightening torque: 24 N⋅m (2.4 kg⋅m/18 lb ft)• Install the rubber hose between the water return
pipe and the thermostat housing.
4HK1
Name1. Water Return Pipe
7. Install the turbocharger oil feed pipe to the top ofthe turbocharger. Tighten the joint bolts to thespecified torque.
• Install the pipe bracket and tighten the bolts to thespecified torque.
Tightening torque: 24 N⋅m (2.4 kg⋅m/18 lb ft)8. Tighten the oil return pipe bolts to the specified
torque.
WSHK0013
1 3 2
Tightening torque: 4HK1: 41 N⋅m (4.2 kg⋅m/30 lb ft),6HK1: 34.5 N⋅m (3.5 kg⋅m/25 lb ft)
Tightening torque (Turbocharger side):4HK1: 9 N⋅m (0.9 kg⋅m/80 lb in),6HK1: 17.6 N⋅m (1.8 kg⋅m/13 lb ft)
Tightening torque (Cylinder block):4HK1: 22 N⋅m (2.2 kg⋅m/16 lb ft),6HK1: 17.6 N⋅m (1.8 kg⋅m/13 lb ft)
1A-30 ENGINE MECHANICAL (4HK1, 6HK1)
* 4HK1 is shown for illustration.
Name1. Oil Return Pipe
9. Install the air intake duct and tighten the bolts tothe specified torque.
Tightening torque: 10 N⋅m (1.0 kg⋅m/89 lb in)10. Install the charge air pipe in the turbo charger and
the charge air cooler.
11. Connect the exhaust pipe.12. Add cooling water to the radiator. (4HK1 only)13. Install the EGR pipe.
• Put the gasket between both ends of the EGR pipeand install to the specified torque.
14. Replenish the coolant. (4HK1 only)
Tightening torque:Duct bolt 21 N⋅m (2.1 kg⋅m/15 lb ft)Duct clip 6 N⋅m (0.6 kg⋅m/53 lb in)
Tightening torque: 24 N⋅m (2.4 kg⋅m/18 lb ft)
ENGINE MECHANICAL (4HK1, 6HK1) 1A-31
Torque Specifications4HK1
1A-32 ENGINE MECHANICAL (4HK1, 6HK1)
6HK1
WSHK0015
32.4 (3.3 / 24)50.5 (5.1 / 37)23.5 (2.4 / 17)
17.6 (1.8 / 13) 34.5 (3.5 / 25)
17.6 (1.8 / 13)
N m(kg m/lb ft)
ENGINE MECHANICAL (4HK1, 6HK1) 1A-33
* 4HK1 is shown for illustration.WSHK0232
N mkg m/lb ft
1A-34 ENGINE MECHANICAL (4HK1, 6HK1)
Timing Gear TrainComponents4HK1
Name1. Idle Gear B Shaft2. Idle Gear A3. Idle Gear B4. PTO Idle Gear5. PTO Idle Gear Cover6. Flywheel
7. Rear Oil Seal8. Flywheel Housing9. Slinger
10. Crankshaft Position Sensor11. Oil Pan12. Fuel Supply Pump
ENGINE MECHANICAL (4HK1, 6HK1) 1A-35
6HK1
Name1. Idle Gear B Shaft2. Idle Gear A3. Idle Gear B4. PTO Idle Gear5. PTO Idle Gear Cover6. Flywheel
7. Rear Oil Seal8. Flywheel Housing9. Slinger
10. Idle Gear A Shaft11. PTO Idle Gear Shaft12. Oil Pump
Removal1. Remove the cylinder head cover.
Refer to “Cylinder Head Cover”.2. Remove the rocker arm shaft ASM.
Refer to “Rocker Arm Shaft ASM”.3. Remove the camshaft ASM.
Refer to “Camshaft ASM”.4. Remove the cylinder head ASM.
Refer to the “Cylinder Head”.5. Remove the fuel supply pump ASM.
WSHK0017
2
10
5 812
3
1
9
11
4
7
6
1A-36 ENGINE MECHANICAL (4HK1, 6HK1)
Refer to “Fuel Supply Pump” in the fuel systemsection.
* 4HK1 is shown for illustration.6. Remove the crankshaft position sensor.• Remove the crankshaft position sensor before
remove flywheel.4HK1
6HK1
7. Remove the flywheel.• Install the crankshaft stopper on the starter part of
the flywheel housing to stop the crankshaft fromrotating.
Caution:Check if the stopper meshes with the ring gear withoutfail and is installed properly.
Special toolCrankshaft stopper: x-xxxx-xxxx-x (xx-xxxxx)
• Loosen the fastening bolts of the flywheel little bylittle according to the order given on the figure.
• After loosening all the bolts, remove the stopper toremove the flywheel.
8. Remove the rear oil seal.Refer to the “Crankshaft Rear Oil Seal”.
9. Use the slinger remover to remove the slinger.
ENGINE MECHANICAL (4HK1, 6HK1) 1A-37
Caution:If the oil seal has been removed, both the oil seal andslinger must be replaced as a set.
Special toolSlinger remover:
1-8521-0027-0 (For 4HK1 and 6HK1)x-xxxx-xxxx-x (For 4HK1)8-9439-6858-0 (For 6HK1)
10. Remove the oil pan.11. Remove the PTO idle gear cover.12. Remove the PTO idle gear.
* 4HK1 is shown for illustration.13. Remove the flywheel housing.
• Never fail to remove the bolt(s) given on the figure.
* 4HK1 is shown for illustration.14. Remove the idle gear A.15. Remove the idle gear A shaft. (6HK1)16. Remove the oil pump. (6HK1)17. Remove the idle gear B.18. Remove the idle gear B shaft.
* 4HK1 is shown for illustration.
Inspection1. Measurement of idle gear backlash• Apply a dial gauge on the teeth of the idle gear to
be measured and move the gear to right and leftlightly to read how much the dial gauge shook(never fail to fix the gear).
• If the measurement exceeds the limit, replace theidle gear.
1A-38 ENGINE MECHANICAL (4HK1, 6HK1)
• Measure backlash of the idle gear before removingthe idle gear A.
2. Measurement of end clearance of the idle gear.• Insert a thickness gauge between the idle gear and
the thrust collar to measure a clearance.
• If the measurement exceeds the limit, replaceeither the idle gear or the thrust collar.
• Measure an end clearance of the idle gear beforeremoving the idle gear B.
3. Outside diameter of idle gear shaft• Use a micrometer to measure an external diameter
of each idle gear shaft.
• If the measurement exceeds the limit, replace theshaft.
4HK1
Backlash of the timing gear mm (in)
Standard 0.10 – 0.17 (0.004 – 0.006)
Limit 0.30 (0.01)
Axial play of idle gear mm (in)
Standard 0.080 – 0.140 (0.003 – 0.006)
Limit 0.20 (0.008)
Outside diameter of idle gear shaft mm (in)
Standard 29.959 – 29.980 (1.179 – 1.180)
Limit 29.80 (1.173)
External diameter of the idle gear A shaft mm (in)
Standard 39.959 – 39.975 (1.573 – 1.574)
Limit 39.80 (1.567)
ENGINE MECHANICAL (4HK1, 6HK1) 1A-39
6HK1
4. Clearance between the idle gear and the idle gearshaft
• Measure an inside diameter of the idle gearbushing to calculate a clearance between the idlegear and the idle gear shaft.
• If the measurement exceeds the limit, replaceeither the idle gear or the shaft.
4HK1
6HK1
Installation1. Install the idle gear B shaft.• Tighten the idle gear B shaft to the specified
torque.
• After installation, apply engine oil to the shaft.
Outside diameter of idle gear shaft mm (in)
Standard 29.959 – 29.980 (1.179 – 1.180)
Limit 29.9 (1.177)
External diameter of the idle gear A shaft mm (in)
Standard 49.950 – 49.975 (1.967 – 1.968)
Limit 49.9 (1.965)
Clearance between the idle gear and the shaft
mm (in)
Standard 0.020 – 0.062 (0.0007 – 0.0024)
Limit 0.200 (0.0079)
Clearance between the idle gear A and the shaft
mm (in)
Standard 0.025 – 0.066 (0.0009 – 0.0026)
Limit 0.200 (0.0079)
Clearance between the idle gear and the shaft
mm (in)
Standard 0.020 – 0.062 (0.0007 – 0.0024)
Limit 0.200 (0.0079)
Clearance between the idle gear A and the shaft
mm (in)
Standard 0.025 – 0.075 (0.0010 – 0.0030)
Limit 0.200 (0.0079)
Tightening torque: 31 N⋅m (3.2 kg⋅m/23 lb ft)
1A-40 ENGINE MECHANICAL (4HK1, 6HK1)
* 4HK1 is shown for illustration.2. Install the idle gear B.• Install the idle gear B in the direction given on the
figure and tighten up the fastening bolts with thespecified torque.
* 4HK1 is shown for illustration.
Name1. Idle Gear2. Thrust Collar3. Bolt
3. Install the oil pump.4. Install the idle gear A shaft. (6HK1)5. Install the idling gear A.• Rotate the crankshaft to make the No.1 cylinder
meet the compression top dead center (TDC).
Name1. Crank Gear2. Idle Gear A
• Align the crankshaft gear (2) L mark and idle gearA (1) 0 marks.
• Tighten the installing bolt to the specified torque.Tightening torque: 4HK1: 110 N⋅m (11.2 kg⋅m/81 lb ft),
6HK1: 95 N⋅m (9.7 kg⋅m/70 lb ft)
Tightening torque: 133 N⋅m (13.6 kg⋅m/98 lb ft)
WSHK0193
ENGINE MECHANICAL (4HK1, 6HK1) 1A-41
Name1. Idle Gear C2. Camshaft Gear3. Idle Gear B4. PTO Gear5. PTO Idle Gear
6. Crankshaft Gear7. Oil pump Drive Gear8. Fuel Supply Pump Gear9. Idle Gear A
6. Install the flywheel housing.• Clean the rear side of the cylinder block. In
particular, remove overflow liquid gasketthoroughly when the crankcase is installed.
• As the figure shows, apply the liquid gasket(ThreeBond 1207B or equivalent) inside a hole ofthe bolt (except the bolt holes indicated with anarrow) evenly.
4HK1
1A-42 ENGINE MECHANICAL (4HK1, 6HK1)
6HK1 • Align with the knock pin of the cylinder block andinstall the flywheel housing.
• Tighten up the Mark 3 from the cylinder block side.
4HK1
Tightening torque of the flywheel housing (4HK1):N⋅m (kg⋅m/lb ft)
1 = 96 (9.8/71) 2 = 77 (7.9/57) 3 = 38 (3.9/28)
ENGINE MECHANICAL (4HK1, 6HK1) 1A-43
6HK1
7. Install the PTO idle gear.• Apply engine oil over the part where the gear of the
idle gear shaft is to be put together.
• Put the idle gear and the shaft together and installit on the location given on the figure and tighten upwith the specified torque.
Tightening torque of the flywheel housing (6HK1):N⋅m (kg⋅m/lb ft)
1 = 96 (9.8/71) 2 = 86 (8.8/63) 3 = 119 (12.1/88)4 = 53 (5.4/39) 5 = 73 (7.4/54) 6 = 26 (2.7/19)
2
1
1
6
11
1
1
3
3
5
4
Tightening torque: 4HK1: 133 N⋅m (13.6 kg⋅m/98 lb ft)6HK1: 119 N⋅m (12.1 kg⋅m/88 lb ft)
1A-44 ENGINE MECHANICAL (4HK1, 6HK1)
8. Install the PTO idle gear cover.• Install the O-ring on the cover and install it on the
flywheel housing and tighten up the tighteningbolts with the specified torque.
4HK1
6HK1
9. Install the oil pan.• Apply the liquid gasket (ThreeBond 1207B or
equivalent) on a joint between the cylinder block,the front cover and the flywheel housing with abeat diameter of 3 mm (0.12 in).
• Install the oil pan within 7 minutes after applyingthe liquid gasket.
4HK1
Tightening torque: 19 N⋅m (1.9 kg⋅m/14 lb ft)
WSHK0194
ENGINE MECHANICAL (4HK1, 6HK1) 1A-45
6HK1
• With the flywheel housing, the front cover and thestud of the crankcase as a guide, put together thegasket and put the oil pan on it.Then, put the rubber ASM on the oil pan and fix itby fastening bolts and nuts.
4HK1
6HK1
Name1. Oil Pan2. Gasket
Tightening4HK1
• After fastening the oil pan at the respective pointsof (1), (2), (3), and (4), fasten other parts.
Tightening torque: 30 N⋅m (3.1 kg⋅m/22 lb ft)
WSHK0195
1A-46 ENGINE MECHANICAL (4HK1, 6HK1)
6HK1• Fastening the oil pan from the part of A or B in
clock wise order.• It tightens again by specified torque.
10. Install the rear slinger using installer, setting tool.Special tool
4HK1Oil seal installer kit: x-xxxx-xxxx-x (x-xxxxx)6HK1Oil seal setting tool: 8-94396-856-0• Install the slinger (1) to the end of adapter (2).
Install the adapter to the crankshaft (3).• Install the slinger sleeve (4) to the adapter. Tighten
the center bolt (5) until the sleeve comes in contactwith the adapter stopper.
• After pressing in the slinger, make sure that thedistance between crankshaft end surface and theslinger is A as specified.
4HK1
Tightening torque: 24.5 N⋅m (2.5 kg⋅m/18 lb ft)
WSHK0196
Distance (A): 17.3±0.3 mm (0.7±0.01 in)Distance (B): 10.8±0.1 mm (0.4±0.004 in)
WSHK0197
WSHK0198
ENGINE MECHANICAL (4HK1, 6HK1) 1A-47
6HK1
Caution:Be sure to replace the slinger and oil seal as a set.11. Install the rear oil seal using installer, setting tool.
Special tool4HK1Oil seal installer kit: x-xxxx-xxxx-x (x-xxxxx)6HK1Oil seal setting tool: 8-94396-856-0• Apply engine oil to the oil seal lip.
Caution:Do not allow engine oil to come in contact with theoutside oil seal and felt ring.
• Insert the oil seal (1) into the adapter (2).• Insert the oil seal sleeve (3) to the adapter.• Tighten the center bolt until the sleeve comes into
contact with the adapter stopper.
•
• After pressing the oil seal, make sure that thedistance between crankshaft end surface and theoil seal as specified.
4HK1
Distance (A): 17±0.3 mm (0.7±0.01 in)WSHK0199
WSHK0200Distance (A): 7.8±0.3 mm (0.3±0.01 in)
WSHK0201
WSHK0202
1A-48 ENGINE MECHANICAL (4HK1, 6HK1)
6HK1
12. Install the flywheel.• Along with the knock pin of the crankshaft, install
the flywheel and tighten up with the specifiedtorque according to the order given on the figure.
13. Rotate the crankshaft to make the No. 1 cylindermeet the compression TDC.
14. Remove the oil drain adapter.15. Install the O-ring on the fuel supply pump and
make the slits with an arrow meet and with the studbolt as a guide, install the fuel supply pumptentatively.
Caution:• When removing the fuel supply pump, if the stud
bolt on the cylinder block side loosens, or the studbolt is replaced, apply the Loctite No. 262 on theside where the stud bolt is to be buried beforeassembly.
* 4HK1 is shown for illustration.• Check if the alignment mark of the gear painted
white is at the location given on the figure whenviewed from the plug hole and tighten up with thespecified torque.
• If the location of the teeth of the painted gear is notin the right place, put it together all over again.
Distance (B): 7.5±0.15 mm (0.3±0.006 in)
Tightening torque:1st step = 78 N⋅m (8.0 kg⋅m/58 lb ft)2nd step = 60°3rd step = 60°
WSHK0203
Nut tightening torque: 50 N⋅m (5.1 kg⋅m/37 lb ft)
Bolt tightening torque: 76 N⋅m (7.7 kg⋅m/56 lb ft)
ENGINE MECHANICAL (4HK1, 6HK1) 1A-49
* 4HK1 is shown for illustration.
Name1. Plug Hole2. Alignment Mark
16. Install the oil drain adapter ASM on the plug holeand tighten with the specified torque.
• Apply engine oil over the O-ring nice and thin andinstall it.
Name1. Adapter2. O-Ring
17. Install the cylinder head ASM.Refer to the “Cylinder Head”.
18. Install the camshaft ASM.Refer to “Camshaft ASM”.
19. Install the rocker arm shaft ASM.Refer to “Rocker Arm Shaft ASM”.
20. Install the cylinder head cover.Refer to “Cylinder Head Cover”.
Tightening torque: 6 N⋅m (0.6 kg⋅m/53 lb in)
1A-50 ENGINE MECHANICAL (4HK1, 6HK1)
Torque Specifications
WSHK0065
30 3.1 / 22
76 7.7 / 56
50 5.1 / 37
31 3.2 / 23
110 11.2 / 81
134 13.7 / 99
134 13.7 / 99
19 1.9 / 14
78 8 / 58
6 0.6 / 4
60 60
8 0.8 / 6
N mkg m/lb ft
ENGINE MECHANICAL (4HK1, 6HK1) 1A-51
Special Tool
Illustration Tool Number/Description/Special Tool Rank
x-xxxx-xxxx-xxx-xxxxx
Crankshaft stopperRank B
1-8521-0027-0Slinger remover
Rank B
x-xxxx-xxxx-xx-xxxxx
Oil seal installer kit (4HK1)Rank A
8-9439-6856-0Oil seal setting tool
(6HK1)Rank A
1A-52 ENGINE MECHANICAL (4HK1, 6HK1)
Rocker Arm Shaft ASMComponents
* 4HK1 is shown for illustration.Name
1. Camshaft Bracket2. Rocker Arm3. Wave Washer4. Rocker Arm
5. Rocker Arm Bracket6. Camshaft Bracket7. Rocker Arm Shaft
Removal1. Remove the cylinder head cover.
Refer to “Cylinder Head Cover”.2. Remove the rocker arm shaft ASM.• Along with the camshaft bracket, remove the
rocker arm shaft ASM.
ENGINE MECHANICAL (4HK1, 6HK1) 1A-53
• Because the bolt(s) shown on the figure is aredesigned to fix the rocker arm shaft, do not removeit for now.
Caution:Pay full attention so as not to drop the bridge cap in thegear case of the rear part of the cylinder head or thehole into which oil pours back in the front.
Disassembly1. Remove the camshaft bracket.2. Remove the rocker arm.3. Remove the wave washer.4. Remove the rocker arm.5. Remove the rocker arm bracket.• Disassemble according to the order (2) – (4)
thereafter.
6. Remove the camshaft bracket to take the shaft out.
* 4HK1 is shown for illustration.
Name1. Camshaft Bracket2. Rocker Arm3. Wave Washer4. Rocker Arm5. Rocker Arm Bracket6. Camshaft Bracket7. Rocker Arm Shaft
7. Check if the oil hole is clogged of the camshaftbracket (on the rear side).
8. Check if the rocker arm shaft is bent.• Place the rocker arm shaft on a V block.
• Check if it is bent by rotating the shaft with a dialgauge on the center of the shaft.
• As a result of measurement, if its bend is slight,press it to rectify it (while cold).
1A-54 ENGINE MECHANICAL (4HK1, 6HK1)
• If the bend of the shaft exceeds the limit, replacethe shaft.
9. Check if the rocker arm shaft is worn.• Use a micrometer to measure 8 places of the
vibrating part of the rocker arm.
• If the measurement falls is the limit or less, replacethe shaft.
10. Inspect a clearance between the rocker arm andthe rocker arm shaft.
• Use a cylinder gauge to measure an insidediameter of the bushing of the rocker arm tomeasure a clearance between the externaldiameter of the shaft.
• If the measurement exceeds the limit, replace therocker arm and the shaft.
11. Inspect a clearance between the roller of therocker arm and the rocker arm pin.a. Pass a string, for instance, through an opening
between the rocker arm and the roller, pull it inthe direction indicated with an arrow stronglyand measure the gap between the rocker armand the roller with the roller stuck out. Figure 1
b. After marking the measuring point, pull thestring out and measure the gap of the markedplace with the roller pushed deep into the end.Figure 2
c. The gap between the measurement takenunder a. and that under b. will be a clearancebetween the roller and the rocker arm pin. If itexceeds the limit, replace the rocker arm.
Bend of the rocker arm shaft mm (in)
Limit 0.3 (0.012)
External diameter of the rocker arm shaft mm (in)
Standard 22.0 (0.866)
Limit 21.85 (0.860)
Clearance between the rocker arm and rocker arm shaft
mm (in)
Standard 0.010 – 0.056 (0.0004 – 0.0022)
Limit 0.2 (0.0079)
Clearance between the roller and the rocker arm pin
mm (in)
Standard 0.068 – 0.099 (0.0026 – 0.0038)
Limit 0.2 (0.0079)
ENGINE MECHANICAL (4HK1, 6HK1) 1A-55
Reassembly1. Install the camshaft bracket to one side of the
rocker arm shaft tentatively first. When the rockerarm shaft ASM is installed on the cylinder head,tighten them up fast.
• Assemble in the reverse order of disassembly.
2. Install the rocker arm.• Apply engine oil in an inside diameter of the rocker
arm, the roller and the rocker arm pin and install iton the rocker arm shaft.
3. Install the wave washer between the rocker arm.4. Install the rocker arm bracket.• Pay attention to the direction in which the bracket
is put together and put it together with the rockerarm shaft.
5. Install the camshaft bracket.• Install the camshaft bracket on the rocker arm
shaft with the bolts indicated with an arrowtightened tentatively. When the rocker arm shaftASM is installed on the cylinder head, tighten themup fast.
1A-56 ENGINE MECHANICAL (4HK1, 6HK1)
* 4HK1 is shown for illustration.
Name1. Camshaft Bracket2. Rocker Arm3. Wave Washer4. Rocker Arm5. Rocker Arm Bracket6. Camshaft Bracket7. Rocker Arm Shaft
Installation1. Install the rocker arm shaft ASM.• If the bridge cap comes off, apply engine oil over
the inside of the bridge cap and put it together withthe bridge.
Caution:Pay full attention so as not to drop the bridge cap in thegear case of the rear part of the cylinder head or thehole into which oil pours back in the front.
Name1. Bridge Cap2. Bridge
• Loosen an adjusting screw of the rocker arm, applyengine oil over the roller part of the rocker arm andinstall it on the cylinder head.
• Loosen the bolts indicated with an arrow a little, itwill become easier to install it.
• Apply engine oil on a screw of the bolts and nuts.
• Tighten up the tightening bolts of the rocker armASM tentatively, and gradually tighten up the entirerocker arm ASM horizontally according to the orderof the nut on the rocker arm side.
Tightening torque:4HK1
Bolt (3) = 56 N⋅m (5.7 kg⋅m/41 lb ft)Nut (1), Bolt (2), (4) = 27 N⋅m (2.8 kg⋅m/20 lb ft)
ENGINE MECHANICAL (4HK1, 6HK1) 1A-57
Name1. Camshaft Bracket Fixing Nut2. Camshaft Bracket Fixing Bolt3. Rocker Arm Bracket Fixing Bolt4. Rocker Arm Shaft Set Bolt
• Adjustment of valve clearanceRefer to “Function Check”.
2. Install the cylinder head cover.Refer to “Cylinder Head Cover”.
6HK1Nut (1) – (4) and Bolt (10) – (13) =
27 N⋅m (2.8 kg⋅m/20 lb ft)Bolt (5) – (9) = 56 N⋅m (5.7 kg⋅m/41 lb ft)
WSHK0204
1A-58 ENGINE MECHANICAL (4HK1, 6HK1)
Torque Specifications
* 4HK1 is shown for illustration.
ENGINE MECHANICAL (4HK1, 6HK1) 1A-59
Camshaft ASMComponents4HK1
Name1. Bearing Cap2. Bearing
3. Knock Pin4. Camshaft Gear
1A-60 ENGINE MECHANICAL (4HK1, 6HK1)
6HK1
Name1. Bolt2. Washer3. Gear4. Pin5. Spring6. Pin
7. Sub Gear8. Dish Spring9. Snap Ring
10. Pin11. Camshaft
Removal1. Remove the cylinder head cover.
Refer to “Cylinder Head Cover”.2. Remove the rocker arm shaft ASM.
Refer to “Rocker Arm Shaft ASM”.3. Remove the camshaft bearing cap.4. Remove the bearing upper.5. Remove the camshaft ASM.6. Remove the bearing lower.
Caution:Put the removed bearings in order with a tag, forexample, by cylinder.
WSHK0055
11
ENGINE MECHANICAL (4HK1, 6HK1) 1A-61
Disassembly1. Remove the scissors gear ASM. (6HK1)• Fix the hexagon portion of the camshaft in a vise
using a mouth ring. Use snap ring pliers to removethe sub gear.
Caution:Take care not to damage to the cam portion and thejournal portion of the camshaft.
Name1. Snap Ring2. Dish Spring3. Sub Gear4. Spring5. Camshaft Gear
2. Remove the camshaft gear.• Remove the fastening bolts of the camshaft gear
and put the block of wood in a puller to remove thecamshaft gear.
Name1. Wood
3. Remove the knock pin.4. Inspect the camshaft visually.• Check if the journal and cam parts of the camshaft
are worn or damaged, if so, replace it.
1A-62 ENGINE MECHANICAL (4HK1, 6HK1)
5. Check the axial play of the camshaft.• Use a thickness gauge to measure an end
clearance of the camshaft gear and the camshaftbracket.
• If the measurement exceeds the limit, replace thecamshaft gear or the camshaft.
Caution:Measure an end clearance of the camshaft beforedisassembling.
6. Check if the cam lobe is worn.• Use a micrometer to measure the height of the
cam lobe.
• If the height of the cam lobe is the limit or less,replace the camshaft.
7. Check if the camshaft journal is worn.• Use a micrometer to measure wear which is not
even with a diameter of the camshaft journal.
• If the measured uneven wear exceeds the limit,replace the camshaft.
End clearance of the camshaft mm (in)
Standard 0.085 – 0.205 (0.033 – 0.008)
Limit 0.25 (0.009)
Height of the cam lobe mm (in)
Intake air Exhaust
Standard 52.8 (2.08) 54.5 (2.15)
Limit 51.8 (2.04) 53.5 (2.11)
External diameter of the camshaft journal part
mm (in)
Standard 39.950 – 39.975 (1.5728 – 1.5738)
Limit 39.850 (1.5688)
Partial wear of the camshaft journal part mm (in)
Limit 0.05 (0.0019)
WSHK0228
H
ENGINE MECHANICAL (4HK1, 6HK1) 1A-63
8. Check for bent of the camshaft.• Place the camshaft on a V block to measure a
bend with a dial gauge.
• Rotate the camshaft slowly to measure how muchthe dial indicator shook. If it exceeds the limit,replace the camshaft.
9. Measure a camshaft journal oil clearance.a. Measure an inside diameter of the camshaft
bearing with a dial gauge.b. Read the difference between the inside
diameter of the camshaft bearing and thediameter of the camshaft journal.If the measured oil clearance exceeds the limit,replace the camshaft bearing.
Reassembly1. Install the knock pin.2. Install the camshaft gear.• With the side of the camshaft gear center boss part
stuck out being on the camshaft side, install thecamshaft gear along with the knock pin.
Caution:Be careful not to damage the cam and journal partswhen tightening up the gear.
3. Install the scissors gear ASM. (6HK1)
Bent of the camshaft mm (in)
Limit 0.05 (0.0019)
Clearance of the journal part mm (in)
Standard 0.020 – 0.087 (0.0008 – 0.0034)
Limit 0.15 (0.0059)
Tightening torque: 142 N⋅m (14.5 kg⋅m/105 lb ft)
1A-64 ENGINE MECHANICAL (4HK1, 6HK1)
• Fix the hexagon portion of the camshaft in a viseusing a mouth ring. Assemble the spring with itsleft end contacting the pin of camshaft main gear tomake a gap on the right.
• Assemble the sub gear so that its pin is insertedinto the gap between the right side of pin of thecamshaft main gear and the right end of the spring.
Name1. Snap Ring2. Dish Washer3. Sub Gear4. Spring5. Camshaft Gear
• Use snap ring pliers to assemble the snap ring andthe dish washer securely.
• Before installing the camshaft to the cylinder head,rotate the sub gear using the special tool toprevent the spring force which acts on the subgear from affecting. Align the hole of the sub gearwith the camshaft main gear and install the phasealignment pin from the sub gear side to match theteeth.
Special toolScissors gear spring wrench: 5-8840-2674-1
• Assemble onto the cylinder head.
WSHK0244
ENGINE MECHANICAL (4HK1, 6HK1) 1A-65
Fixing torque
Special Tool
WSHK0060
142 (14.5 / 105)
N m(kg m/lb ft)
Illustration Tool Number/Description/Special Tool Rank
5-8840-2674-1Scissors gear spring
wrenchRank A
WSHK0245
1A-66 ENGINE MECHANICAL (4HK1, 6HK1)
Installation1. Rotate the crankshaft to make the No. 1 cylinder
meet the compression TDC.4HK1
6HK1
2. Install the camshaft bearing lower.• Apply engine oil over the camshaft bearing lower
and install it on the cylinder head.
3. Install the camshaft ASM.• Put together the camshaft ASM so as to make the
“B” (4HK1) or “•” (6HK1) mark meets the upperface of the cylinder head.
4HK1
6HK1
4. Install the baring upper to the bearing cap.5. Install the bearing cap.• Apply engine oil on the bearing upper.
• Direct the front mark of the bearing cap toward thefront of the engine and put it together with thecylinder head in numerical order.
ENGINE MECHANICAL (4HK1, 6HK1) 1A-67
• Apply engine oil over the screw part and tighten upthe bearing cap with the specified torque.
* 4HK1 is shown for illustration.6. Install the rocker arm shaft ASM.
Refer to “Rocker Arm Shaft ASM”.7. Install the cylinder head cover.
Refer to “Cylinder Head Cover”.
Tightening torque: 27 N⋅m (2.8 kg⋅m/20 lb ft)
1A-68 ENGINE MECHANICAL (4HK1, 6HK1)
Torque Specifications
* 4HK1 is shown for illustration.
ENGINE MECHANICAL (4HK1, 6HK1) 1A-69
Valve Stem Seal, Valve SpringComponents
* 4HK1 is shown for illustration.Name
1. Camshaft Bearing Cap2. Camshaft Bearing3. Camshaft4. Rocker Arm Shaft ASM5. Valve Stem Oil Seal
6. Valve Spring7. Spring Upper Seat8. Split Collar9. Bridge
10. Valve Spring Seat
Removal1. Remove the cylinder head cover.
Refer to “Cylinder Head Cover”.2. Remove the rocker arm shaft ASM.
Refer to “Rocker Arm Shaft ASM”.3. Remove the camshaft ASM.
Refer to “Camshaft ASM”.4. Remove the bridge cap (1).
5. Remove the bridge (2).
Caution:Keep the removed bridge and bridge cap properly sothat they may be put back to the original place.
1A-70 ENGINE MECHANICAL (4HK1, 6HK1)
Name1. Bridge Cap2. Bridge
Caution:Pay full attention so as not to drop the bridge cap in thegear case of the rear part of the cylinder head or thehole into which oil pours back in the front.
6. Remove the split collar.• Apply compressed air over the cylinder from the
glow plug holes to keep the valve at the homeposition.
• Use a replacer to compress the valve spring toremove the split collar.
Special toolValve spring replacer: 5-8840-2621-0 (J-43263)Pivot: 8-9439-6862-0 (EN-46721)
7. Remove the spring upper seat.• Remove the special tool to remove the upper seat.
8. Remove the valve spring.Put the removed valve springs in order by cylindernumber.
9. Remove the valve stem oil seal.• Use pliers to remove the oil seal.
10. Remove the valve spring seat.
Caution:Do not reuse the removed oil seal.
InspectionCheck the valve spring.Caution:Check the valve spring visually and if there is cleardamage or wear-out, replace it.
1. Free length• Measure free length of the spring and if it is shorter
than the specified limit, replace the spring.
4HK1
6HK1
Free length of the valve spring mm (in)
Intake air Exhaust
Standard 65.9 (2.59) 68.1 (2.68)
Limit 62.9 (2.48) 65.1 (2.56)
Free length of the valve spring mm (in)
Intake air Exhaust
Standard 59.9 (2.36) 68.1 (2.68)
Limit 58.7 (2.31) 66.7 (2.63)
ENGINE MECHANICAL (4HK1, 6HK1) 1A-71
2. Valve spring squareness• Use a surface plate and a square to measure the
valve spring squareness.If the measured value exceeds the specified limit, the valve spring must be replaced.
4HK1
6HK1
3. Tension• Use a spring tester to compress the spring to the
installation height. Measure tension of thecompressed spring. If the measurement is lowerthan the limit, replace the spring.
4HK1
6HK1
Installation1. Install the valve stem oil seal.• Apply engine oil over the peripheral part of the
valve guide and install the oil seal by using a valvestem seal installer.
Caution:After installing the valve stem oil seal, check if it isinserted nice and deep and the oil seal is not tilted orthe garter spring has not come off.
Valve spring squareness mm (in)
Limit 3.0 (0.12)
Valve spring squareness mm (in)
Limit 3.4 (0.13)
Tension of the valve spring N (lb)
Intake air Exhaust
Installation length mm (in) 46.0 (1.81) 46.0 (1.81)
Standard 348 (78) 383 (86)
Limit 330 (74) 356 (80)
Tension of the valve spring N (lb)
Intake air Exhaust
Installation length mm (in) 46.0 (1.81) 46.0 (1.81)
Standard 348 (78) 378 (85)
Limit 309 (69) 329 (74)
1A-72 ENGINE MECHANICAL (4HK1, 6HK1)
Special tool4HK1
Valve stem seal installer: 8-9439-6815-0 (EN-47685)6HK1
Valve guide oil seal installer: 5-8840-2625-0 (J-43267)
2. Install the valve spring.• Install it with the paint mark or the narrow side of
the spring pitch being the lower side (cylinder headside).
Name1. Spring Pitch2. Paint Mark
3. Install the spring upper seat.4. Install the split collar.• Apply compressed air over the cylinder from the
glow plug holes to keep the valve at the homeposition.
• Use a replacer to compress the valve spring andinstall the split collar.
Special toolValve spring replacer: 5-8840-2621-0 (J-43263)Pivot: 8-9439-6862-0 (EN-46721)
5. Apply engine oil over the bridge and install it.
Caution:Move it up and down to check if it moves smoothly.
6. Apply engine oil over the bridge cap and install it.
Caution:Pay full attention so as not to drop the bridge cap in thegear case of the rear part of the cylinder head or thehole into which oil pours back in the front.
Paint mark
Intake air Light blue
Exhaust Yellow
ENGINE MECHANICAL (4HK1, 6HK1) 1A-73
Name1. Bridge Cap2. Bridge
7. Install the camshaft ASM.Refer to “Camshaft ASM”.
8. Install the rocker arm shaft ASM.Refer to “Rocker Arm Shaft ASM”.
9. Install the cylinder head cover.Refer to “Cylinder Head Cover”.
Special Tool
Illustration Tool Number/Description/Special Tool Rank
5-8840-2621-0J-43263
Valve spring removerRank B
8-9439-6862-0EN-46721Pivot ASM
Rank B
8-9439-6815-0EN-47685
Valve stem seal installer(4HK1)Rank B
5-8840-2625-0J-43267
Valve guide oil seal installer(6HK1)Rank B
1A-74 ENGINE MECHANICAL (4HK1, 6HK1)
Cylinder HeadComponents
* 4HK1 is shown for illustration.Name
1. Bridge Cap2. Bridge3. Bridge Guide4. Split Collar5. Spring Upper Seat6. Valve Spring7. Valve Stem Oil Seal8. Valve Guide
9. Idle Gear C Cover10. Idle Gear C11. Glow Plug12. Intake And Exhaust Valves13. Cylinder Head14. Valve Spring Seat15. Thermostat16. Water Outlet Pipe
Caution:To avoid electric shock;Set the switch to the ‘OFF’ position and disconnectbattery negative cable before checking or repairing thefuel injector, wiring or/and connectors.
Removal1. Drain the coolant.2. Remove the engine harness.3. Disconnect the exhaust pipe.
ENGINE MECHANICAL (4HK1, 6HK1) 1A-75
4. Remove the turbocharger.Refer to the “Turbocharger and Exhaust Manifold”.
5. Remove the left-hand EGR adapter and right-handEGR pipe.
6. Remove the EGR water feed pipe.7. Remove the EGR water return pipe.8. Remove the EGR cooler.9. Remove the water feed pipe for coolant water for
the EGR cooler and the water return pipe.
* 4HK1 is shown for illustration.
Name1. EGR Adapter2. Water Return Pipe3. EGR Cooler4. EGR Pipe5. Water Feed Pipe
10. Remove the fan guide bracket.11. Remove the left-hand intake pipe between the
inter-cooler and the inlet duct.12. Remove the cylinder head cover.
Refer to “Cylinder Head Cover”.13. Remove radiator upper hose.14. Loosen the fuel injector terminal nuts alternately to
the same level, and remove the terminal.15. Loosen the fuel injector harness bracket bolt,
remove the inside connector, and remove theharness bracket.
16. Remove the nozzle leak-off pipe (4).
* 4HK1 is shown for illustration.
Name1. Harness Bracket2. Harness Connector3. Fuel Injector Terminal Nut4. Nozzle Leak-Off Pipe
17. Remove the fuel leak-off hose.18. Remove the fuel leak-off pipe (2).4HK1
Name1. High Pressure Pipe2. Leak-Off Pipe
1A-76 ENGINE MECHANICAL (4HK1, 6HK1)
6HK1
Name1. High Pressure Pipe2. Leak-Off Pipe
19. Remove the water bypass hose from the cylinderhead side.
• Remove the engine coolant temperature sensorconnector.
4HK1
Name1. Water Bypass
6HK1
Name1. Water Bypass
20. Remove the EGR valve and EGR valve connector.21. Remove the cam angle sensor connector.22. Remove the rocker arm shaft ASM.
Refer to “Rocker Arm Shaft ASM”.23. Remove the camshaft ASM.
Refer to “Camshaft ASM”.24. Remove the bridge cap carefully so that it does not
fall into inside the engine.25. Remove the bridge.
Caution:Store the removed bridge and bridge cap so that theycan be placed in their original locations.26. Remove the glow plug connector.27. Remove the glow plug.
WSHK0019
1 2
1
ENGINE MECHANICAL (4HK1, 6HK1) 1A-77
28. Remove the injection pipe clip, and remove theinjection pipe.
Important:Do not reuse the high-pressure pipe in fuel system if ithas been removed.4HK1
Name1. Fuel Injection Pipe2. Fuel Injection Pipe Clip
6HK1
Name1. Fuel Injection Pipe2. Fuel Injection Pipe Clip
29. Remove the common rail.• Remove the common rail pressure sensor
connector.
30. Remove the fuel injector bracket.
31. If you have difficulty in removing the fuel injector,set the fuel injector remover in the fuel injector,tighten the attachment part on the joint of the leak-off pipe and pull out the fuel injector upward.
Special toolFuel injector remover: 5-8840-2826-0 (EN-46720)Sliding hammer: 5-8840-0019-0 (J-23907)
Caution:When pulling out the fuel injector using a special tool,check that the fuel injector sleeve does not come off.
Name1. Sliding Hammer2. Fuel Injector Remover3. Fuel Injector ASM
Caution:Attach a cylinder number to the removed fuel injectorwhen storing it.Be sure not to make the nozzle touch something.WSHK0021
1
2
1A-78 ENGINE MECHANICAL (4HK1, 6HK1)
32. Remove the lower head cover.33. Remove the cylinder head ASM.
• Loosen the cylinder head bolts in the orderdescribed in the drawing.
Caution:Be sure not to overlook (1) and (2) because they areattached with the flywheel housing with M10 bolts.
• Remove the cylinder head gasket.
Caution:Replace the head gasket with a new one once it wasremoved.4HK1
6HK1
Disassembly1. Remove the case ASM.• Be sure not to lose the gasket.
2. Remove the boost pressure sensor and bracket.
Name1. Boost Pressure Sensor2. Bracket
3. Remove the inlet cover.• Remove liquid gasket adherent to the removed
inlet cover.
WSHK0022
WSHK0236
2
1
ENGINE MECHANICAL (4HK1, 6HK1) 1A-79
* 4HK1 is shown for illustration.4. Remove the A/C compressor bracket.5. Remove the exhaust manifold.• Remove the heat protector and remove the
exhaust manifold.
6. Remove the exhaust gasket.7. Disconnect the water outlet pipe.8. Remove the thermostat.
* 4HK1 is shown for illustration.9. Remove the idle gear C cover.• Put the edge of a driver on the outer circle of the
sealing cup as shown in the drawing, tap it lightly,reverse it, then pull it out with pliers or otherequipment.
10. Remove the idle gear C.
Name1. Idle Gear C2. Shaft
11. Remove the split collar.12. Remove the spring upper seat.13. Remove the valve spring.
• Use a replacer to compress the valve spring toremove the split collar.
Special toolValve spring replacer: 5-8840-2621-0 (J-43263)Pivot: 8-9439-6862-0 (EN-46721)• Remove the special tool, then remove the upper
sheet and springs.
Sort the removed valve springs by cylindernumber.
1A-80 ENGINE MECHANICAL (4HK1, 6HK1)
14. Remove the intake and exhaust valves.• Sort the removed valves according to cylinders by
using tags and others.
15. Remove the valve stem oil seal.• Use pliers to remove the oil seals.
16. Remove the valve guide.• Use the valve guide replacer to press out the
valve guides from the bottom side of the cylinderhead.
Special toolValve guide replacer: 5-8840-2628-0 (J-43272)
* 4HK1 is shown for illustration.17. Put the nozzle sleeve remover on the nozzle
sleeve from the bottom side of the cylinder head,then pull out the nozzle sleeve.
Special toolNozzle sleeve remover: 5-8840-2623-0 (J-43265)
Caution:• Be sure not to scratch the bottom side of the
cylinder head.• Do not reuse the removed nozzle sleeve.• Carefully remove sawdust in the screw groove.
ENGINE MECHANICAL (4HK1, 6HK1) 1A-81
Name1. Nozzle Sleeve
18. Remove the bridge guide.• Electrically weld the nut on the head of the bridge
guide, attach the sliding hammer and pull it out.
Name1. Nut
19. Remove the oil seal.• Press the tool against the oil seal. Strike the tool to
remove the seal from the inside of the cylinderhead.
Inspection1. Check the cylinder head ASM.• Remove varnish, soot and others adhered on the
metal surface completely. Use metal brush andothers so that the seal surface of the surfacewhere the gasket is installed is not hurt.
• Check the following causes in the case of leak ofthe seal surface of the cylinder head, corrosion, airleak and defective gasket.
– Improper installation– Defective tightening of the cylinder head.– Winding seal surface of the cylinder block.
a. Damage on the screw surface or extractedcylinder head bolt due to extra tightening torque
Caution:Replace suspicious bolt.
b. Inside the combustion chamber, glow plug hole.
1A-82 ENGINE MECHANICAL (4HK1, 6HK1)
• Check whether there is a crack between thevalve seats and in the cylinder head of theexhaust port part, and replace the cylinder headif there is serious damage or crack. Check thecollar if necessary.
c. Flatness of the under surface of the cylinderhead
• Use a straight edge ruler and thickness gaugeto measure the four sides and diagonal lines asshown in the drawing, and replace if theyexceed the limit.
* 4HK1 is shown for illustration.d. Flatness of the surface where the exhaust
manifold and inlet cover are installed
• Use a straight edge ruler and thickness gaugeto measure the four sides and diagonal lines asshown in the drawing, and replace if theyexceed the limit.
* 4HK1 is shown for illustration.e. Flatness of the exhaust manifold• Use a straight edge ruler and thickness gauge
to measure the flatness. If it exceeds the limit,replace the exhaust manifold.
Distortion of the under surface of the cylinder head
mm (in)
Standard 0.05 (0.002) or less
Limit 0.20 (0.0079)
Distortion of the surface where the manifold and cover are installed
mm (in)
Standard 0.05 (0.002) or less
Limit 0.2 (0.0079)
Distortion of the exhaust manifold mm (in)
Standard 0.3 (0.0118) or less
Limit 0.5 (0.0197)
ENGINE MECHANICAL (4HK1, 6HK1) 1A-83
* 4HK1 is shown for illustration.2. Bridge cap• Inspect abrasion and deformation of the surface
where the cap and the rocker arm adjust boltcontact.
• If the amount of abrasion is 0.1 mm (0.0039 in) orlarger, or if it abrades away in a zonal shape,replace it.
3. Bridge• Make sure the bridge moves smoothly along the
bridge guide.
• Measure the gap between the bridge and bridgeguide.
Name1. Bridge2. Bridge Guide
4. Check the valve guide.
Caution:If there is a scratch or abnormal abrasion in the valvestem and the inner diameter part of the valve guide,replace it with new one along with valve guide.
a. Measure the valve guide clearance.• Measure the diameter of the valve stem with a
micro meter.If the diameter of the valve stem is smaller thanthe limit, replace the valve and valve guidealtogether.
4HK1
Abrasion of the bridge cap mm (in)
Limit 0.1 (0.0039)
Gap mm (in)
Assembly standard 0.020 (0.00079) –0.057 (0.00224)
Usage limit 0.1 (0.0039)
The external diameter of the valve stem mm (in)
Standard Limit
Intake valve 8.946 (0.3522) – 8.962 (0.3528)
8.88 (0.3496)
Exhaust valve 8.921 (0.3512) – 8.936 (0.3518)
8.80 (0.3465)
1A-84 ENGINE MECHANICAL (4HK1, 6HK1)
6HK1
• Measure the gap between the valve guide andvalve stem within 10 mm (0.39 in) from thevalve guide, using a dial gauge.
• If the measured value exceeds the limit, replacethe valve guide and valve altogether.
4HK1
6HK1
5. Inspect abrasion of the bridge gap.• Measure the contact surface of bridge cap and the
rocker arm, using a dial gauge.
• If the abrasion exceeds the limit, or there is anabnormal abrasion (zonal abrasion), replace thebridge cap.
6. Check the valve.Thickness of valve• Measure the thickness of the valve.• If the measured value exceeds the limit, replace
the valve and valve guide altogether.
The external diameter of the valve stem mm (in)
Standard Limit
Intake valveExhaust valve
8 (0.315) 7.88 (0.3102)
Gap between the valve guide andvalve stem
mm (in)
Standard Limit
Intake valve 0.038 (0.00150) – 0.071 (0.00280)
0.20 (0.00787)
Exhaust valve 0.064 (0.00252) – 0.096 (0.00378)
0.25 (0.00984)
Gap between the valve guide andvalve stem mm (in)
Standard Limit
Intake valve 0.039 (0.00153) – 0.062 (0.00244)
0.20 (0.00787)
Exhaust valve 0.064 (0.00252) – 0.096 (0.00378)
0.25 (0.00984)
Abrasion of the bridge cap mm (in)
Limit 0.1 (0.00394)
ENGINE MECHANICAL (4HK1, 6HK1) 1A-85
4HK1
6HK1
Valve seat• Remove carbon, water stain and others on the
under surface of the cylinder head.Install the valve in the cylinder head.Measure the depth of the valve from the undersurface of the cylinder head, using a depthgauge or straight edge ruler.If the value exceeds the limit, replace the valveinsert or the cylinder head ASM.
4HK1
6HK1
• Measure the contact width of the valve seat. Ifthe seat contact surface has a scratch or isrough, or if the abrasion of the contact surfaceexceeds the limit, modify or replace it.
Contact surface of the valve seat• If the contact surface of the valve seat is
defective, modify it or replace the valve, valveguide and valve seat altogether.
Thickness of valve mm (in)
Standard Limit
Intake valve 1.8 (0.0709) 1.3 (0.0512)
Exhaust valve 1.75 (0.0689) 1.3 (0.0512)
Thickness of valve mm (in)
Standard Limit
Intake valve 1.88 (0.074) 1.3 (0.0512)
Exhaust valve 1.75 (0.0689) 1.3 (0.0512)
Depth of the valve mm (in)
Standard 0.7 (0.0276) – 1.2 (0.0472)
Limit 2.5 (0.0984)
Depth of the valve mm (in)
Standard Limit
Intake valve 1 (0.039) 2.5 (0.098)
Exhaust valve 1.3 (0.051) 2.8 (0.11)
Contact width of the valve seat mm (in)
Standard Limit
Intake valve 2.5 (0.0984) 3.0 (0.1181)
Exhaust valve 2.0 (0.0787) 2.5 (0.0984)
Angle of the contactsurface:
Exhaust side of 4HK1 and6HK1: 45°Intake side of 6HK1: 30°
1A-86 ENGINE MECHANICAL (4HK1, 6HK1)
Repair of the seat surface• Remove carbon from the surface of the valve
seat.• Use a seat cutter to minimize the scratch and
other roughness (15/45/75°-blade), therebyreturning the contact width to the standardvalue.
Caution:Remove only scratches and roughness, and do not cutthe surface too much.Use the free adjustment valve cutter pilot.Do not let the valve cutter pilot waver inside the valveguide.
• Attach compound in the valve insert seat.• Insert the valve into the valve guide.• Attach compound on the valve seat surface,
rotate the valve and hit it lightly to grind them,and confirm that it has even contact all round.
Caution:Remove compound completely after grinding.
ENGINE MECHANICAL (4HK1, 6HK1) 1A-87
Replace the valve seat insertRemove the valve seat insert• Arc-weld the entire inner diameter of the valve
seat insert.• Cool the valve seat insert for two to three
minutes. Contraction fur to cooling makes iteasier to remove the valve seat insert.
• Remove the valve seat insert, using a screwdriver. Be sure not to hurt the cylinder head.
Name1. Arc-Weld2. Valve Seat Insert3. Screw Driver
Install the valve seat insert• Carefully place a washer (the outer diameter is
smaller than the valve seat insert) on the valveseat insert.
• Use the press to apply pressure gradually onthe washer, thereby pushing the valve seatinsert.
• After replacement of the valve seat, Attachcompound on the valve seat surface, rotate thevalve and hit it lightly to grind them, and confirmthat it has even contact all round.
Caution:Do not apply too much pressure with the press.Remove compound completely after grinding.
Name1. Washer2. Valve Seat3. Press
Reassembly1. Install the oil seal.• Install on the surface of injection pipe insert.
• Hammer it in so that the seal does not incline.
Caution:Be sure not to hurt the rip.Special tool
Oil seal installer: 5-8840-2627-0 (J-43269)
1A-88 ENGINE MECHANICAL (4HK1, 6HK1)
Name1. Cylinder Head2. Oil Seal Installer
2. Install the bridge guide.• Apply engine oil on the outer diameter of the guide,
then use the installer to hammer it into the depth ofthe finishing part of the hole of the cylinder head.(Note: the height of the bridge guide is about37.5 mm 1.48 in from the upper surface of thehead)
Special toolBridge guide installer: 5-8840-2626-0 (J-43268)Engine oil
3. Nozzle sleeve• Install the O-ring on the nozzle sleeve, apply
engine oil.
• Apply seal material on the taper section.
Loctite No. TL620
Name1. O-Ring2. O-Ring3. Apply Seal Material4. Engine Oil
• Install the nozzle sleeve on the cylinder head,insert the guide sleeve.
• Use the guide sleeve to push in so that the nozzlesleeve fully contacts with the under surface of thecylinder head.
• Insert the sleeve and fix it with the tighten and bolt.
• Insert the ball (bearing steel ball 9.525 mm0.375 in) into the guide sleeve, attach the punchbar and hammer out the ball.
Caution:• Leave the cylinder head floating so that the ball
comes off from the under surface.
ENGINE MECHANICAL (4HK1, 6HK1) 1A-89
Special toolNozzle sleeve installer: 5-8840-2624-0 (J-43266)
Name1. Punch Bar2. Ball3. Guide Sleeve4. Nozzle Sleeve5. Bracket6. Bolt
4. Install the valve guide.• Hammer in the valve guide from the upper surface
of the cylinder head, using the valve guidereplacer.
Special toolValve guide replacer: 5-8840-2628-0 (J-43272)
Height from the upper surface of the cylinder headto the edge surface of the valve guide: 13.9 mm(0.5472 in) – 14.3 mm (0.5630 in)
Caution:When replacing the valve guide, it must be replacedtogether with the valve.
5. Install the valve stem oil seal.• Apply engine oil on the outer diameter of the valve
guide, use the valve stem seal installer to installthe oil seal.
Caution:After installation of the valve stem seal, confirm that theoil seal is not inclining and the garter spring is in place.
1A-90 ENGINE MECHANICAL (4HK1, 6HK1)
Special tool4HK1
Valve stem seal installer: 8-9439-6815-0 (EN-47685)6HK1
Valve guide oil seal installer: 5-8840-2625-0 (J-43267)
6. Install the intake and exhaust valves.• Apply engine oil on the valve stem part and install
the valve.
7. Install the valve spring.• Install the valve spring with the paint mark or the
narrower side of the spring pitch on the under side(the cylinder head side).
Name1. Spring Pitch2. Paint Mark
8. Install the spring upper seat.9. Install the split collar.• Use a replacer to compress the valve spring and
install the split collar.
Special toolValve spring replacer: 5-8840-2621-0 (J-43263)Pivot: 8-9439-6862-0 (EN-46721)
10. Install the idle gear C.• Apply engine oil on the idle gear C shaft and the
inner diameter of the idle gear, install the idle gearC so that the side with gear groove is on the side ofthe rear surface of the engine.
• Tighten the idle gear C to the specified torque.
• Do not use impact wrench and like.
Paint mark
Intake side Light blue
Exhaust side Yellow
ENGINE MECHANICAL (4HK1, 6HK1) 1A-91
Name1. Idle Gear C2. Shaft
11. Install the idle gear C cover.• Apply liquid gasket (Loctite 262 or 962T) on the
outer diameter of the idle gear C cover, use thesealing cup setting tool to hammer it in so that themeasurements follow the drawing.
Special toolSealing cup installer: 5-8840-2222-0 (EN-47690)
12. Install the thermostat.• Install the thermostat on the position shown in the
drawing.
4HK1
Name1. Thermostat
6HK1
Name1. Thermostat
13. Connect the water outlet pipe.• Tighten the water outlet pipe to the specified
torque.
• Tighten it up together with the fan shroud bracket.
Tightening torque: 95 N⋅m (9.7 kg⋅m/70 lb ft)
WSHK0023
Tightening torque: 24 N⋅m (2.4 kg⋅m/18 lb ft)
WSHK0024
1
1A-92 ENGINE MECHANICAL (4HK1, 6HK1)
4HK1
6HK1
14. Install the exhaust gasket.15. Install the exhaust manifold.
• Install the distance tube conical spring and the nuton the stud of the cylinder head in this order.
Name1. Distance Tube2. Conical Spring3. Nut
• Tighten the exhaust manifold in the orderdescribed in the drawing.
Caution:Do not tighten it too much so that it hinders extractionand contraction of the manifold due to heat.4HK1
WSHK0025
Tightening torque: 34 N⋅m (3.5 kg⋅m/25 lb ft)
ENGINE MECHANICAL (4HK1, 6HK1) 1A-93
6HK1
• Install the heat protector.
16. Install the inlet cover.• Apply liquid gasket (ThreeBond 1207C or
equivalent) in accordance with the groove of theinlet cover, with the bead diameter of φ2.5 mm(0.0984 in) – 5.5 mm (0.2165 in).
* 4HK1 is shown for illustration.• Tighten in the order described in the drawing.
• Tighten the stud bolts (6) and (9) jointly with thecommon rail.
4HK1
6HK1
17. Install the boost pressure sensor and bracket.Apply Loctite to the bolt shown on the illustrationand install it.
Tightening torque: 10 N⋅m (1.0 kg⋅m/89 lb in)
Tightening torque: 22 N⋅m (2.2 kg⋅m/16 lb ft)
WSHK0014
Tightening torque: 21.6 N⋅m (2.2 kg⋅m/16 lb ft)
WSHK0026
1 2
345
6 7
89
10 11
1213
14
1A-94 ENGINE MECHANICAL (4HK1, 6HK1)
Name1. Boost Pressure Sensor2. Bracket
18. Install the inlet pipe.
* 4HK1 is shown for illustration.
Installation1. Install the cylinder head gasket.• Select the cylinder head gasket. (4HK1 only)
• Clean the head of the piston and the upper surfaceof the cylinder block.
• Use a dial gauge to measure the extrusion of thepiston. Measure at two points of each cylinder.
• The following drawing shows the measurementpoints and the standard point of the cylinder block.
Caution:Note that there are three options for the head gasketaccording to the amount of extrusion of piston shown inthe following table. (4HK1 only)
• Calculate the piston extrusion amount of eachcylinder. (4HK1 only)
• Select a gasket of an appropriate grade based onthe maximum extrusion amount among all thecylinders. (4HK1 only)
Tightening torque: 24 N⋅m (2.4 kg⋅m/18 lb ft)
WSHK0236
2
1
Measurement points:
Head of the piston (2) and (3)
Standard point: Upper surface of the cylinder block
(1)
Extrusion amount = (measurement of (2) +measurement of (3)) /2
WSHK0231
70
ENGINE MECHANICAL (4HK1, 6HK1) 1A-95
(4HK1 only)4HK1 only
Name1. Grade Recognition Hole
• Apply liquid gasket
• Apply liquid gasket (ThreeBond 1207B orequivalent) on the joint (1) of the cylinder block andthe flywheel housing with the bead diameter of3 mm (0.118 in).
• Install the cylinder head within seven minutes afterapplying liquid gasket.
• Install the cylinder head gasket.
• Install the cylinder head gasket with the partsnumber upside, along with the cylinder head reargear case and knock pin.
* 4HK1 is shown for illustration.2. Install the cylinder head ASM.• Install the cylinder head, adjusting the knock pin of
the cylinder block.
Caution:Be sure not to hurt the head gasket when installing it.
Gasket Grade
Recognized Piston Protrusion amountmm (in)
A (no hole) 0.520 (0.02047) –0.600 (0.02362)
B (1 hole) 0.601 (0.02366) – 0.680 (0.02677)
C (2 holes) 0.681 (0.02681) –0.760 (0.02992)
1A-96 ENGINE MECHANICAL (4HK1, 6HK1)
* 4HK1 is shown for illustration.• Apply molybdenum disulfide on the screw part and
setting face of the head bolt of M14, and applyengine oil on the screw part and setting face of thehead bolt of M10.
• Use a torque wrench and angle gauge to tightenthe head bolts in the order described in thedrawing.
Special toolAngle gauge: 5-8840-0266-0 (J-45059, KM470-B)
4HK1
6HK1
3. Install the fuel injector on the cylinder head.4. Apply molybdenum disulfide on the screw part and
setting face of the fuel injector tighten bolt andtighten it tentatively.
Important:Reinstall each fuel injector to the original cylinder fromwhich it was removed during the disassemblyprocedure.
Tightening torque:M14 bolt (4HK1: 1 – 18, 6HK1: 1 – 26)
1st step = 98 N⋅m (10.0 kg⋅m/72 lb ft)2nd step = 147 N⋅m (15.0 kg⋅m/108 lb ft)3rd step = 30° – 60°
M10 bolt (4HK1: 19, 20; 6HK1: 27, 28)4th step = 38 N⋅m (3.9 kg⋅m/28 lb ft)
Use a stud bolt for (4HK1: 16).
WSHK0027
ENGINE MECHANICAL (4HK1, 6HK1) 1A-97
Name1. Fuel Injector ASM2. Fuel Injector Tighten Bolt
5. Install the common rail.
• Install the common rail pressure sensor.
6. Install the injection pipe.
Important:Replace the high-pressure pipe in fuel system with newone if it has been removed.
• Apply a thin coat of engine oil on the outerdiameter of the sleeve nut on the side of the fuelinjector and install the injection pipe.
• Use a spanner to tighten the sleeve nut until itcompletely contacts both on the fuel injector andcommon rail.
• Tighten the injection pipe clip with the designatedtorque.
* 4HK1 is shown for illustration.
Name1. Fuel Injection Pipe2. Fuel Injection Pipe Clip
7. Final tighten the injection clamp bolts to thespecified torque.
8. Tighten the injection pipes to the specified torque.
Tightening torque: 19 N⋅m (1.9 kg⋅m/14 lb ft)
Tightening torque: 6 N⋅m (0.6 kg⋅m/53 lb in)
Tightening torque: 30 N⋅m (3.1 kg⋅m/22 lb ft)
Tightening torque: 44 N⋅m (4.5 kg⋅m/32 lb ft)
1A-98 ENGINE MECHANICAL (4HK1, 6HK1)
* 4HK1 is shown for illustration.
Name1. Injection Clamp Bolt2. Injection Pipe Sleeve Nut
9. Install the glow plug.
10. Install and tighten the glow connector with thedesignated torque.
11. Apply engine oil over the bridge and install it.
Caution:Move it up and down to check if it moves smoothly.12. Apply a thin coat of engine oil inside the bridge
cap, install it.
Name1. Bridge Cap2. Bridge
13. Install the camshaft ASM.Refer to “Camshaft ASM”.
14. Install the rocker arm shaft ASM.Refer to “Rocker Arm Shaft ASM”.
15. Install and tighten the camshaft speed sensor withthe designated torque.
16. Connect the water bypass hose.• Install the engine coolant temperature sensor on
the thermostat housing.
17. Install the leak off pipe.
18. Install the fuel leak-off hose.
Tightening torque: 20 N⋅m (2.0 kg⋅m/15 lb ft)
Tightening torque: 1.2 N⋅m (0.1 kg⋅m/10.6 lb in) Tightening torque: 8 N⋅m (0.8 kg⋅m/71 lb in)
Leak off pipe tightening torque:Tightening torque: 12 N⋅m (1.2 kg⋅m/106 lb in)
ENGINE MECHANICAL (4HK1, 6HK1) 1A-99
• Install the fuel leak-off hose on the fuel leak-offpipe and fix it with a clip.
19. Clip a new gasket to the fuel nozzle leak-off pipeand install the fuel leak-off pipe.
* 4HK1 is shown for illustration.
20. Install the fuel injector harness connector frominside, tighten the harness bracket with thedesignated torque.
4HK1
6HK1
21. Install the terminal nuts on the fuel injector.
Caution:• Tighten the terminal nuts alternately in order to
prevent imbalance in tightening because they areunified.
• Do not tighten the nuts too tightly because it leadsto damage to the terminal stud.
Tightening torque: 12 N⋅m (1.2 kg⋅m/106 lb in)
Tightening torque: 48 N⋅m (4.9 kg⋅m/35 lb ft)
Tightening torque: 2 N⋅m (0.2 kg⋅m/18 lb in)
1A-100 ENGINE MECHANICAL (4HK1, 6HK1)
Name1. Fuel Injector2. Fuel Injector Harness3. Fuel Injector Terminal Nut
22. Install the cylinder head cover.Refer to “Cylinder Head Cover”.
23. Connect the radiator upper hose.24. Install the EGR valve & EGR cooler.
For details of installation, refer to “EGR Valve andEGR Cooler” of the section of exhaust system.
* 4HK1 is shown for illustration.
Name1. EGR Adapter2. Water Return Pipe3. EGR Cooler4. EGR Pipe5. Water Feed Pipe
25. Install the oil level gauge and guide tube.
26. Connect the exhaust pipe.27. Install the engine harness.28. Replenish the coolant.
ENGINE MECHANICAL (4HK1, 6HK1) 1A-101
Torque Specifications
* 4HK1 is shown for illustration.
Special Tool
Illustration Tool Number/Description/Special Tool Rank
5-8840-0019-0J-23907
Sliding hammerRank B
5-8840-2628-0J-43272
Valve guide removerRank B
8-9439-6815-0EN-47685
Valve stem seal installer(4HK1)Rank B
5-8840-2625-0J-43267
Valve guide oil seal installer(6HK1)Rank B
Illustration Tool Number/Description/Special Tool Rank
1A-102 ENGINE MECHANICAL (4HK1, 6HK1)
5-8840-0266-0J-45059
KM470-BAngle gauge
Rank B
5-8840-2624-0J-43266
Nozzle sleeve installerRank A
5-8840-2626-0J-43268
Bridge guide installerRank A
5-8840-2627-0J-43269
Oil seal installerRank A
5-8840-2623-0J-43265
Nozzle sleeve removerRank A
5-8840-2826-0EN-46720
Injector removerRank A
Illustration Tool Number/Description/Special Tool Rank
5-8840-2621-0J-43263
Valve spring removerRank B
8-9439-6862-0EN-46721Pivot ASM
Rank B
5-8840-2222-0EN-47690
Seal ring installerRank A
Illustration Tool Number/Description/Special Tool Rank
ENGINE MECHANICAL (4HK1, 6HK1) 1A-103
Piston, Connecting RodComponents
Name1. Snap Ring2. Piston3. Bearing4. Connecting Rod Cap
5. Connecting Rod6. Piston Pin7. Piston Ring
Removal1. Remove the oil pan.
Refer to “Oil Pan”.2. Remove the cylinder head cover.
Refer to “Cylinder Head Cover”.3. Remove the rocker arm shaft ASM.
Refer to “Rocker Arm Shaft ASM”.4. Remove the camshaft ASM.
Refer to “Camshaft ASM”.5. Remove the cylinder head.
Refer to the “Cylinder Head”.6. Remove the connecting rod cap.
Caution:Sort the removed bearings according to cylinders byusing tags.
7. Remove the piston and connecting rod.
1
3
4
5
1
62
7
WSHK0184
1A-104 ENGINE MECHANICAL (4HK1, 6HK1)
• Remove carbon on the upper side of the cylinderliner with a scraper.
• Pull out the piston and connecting rod towards thecylinder head.
Caution:Be sure not to damage the oil jet and cylinder linerwhen pushing out the connecting rod.
8. Remove the connecting rod bearing.
Caution:Sort the bearings in the order of cylinders when reusingthem so that they will not be confused with the bearingof other cylinders.
Disassembly1. Remove the piston ring.• Use ring pliers to remove the piston ring.
Caution:Sort the piston rings in the order of cylinders whenreusing them so that they will not be confused with thepistons and piston rings of other cylinders.
2. Remove the snap ring.3. Remove the piston pin.
Caution:Sort the disassembled piston pins, pistons andconnecting rods together in the order of cylinders.
4. Remove the connecting rod from the piston.5. Piston• Clean carbon carefully that is adhered to the head
of the piston and the groove of the piston ring.
Caution:Do not use wire brush to clean the piston because itscratches the piston.Inspect the piston with eyes for cracks, burns and otherexcessive wear, and replace it if there is anyabnormality.
6. Measure the gap between the piston and the innerdiameter of the cylinder liner.
ENGINE MECHANICAL (4HK1, 6HK1) 1A-105
Cylinder liner inner diameter• Use a cylinder bore dial indicator to measure the
liner inner diameter both in the thrust and radialdirections in the designated position.
• Measurement position (from the upper surface ofthe cylinder block)1. 20 mm (0.79 in) 2. 110 mm (4.33 in) 3. 190 mm (7.48 in)
• Measure the liner inner diameter based on theaverage value of the actual measurement valueson 6 positions.
Name1. 20 mm (0.79 in)2. 110 mm (4.33 in)3. 190 mm (7.48 in)
Piston outside diameter• Use a micrometer to measure the outside diameter
of the piston in the right angle to the piston pin inthe designated position.
• Measurement position (from the upper surface ofthe piston) 82 mm (3.2 in).
4HK1
6HK1
Caution:If it is found that the gap between the cylinder linerinner diameter and the piston exceeds the standardvalue, replace the piston or cylinder liner.
7. Piston replacement• You do not need to select grades because there is
only one grade for each of the piston and thecylinder liner inner diameter.If you replace the cylinder liner, you must select the cylinder block (1, 2, 3) because there are two types of the liner outer diameter.
• Refer to “Cylinder Block” if you replace the cylinderliner.
Caution:The head of piston has a marking of grade B or C whenit is shipped from the factory.
Cylinder liner inner diameter mm (in)
115.021 – 115.050 (4.52838 – 4.52952)
Piston diameter mm (in)
Standard 114.920 – 114.949 (4.52440 – 4.52554)
Gap between the piston and the inner diameter of the cylinder liner
mm (in)
Standard 0.082 – 0.130 (0.0032 – 0.0051)
Piston diameter mm (in)
Standard 114.974 – 114.989 (4.52652 – 4.52711)
Gap between the piston and the inner diameter of the cylinder liner
mm (in)
Standard 0.042 – 0.066 (0.00165 – 0.00259)
1A-106 ENGINE MECHANICAL (4HK1, 6HK1)
Name1. Front Mark Cut
8. Inspect the piston ring.Measure the joint of the piston ring (remove carbonon the ring joint)
• Insert the piston ring into the cylinder liner.
• Use the piston to push the ring to reach the underedge of the cylinder liner.
• Use a thickness gauge to measure the gap of thering joint.
• If the measurement exceeds the limit, replace thepiston ring.
Measure the clearance between the piston ringgroove and the piston.
• Remove carbon on the piston ring groovecompletely.
• Put the piston ring in the piston ring groove, use athickness gauge to measure the gap betweenthem.
• If the clearance between the piston ring grooveand the piston exceeds the limit, replace the pistonand the piston ring.
Piston ring gap mm (in)
Standard Limit
Top ring 0.18 – 0.28(0.0071 – 0.0110)
1.2(0.047)
Second ringThird ring
0.35 – 0.50(0.0138 – 0.0197)
1.2(0.047)
Oil ring 0.15 – 0.35(0.0059 – 0.0138)
1.2(0.047)
Piston ring and piston ring groove clearance
mm (in)
Piston ring Standard Limit
Top ring 0.057 – 0.097(0.0022 – 0.0038)
0.20(0.0079)
Second ringThird ring
0.085 – 0.120(0.0033 – 0.0047)
0.20(0.0079)
Oil ring 0.020 – 0.060(0.0008 – 0.0024)
0.20(0.0079)
ENGINE MECHANICAL (4HK1, 6HK1) 1A-107
9. Inspect the piston pin.• Inspect the piston pin with eyes for cracks,
scratches and other damages, replace it ifnecessary.
• Use a micrometer to measure the outer diameterof the piston pin. If the measured value exceedsthe limit, replace the piston pin.
4HK1
6HK1
• Inspect to make sure that there is a resistance tothe extent which the piston can push the piston pinlightly in normal temperatures.
• If it feels a large looseness or instability in normaltemperatures, replace the piston or piston pin.
• Measure the bush of the small edge of theconnecting rod. If the clearance between thebushing inner diameter and the pin diameterexceeds the limit, replace the bushing orconnecting rod ASM, and the pin.
Expansion force N (kgf/lbf)
Standard Limit
Top ring 22.7 – 30.7 (2.31 – 3.13/5.10 – 6.90)
11.8 (1.2/2.7)
Second ring 16.7 – 22.6 (1.70 – 2.30/3.75 – 5.08)
5.9 (0.6/1.3)
Third ring 20.8 – 28.2 (2.12 – 2.88/4.68 – 6.34)
4.9 (0.5/1.1)
Oil ring 43.0 – 58.1 (4.38 – 5.92/9.67 – 13.06)
41.2 (4.2/9.3)
Piston pin outer diameter mm (in)
Standard 35.995 – 36.000 (1.4171 – 1.4173)
Limit 35.970 (1.4161)
Piston pin outer diameter mm (in)
Standard 40.0 (1.5748)
Limit 39.95 (1.5728)
Piston pin and connecting rod small end bushing clearance
mm (in)
Standard 0.012 – 0.027(0.0005 – 0.0011)
Limit 0.05(0.0020)
1A-108 ENGINE MECHANICAL (4HK1, 6HK1)
10. Measure the clearance between the piston and thepiston pin.
• Apply engine oil on the piston pin. Use your fingerto push it in the piston hole and rotate it. If the pinsmoothly rotates without instability, the clearanceis normal. If there is instability, measure theclearance. If the clearance exceeds the limit,replace the piston and the piston pin.
11. Remove the bushing.• Set the collar, connecting rod and collar on the
setting bar as shown in the drawing.
• Tighten the nut.
Name1. Setting Bar2. Connecting Rod3. Nut4. Collar5. Bushing6. Collar
• Place the connecting rod bushing replacer base onthe bench press, tighten the fixation bolt.
• Use the bench press to replace the bush.
Special toolConnecting rod bushing replacer: 5-8840-2340-0(EN-47682)
Name1. Bolt2. Connecting Rod Bushing Replacer
12. Measure the connecting rod alignment.
Piston pin and piston pin hole clearance mm (in)
Standard 0.004 – 0.017 (0.00016 – 0.00067)
Limit 0.04 (0.0016)
ENGINE MECHANICAL (4HK1, 6HK1) 1A-109
• Use a connecting rod aligner to measure thetorsion and parallel level of the big end hole andthe small end hole. If the measured value exceedsthe limit, replace it.
13. Measure the bearing oil clearance.• Measure the oil clearance between the connecting
rod bearing and the crank pin with the followingmethod.
– Remove the connecting rod cap. Sort theremoved caps according to the cylindernumber.
– Clean the bearing and the shaft pin.– Check the bearing. If it is damaged or worn
seriously, replace the bearing ASM.• Place the plastigauge on the crankshaft pin.
• Install the bearing cap and tighten the bolt with thedesignated torque.Apply molybdenum disulfide on the screw part and the bearing surface.
Caution:Do not rotate the crankshaft.
– Remove the cap.– Measure the largest width of the plastigauge to
calculate the oil clearance. If the clearanceexceeds the limit, replace the bearing ASM.
– Remove the plastigauge from the bearing andcrank pin.
14. Select the connecting rod bearing.• Refer to the bearing selection table when installing
a new connecting rod or replacing bearings in use.
• Select and install the bearing, paying attention tothe large edge hole diameter of the connecting rod.
Connecting rod alignment(per length of 100 mm 3.94 in)
mm (in)
Standard Limit
Distortion and Parallelism
0.05 (0.002) 0.20 (0.008)
Connecting rod bearing cap bolt torque: N⋅m(kg⋅m/lb ft)
1st step 39 (4.0/29)2nd step 60°
3rd step 30°
Crank pin and bearing clearance mm (in)
Standard 0.036 – 0.077 (0.0014 – 0.0030)
Limit 0.10 (0.0039)
1A-110 ENGINE MECHANICAL (4HK1, 6HK1)
Name1. Recognition Boss: When putting, 4HK1:Front,
6HK1:Back2. Big End Diameter Grade Mark3. Cylinder Number
Bearing selection table
Name1. Grade Identification Color
Reassembly1. Install the bush• Place the connecting rod bushing replacer base on
the bench press, set the connecting rod andtighten the fixation bolt.
Special toolConnecting rod bushing replacer: 5-8840-2340-0(EN-47682)
Name1. Bolt2. Connecting Rod Bushing Replacer
• Set the collar, new bushing and collar on thesetting bar as shown in the drawing.
• Tighten the nut.
• Adjust the oil hole of the connecting rod and the oilhole of the bush, and use the bench press to installthe bush.
Big end hole diameter Grade
Bearing recognition
color
Oil clearance
mm (in)
A Green 0.036 – 0.077(0.0014 – 0.0030)
B Yellow 0.036 – 0.077(0.0014 – 0.0030)
ENGINE MECHANICAL (4HK1, 6HK1) 1A-111
Name1. Setting Bar2. Connecting Rod3. Nut4. Collar5. Bushing6. Collar
• After installing the new bush, use a grinder tomachine the pin hole so that the pin clearanceequals the standard value.
2. Install the piston.3. Install the connecting rod.• 4HK1: Install it so that the front mark of the head of
the piston and the connecting rod forging mark(projecting) on the connecting rod face the samedirection.
• 6HK1: Install it so that the front mark of the head ofthe piston and the connecting rod forging mark(projecting) on the connecting rod face theopposite direction.
• Use snap ring pliers to install the snap ring of oneside.
Name1. Snap Ring2. Front Mark3. Forging Mark (Projecting): 4HK1: Front, 6HK1:
Back
4. Apply enough engine oil on the piston pin, push itin the piston and the connecting rod small edge.
5. Use snap ring pliers to install the snap ring.
Caution:Make sure that the snap ring is installed in the ringgroove properly. Make sure that the connecting rodmoves smoothly.
6. Use piston ring setting tool to install the piston ring.
1A-112 ENGINE MECHANICAL (4HK1, 6HK1)
• Install the oil ring so that the joint angle of the ringand coil expander is in the opposite 180° direction.
• Install the piston ring so that the marks “N” faceupward.
Special toolPiston ring setting tool: 1-8522-1029-0
Name1. Top Ring2. Second Ring3. Third Ring4. Oil ring
Caution:Note that the shapes are different for each piston ring.Make sure that there is not gap in the position indicatedin the drawing when the oil ring coil expander wasinstalled.
Installation1. Install the connecting rod bearing.• Install the bearing on the connecting rod, apply
engine oil on the bearing.
2. Install pistons and connecting rod ASM.• Apply enough engine oil on the piston ring, ring
groove and piston side surface.
• Dislocate the piston ring joint so that (1) is top ring,(3) is 2nd ring, (2) is 3rd ring and (4) is oil ring, asshown in the drawing.
• Face the piston front mark cut to forward, use thepiston ring compressor to insert the piston in thecylinder liner.
Caution:• Be sure not to make the connecting rod touch the
oil jet when pushing in the piston.• Be sure not to hurt the inside of the liner when
pushing in the piston.
Special toolPiston ring compressor: 5-8840-9018-0 (J-8037)
3. Install the connecting rod cap.• Install the bearing on the connecting rod cap and
apply engine oil.
• Install the cap, matching the numbers (1, 2, 3, 4) ofthe caps and connecting rods.
ENGINE MECHANICAL (4HK1, 6HK1) 1A-113
Name1. Recognition Boss: When putting, 4HK1:Front,
6HK1:Back2. Big End Diameter Grade Mark3. Cylinder Number
• Apply molybdenum disulfide on the screw part andthe setting face of the tightening bolt and tighten itwith the designated torque.
Special toolAngle gauge: 5-8840-0266-0 (J-45059, KM470-B)
Caution:Make sure that the crankshaft rotates smoothly.
4. Install the cylinder head.Refer to the “Cylinder Head”.
5. Install the camshaft ASM.Refer to “Camshaft ASM”.
6. Install the rocker arm shaft ASM.Refer to “Rocker Arm Shaft ASM”.
7. Install the cylinder head cover.Refer to “Cylinder Head Cover”.
8. Install the oil pan.Refer to “Oil Pan”.
Tightening torque:1st step = 39 N⋅m (4.0 kg⋅m/29 lb ft)
2nd step = 60°3rd step = 30°
1A-114 ENGINE MECHANICAL (4HK1, 6HK1)
Torque Specifications
Special Tool
Illustration Tool Number/Description/Special Tool Rank
5-8840-2340-0EN-47682
Connecting rod bushing removerRank B
x-xxxx-xxxx-xx-xxxx
Piston ring compressorRank B
x-xxxx-xxxx-xPiston ring setting tool
Rank B
5-8840-0266-0J-45059
KM470-BAngle gauge
Rank B
Illustration Tool Number/Description/Special Tool Rank
ENGINE MECHANICAL (4HK1, 6HK1) 1A-115
FlywheelComponents
Name1. Flywheel Housing2. Flywheel ASM
3. Washer4. Crankshaft Position Sensor
Removal1. Remove the starter motor.• Remove the ground cable of the starter motor.
• Remove the two nuts on the upper side and lowerside that fix the starter, remove the starter from thefly wheel housing.
4HK1
1A-116 ENGINE MECHANICAL (4HK1, 6HK1)
6HK1
2. Remove the crankshaft position sensor.• Remove to prevent contact damage when the
flywheel is removed.
• Do not throw or drop because it is vulnerable toshock.
* 4HK1 is shown for illustration.
3. Remove the washer and flywheel.• Install the crankshaft stopper to the starter
installing portion of the flywheel housing.
Caution:Make sure that the stopper is properly fitted andengaged with the ring gear.
Special toolCrankshaft stopper: x-xxxx-xxxx-x (xx-xxxxx)
• Gradually loosen the flywheel installation bolts inthe order shown in the drawing so that the flywheeldoes not rotate.
• After loosening all the bolts, remove the stopper toremove the flywheel.
4. Take out the ring gear.• Put a bar on the ring gear and hit it with a hammer
to remove it.
ENGINE MECHANICAL (4HK1, 6HK1) 1A-117
Inspection1. Visual check• Inspect the flywheel friction surface for cracks and
damages, and replace it if it has abnormality.
• Inspect the tooth part of the ring gear, replace thering gear if it has damage or serious wear.
2. Measurement of the friction surface• Measure the depth of the flywheel friction surface.
• Adjust it if the measured value is within thestandard value and the limit.
• If the measured value exceeds the limit, replacethe flywheel.
Depth = From the pressure installation surface to thefriction surface.
Installation1. Install the ring gear.• After heating the ring gear with a gas burner
equally, install it in the flywheel.
• In the case of shrinkage cooling of the ring gear,maintain the flatness by applying weight of 68.6 kN(15,400 lbf).
Caution:• Install the ring gear so that the side with a pattern
faces forward.• Shrink fit the ring gear to the flywheel.
Make sure that flywheel and ring gear adhesion iscomplete.
2. Install the flywheel.3. Install the washer.• Install the flywheel to match with the knock pins of
the crankshaft, tighten them in the order shown inthe illustration.
Depth of the friction surface of the flywheel mm (in)
Standard 19 (0.75)
Limit 20 (0.79)
1A-118 ENGINE MECHANICAL (4HK1, 6HK1)
• Apply molybdenum disulfide on the screw part andsetting face of the bolt.
• Install the crankshaft stopper to the starterinstalling portion of the flywheel housing.
Special toolCrankshaft stopper: x-xxxx-xxxx-x (xx-xxxxx)Angle gauge: 5-8840-0266-0 (J-45059)
4. Install and tighten the crankshaft position sensorwith the designated torque.
5. Install the starter motor on the flywheel housingwith nuts and tighten them with the designatedtorque.
4HK1
6HK1
• Install the ground cable of the starter motor.
Tightening torque:1st step = 78 N⋅m (8.0 kg⋅m/58 lb ft)
2nd step = 120° – 150°
Tightening torque: 8 N⋅m (0.8 kg⋅m/71 lb in)
Tightening torque: 76 N⋅m (7.7 kg⋅m/56 lb ft)
ENGINE MECHANICAL (4HK1, 6HK1) 1A-119
Torque Specifications
Special Tool
WSHK0067
60 6078 8 / 58
8 0.8 / 5.9
N mkg m/lb ft
Illustration Tool Number/Description/Special Tool Rank
x-xxxx-xxxx-xxx-xxxxx
Crankshaft stopperRank B
5-8840-0266-0J-45059KM470-B
Angle gaugeRank B
1A-120 ENGINE MECHANICAL (4HK1, 6HK1)
Front CoverComponents4HK1
WSHK0239
4
1
2
3
5
6
78
9
10
ENGINE MECHANICAL (4HK1, 6HK1) 1A-121
6HK1
Name1. Front Cover2. Oil Pan Gasket3. Oil Pan4. Front Oil Seal5. Crankshaft Pulley6. Water Pump ASM
7. Fan Belt8. Water Pump Pulley9. Spacer
10. Fan ASM11. Adjusting Plate12. Generator
Removal1. Remove the front oil seal.
Refer to “Crankshaft Front Oil Seal”.2. Remove the oil pan.
Refer to “Oil Pan”.3. Remove the water pump.
Refer to the “Water Pump” in the cooling systemsection.
4. Remove the front cover.• Remove the generator adjust plate. (6HK1 only)
• Remove the oil relief valve (arrow), loosen the frontcover installation bolts and remove the front cover.
WSHK0240
11
12
5
678
9
10
1
2
3
4
1A-122 ENGINE MECHANICAL (4HK1, 6HK1)
Installation
1. Install the front cover.• Clean the cylinder block front surface. In particular,
remove liquid gasket leaked during installation ofthe crankcase.
• Install two O-rings and apply liquid gasket(ThreeBond 1207B or equivalent), or eachequivalent along with the groove of the front coverinstallation surface.
• Install within seven minutes after applying liquidgasket.
Caution:Apply liquid gasket so that it does not adhere to the O-ring.
4HK1
Name1. O-Ring
6HK1
Name1. O-Ring
• Align with the knock pin of the cylinder block andinstall the front cover.
Caution:Along with the front cover, install the water pump ASM(before liquid gasket hardens).4HK1
Beat width 1.5 – 5mm (0.059 – 0.20 in)Beat height 0.3 mm – 1.5 mm
(0.012 – 0.059 in) from the jointsurface
Tightening torqueFront cover bolt (1): 23.5 N⋅m (2.4 kg⋅m/17 lb ft)Front cover bolt (2): 52 N⋅m (5.3 kg⋅m/38 lb ft)Front cover bolt (3): 23.5 N⋅m (2.4 kg⋅m/17 lb ft)
WSHK0243
11
1
020EY00062
ENGINE MECHANICAL (4HK1, 6HK1) 1A-123
• Tighten the oil relief valve (4) to the specifiedtorque.
Name1. Bolt: L = 352. Bolt: L = 303. Bolt: L = 654. Oil Relief Valve
6HK1
• Tighten bolt with (*) mark together with the adjustplate of the generator.
• When you remove the stud bolt (1), install inoriginal position.
2. Install the water pump.Refer to the “Water Pump” of the section of the“Cooling System”
3. Install the oil pan.Refer to “Oil Pan”.
4. Install the front oil seal.Refer to “Crankshaft Front Oil Seal”.
Tightening torqueOil relief valve: 39 N⋅m (4.0 kg⋅m/29 lb ft)
Tightening torqueFront cover bolts (13 bolts): 18 N⋅m (1.8 kg⋅m/13lb ft)
Tightening torqueStud bolt for water pump: 12.7 N⋅m (1.3 kg⋅m/9.4lb ft)
WSHK0233
1
WSHK0032
1A-124 ENGINE MECHANICAL (4HK1, 6HK1)
Torque Specifications4HK1
N mkg m/lb ft
WSHK0241
52 5.3 / 38
39 4 / 29
23.5 2.4 / 17
ENGINE MECHANICAL (4HK1, 6HK1) 1A-125
6HK1
WSHK0164
39 (4 / 29)
20 (2 / 14)
39 (4 / 29)
18 (1.8 / 13)
N m(kg m/lb ft)
1A-126 ENGINE MECHANICAL (4HK1, 6HK1)
Crankshaft Front Oil SealComponents
* 4HK1 is shown for illustration.Name
1. Crankshaft Pulley 2. Crankshaft Front Oil Seal
Removal1. Drain coolant.2. Remove the starter.• Disconnect the starter ground cable.
• Unscrew two mounting nuts, upper and lower, fromthe starter to dismount the starter from the flywheelhousing.
4HK1
ENGINE MECHANICAL (4HK1, 6HK1) 1A-127
6HK1
3. Disconnect the upper radiator hose on the engineside.
4. Disconnect the coolant reserve tank hose on theradiator side.
5. Disconnect the lower radiator hose on the engineside.
6. Remove the radiator (with the fan guide) detachingright and left brackets.
7. Remove the fan ASM.• Remove the fan ASM unscrewing four mounting
bolts.
8. Remove the fan belt.9. Remove the crankshaft pulley.• Loosen the pulley nut blocking the crankshaft from
turning by placing a crankshaft stopper on thestarter mounting position on the flywheel housing.
Caution:Make sure that the stopper is properly fitted andengaged with the ring gear.
Special toolCrankshaft stopper: x-xxxx-xxxx-x (xx-xxxxx)
10. Remove the crankshaft front oil seal.• Remove the oil seal off with a screwdriver or the
like avoiding damage to the oil seal contact surfaceon the front cover and the shaft.
Name1. Felt2. Slinger3. Oil Seal
Caution:Be sure to replace the slinger and oil seal as a set.11. Remove the front slinger.
• Use the slinger remover to remove the frontslinger.
1A-128 ENGINE MECHANICAL (4HK1, 6HK1)
Special toolSlinger remover:
1-8521-0027-0 (For 4HK1 and 6HK1)x-xxxx-xxxx-x (For 4HK1)8-9439-6858-0 (For 6HK1)
Installation1. Install the front slinger using installer, setting tool.
Special tool4HK1Oil seal installer kit: x-xxxx-xxxx-x (x-xxxxx)6HK1Oil seal setting tool: 8-94396-856-0• Install the slinger (1) to the end of adapter (2).
Install the adapter to the crankshaft (3).• Install the slinger sleeve (4) to the adapter. Tighten
the center bolt (5) until the sleeve comes in contactwith the adapter stopper.
• After pressing in the slinger, make sure that thedistance between crankshaft end surface and theslinger is A as specified.
4HK1WSHK0205
Distance (A): 40.5±0.3 mm (1.6±0.01 in)Distance (B): 34±0.1 mm (1.3±0.004 in)
WSHK0197
WSHK0206
ENGINE MECHANICAL (4HK1, 6HK1) 1A-129
6HK1
Caution:Be sure to replace the slinger and oil seal as a set.
2. Install the crankshaft front oil seal.• Press fit the oil seal using an oil seal installer,
setting tool.
Name1. Oil Seal2. Adapter (Front)3. Adapter Ring (Front)4. Fixing Bolt5. Sleeve (Front)6. Washer (Front)7. Center Bolt
Special tool4HK1Oil seal installer kit: x-xxxx-xxxx-x (x-xxxxx)6HK1Oil seal setting tool: 8-94396-856-0(Use the parts listed below for the front oil seal.)
• Mount the adapter onto the crankshaft with fixingbolts.
Name1. Adapter
• Apply engine oil to the lip of the oil seal and place iton the front side adapter.
• Put the front side adapter ring in the sleeve and fixthe sleeve on the adapter with the center bolt anda washer.
• Tighten the bolt until the sleeve touches theadapter to press fit the front oil seal.
Distance (A): 18±0.3 mm (0.7±0.01 in)
WSHK0199
No. Part Name Oil seal
1 Sleeve (front)
2 Adapter (front)
3 Adapter ring (front)
4 Washer (front)
5 Center bolt
6 Fixing bolt
1A-130 ENGINE MECHANICAL (4HK1, 6HK1)
Name1. Oil Seal2. Adapter Ring3. Sleeve4. Bolt and Washer
• After you have press-fitted the front oil seal,confirm the measurement shown (depth from theend surface of the crankshaft to the oil seal) andcheck for deflection of the oil seal.
4HK1
Name1. Adapter Ring2. Sleeve3. Adapter4. Oil Seal
6HK1
3. Install the damper to the crankshaft pulley. (6HK1)• Tighten in the sequence shown.
Distance (B): 8.5±0.15 mm (0.33±0.006 in)
Tightening torque: 48 N⋅m (4.9 kg⋅m/35 lb ft)
WSHK0203
ENGINE MECHANICAL (4HK1, 6HK1) 1A-131
4. Install the crankshaft pulley.• Apply engine oil to the threads of the fastening
bolts.
• Install the crankshaft pulley aligning with the knockpins on the crankshaft.
• Tighten in the sequence shown.
5. Install the fan belt.a. Inspection of fan belt deflection• Check with a scale if the belt deflection is within
the specified limits when pressure of 98 N(22 lb) is applied mid-way along the belt’slongest run. Also check the belt for damage.
Name1. Crankshaft Pulley2. Generator3. Fan Pulley
b. Fan belt adjustment• Loosen the adjustment bolt (1) of the AC
generator and adjust the fan belt moving thegenerator.
Name1. Adjusting Bolt2. Fixing Bolt3. Fixing Bolt
6. Tighten the fan ASM to the specified torque.
7. Install the radiator.
Tightening torque: 200 N⋅m (20.4 kg⋅m/148 lb ft)
Amount of fan belt deflection mm (in)for new belt 5.0 – 5.8 (0.19 – 0.23)
for reused belt 6.1 – 6.9 (0.24 – 0.27)
WSHK0033
Tightening torque: (2) = 24 N⋅m (2.4 kg⋅m/18 lb ft)(3) = 40 N⋅m (4.1 kg⋅m/30 lb ft)
Tightening torque: 24 N⋅m (2.4 kg⋅m/18 lb ft)
1A-132 ENGINE MECHANICAL (4HK1, 6HK1)
8. Connect the lower radiator hose.9. Connect the coolant reserve tank hose.
10. Connect the upper radiator hose.11. Install the starter in the flywheel housing with nuts
and tighten to the specified tightening torque.
• Connect the starter ground cable.
* 4HK1 is shown for illustration.12. Fill the radiator with coolant.
Tightening torque: 76 N⋅m (7.7 kg⋅m/56 lb ft)
ENGINE MECHANICAL (4HK1, 6HK1) 1A-133
Torque Specifications
* 4HK1 is shown for illustration.
Special Tool
Illustration Tool Number/Description/Special Tool Rank
x-xxxx-xxxx-xxx-xxxxx
Crankshaft stopperRank B
1-8521-0027-0Slinger remover
Rank B
x-xxxx-xxxx-xx-xxxxx
Oil seal installer kit(4HK1)Rank A
8-94396-856-0Oil seal setting tool
(6HK1)Rank A
Illustration Tool Number/Description/Special Tool Rank
1A-134 ENGINE MECHANICAL (4HK1, 6HK1)
Crankshaft Rear Oil SealComponents
Name1. Flywheel 2. Crankshaft Rear Oil Seal
Removal1. Remove the flywheel.
Refer to the “Flywheel”.2. Remove the crankshaft rear oil seal.• Remove the oil seal off with a screwdriver or the
like avoiding damage to the oil seal contact surfaceon the flywheel housing and the shaft.
Name1. Felt2. Slinger3. Oil Seal
ENGINE MECHANICAL (4HK1, 6HK1) 1A-135
3. Use the slinger remover to remove the slinger.
Caution:If the oil seal has been removed, both the oil seal andslinger must be replaced as a set.
Special toolSlinger remover:
1-8521-0027-0 (For 4HK1 and 6HK1)x-xxxx-xxxx-x (For 4HK1)8-9439-6858-0 (For 6HK1)
Installation1. Install the front slinger using installer, setting tool.
Special tool4HK1Oil seal installer kit: x-xxxx-xxxx-x (x-xxxxx)6HK1Oil seal setting tool: 8-94396-856-0• Install the slinger (1) to the end of adapter (2).
Install the adapter to the crankshaft (3).• Install the slinger sleeve (4) to the adapter. Tighten
the center bolt (5) until the sleeve comes in contactwith the adapter stopper.
• After pressing in the slinger, make sure that thedistance between crankshaft end surface and theslinger is A as specified.
WSHK0197
1A-136 ENGINE MECHANICAL (4HK1, 6HK1)
4HK1
6HK1
Caution:Be sure to replace the slinger and oil seal as a set.
2. Install the crankshaft rear oil seal.• Press-fit the rear oil seal using an oil seal installer,
setting tool.
Name1. Adapter (Rear)2. Fixing Bolt3. Center Bolt4. Sleeve (Rear)5. Collar (Rear)6. Adapter Ring (Rear)7. Oil Seal
Special tool4HK1Oil seal installer kit: x-xxxx-xxxx-x (x-xxxxx)6HK1Oil seal setting tool: 8-94396-856-0
• Put a collar on the fixing bolt and mount theadaptor onto the crankshaft.
Distance (A): 17.3±0.3 mm (0.7±0.01 in)Distance (B): 10.8±0.1 mm (0.4±0.004 in)
Distance (A): 17±0.3 mm (0.7±0.01 in)
WSHK0198
WSHK0199
No. Part Name Oil seal
1 Sleeve (rear)
2 Adapter (rear)
3 Collar (rear)
4 Adapter ring (rear)
5 Center bolt
6 Fixing bolt
ENGINE MECHANICAL (4HK1, 6HK1) 1A-137
* 4HK1 is shown for illustration.
Name1. Collar2. Fixing Bolt3. Adapter
• Apply engine oil to the lip of the oil seal and place itin the rear side adapter.
• Put the rear side adapter ring in the sleeve and putthe sleeve on the adapter and fix with the centerbolt.
* 4HK1 is shown for illustration.
Name1. Sleeve2. Adapter Ring
• Tightening the center bolt until the sleeve touchesthe adapter to press fit the oil seal.
* 4HK1 is shown for illustration.• After you have pressed in the rear oil seal, confirm
the measurement shown (depth from the endsurface of the crankshaft to the oil seal).
Name1. Rear Part of The Crankshaft2. Oil Seal3. 4HK1: 7.8 ± 0.3 mm (0.31 ± 0.012 in),
6HK1: 7.5 ± 0.15 mm (0.3 ± 0.006 in)4. Collar5. Adapter Ring6. Sleeve7. Adapter
3. Install the flywheel.Refer to the “Flywheel”.
1A-138 ENGINE MECHANICAL (4HK1, 6HK1)
Special Tool
Illustration Tool Number/Description/Special Tool Rank
1-8521-0027-0Slinger remover
Rank B
x-xxxx-xxxx-xx-xxxxx
Oil seal installer kit(4HK1)Rank A
8-94396-856-0Oil seal setting tool
(6HK1)Rank A
ENGINE MECHANICAL (4HK1, 6HK1) 1A-139
CrankshaftComponents
* 4HK1 is shown for illustration.Name
1. Upper Bearing2. Upper Thrust Bearing3. Gear4. Crankshaft
5. Lower Bearing6. Lower Thrust Bearing7. Crankcase
Removal1. Remove the cylinder head cover.
Refer to “Cylinder Head Cover”.2. Remove the rocker arm shaft.
Refer to “Rocker Arm Shaft ASM”.3. Remove the camshaft.
Refer to “Camshaft ASM”.
4. Remove the cylinder head.Refer to the “Cylinder Head”.
5. Remove the fuel supply pump.Refer to “Fuel Supply Pump” in the fuel systemsection.
6. Remove the crankshaft front oil seal.Refer to “Crankshaft Front Oil Seal”.
1A-140 ENGINE MECHANICAL (4HK1, 6HK1)
7. Remove the crankshaft rear oil seal.Refer to the “Crankshaft Rear Oil Seal”.
8. Remove the oil pan.Refer to “Oil Pan”.
9. Remove the water pump.Refer to the “Water Pump” in the Cooling SystemSection.
10. Remove the front cover.Refer to the “Front Cover”.
11. Remove the timing gear train.Refer to the “Timing Gear Train”.
12. Remove the oil pump.Refer to the “Oil Pump”.
13. Remove the piston and connecting rod.Refer to the “Pistons and Connecting Rod”.
14. Remove the crankcase.• Gradually loosen crankcase mounting bolts in the
sequence shown and remove the crankcase usingthe replacer holes (arrowed holes in the figure).
4HK1
6HK1
15. Remove the lower thrust bearing.16. Remove the lower crankshaft bearings.
* 4HK1 is shown for illustration.17. Remove the crankshaft ASM.18. Remove the upper thrust bearing.19. Remove the upper crankshaft bearings.
WSHK0034
3 7 11 15 19 23 24 20 16 12 8 4 1
2 6 10 14 18 22 25 21 17 13 9 5
26
27
30
31
34
35
38
39
37
36
33
32
29
28
ENGINE MECHANICAL (4HK1, 6HK1) 1A-141
* 4HK1 is shown for illustration.
Disassembly1. Remove the gear.• Remove the gear using a gear puller.
Special toolCrankshaft gear puller: 8-9439-6818-0 (EN-47684)
Reassembly1. Install the gear.• Heat the gear to 170 – 250°C (338 – 482°F) and
install it aligning the groove on the gear with thepin on the crankshaft.
• Insert the gear at one push into the flange with itsend side with the alignment mark “S” facingoutward. If you are fitting the gear while it is cold,beat the gear in until it impinges on the end usingthe installer.
Special toolCrankshaft gear puller: 8-9439-6819-0 (EN-41222)
Name1. Alignment Mark
Inspection1. Thrust clearance• Set a dial gauge as shown and measure the
crankshaft thrust clearance.
• If the thrust clearance exceeds the limit, replacethe thrust bearings in a pair.
Caution:Measure the thrust clearance before dismounting.
Axial play of the crankshaft mm (in)
Standard 0.104 – 0.205 (0.0041 – 0.0081)
Limit 0.35 (0.0138)
1A-142 ENGINE MECHANICAL (4HK1, 6HK1)
* 4HK1 is shown for illustration.2. Main bearing clearance• Remove the crankcase.
Set out disassembled main bearings in the order of the numbers.
• Remove the crankshaft. Remove the main bearing.
• Clean the crankshaft journal and the upper andlower bearings.
• Check the bearings for damage or excessive wear.
If you find damage or excessive wear in the check, replace the bearings in pairs.
• Place the upper bearings and the crankshaft onthe cylinder block. Install the crankshaft so that itbecomes horizontal.
Caution:Turn the crankshaft about 30° to allow the bearings tosettle in.
* 4HK1 is shown for illustration.• Place Plastigauge on the crankshaft journal as
shown.
• Place the lower bearings at original positions onthe crankcase.
• Install the crankcase and tighten bolts to thespecified tightening torque.
• Tighten the crankcase in the sequence shownusing a torque wrench and an angle gauge.
ENGINE MECHANICAL (4HK1, 6HK1) 1A-143
* 4HK1 is shown for illustration.4HK1
6HK1
• Tighten bolts from 1 to 10 (M14) and confirm thatthey are tightened to a torque of 142 N⋅m (14.5kg⋅m/105 lb ft) or more.
Special toolAngle gauge: 5-8840-0266-0 (J-45059, KM470-B)
Caution:Do not rotate the crankshaft after tightening thecrankcase.
• Loosen the bolts and gently remove thecrankcase.
• Measure the widest part of the Plastigaugeflattened by tightening the crankcase to determinethe clearance.
4HK1
6HK1
WSHK0035
37 33 29 25 21 17 16 20 24 28 32 3639
38 34 30 26 22 18 15 19 23 27 31 35
14
13
10
9
6
5
2
1
3
4
7
8
11
12
Tightening torque:M14 bolt 4HK1: (1 – 10), 6HK1: (1 – 14)
1st step = 98 N⋅m (10.0 kg⋅m/72 lb ft)2nd step = 132 N⋅m (13.5 kg⋅m/97 lb ft)3rd step = 30° – 60°
M10 bolt 4HK1: (11 – 27), 6HK1: 15 – 39)4th step = 37 N⋅m (3.8 kg⋅m/27 lb ft)
Journal oil clearance mm (in)
Standard Limit
No.1, 2, 4, 5 0.037 – 0.072 (0.0015 – 0.0028)
0.11 (0.0043)
No.3 0.051 – 0.086 (0.0020 – 0.0034)
0.11 (0.0043)
Journal oil clearance mm (in)
Standard Limit
No. 1, 2, 3, 5, 6,7
0.063 – 0.094 (0.0025 – 0.0037)
0.14 (0.0055)
No. 4 0.093 – 0.124 (0.0037 – 0.0049)
0.14 (0.0055)
1A-144 ENGINE MECHANICAL (4HK1, 6HK1)
• If the journal oil clearance exceeds the limit,replace the main bearings altogether or thecrankshaft.
• Remove the plastigauge from the bearing andcrank pin.
Inspection of crankshaft• Check the crankshaft journal and crank pin
surfaces for wear and damage. Check the oil sealcontact surface for excessive wear and damage.
• Check the oil port for clogging.
3. Crankshaft run-outCarefully set the crankshaft on the V block. Slowlyturn the crankshaft to measure the run-out. If thecrankshaft run-out exceeds the limit, replace thecrankshaft.
4HK1
6HK1
4. Measure the journal and the crank pin diametersand uneven wear.
• Measure outer diameters of the journal and the pinand calculate differences between the maximumand the minimum values. Take measurements atfour positions for both the journal and the pin.
4HK1
Crankshaft run-out mm (in)
Standard 0.05 or less (0.0020 or less)
Limit 0.30 (0.012)
Crankshaft run-out mm (in)
Standard 0.06 or less (0.0024 or less)
Limit 0.45 (0.018)
Crankshaft outside diameter mm (in)
Standard Limit
Journal #1, 2, 4, 5 81.905 – 81.925(3.22460 – 3.22538)
81.85(3.222)
Journal #3 81.891 – 81.911(3.22408 – 3.22483)
81.85(3.222)
Pin 65.902 – 65.922(2.59456 – 2.59535)
65.850(2.5925)
ENGINE MECHANICAL (4HK1, 6HK1) 1A-145
6HK1
Caution:Tufftriding (soft nitriding treatment) is applied toenhance strength of the crankshaft. Therefore, youshall not polish the surface of the crankshaft.
Selection of crankshaft bearing• When installing new crankshaft bearings or
replacing bearings in use, make reference to theBearing Selection Table.
• Select and install new bearings paying closeattention to the cylinder block journal internaldiameter grade and the crankshaft journaldiameter grade.
• Journals are numbered from 1 to 5 (4HK1) or 1 to7 (6HK1) from left to right when viewed so that thenumbers are in normal reading orientation.
Caution:Be careful about difference in the shape of the bearingswhen installing them.
Name1. Upper Bearing2. Oil Gallery3. Grade Identification Color4. Oil Groove5. Lower Bearing6. Grade Identification Color
Crankshaft outside diameter mm (in)
Standard Limit
Journal No. 1, 2, 3, 5, 6, 7
81.905 – 81.925(3.22460 – 3.22538)
81.85(3.222)
Journal No. 4 81.875 – 81.895(3.22341 – 3.22421)
81.85(3.222)
Pin 72.902 – 72.922(2.87015 – 2.87093)
72.850(2.8681)
1A-146 ENGINE MECHANICAL (4HK1, 6HK1)
Bearing selection table4HK1
6HK1
Installation1. Install the crankshaft upper bearing.• Install the upper bearing in the cylinder block and
apply oil.
Caution:When replacing the crankshaft bearings, select gradesreferring to the Crankshaft Bearing Grade Selection.Do not apply oil to the bearing installation surface onthe cylinder block and external surface of the bearing.
* 4HK1 is shown for illustration.2. Install the upper thrust bearing.
Combination of grades Oil clearance mm (in)
Cylinder blockGrade
Crank journalGrade
Bearing identification color
#1, 2, 4, 5 #3
1 1 Black 0.039 – 0.070(0.00154 – 0.00276)
0.053 – 0.084(0.00209 – 0.00331)
1 2 Brown 0.037 – 0.068(0.00146 – 0.00267)
0.051 – 0.082(0.00201 – 0.00323)
2 1 Blue 0.041 – 0.072(0.00161 – 0.00283)
0.055 – 0.086(0.00217 – 0.00339)
2 2 Black 0.039 – 0.070(0.00154 – 0.00276)
0.053 – 0.084(0.00209 – 0.00331)
Combination of grades Oil clearance mm (in)
Cylinder blockGrade
Crank journalGrade
Bearing identification color
#1, 2, 3, 5, 6 #4
1 1 Black 0.065 – 0.092(0.00256 – 0.00362)
0.095 – 0.122(0.00374 – 0.00480)
1 2 Brown 0.063 – 0.089(0.00248 – 0.00350)
0.093 – 0.119(0.00366 – 0.00469)
2 1 Blue 0.067 – 0.094(0.00264 – 0.00370)
0.097 – 0.124(0.00382 – 0.00488)
2 2 Black 0.065 – 0.091(0.00256 – 0.00358)
0.095 – 0.121(0.00374 – 0.00476)
ENGINE MECHANICAL (4HK1, 6HK1) 1A-147
• Install the upper thrust bearing in the front side ofthe cylinder block journal No.5 (4HK1) or No.7(6HK1). In doing this, you may attach the upperthrust bearing to the cylinder block with grease.Then, be sure to wipe up excess grease.
Caution:Install the thrust bearing so that the oil groove contactsthe crankshaft.
3. Install the crankshaft ASM.• Apply engine oil to the crankshaft journal and
gently place the crankshaft on the cylinder block.
• Press the crankshaft to the rear and insert theupper thrust bearing in the rear side of the cylinderblock journal No.5 (4HK1) or No.7 (6HK1).
Caution:Install the thrust bearing so that the oil groove contactsthe crankshaft.
* 4HK1 is shown for illustration.4. Install the lower crankshaft bearing.
5. Install the lower thrust bearing.• Install the lower thrust bearing in the rear side of
the crankcase journal No.5 (4HK1) or No.7(6HK1).
• Install the thrust bearing so that the oil groovecontacts the crankshaft.
* 4HK1 is shown for illustration.6. Install the crankcase.• Apply liquid gasket (ThreeBond 1207B or
equivalent) to the crankcase forming beads withdiameters of 3 – 4 mm (0.12 – 0.16 in).
• Install the crankcase within 7 minutes after youhave applied the liquid gasket.
• Gently place the crankcase on the cylinder block.
1A-148 ENGINE MECHANICAL (4HK1, 6HK1)
4HK1
6HK1
2(0.08)
12(0.47)10(0.4)
15(0.59) 10(0.4)
5(0.
2)
2.5(0.1)
2.5(0.1)
8(0.
31)
8(0.31)
2.5(0.1)
WSHK0036
8(0.
31)
mm(in)
ENGINE MECHANICAL (4HK1, 6HK1) 1A-149
• Apply Molybdenum Disulfide to M14 bolts’ threadsand setting faces and tighten them to the specifiedtightening torque in the sequence shown.
• You need not apply engine oil to M10 bolts.
• Tighten the bolts (M14) from 1 to 10 (4HK1) or 1 to14 (6HK1) and confirm that they are tightened to atorque of 142 N⋅m (14.5 kg⋅m/105 lb ft) or more.
Special toolAngle gauge: 5-8840-0266-0 (J-45059, KM470-B)
Caution:Confirm that the crankshaft turns smoothly.4HK1
6HK1
7. Install pistons and connecting rods.Refer to the “Pistons and Connecting Rod”.
8. Install the oil pump.Refer to the “Oil Pump”.
9. Install the timing gear train.Refer to the “Timing Gear Train”.
10. Install the front cover.Refer to the “Front Cover”.
11. Install the water pump.Refer to the “Water Pump” in the Cooling SystemSection.
12. Install the oil pan.Refer to “Oil Pan”.
13. Install the crankshaft rear oil seal.Refer to the “Crankshaft Rear Oil Seal”.
14. Install the crankshaft front oil seal.Refer to “Crankshaft Front Oil Seal”.
15. Install the fuel supply pump.Refer to the “Fuel Supply Pump”.
16. Install the cylinder head.Refer to the “Cylinder Head”.
17. Install the camshaft ASM.Refer to “Camshaft ASM”.
18. Install the rocker arm shaft ASM.Refer to “Rocker Arm Shaft ASM”.
19. Install the cylinder head cover.Refer to “Cylinder Head Cover”.
Tightening torque:M14 bolt 4HK1: (1 – 10), 6HK1: (1 – 14)
1st step = 98 N⋅m (10.0 kg⋅m/72 lb ft)2nd step = 132 N⋅m (13.5 kg⋅m/97 lb ft)3rd step = 30° – 60°
M10 bolt 4HK1: (11 – 27), 6HK1: (15 – 39)4th step = 37 N⋅m (3.8 kg⋅m/27 lb ft)
WSHK0035
37 33 29 25 21 17 16 20 24 28 32 3639
38 34 30 26 22 18 15 19 23 27 31 35
14
13
10
9
6
5
2
1
3
4
7
8
11
12
1A-150 ENGINE MECHANICAL (4HK1, 6HK1)
Torque Specifications
* 4HK1 is shown for illustration.
Special Tool
Illustration Tool Number/Description/Special Tool Rank
8-9439-6818-0EN-47684
Crankshaft gear removerRank B
8-9439-6819-0J-41222
Crankshaft gear installerRank B
Illustration Tool Number/Description/Special Tool Rank
ENGINE MECHANICAL (4HK1, 6HK1) 1A-151
5-8840-0266-0J-45059KM470-B
Angle gaugeRank B
Illustration Tool Number/Description/Special Tool Rank
1A-152 ENGINE MECHANICAL (4HK1, 6HK1)
Cylinder BlockComponents
* 4HK1 is shown for illustration.Name
1. Cylinder Liner 2. Cylinder Block
Removal1. Remove the cylinder head cover.
Refer to “Cylinder Head Cover”.2. Remove the rocker arm shaft ASM.
Refer to “Rocker Arm Shaft ASM”.3. Remove the camshaft ASM.
Refer to “Camshaft ASM”.4. Remove the cylinder head.
Refer to the “Cylinder Head”.
5. Remove the fuel supply pump.Refer to “Fuel Supply Pump” in the fuel systemsection.
6. Remove the crankshaft front oil seal.Refer to “Crankshaft Front Oil Seal”.
7. Remove the crankshaft rear oil seal.Refer to the “Crankshaft Rear Oil Seal”.
8. Remove the oil pan.Refer to “Oil Pan”.
ENGINE MECHANICAL (4HK1, 6HK1) 1A-153
9. Remove the water pump.Refer to the “Water Pump” in the Cooling SystemSection.
10. Remove the front cover.Refer to the “Front Cover”.
11. Remove the timing gear train.Refer to the “Timing Gear Train”.
12. Remove the oil pump.Refer to the “Oil Pump”.
13. Remove the piston and connecting rod.Refer to the “Pistons and Connecting Rod”.
14. Remove the crankshaft.Refer to the “Crankshaft”.
15. Remove the piston oil jet
16. Remove the cylinder liner.
If the cylinder liner cannot be pulled free by hand,tap around the lower side of the liner with ahammer grip or similar object loosen it.
Inspection1. Carefully remove water stains or other foreign
matters on the surface of the cylinder block.• Be careful not to damage the cylinder block.
2. Carefully remove the liquid gasket on thecrankcase mounting surface.
3. Clean up the cylinder block.4. Visually inspect the cylinder block.• Conduct color check and hydraulic (or pneumatic)
test and if you find crack or other damage, replacethe cylinder block.
5. Cylinder liner wear measurement• Check the internal surface of the liner for flaw or
damage.
• Measure the liner bore diameter at the most wornpart (it wears more in the rotation direction) at 15 –20 mm (0.59 – 0.79 in) from the top end of the linerwith the liner installed in the cylinder block. If thewear is over the application limit, replace it.
1A-154 ENGINE MECHANICAL (4HK1, 6HK1)
Caution:You need not select cylinder liner bore grade since theliners are only available in one size.
6. Cylinder block upper face warpage• Pull out the cylinder liners and remove water stains
on the cylinder block.
• Measure four sides and two diagonals of the topsurface of the cylinder block using a straight edge(1) and a thickness gauge (2).
• Replace the cylinder block if the measurementsexceed limit values.
* 4HK1 is shown for illustration.
Installation1. Cylinder liner grade selection• Select liner outer diameter grades according to the
cylinder block bore grades stamped on the cylinderblock at arrowed positions in the figure.
• The cylinder liner grade is stamped on the outsideof the cylinder liner (1).
• Matching the grades of the cylinder block and theliner outer diameter
Cylinder liner bore diameter mm (in)
Standard 115.021 – 115.050(4.52837 – 4.52952)
Limit 115.20 (4.5354)
Cylinder block upper face warpage mm (in)
Standard 0.05 or less (0.002 or less)
Limit 0.20 (0.079)
Cylinder block (stamp) 1, 2 3
Liner outside diameter 1X 3X
ENGINE MECHANICAL (4HK1, 6HK1) 1A-155
4HK1
6HK1
(Reference)When replacing liners, a “liner set” let you obtain apiston of proper grade for a given liner borediameter only by specifying a liner outsidediameter grade.
2. Install the cylinder liners.• Install the cylinder liners perpendicular to the
cylinder block.
• Do not hammer the liner or apply excessive forth toinsert it.
Caution:Clean up and blow with compressed air the cylinderblock and the cylinder liners before installing them.
3. Amount of the cylinder liner extrusionMeasure the amount of the cylinder liner extrusionusing a dial gauge.Difference of the amount of the extrusion betweenadjacent two cylinders should be within 0.03 mm(0.0012 in).
1
WSHK0636
Cylinder block bore and liner grade(Reference)
mm (in)
Grade (1, 2) / (1X) (3) / (3X)
Cylinder blockBore
diameter
118.001 – 118.020(4.64699 – 4.64654)
118.021 – 118.030(4.64649 – 4.64684)
Liner outside
diameter
117.991 – 118.000(4.64531 – 4.64566)
118.001 – 118.010(4.64570 – 4.64605)
Amount of the cylinder liner extrusion mm (in)Standard 0.05 – 0.10 (0.0020 – 0.0039)
1A-156 ENGINE MECHANICAL (4HK1, 6HK1)
Caution:Be sure to measure the cylinder liner extrusionwhenever you have replaced cylinder liners.
4. Install the piston oil jet.• Align the knock pin of the oil jet with the pin hole of
the cylinder block and tighten with the check valve.
Caution:Be careful not to deform or damage the oil jet nozzle.
5. Install the crankshaft.Refer to the “Crankshaft”.
6. Install pistons and connecting rods.Refer to the “Pistons and Connecting Rod”.
7. Install the oil pump.Refer to “Oil Pump”.
8. Install the timing gear train.Refer to the “Timing Gear Train”.
9. Install the front cover.Refer to the “Front Cover”.
10. Install the water pump.Refer to the “Water Pump” in the Cooling SystemSection.
11. Install the oil pan.Refer to “Oil Pan”.
12. Install the crankshaft rear oil seal.Refer to the “Crankshaft Rear Oil Seal”.
13. Install the crankshaft front oil seal.Refer to “Crankshaft Front Oil Seal”.
14. Install the fuel supply pump.Refer to “Fuel Supply Pump” in the Fuel Systemsection.
15. Install the cylinder head.Refer to the “Cylinder Head”.
16. Install the camshaft ASM.Refer to “Camshaft ASM”.
17. Install the rocker arm shaft ASM.Refer to “Rocker Arm Shaft ASM”.
18. Install the cylinder head cover.Refer to “Cylinder Head Cover”.
Tightening torque: 21 N⋅m (2.1 kg⋅m/15 lb ft)
ENGINE MECHANICAL (4HK1, 6HK1) 1A-157
Lubrication SystemPrecautions on Service Work
• During each disassembly, remove the old gasketadhering to each part and mating part completelyusing a scraper at the location, where the fluidgasket is to be used, clean the traces of oil,moisture, and dirt completely using waste cottonand apply the specified new fluid gasket at eachlocation.
• Avoid excessive or insufficient coating volume.Note that seizure may occur in case of excessivecoating due to clogging of the oil gallery and oil jet,and oil and water leakage may occur if the coatingis insufficient.
• Always, the start and end of the application shouldbe overlapped.
Explanations on functions and operationThe lubrication system uses the filter elementcombined with a full flow bypass, water-cooled oilcooler, and oil jet for piston cooling.
Lubricating system diagram
1A-158 ENGINE MECHANICAL (4HK1, 6HK1)
Function CheckOil pressure check
1. Check whether the engine oil is contaminated withdirt, light oil, or water. If contaminated with dirt,light oil, or water (after examining the cause andtaking the appropriate measures for light oil orwater contamination), replace the oil.
2. Check the engine oil level. The oil level should bebetween the two holes of the level gauge. If the oillevel is insufficient, replenish it.
3. Remove the oil pressure switch on the oil filterbody.
4. Install the oil pressure gauge on the oil filter body.
Special toolOil pressure gauge: J43620-20Hose: J43630Connector (4HK1 only): J43630-14Oil pressure testing adapter (4HK1 only): EN-46333
* 6HK1 is shown for illustration.
Name1. Oil Port2. Oil Gallery3. Hose4. Oil Pressure Gauge
Name1. 4HK1 Oil Pressure (Oil Port)2. 4HK1 Oil Pressure (Oil Gallery)3. 6HK1 Oil Pressure (Oil Port)4. 6HK1 Oil Pressure (Oil Gallery)
5. Warm the engine.6. Measure the oil pressure, to check whether it is
more than 550 kPa (80 psi) at 2000 rpm.7. Stop the engine.8. Remove the oil pressure gauge.9. Install the oil pressure switch.
10. Start the engine and check for oil leakage.
Engine oil• Ensure the engine is at a level ground. Before
starting the engine or when 5 minutes or morehave elapsed after stopping the engine, check theengine oil volume using the level gauge. Thevolume is appropriate if the engine oil is betweenthe upper and lower limits of the level gauge.Replenish the engine oil, if level is below the lowerlimit. Also, check for contamination of the engineoil.
4
3
2WSHK0237
1
WSHK0238
600 800 1000 1200 1400 1600 1800 2000 2200
0(0)
100(14.5)
200(29.0)
300(43.5)
400(58.0)
500(72.5)
600(87.0)
700(101.5)
800(116.0)
900(130.5)
1000(145.0)
F)
12
34
Engine speed (rpm)
Oil
Pre
ssur
e k
Pa(
psi)
Oil Temperature 85 (185
ENGINE MECHANICAL (4HK1, 6HK1) 1A-159
* 4HK1 is shown for illustration.
Name1. Upper Limit2. Lower Limit
Engine oil leakage• In the lift up condition, confirm that there are no
leaks from the cylinder head cover and oil pan.
Special Tool
Illustration Tool Number/Description/Special Tool Rank
J-43620-20Oil pressure gauge
Rank B
J-43630Hose
Rank B
J-43630-14Connector
(4HK1)Rank A
J-46333Oil pressure gauge
testing adapter(4HK1)Rank A
1A-160 ENGINE MECHANICAL (4HK1, 6HK1)
Oil Port Cover ASMComponents
Name1. Oil Pressure Switch2. Oil Port Cover
3. O-Ring
Removal1. Remove the oil pressure switch.2. Remove the oil port cover.3. Remove the O-ring.
Installation1. Install the O-ring on the oil port cover.
Name1. O-Ring2. O-Ring
ENGINE MECHANICAL (4HK1, 6HK1) 1A-161
2. Install the oil port cover on the cylinder block andtighten it to the specified torque.
Name1. Bolt M10X L = 802. Bolt M10X L = 25
3. Install the oil pressure switch to the oil port cover.• Apply the liquid gasket (Loctite 262) on 2 to 3
peaks from the tip of the threaded part of the oilpressure switch and install it at the position shownin the figure.
Tightening torque:4HK1 48 N⋅m (4.9 kg⋅m/35 lb ft)6HK1 39.2 N⋅m (4.0 kg⋅m/29 lb ft)
Tightening torque: 41.2 N⋅m (4.2 kg⋅m/30 lb in)
1A-162 ENGINE MECHANICAL (4HK1, 6HK1)
Oil CoolerComponents4HK1
Name1. Bypass Hose2. EGR Cooler Water Return Pipe3. Oil Cooler4. Common Rail
5. Fuel Supply Pump6. EGR Cooler Water Feed Pipe7. Suction Pipe
ENGINE MECHANICAL (4HK1, 6HK1) 1A-163
6HK1
Name1. EGR Cooler Water Return Pipe2. Oil Cooler3. Common Rail
4. Fuel Supply Pump5. Suction Pipe
Removal1. Remove the common rail.
Refer to the “Common Rail” in the fuel systemsection.
2. Remove the fuel supply pump.
* 4HK1 is shown for illustration.3. Remove the EGR cooler water return pipe.• Remove the brackets to the water pipe at two
locations to make the pipe unsupported.
5 1 2 3 4
1A-164 ENGINE MECHANICAL (4HK1, 6HK1)
4. Remove the EGR cooler water feed pipe. (4HK1)5. Remove the clip on the head side of the water
bypass hose (4HK1) and remove the hose fromthe suction pipe ASM.
4HK1
Name1. Bypass Hose2. EGR Cooler Water Return Pipe3. EGR Cooler Water Feed Pipe4. Suction Pipe
6HK1
Name1. Suction Pipe2. EGR Cooler Water Return Pipe
6. Remove the oil cooler ASM with glow plugcontroller bracket (4HK1 only).
• Screw the removed fixing bolt of the oil cooler intothe replacer hole at the location 1 of the figure andremove the oil cooler.
* 4HK1 is shown for illustration.7. Remove the O-ring.
Disassembly1. Remove the element mounting bolts.2. Remove the element.3. Remove the O-ring.
* 4HK1 is shown for illustration.
Name1. Element2. O-Ring
Reassembly1. Install the O-ring on the oil cooler case.2. Install the element.
21
ENGINE MECHANICAL (4HK1, 6HK1) 1A-165
3. Tighten the element fixing bolts using the specifiedtorque.
* 4HK1 is shown for illustration.
Name1. Element2. O-Ring
Installation1. Install the oil cooler ASM.• Apply liquid gasket (ThreeBond 1207B or
equivalent) to the flange surface groove (cylinderblock). Bead diameter must be between 2 and 4mm (0.08 and 0.16 in).Refer to the illustration for the offset position (nomore than 1 mm 0.04 in).
• Install the O-rings (1) and (2) to the oil passageinlet and outlet. Do not allow the liquid gasket tocontact the O-ring.
* 4HK1 is shown for illustration.
Name1. O-Ring2. O-Ring3. Liquid Gasket
– Align the oil cooler holes with the cylinder blockstuds.
– Install the oil cooler and glow plug controllerbracket to the cylinder block.
– Tighten the bolts to the specified torque in theorder shown in the illustration.
• Liquid gasket quickly hardens.Make it complete within 7 minutes afterapplying the liquid gasket.
4HK1
Tightening torque: 20 N⋅m (2.0 kg⋅m/15 lb ft)
Tightening torque: 24 N⋅m (2.4 kg⋅m/18 lb ft)
WSHK0242
1(0.04)2(0.08 0.16)2
(0.0
40.
08)
1A-166 ENGINE MECHANICAL (4HK1, 6HK1)
6HK1
2. Connect the water suction pipe.• Apply liquid gasket (ThreeBond 1207B) to the
flange of the water suction pipe. Bead diametermust be between 2 and 5 mm (0.08 and 0.20 in).Refer to the illustration for the offset position (nomore than 1 mm 0.04 in). (4HK1)
• Install the water suction pipe to the oil cooler. Referto the illustration.
• Tighten the bolts to the specified torque.
4HK1
Name1. Liquid Gasket
6HK1
Name1. Gasket2. Suction Pipe
Caution:The water suction pipe must be installed immediatelyafter the oil cooler (the pipe and cooler use the sameliquid gasket).4HK1
3. Install the EGR cooler water feed pipe. (4HK1)• Install the O-ring on the EGR cooler water feed
pipe.
• Install at the position shown in the figure andtighten using the specified torque.
Tightening torque: 4HK1: 24 N⋅m (2.4 kg⋅m/18 lb ft)6HK1: 20 N⋅m (2.0 kg⋅m/15 lb ft)
Tightening torque: 24 N⋅m (2.4 kg⋅m/18 lb ft)
1
2
ENGINE MECHANICAL (4HK1, 6HK1) 1A-167
4HK1
4. Install the EGR cooler water pipe. (4HK1)
5. Install the body cover ASM LH on the surface ofthe oil cooler and cylinder block and tighten it usingthe specified torque. (4HK1)
6. Remove the oil drain adapter. (4HK1)7. Install the fuel supply pump.• Refer to “Fuel Supply Pump” in the fuel system
section.
8. Install the common rail.• Refer to the “Common Rail” in the fuel system
section.
Tightening torque: 19 N⋅m (1.9 kg⋅m/14 lb ft)
1A-168 ENGINE MECHANICAL (4HK1, 6HK1)
Oil PanComponents
* 4HK1 is shown for illustration.Name
1. Oil Pan Gasket 2. Oil Pan
Removal1. Drain engine oil.2. Remove the oil pan.
ENGINE MECHANICAL (4HK1, 6HK1) 1A-169
3. Remove the Oil strainer.
4. Remove the O-ring.
Installation1. Install the oil strainer with new O-ring to the crank
case.
2. Install the oil pan.• At the seam between the cylinder block and the
front cover with the flywheel housing, apply theliquid gasket (4H: ThreeBond 1207B or 6H:1207C) to a bead diameter of 3 mm (0.12 in).
• Apply the liquid gasket and install the oil pan within7 minutes.
4HK1
6HK1
• Install the gasket using the studs of the crankcase,flywheel housing, and front cover as guide andmount the oil pan.Install the rubber ASM on the oil pan and secure itusing nuts and bolts.
Tightening torque:M8 Bolt (4HK1): 32 N⋅m (3.3 kg⋅m/24 lb ft)M8 Bolt (6HK1): 24 N⋅m (2.4 kg⋅m/18 lb ft)
M10 Bolt: 48 N⋅m (4.9 kg⋅m/35 lb ft)
WSHK0180
WSHK0181
1A-170 ENGINE MECHANICAL (4HK1, 6HK1)
4HK1
6HK1
Name1. Oil Pan2. Gasket
4HK1• Tighten the locations (1), (2), (3), and (4) as shown
in the figure and then tighten others. (In anysequence)
6HK1• Fastening the oil pan from the part of A or B in
clock wise order.• It tightens again by specified torque.
Tightening torque: 30 N⋅m (3.1 kg⋅m/22 lb ft)
WSHK0195
Tightening torque: 24.5 N⋅m (2.5 kg⋅m/18 lb ft)
WSHK0196
ENGINE MECHANICAL (4HK1, 6HK1) 1A-171
Oil Pump
Components
* 4HK1 is shown for illustration.Name
1. Oil Pump ASM2. Spring3. Ball4. Split Pin
5. Driven Gear And Shaft6. Oil Pump Body7. Gasket
Removal1. Drain engine oil.2. Drain out the cooling water.3. Remove the cylinder head cover.
Refer to “Cylinder Head Cover”.4. Remove the rocker arm shaft ASM.
Refer to “Rocker Arm Shaft ASM”. 5. Remove the camshaft ASM.
Refer to “Camshaft ASM”.6. Remove the cylinder head ASM.
Refer to “Cylinder Head Cover”.7. Remove the fuel supply pump ASM.
Refer to “Fuel Supply Pump” in the Fuel Systemsection.
8. Remove the flywheel.Refer to the “Flywheel”.
9. Remove the rear oil seal of the crankshaft.Refer to “Rear oil seal of Crankshaft”.
10. Remove the oil pan.
1A-172 ENGINE MECHANICAL (4HK1, 6HK1)
11. Remove the flywheel housing.• Make sure you remove the bolts shown in the
figure.
* 4HK1 is shown for illustration.12. Remove the idle gear A.
13. Remove the oil pump ASM and gasket.
Disassembly1. Remove the driven gear and shaft.2. Remove the split pin.3. Remove the spring.4. Remove the ball.
Reassembly1. Install the ball. 2. Install the spring.3. Install the split pin and fold it according to (1).
4. Apply engine oil on the driven gear and shaft andmount them on the oil pump body.
ENGINE MECHANICAL (4HK1, 6HK1) 1A-173
Inspection1. Measure the clearance between the gear and the
inner wall of the oil pump body. • Measure the clearance between the gear and oil
pump body using a thickness gauge.
• If the gap between the gear and the body innerwall exceeds the limit, replace the gear ASM or thedriven gear ASM.
2. Measure the clearance between the gear sidesurface and the upper surface of the oil pumpbody.
• Measure the clearance between the gear surfaceand the upper surface of the oil pump body usingthe thickness gauge and square.
• If the gap between the gear and the body innerwall exceeds the limit, replace the gear ASM or thedriven gear ASM.
3. Measure the clearance between the driven gearshaft and the bush.
• Measure the outside diameter of the driven gearshaft using a micrometer.
Clearance between the gear and inner wall of the body
mm (in)
Standard 0.125 – 0.220 (0.0049 – 0.0087)
Limit 0.30 (0.0118)
Clearance between the gear side surface and the upper surface of the oil pump body
mm (in)
Standard 0.064 – 0.109 (0.0025 – 0.0043)
Limit 0.20 (0.0079)
Outside diameter of the driven gear shaft mm (in)
Standard 15.989 – 16.000 (0.62949 – 0.62992)
Limit 15.900 (0.62598)
1A-174 ENGINE MECHANICAL (4HK1, 6HK1)
• Measure the inside diameter of the bushes of theoil pump body and cylinder block using the dialgauge.
• If the clearance between the driven gear shaft andbushing exceeds the limit, replace the driven gearASM.
Installation1. Install the gasket.2. Install the oil pump ASM.
3. Install the idling gear A.• Install the idling gear shaft at the position shown in
the figure and apply engine oil on the shaft.
• Rotate the crankshaft clockwise and bring thepiston of the No.1 cylinder to the top dead center.
* 4HK1 is shown for illustration.• Match the alignment marks of the crankshaft gear
and the idle gear A, and install them on thecylinder block.
* 4HK1 is shown for illustration.• Tighten the mounting bolts using the specified
torque.
4. Install the flywheel housing.• Clean the rear side of the cylinder block. Remove
the protruding fluid gasket thoroughly, especially,when mounting the crankcase.
Clearance between the driven gear shaft and bush
mm (in)
Standard 0.04 – 0.07 (0.0016 – 0.0028)
Limit 0.20 (0.0079)
Tightening torque: 24 N⋅m (2.4 kg⋅m/18 lb ft)
Tightening torque: 133 N⋅m (13.6 kg⋅m/98 lb ft)
ENGINE MECHANICAL (4HK1, 6HK1) 1A-175
• Apply the liquid gasket (ThreeBond 1207B)uniformly on the inside surface of the bolt holes(excluding the bolt holes indicated by arrows) asshown in the figure.
• After applying the liquid gasket, quickly install it.4HK1
6HK1
• Align with the knock pin of the cylinder block andinstall the flywheel housing.
• The seal is tightened from the cylinder block side.
Tightening torque: (4HK1)Bolt holes marked with “1” =
96 N⋅m (9.8 kg⋅m/71 lb ft)Bolt holes marked with “2” =
77 N⋅m (7.9 kg⋅m/57 lb ft)Bolt holes marked with “3” =
38 N⋅m (3.9 kg⋅m/28 lb ft)
WSHK0235
Tightening torque: (6HK1)Bolt holes marked with “1” =
96 N⋅m (9.8 kg⋅m/71 lb ft)Bolt holes marked with “2” =
86 N⋅m (8.8 kg⋅m/63 lb ft)Bolt holes marked with “3” =
119 N⋅m (12.1 kg⋅m/88 lb ft)Bolt holes marked with “4” =
53 N⋅m (5.4 kg⋅m/39 lb ft)Bolt holes marked with “5” =
73 N⋅m (7.4 kg⋅m/54 lb ft)Bolt holes marked with “6” =
26 N⋅m (2.7 kg⋅m/19 lb ft)
1A-176 ENGINE MECHANICAL (4HK1, 6HK1)
4HK1
6HK1
2
1
1
6
11
1
1
3
3
5
4
ENGINE MECHANICAL (4HK1, 6HK1) 1A-177
5. Install the oil pan.Refer to “Oil Pan”.
6. Install the rear seal of the crankshaft.Refer to “Rear Oil Seal of Crankshaft”.
7. Install the flywheel.Refer to the “Flywheel”.
8. Install the fuel supply pump ASM.Refer to “Fuel Supply Pump” in the Fuel Systemsection.
9. Install the cylinder head ASM.Refer to “Cylinder Head Cover”.
10. Install the camshaft ASM.Refer to “Camshaft ASM”.
11. Install the rocker arm shaft ASM.Refer to “Rocker Arm Shaft ASM”.
12. Tighten the cylinder head cover.Refer to “Cylinder Head Cover”.
1A-178 ENGINE MECHANICAL (4HK1, 6HK1)
Oil Pressure SwitchInspectionCheck the continuity between the switch terminal andthe body grounding in the no-load condition.If there is no connectivity, replace with normal parts.
Circuit check1. Turn the key switch to ON.2. Disconnect the oil pressure switch connector, and
confirm that the oil pressure-warning lamp lightswhen the connector on the harness side isgrounded.If the warning lamp does not light up, check thecircuit between the meter and the oil pressureswitch, and repair the disconnected locations.
Cooling System
ENGINECooling System
TABLE OF CONTENTSCooling System . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1B-2
Precautions on Service Work. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1B-2Function Check . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1B-5A List of Defective Phenomena . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1B-8Main Data and Specifications. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1B-8
Water Pump (4HK1) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1B-9Components. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1B-9Removal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1B-9Inspection. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1B-10Installation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1B-11Torque Specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1B-12
Water Pump (6HK1) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1B-13Removal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1B-13Installation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1B-15Torque Specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1B-17Disassembly. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1B-18Inspection and Repair . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1B-19Reassembly . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1B-20
Thermostat . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1B-23Components. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1B-23Removal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1B-23Inspection. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1B-23Installation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1B-24
Drive Belt. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1B-25Components. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1B-25Inspection. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1B-25Torque Specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1B-27
Cooling System
Cooling System 1B-1
1B-2 Cooling System
Cooling SystemPrecautions on Service WorkWARNING:Do not remove the radiator cap when the cooling wateris at high temperature. Steam or boiling water will gushout and you may be burnt. To open the radiator cap,cover the cap with a thick cloth when the cooling wateris cool, release the pressure by slowly turning the cap,and then remove the cap.
Explanations on functions and operationCooling water systemThe cooling water system, which is the forcedcirculation system, consists of a water pump,thermostat, and radiator as its main components.
4HK1
Name1. Water Jacket2. Drain Plug3. Oil Cooler4. Water Pump5. Drain Cock6. Radiator7. Cooling Fan8. Radiator Cap9. Heater Core
10. Reservoir Tank11. Air Bleeding Plug12. Water Outlet Pipe13. Thermostat (2 units)14. Thermometer Unit15. Bypass Route16. Turbocharger17. EGR Cooler
Cooling System 1B-3
6HK1
Name1. Water Jacket2. Drain Plug3. Oil Cooler4. Water Pump5. Drain Cock6. Radiator7. Cooling Fan
8. Radiator Cap9. Reservoir Tank
10. Water Outlet Pipe11. Thermostat (2 units)12. Thermometer Unit13. Bypass Route14. EGR Cooler
8
6
5
4
7
910
11
12
13
3 2
1
14
1B-4 Cooling System
Water pumpThe water pump, which uses the centrifugal impellersystem, is driven by the engine fan belt.
* 4HK1 is shown for illustration.Name
1. Fan Center2. Bearing
3. Impeller4. Seal Unit
Cooling System 1B-5
ThermostatThe thermostat is a wax pellet type and consists of twounits, in which one unit (bottom bypass type) has anvalve initial opening temperature of 82 °C (180 °F) andthe second (inline type) has an valve initial openingtemperature of 85 °C (185 °F). It is designed such thatthe water temperature can be adjusted finely and it ismounted within the thermostat-housing unit.
Name1. Jiggle Valve2. Stamp Mark (Valve Initial Opening Temperature)3. Valve
4. Gasket5. Piston
Function CheckCooling water level check
• Check the cooling water level within the reservetank and the level is appropriate when the coolingwater level is within the MAX (upper limit) and MIN(lower limit) range. In case the volume of thecooling water is deficient, remove the reserve tankcap and replenish with a mixture of tap water andengine coolant in the ratio of 1:1 until the levelcomes close to the MAX line.
4HK1
6HK1
InspectionCooling water leak check
• Use the radiator cap tester and apply a pressure of200 kPa (29.0 psi) and check for leaks in thelocations given below. Check that the radiator hoseand heater hose are not damaged or degradedand the hose clamp is not loose.Standard value
Cooling waterlevel
14 L (14.8 qts)(between MIN and MAX levels)
Standard valueCooling waterlevel
14.5 L (15.3 qts)(Engine only)
1B-6 Cooling System
Inspection location• Radiator ASM, water pump ASM, radiator hose,
heater hose
Coolant1. About the engine coolant concentration
• Take the concentration corresponding to theminimum temperature because the freezingtemperature varies according to theconcentration of the engine coolant.
• Use only genuine engine coolant.• Use engine coolant with a mix ratio in the range
of 30 to 60% because over heating is likely tooccur if the ratio is greater than 60% andcorrosion prevention is inadequate if the ratio isless than 30%.
2. Engine coolant density measurement
Methods for measuring specific gravity• Measure the specific gravity and the temperature
of the cooling water using an anti-freeze specificgravity meter and thermometer.Take precautionary measures as the boiled coolingwater may gush out at high temperatures if the capis removed.
• Use a deep container to suit the height of thespecific gravity meter.
Name1. Antifreeze Hydrometer2. Radiator
• Fix the temperature of the cooling water beingmeasured in the range of 0 to 50 °C (32 to 122 °F).
• Measure the temperature and specific gravity anddetermine the concentration from the table givenbelow.
Coolant scooping method• Measure the concentration using the coolant scoop.
Freezing temperature
guideline
Mix ratioLiter (qts)
Concentration of engine coolantEngine
coolantTap
water
-18°C (-0.4°F) 4.2 (4.4) 7.8 (8.2) 35%
-25°C (-13°F) 5.0 (5.3) 7.0 (7.4) 42%
-35°C (-31°F) 6.0 (6.3) 6.0 (6.3) 50%
-40°C (-40°F) 6.4 (6.8) 5.6 (5.9) 53%
Cooling System 1B-7
EGR cooler air bleeding procedureWhen replacing the coolant, bleed air from the EGRcooler with the following procedure.Caution:Be sure to replace the coolant when it is cooled.Loosen the air bleeder plug (1) on the EGR cooler.
3. Pour coolant into the radiator via its opening.4. Tighten the plug when the coolant spills over from
the air bleeder plug.• Replace the copper packing if it is faulty.
Caution:• Take care to prevent the spilt coolant from getting
the exhaust system parts wet.• Be sure to wipe off the spilt coolant.
• Pour coolant into the radiator via its opening againuntil it is filled.
• Bleed air from the engine body coolant with idlingthe engine.
Tightening torque: 24.5—30.5 N⋅m (2.5—3.1 kg⋅m/18—23 lb ft)
WSHK0246
1
1B-8 Cooling System
A List of Defective Phenomena• Engine overheats• Engine overcools
Engine overheats
Engine overcools
Main Data and Specifications
Condition Possible Cause CorrectionEngine overheats Cooling water volume is deficit. Replenish.
Thermometer unit is defective. Replace.Thermostat is defective. Replace.Radiator pump is defective. Replace.Radiator is clogging. Clean or replace.Radiator cap is defective. Replace.Engine oil volume is deficient orincorrect engine oil is used.
Replenish or change the engine oil.
Cylinder head gasket is defective. Replace.The fan belt is loose. Adjust.Exhaust system is clogging. Clean or replace.The fuel injection quantity is in surplus. Diagnose the engine control system.Fuel injection timing is incorrect. Diagnose the engine control system.Starting pressure of fuel injection islow.
Diagnose the engine control system.
Condition Possible Cause CorrectionEngine overcools Thermostat is defective. Replace.
Water pump Centrifugal impeller system
Pulley ratio 0.950
Thermostat Wax pellet system
Valve opening temperature °C (°F) With jiggle valve 85 (185)Without jiggle valve 82 (180)
Temperature when fully open °C (°F) With jiggle valve 100 (212)Without jiggle valve 95 (203)
Cooling System 1B-9
Water Pump (4HK1)Components
Name1. Fan2. Spacer3. Water Pump Pulley
4. Fan Belt5. Water Pump ASM6. Gasket
Removal1. Drain the coolant.2. Remove the four mounting bolts and then the fan
ASM and spacer, water pump pulley.
1B-10 Cooling System
Name1. Fan2. Spacer3. Water Pump Pulley4. Bolt
3. (2) and (3) that tighten the setting plate and waterpump together. Loosen the adjusting bolts (1) inthe generator and remove the fan belt.
Name1. Adjusting Bolt2. Lock Nut3. Bolt
4. Remove the water pump ASM while inserting andscraping with the driver at the position shown inthe figure.
Name1. Water Pump
5. Remove the gasket.
Inspection1. Appearance check
• Check for cracks or damage in the pump body.• Check for cracks and corrosion in the impeller.• Check for water leakage from the seal unit.• If you find abnormalities, replace with the water
pump ASM.2. Bearing nut check
• Rotate the fan center while pushing it along theradial direction. Confirm that there is noabnormal noise and no excessive play.
• If you find abnormalities, replace with the waterpump ASM.
Cooling System 1B-11
Installation1. Install the gasket.2. Install the water pump ASM.
• Mount the water pump to match with the studsof the front cover.
3. Temporarily fit the bolts until the water pump pulleyand the spacer and fan are properly seated in thewater pump ASM.
4. Mount the fan belt, tighten the adjusting bolts ofthe generator, and adjust the tension.• Refer to the “Drive Belt”.
5. After fan belt adjustments, tighten the generatorusing the specified torque.
Name1. Adjusting Bolt2. Lock Nut3. Bolt
6. After the fan belt adjustments, tighten thetemporarily fitted fan pulley and spacer and fanusing the specified torque.
Name1. Fan ASM2. Spacer3. Water Pump Pulley4. Bolt
7. Pour coolant.
Tightening torque:M8: 24 N⋅m (2.4 kg⋅m/18 lb ft)M10: 45 N⋅m (4.6 kg⋅m/33 lb ft)
1B-12 Cooling System
Torque Specifications
WSHK0247
52(5.3 / 38)
76(7.7 / 56)
24(2.4 / 18)
24(2.4 / 18)
127(13 / 94)
M8:24(2.4 / 18)M10:45(4.6 / 33)
Cooling System 1B-13
Water Pump (6HK1)
Removal1. Loosen the fan fixing nuts to remove the cooling
fan.
2. Remove the fan guide.
Name1. Bolt2. Washer3. Rubber mount4. Rubber mount5. Guide tube6. Fan guide
3. Loosen the fan pulley fixing bolts.4. Remove the fan belt.
• Loosen the mounting bolt (2) and the slidingpiece nut (1).
• Pivot the alternator at the mounting bolt towardthe center of the engine.
WSHK0207
WSHK0208
WSHK0209
1B-14 Cooling System
5. Remove the adapter and fan pulley.
Name1. Adapter2. Fan pulley3. Water pump
4. Bypass hose5. Water duct6. Water duct
6. Disconnect the bypass hose.7. Loosen the fixing nuts and bolts from the water
pump.8. Remove the water pump from the front plate.9. Discard the gaskets.
WSHK0210
Cooling System 1B-15
Installation1. Install the water pump with new gaskets to the
front plate. Use the locating pin.2. Tighten the fixing nuts and bolts to the specified
torque.
3. Install the water duct with new gasket to thecylinder head.Tighten the bolts to the specified torque.
4. Install the water duct with new gasket to the oilcooler and water pump.Tighten the bolts to the specified torque.
5. Connect the bypass hose.
6. Clamp the bypass hose.7. Install the fan pulley and adaptor to the water
pump.Tighten the fixing bolts to the specified torque.
8. Install the fan belt.9. Adjust the fan belt tension.
• Depress the drive belt midway between thealternator and fan pulley.
Tightening torque:Nut A: 39 N⋅m (4.0 kg⋅m/29 lb ft)Bolt: 20 N⋅m (2.0 kg⋅m/15 lb ft)
Tightening torque:Bolt (1) : 221.6 N⋅m (22.6 kg⋅m/163 lb ft)Bolt (2) : 24.5 N⋅m (2.5 kg⋅m/18 lb ft)
Tightening torque: 20 N⋅m (2.0 kg⋅m/15 lb ft)
WSHK0211
WSHK0212
Tightening torque: 52 N⋅m (5.3 kg⋅m/38 lb ft)
Drive Belt Deflection: 8 — 11 mm (0.31 — 0.43 in)
WSHK0213
WSHK0214
Alternator
Crankshaft
Water pump
1B-16 Cooling System
10. Install the cooling fan.Tighten the fixing nuts to the specified torque.
11. Install the fan guide.Tighten the fixing bolts to the specified torque.
Name1. Bolt2. Washer3. Rubber mount4. Rubber mount5. Guide tube6. Fan guide
Tightening torque: 52 N⋅m (5.3 kg⋅m/38 lb ft)
Tightening torque: 30 N⋅m (3.1 kg⋅m/22 lb ft)
WSHK0207
WSHK0208
Cooling System 1B-17
Torque Specifications
221.6(22.6 / 163)20(2 / 14)
20(2 / 14)
20(2 / 14) 24.5(2.5 / 18)
39(4 /29)
52(5.3 / 38)
F06E100076
N m(kg m/lb ft)
1B-18 Cooling System
Disassembly
Name1. Center2. Dust cover3. Snap ring4. Bearing5. Bearing6. Spacer7. Bearing8. Washer
9. Shaft10. Water pump body11. Dowel pin12. Seal unit13. Impeller14. Gasket15. Cover16. Bolt
WSHK0215
Cooling System 1B-19
1. Remove the rear cover from the water pump body.2. Use a remover 1-8521-0062-0 to remove the
impeller from the water pump.3. Use a puller to remove the water pump center.4. Remove the dust cover and snap ring.5. Remove the water pump shaft with ball bearings.
• Use a plastic hammer to lightly tap on the waterpump shaft from the impeller side.
6. Use a bench press to remove the bearing from theshaft.
7. Remove the seal unit.
Inspection and RepairMake the necessary adjustments, repairs and partreplacements if excessive wear or damage isdiscovered during inspection.
Water pump impeller1. Check the impeller for corrosion.
Water pump shaft1. Measure the water pump shaft and center or
impeller interference.If the measured interference is less than thespecified limit, the pump shaft and / or the centerand impeller must be replaced.
WSHK0216
WSHK0217
Pump shaft and center interference:Limit: 0.048 – 0.078 mm (0.0019 – 0.0031 in)
Pump shaft and impeller interference:Limit: 0.022 – 0.062 mm (0.0009 – 0.0024 in)
WSHK0218
WSHK0219
1B-20 Cooling System
2. Carefully wipe away any bearing grease.3. Listen for excessive bearing operating noise.
Excessive bearing operating noise indicatessevere bearing wear.
Reassembly1. Install the ball bearing to the water pump shaft.
• Apply engine oil to the water pump shaft.• Place the water pump shaft and the bearings
on the base plates.• Install the washer (4), ball bearing (3), spacer
(2), and bearings (1).
• Use a bench press to gradually press the waterpump shaft down until the bearings are seatedcorrectly.
2. Install the water pump shaft with bearings to thewater pump body.• Repack the bearings with multipurpose grease.
• Place the water pump body on bench pressbase plate.
NOTE : To prevent damage to the water pump shaft, place softbrass or copper sheets between the base plates andthe water pump shaft.
WSHK0220
WSHK0221
WSHK0222
WSHK0223
Cooling System 1B-21
• Position the pump shaft with bearings to thewater pump body.
• Use a bench press to gradually press the waterpump shaft into the water pump body.
NOTE : Do not drive the bearing into position with a hammer orsimilar object. Bearing damage will result.
3. Install the snap ring and dust cover.• Use pliers to install the snap ring into water
pump body groove.• Install the dust cover with the flange facing out.
4. Install the seal unit to the water pump body.• Press in the seal unit to the specified position
using a bench press and installer 1-85220-047-0.
5. Install the water pump impeller to the water pumpshaft.• Use a bench press to press in the impeller.• The impeller must be flush with the water pump
shaft end.6. Use a bench press to gradually press the water
pump center onto the water pump shaft to thespecified dimension.
7. Install the rear cover with new gasket to the waterpump body.
WSHK0224
WSHK0225
Seal unit installation position A:11.0 – 11.6 mm (0.433 – 0.457 in)
Dimension A: 202.9 mm (7.988 in)
WSHK0226
WSHK0227
1B-22 Cooling System
Special tool
Illustration Tool Number/Description
1-8521-0062-0Impeller remover
1-8522-0047-0Seal unit installer
Cooling System 1B-23
ThermostatComponents
* 4HK1 is shown for illustration.Name
1. Water Outlet Pipe2. Thermostat
3. Gasket
Removal1. Drain the coolant. Prepare the container for
discharging and use it for replenishment whenmounting the thermostat. Set the discharge ofcooling water such that the water does not flow outof the thermostat housing.
2. Disconnect the water outlet pipe.3. Remove the thermostat.4. Remove the gasket from the thermostat.
Inspection• Place the thermostat in water and increase the
temperature while stirring it sufficiently.• Measure the temperature when the valve is just
opened and when it is fully open.
1B-24 Cooling System
Installation1. Mount the gasket on the thermostat and mount it at
the position shown in the figure.• The thermostat with the jiggle valve (A) is
installed to the left side of the engine. The jigglevalve faces the rear of engine.
• Fit the thermostat gasket ensuring that it doesnot come out of and on top of the externalhousing on the cylinder head side.
4HK1
Name1. Thermostat2. Cylinder Head
6HK1
Name1. Thermostat
2. Connect the water outlet pipe.
* 4HK1 is shown for illustration.3. Replenish the cooling water stored during the
discharge, and check the volume of the coolingwater.
A
031EY00026
Tightening torque: 24 N⋅m (2.4 kg⋅m/18 lb ft)
WSHK0024
1
Cooling System 1B-25
Drive BeltComponents
Name1. Crankshaft Pulley2. Generator Drive Belt3. Bolt4. Generator
5. Adjusting Bolt6. Lock Nut7. Adjusting Plate8. Water Pump Pulley
InspectionCheck for the presence of wear or damage in the drivebelt and renew the parts if necessary.Check the tension of the belt and adjust if necessary.Inspection procedureApply a pressure of 98 N (22 lb) at the center of thelong span of each belt and check the deflection of thebelt.
Drive Belts AdjustmentAdjustment procedureAdjust simultaneously the generator drive belt foradjustment of belt.
1. Loosen the adjusting plate lock nuts and themounting bolts of generator on the underside ofthe generator.
2. Rotate the adjusting bolts of generator and adjustthe belt (remove and fit).• When replacing the belt, you must always
replace both the belts.3. After adjustments, tighten the adjusting plate lock
nuts and the mounting bolts of generator on theunderside of the generator using the specifiedtorque.
Deflection of generator drive beltWhen the belt is new
5.0 to 5.8 mm (0.19 to 0.23 in)When the belt is reused
6.1 to 6.9 mm (0.24 to 0.27 in)
Tightening torque:Lock nut: 76 N⋅m (7.7 kg⋅m/56 lb⋅ft)Bolt: 127 N⋅m (13.0 kg⋅m/94 lb⋅ft)
1B-26 Cooling System
Name1. Crankshaft Pulley2. Bolt3. Generator4. Adjusting Bolt5. Lock Nut6. Water Pump Pulley7. Generator Drive Belt
Cooling System 1B-27
Torque Specifications
* 4HK1 is shown for illustration.
1B-28 Cooling System
Fuel System
ENGINEFuel System
TABLE OF CONTENTSFuel System . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1C-2
Precautions on Service Work. . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1C-2Special Tool . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1C-12
Fuel Filter ASM . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1C-13Components. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1C-13Removal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1C-13Installation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1C-13
Fuel Filter Element . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1C-14Removal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1C-14Installation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1C-14Special Tool . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1C-14
Fuel Injector . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1C-15Components. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1C-15Removal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1C-16Installation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1C-19Torque Specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1C-22Special Tool . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1C-23
Fuel Supply Pump. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1C-24Components. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1C-24Removal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1C-25Installation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1C-26Torque Specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1C-29
Gauze filter . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1C-30Removal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1C-30Installation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1C-30
Electromagnetic Pump Filter . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1C-31Removal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1C-31Installation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1C-31
Common Rail . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1C-32Components. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1C-32Removal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1C-33Disassembly. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1C-35Reassembly . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1C-36Installation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1C-36Torque Specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1C-39
Fuel System
Fuel System 1C-1
1C-2 Fuel System
Fuel SystemPrecautions on Service WorkParts of the fuel system such as the internal part of thefuel injector, holes and clearances that form passagesfor fuel are finished to a very high degree of accuracy.They are therefore highly sensitive to foreign matterand the entry of foreign matter could cause damage tothe fuel passage. Therefore, effective measures shouldbe taken to prevent the entry of foreign matter.If water removal agent is used in the fuel then it willabsorb moisture in the light oil and may cause rust.Therefore, do not use water removal agent in the fueltank.When servicing the fuel system, every precaution mustbe taken to prevent the entry of foreign material into thesystem.
• Before beginning the service procedure, wash thefuel line and the surrounding area.
• Perform the service procedures with clean hands.Do not wear work gloves.
• Immediately after removing the fuel hose and/orfuel pipe, carefully tape vinyl bags over theexposed ends of the hose or pipe.
• Always replace the high-pressure pipe in fuelsystem with new one if it has been removed.Reuse of it causes damage the seal surface,resulting in fuel leakage.
• If parts are to be replaced (fuel hose, fuel pipe,etc.) do not open the new part packaging untilinstallation.
Discard gaskets and O-rings and replace them withnew ones.Work procedure
• The fuel opening must be quickly sealed whenremoving the fuel pipe, injection pipe, fuel injector,fuel supply pump, and common rail.
• The eyebolts and gasket must be stored in a cleanparts box with a lid to prevent adhesion of foreignmatter.
• Fuel leakage could cause fires. Therefore, afterfinishing the work, wipe off the fuel that has leakedout and make sure there is no fuel leakage afterstarting the engine.
Fuel System 1C-3
Explanations on functions and operationFuel system diagram
Name1. Common Rail2. Fuel Filter3. Electromagnetic Pump4. Pre-fuel Filter5. Fuel Tank
6. Supply Pump7. Fuel Injector8. Leak-Off Pipe9. Fuel Return Pipe
WSHK0248
4HK1
1
2
3
4
5
67
8
9
6HK1
6
7
8
9
1C-4 Fuel System
Removal of Foreign Material between Main Filter and Supply Pump
IMPORTANT: When the bolt at fuel outlet side in
main filter is loosened or the hose is removed, remove foreign material between main filter and supply pump.
When the main filter or the hose between main filter and supply pump is replaced, remove foreign material between main filter and supply pump. 1. Install the base to the fuel outlet in main filter.
: 19 mm : 44±5 N⋅m (4.5±0.5 kgf⋅m, 32±3.69 lbf⋅ft)
2. Install the hose to the base and secure with the
clamp.
3. Remove the hose at the fuel inlet side in supply pump.
ZX200-3 class
M1U1-07-014
W1GR-01-01-001
W1GR-01-01-002
W1GR-01-01-003
Main FilterBolt
Base Fuel Outlet
Clamp
Hose
To Supply Pump
4HK1 Supply Pump Fuel Inlet
6HK1 Supply Pump Fuel Inlet
Fuel System 1C-5
4. Turn the key switch ON and operate the fuel solenoid pump. Put fuel from the hose into the container.
CAUTION: Use the container which can measure beyond 10 liters. Make the hose extend straight in order not to accumulate foreign material inside. Keep away the hose end from the container or fuel in the container in order not to enter foreign material.
5. When fuel in the container is beyond 4 liters, turn
the key switch OFF and stop the fuel solenoid pump.
6. Install the hose to the fuel inlet in supply pump and
secure with the clamp.
7. Release any pressure in the fuel system. (Refer to Bleeding Air in Fuel System on the Operator’s Manual.)
8. Start the engine. Check for any leaks in fuel
system.
W1GR-01-01-004
W1GR-01-01-005
W1GR-01-01-002
W1GR-01-01-003
Hose
Incorrect Correct
Hose
Container
4HK1 Supply Pump Fuel Inlet
6HK1 Supply Pump Fuel Inlet
1C-6 Fuel System
Common rail4HK1
Name1. Flow Damper2. Pressure Limiter
3. Pressure Sensor
Caution:• Be careful foreign material does not into the fuel
system, because the precise fuel system is used.
6HK1
Name1. Flow Damper2. Pressure Limiter
3. Fuel Inlet4. Pressure Sensor
MFW41DMF000201
Fuel System 1C-7
1C-8 Fuel System
Fuel supply pump4HK1
Name1. Fuel Temperature Sensor2. Suction Control Valve3. High Pressure Pipe
4. Camshaft Key5. Camshaft Nut
Fuel System 1C-9
6HK1
Name1. Fuel Temperature Sensor2. Suction Control Valve
3. High Pressure Pipe4. Camshaft Key
4
1
2
3
1C-10 Fuel System
Fuel injector
Name1. Terminal Stud2. Part for Mounting Leak Off Pipe3. O-ring4. Part for Mounting Injection Pipe5. Parts Number6. ID Plate
Fuel filter
Name1. Priming Pump2. Air Bleed3. Case4. Drain Plug
Function checkAir bleeding
1. Before starting the enginea. Fit a tray below the fuel filter (below the air
bleed plug).b. Turn the key switch to ON, and activate the
electromagnetic pump. (on the machine withelectromagnetic pump)
c. Loosen the plug adequately and operate thepriming pump more than 20 times until the fuelnear the plug overflows.
d. Tighten the plug, and operate the priming pumpmore than 10 times until it is filled with fuel.After waiting for approximately a minute, loosenthe plug and bleed out the air in the fuel filter.(This work must be repeated a minimum ofthree times until no more air comes out from theplug.)
Fuel System 1C-11
e. Tighten the plug firmly and wipe the fuel in thesurrounding area. Operate the priming pump(10 to 15 times) till it is filled with fuel and thensend fuel to the engine.
2. After starting the enginea. Start the engine, but do not control the engine
speed on machine side.b. After starting, maintain the idling rotation for 5
seconds.c. Increase the engine speed slowly and keep this
for three minutes.d. Operate the engine speed to maximum on the
machine side. (Repeat this operation severaltimes)
e. Return to idling speed.
Caution:If the air bleeding work is insufficient then it could leadto faults in the engine. Therefore, the procedures afterstarting the engine should always be implemented.
Water drainIt is designed that the float inside of the watersedimenter floats when water accumulates.When the float level goes up to the aluminum bodysection, be sure to drain the water.
Water draining procedureLoosen the air bleed plug at the top of the watersedimenter. Then loosen the drain plug to drain thewater inside of it. After draining, tighten each plugsecurely. Then bleed air from the fuel.
Fuel system vacuum checkUse this procedure to measure the vacuum (negativepressure) discharge side the fuel system.
Important:The fuel pressure/vacuum gauge ASM (gauge (1)) andthe fuel pressure/vacuum gauge adapter (adapter (5))must be cleaned before connecting to the fuel line.Otherwise, foreign material adherent to the tools maydamage the fuel supply pump.
1. Disconnect the fuel hose from the fuel filterhousing. (fuel supply pump side).
2. Install the adapter.
Special toolFuel pressure/vacuum gauge adapter (4HK1 only):EN-47667
3. Connect the gauge (1) with hose to the adapter(3).
Special toolFuel pressure/vacuum gauge ASM:J-44638
Name1. Fuel Pressure/Vacuum Gauge ASM2. Fuel Pipe (Discharge Side)3. Fuel Pressure/Vacuum Gauge Adapter (4HK1
only)
4. Loosen the air bleeding plug on the supply pump.5. Use your hand to operate the fuel filter priming
pump. Operate the pump until all the air has beenbled from the system.
6. Start the engine and allow it to idle. 7. Note the gauge (1) reading. If the reading is
normal, go to Step 8. If the fuel vacuum is greaterthan the specified value, there is a problem in thefuel system. Perform the procedures outlinedbelow.
• Replace the cartridge fuel filter element. • Check the fuel delivery pipe. If it is clogged, it must
be replaced.• Remove the fuel pipe at the fuel filter inlet. Use
high-pressure air forced through the fuel pipe toclean the fuel system.
Caution:• Remove the fuel filler cap before applying high-
pressure air.
Standard fuel vacuum Less than 17 kPa (170 mbar)
1C-12 Fuel System
• Do not perform this procedure if the fuel tank isnearly full (fuel approaching or flowing into the fuelfiller neck). The forced air will spray fuel from thefuel filler neck.
8. Remove the gauge (1) and hose from the adapter(3).
9. Remove the adapter (3).10. Connect the fuel hose.11. Use your hand to operate the fuel filter priming
pump. Operate the pump until all the air has beenbled from the system.
12. Start the engine and allow it to idle.13. Inspect the fuel system for fuel leakage.
Special Tool
Illustration Tool Number/Description/Special Tool Rank
EN-47667Fuel pressure/vacuum
gauge adapter(4HK1)Rank B
J-44638Fuel pressure/vacuum
gauge ASMRank B
Fuel System 1C-13
Fuel Filter ASMComponents
Name1. Priming Pump2. Air Bleed3. Case4. Drain Plug
Removal1. Remove the feed hose and the return hose from
the fuel filter and plug it so that the fuel does notflow out.
2. Remove the bolts for mounting the fuel filter.3. Remove the fuel filter ASM.
Installation1. Install the fuel filter ASM.2. Install the bolts for mounting the fuel filter.3. Install the feed hose and the return hose.4. Bleed out the air.• Refer to “Fuel System”.
1C-14 Fuel System
Fuel Filter ElementRemoval
1. Remove the case using the filter wrench.
Special toolMain filter wrench: 8-9801-3170-0
2. Remove the Fuel Filter element.
Name1. Priming Pump2. Air Bleed3. Case4. Drain Plug
Installation1. Assemble the Fuel Filter element.2. To simplify air bleed, fill light oil in the case.3. Tighten the case by hand. During this process take
adequate care that the light oil that is inside doesnot flow out.
4. Use the filter wrench and tighten rotating by 1/3 to2/3.
Special toolMain filter wrench: 8-9801-3170-0
Special Tool
Illustration Tool Number/Description/Special Tool Rank
8-9801-3170-0Main filter wrench
Rank A
Fuel System 1C-15
Fuel InjectorComponents4HK1
1C-16 Fuel System
6HK1
Name1. Fuel Injection Pipe Clip2. Fuel Injection Pipe3. Fuel Injector Leak-Off Pipe4. Fuel Injector5. Fuel Injector Clamp6. Fuel Injector Clamp Bolt
7. EGR Adapter8. EGR Cooler9. EGR Valve
10. Cylinder Head Cover11. Fuel Injector Harness Bracket12. Fuel Injector Terminal
The fuel system consists of many tiny holes andspaces that allow the movement of fuel from one placeto another. These holes and spaces are milled toextremely high precision. This is especially true of thefuel injectors.The fuel injector is very sensitive to foreign material.Foreign material will result in fuel system breakdown.Exercise great care not to allow the entry of foreignmaterial into the fuel system or fuel injectors during theremoval and installation procedure.
Caution:To avoid electric shock;Set the switch to the ‘OFF’ position and disconnectbattery negative cable before checking or repairing thefuel injector, wiring or/and connectors.
Removal1. Remove the engine harness, the EGR valve, the
pressure sensor, and all of the fuel injectorconnectors.
2. Remove the EGR valve and the EGR adapter.
WSHK0162
12
11
10
9
8
7
3
6
5
4
1
2
Fuel System 1C-17
3. Tape the EGR case holes shut to prevent the entryof foreign material.
4HK1
6HK1
Name1. EGR Adapter2. EGR Valve
4. Remove the cylinder head cover.
* 4HK1 is shown for illustration.
Name1. Cylinder Head Cover
5. Alternately loosen the fuel injector terminal nuts alittle at a time in sequence. Several looseningcycles should be required before the nuts areloose.
6. Loosen the fuel injector harness bracket bolts.Remove the inside connector and the harnessbracket.
7. Remove the fuel injector leak-off pipe.8. Remove the lower cover.
* 4HK1 is shown for illustration.
Name1. Harness Bracket2. Harness Connector3. Fuel Injector Terminal4. Fuel Leak Off Pipe
WSHK0163
2
1
1C-18 Fuel System
9. Remove the fuel injection pipe clips and theinjection pipes.
Important:Do not reuse the high-pressure pipe in fuel system if ithas been removed.
4HK1
6HK1
Name1. Fuel Injection Pipe2. Pipe Clip
10. Loosen the fuel injector clamp fixing bolts andremove the fuel injectors.
If the fuel injectors are difficult to remove, use the fuelinjector remover. Install the fuel injector remover to theleak-off pipe attachment part on the fuel injector. Use asliding hammer to force the fuel injector clamp off thefuel injector.
Caution:Do not remove the fuel injector sleeve.
Special toolFuel injector remover: 5-8840-2826-0 (EN-46720)Sliding hammer: 5-8840-0019 (J-23907)
Name1. Sliding Hammer2. Remover3. Fuel Injector ASM
11. Mark each fuel injector with the number of thecylinder from which it was removed. Store the fuelinjectors in a safe place. Position the fuel injectorso that the nozzle is protected.
Caution:• Do not tamper with the electromagnetic portion of
the fuel injector. Reduced electromagnetic functionwill result in injector failure.
Recording Injector ID Code Information from theInjector ID plate on the replaced fuel injectorhousing;Record all numbers of replaced fuel injector’s from IDplate.
WSHK0021
1
2
Fuel System 1C-19
Name1. Injector ID Plate2. Injector ID Code3. Fuel Injector
InstallationImportant:Install each of the fuel injectors on its original position.(the cylinder from which it was removed)
1. Install a new gasket and O-ring to each of the fuelinjector clamps. Refer to the illustration.
Name1. Gasket2. Fuel Injector3. Bolt4. Fuel Injector Clamp
2. Apply molybdenum to the threads and seatingsurfaces of the clamp bolts.
3. Install the fuel injector clamps to the cylinder head.4. Temporarily tighten the clamp bolts.5. Apply a thin coat of engine oil to the outer surface
of the fuel injector side sleeve nuts.6. Install the fuel injector pipes to the position shown
in the illustration.
Important:Replace the high-pressure pipe in fuel system with newone if it has been removed.
7. Use a spanner to carefully the sleeve nuts until thefuel injector pipes contact the fuel injector andcommon rail.
8. Tighten the fuel injection pipe clips to the specifiedtorque.
Tightening torque: 6 N⋅m (0.6 kg⋅m/53 lb in)
* 4HK1 is shown for illustration.
Name1. Fuel Injection Pipe2. Pipe Clip
9. Final tighten the injection clamp bolts to thespecified torque.
Tightening torque: 30 N⋅m (3.1 kg⋅m/22 lb ft)10. Tighten the injection pipes to the specified torque.
Tightening torque: 44 N⋅m (4.5 kg⋅m/32 lb ft)
1C-20 Fuel System
* 4HK1 is shown for illustration.
Name1. Clamp Bolt2. Sleeve Nut
11. Install the nozzle leak off pipes together with thenew gaskets. Tighten the pipes to the specifiedtorque.
Tightening torque: 12 N⋅m (1.2 kg⋅m/106 lb in)
* 4HK1 is shown for illustration.12. Install the fuel injector harness connectors. Work
from the inside out.13. Install the harness bracket and tighten the bolts to
the specified torque.
4HK1
6HK1
14. Install the fuel injector terminal nuts to the injector.15. Alternately tighten each nut 2 or 3 turns at a time
until the specified torque is reached.
Tightening torque: 2 N⋅m (0.2 kg⋅m/18 lb in)
Caution:Do not overtighten the nuts. Damage to the terminalstuds will result.
Tightening torque: 4HK1: 48 N⋅m (4.9 kg⋅m/35 lb ft)6HK1: 22 N⋅m (2.2 kg⋅m/16 lb ft)
Fuel System 1C-21
Name1. Fuel Injector2. Harness3. Terminal Nut
16. Install the gasket to the cylinder head cover.17. Install the cylinder head cover and tighten the bolts
to the specified torque.
* 4HK1 is shown for illustration.
Name1. Cylinder Head Cover
18. Install the gasket to the EGR valve and tighten thebolts to the specified torque.
Tightening torque: 24 N⋅m (2.4 kg⋅m/18 lb ft)19. Install the gasket to the EGR adapter and tighten
the bolts to the specified torque.
Tightening torque: 24 N⋅m (2.4 kg⋅m/18 lb ft)
* 4HK1 is shown for illustration.
Name1. EGR Adapter2. EGR Valve
20. Attach the engine harness connectors. Eachcomposite connector should make a loud clickwhen it is securely attached.
Before Programming the Injector ID CodeImportant:DO NOT program the fuel injector ID code data unlessyou are directed by a service procedure or you aredirected by a service bulletin. Programming the fuelinjector at any other time will not permanently correct acustomers concern.Ensure the following conditions are met beforeprogramming the ECM.
• System voltage for machine– There is no charging system concern. All
charging system concerns must be repairedbefore programming the ECM.
– Battery voltage is 12 volts or 24 volts (variesdepending on the machine). The battery mustbe charged before programming the ECM if thebattery voltage is low.
– A battery charger is NOT connected to themachine’s battery. Incorrect system voltage orvoltage fluctuations from a battery charger maycause programming failure or ECM damage.
– Turn OFF or disable and system that may put aload on the machine’s battery.
• The key switch is in the proper position. DO NOTchange the position of the key switch during theprogramming procedure, unless instructed to doso.
• All tool connections are secure.– RS-232
Tightening torque: 4HK1: 18 N⋅m (1.8 kg⋅m/13 lb ft)6HK1: 13 N⋅m (1.3 kg⋅m/9.6 lb ft)
1C-22 Fuel System
– The connection at the data link connector(DLC) is secure.
– Voltage supply circuit• DO NOT disturb the tool harness while
programming. If an interruption occurs during theprogramming procedure, programming failure orECM damage may occur.
• Surrounding environment– Surrounding temperature must be between 0
and 50°C (32 and 122°F) during theprogramming procedure. Excessively low orhigh temperature may cause the programmingfailure or ECM damage.
– Electromagnetic interference (EMI) on the toolharness and ECM may cause the programmingfailure or ECM damage.
Injector ID Code Programming ProcedureProgramming of the injector ID code is refered to“Injector Replacement” in the EMPS or EMPS IIIoperating instructions manual.
Torque Specifications
* 4HK1 is shown for illustration.WSHK0047
4HK1 : 48 (4.9 / 35)6HK1 : 22 (2.2 / 16)
4HK1 : 18 (1.8 / 13)6HK1 : 13 (1.3 / 9.6)
2 (0.2 / 1.5)
24 (2.4 / 17)
6 (0.6 / 4.4)
44 (4.5 / 32)
30 (3.0 / 22)12 (1.2 / 8.9)
N m(kg m/lb ft)
Fuel System 1C-23
Special Tool
Illustration Tool Number/Description/Special Tool Rank
5-8840-0019-0J-23907
Sliding hammerRank B
5-8840-2826-0EN-46720
Injector removerRank A
1C-24 Fuel System
Fuel Supply PumpComponents
* 4HK1 is shown for illustration.Name
1. Fuel Leak Off Pipe2. Fuel Pipe3. Fuel Supply Pump4. O-ring
5. Bracket6. Bracket O-ring7. Drive Gear8. Oil Drain Adapter
The fuel system consists of many tiny holes andspaces that allow the movement of fuel from one placeto another. These holes and spaces are milled toextremely high precision. This is especially true of thefuel injectors.The fuel injector is very sensitive to foreign material.Foreign material will result in fuel system breakdown.Exercise great care not to allow the entry of foreignmaterial into the fuel system or fuel injectors during theremoval and installation procedure.
Fuel System 1C-25
Removal1. Remove the intake pipe and case ASM.2. Remove the fuel pipe and fuel leak-off pipe.
Important:Do not reuse the high-pressure pipe in fuel system if ithas been removed.
4HK1
6HK1
3. Disconnect the fuel feed hose.4. Disconnect the connector of fuel temperature
sensor and the common rail pressure regulatorfrom the fuel supply pump.
5. Remove the fuel supply pump.
Note:A single bolt (1) secures the pump and the flywheelhousing.
* 4HK1 is shown for illustration.6. Use a gear puller to remove the fuel supply pump
gear and the bracket O-ring.
* 4HK1 is shown for illustration.7. Loosen the 3 bolts holding the fuel supply pump
bracket. Remove the bracket and the O-ring.
Caution:• Do not hold the high pressure pipe, during the
supply pump removal procedure.• Do not grasp the high pressure pipe, when moving
the supply pump form one location to another.
1C-26 Fuel System
* 4HK1 is shown for illustration.
Name1. Fuel Supply Pump2. O-ring3. Fuel Supply Pump Bracket
Installation1. Install the O-ring to the fuel supply pump.2. Install the pump to the bracket and tighten the 3
bolts to the specified torque.
Tightening torque: 19 N⋅m (1.9 kg⋅m/14 lb ft)
Caution:Take care not to twist the O-ring.
* 4HK1 is shown for illustration.
Name1. Fuel Supply Pump2. O-ring3. Fuel Supply Pump Bracket
3. Align the fuel supply pump shaft key and gear.Install the gear and tighten the nut to the specifiedtorque.
There is a round alignment mark on the gear (whitepaint).
Tightening torque: 64 N⋅m (6.5 kg⋅m/47 lb ft)
* 4HK1 is shown for illustration.
Name1. Fuel Supply Pump2. Fuel Supply Pump Gear3. Nut
Fuel System 1C-27
4. Apply white paint to the top of the fuel supply pumpgear tooth directly above the stamped ‘O’ mark.Refer to the illustration.
* 4HK1 is shown for illustration.5. Turn the crankshaft in the normal direction of
engine rotation until the No. 1 or No. 4 cylinder isat TDC on the compression stroke.
Refer to the illustration.4HK1
6HK1
6. Remove the oil drain adapter.7. Install the O-ring to the fuel supply pump.8. Align the slits as shown in the illustration.9. Insert the stud bolts into the guides and
temporarily tighten them.
Caution:• If the stud bolts (cylinder block side) have been
loosened or replaced, apply Loctite 262 to therecessed portion of the bolts.
* 4HK1 is shown for illustration.• Check that the round alignment mark (white paint)
is positioned as shown in the illustration whenviewed from the plug hole. If necessary, repositionthe gear.
• Tighten the stud bolts and the nuts to the specifiedtorque.
Tightening torque Nut: 50 N⋅m (5.1 kg⋅m/37 lb ft)Bolt: 76 N⋅m (7.7 kg⋅m/56 lb ft)
1C-28 Fuel System
* 4HK1 is shown for illustration.
Name1. Plug Hole2. Alignment Mark
10. Apply a light coat of engine oil to the O-ring.11. Install the oil drain adapter to the plug hole.
Tighten the bolts to the specified torque.
Tightening torque: 8 N⋅m (0.8 kg⋅m/71 lb in)
* 4HK1 is shown for illustration.
Name1. Oil Drain Adapter2. O-ring
12. Connect the fuel temperature sensor and thesuction control valve connectors to the fuel supplypump.
13. Connect the fuel feed hose.
14. Install the case ASM.• Apply the liquid gasket and mount within 7
minutes.
Tightening torque: 24 N⋅m (2.4 kg⋅m/18 lb ft)4HK1
6HK1
15. Install the fuel pipe and fuel leak-off pipe.
Important:Do not reuse the high-pressure pipe in fuel system if ithas been removed.
16. Start and idle the engine.
Important:In order to make the fuel supply pump characteristiclearn into the ECM, let the engine idle until warm-up. Ifthe fuel system DTC’ stored in the meantime, onceclear DTD and warm-up the engine again.
Fuel System 1C-29
Torque Specifications
* 4HK1 is shown for illustration.
1C-30 Fuel System
Gauze filter4HK1
6HK1
Name1. Fuel Supply Pump2. Eyebolt
3. Gauze Filter
Removal1. Remove the eyebolt.2. Disconnect the C-ring from the eyebolt and detach
the gauze filter.3. Clean the gauze filter with solvents, then blow dust
particles off with compressed air.
Installation1. Attach the gauze filter to the eyebolt, then secure it
using a C-ring.2. Install the eyebolt to the supply pump.
3. Bleed out the air.• Refer to «Fuel System».
WSHK0249
32
1
WSHK0250
3 2
1
Tightening torque: 14.6 — 24.6 N⋅m(1.5 — 2.5 kg⋅m/11 — 18 lb ft)
Fuel System 1C-31
Electromagnetic Pump Filter
Name1. Electromagnetic Pump2. Filter Element
3. Pump Cover4. Ground Cable
Removal1. Remove the ground cable that is installed on the
electromagnetic pump cover.2. Turn the pump cover with your hand to remove it
and take out the filter element.3. Clean the filter element with solvents, then blow
dust particles off with compressed air.
Installation1. Insert the filter element to the pump, then attach
the cover.2. Install the ground cable to the cover.3. Bleed out the air.• Refer to «Fuel System».
WSHK0251
1
2
34
1C-32 Fuel System
Common RailComponents4HK1
Name1. Fuel Leak Off Pipe2. Fuel Pipe3. EGR Valve4. EGR Cooler5. EGR Adapter
6. Injection Pipe Clip7. Injection Pipe (#1 to #4)8. Common Rail9. Common Rail Bracket
Fuel System 1C-33
6HK1
Name1. Fuel Leak Off Pipe2. Fuel Pipe3. EGR Valve4. EGR Cooler
5. EGR Adapter6. Injection Pipe Clip7. Injection Pipe (#1 to #6)8. Common Rail
Parts of the fuel system such as the internal part of thefuel injector, holes and clearances that form passagesfor fuel are finished to a very high degree of accuracy.They are therefore highly sensitive to foreign matterand the entry of foreign matter could cause damage tothe fuel passage. Therefore, effective measures shouldbe taken to prevent the entry of foreign matter.
Removal1. Remove the air intake pipe.
• Disconnect the connector for the intake airtemperature sensor.
2. Remove the fuel leak off hose from the leak offpipe.
• Cover the removed fuel hose with a lid, keep itfacing upward and secure it using wire, etc.
Note:Cover the areas exposed during part removal toprevent the entry of foreign material into the fuelsystem.
3. Disconnect the connected of common rail pressuresensor, and all the connectors.
4. Remove the EGR valve and the EGR adapter.5. Tape the EGR case holes shut to prevent the entry
of foreign material.
WSHK0165
6
7
8
2
1
3
4
5
1C-34 Fuel System
4HK1
6HK1
Name1. EGR Adapter2. EGR Valve
6. Remove the injection pipe clip and remove theinjection pipes.
Important:Do not reuse the high-pressure pipe in fuel system if ithas been removed.
Note:Cover the areas exposed during part removal toprevent the entry of foreign material into the fuelsystem.
4HK1
6HK1
Name1. Fuel Injection Pipe2. Pipe Clip
7. Remove the fuel pipe.
Note:Cover the areas exposed during part removal toprevent the entry of foreign material into the fuelsystem.
8. Remove the clip and the fuel leak off pipe.
Note:Cover the areas exposed during part removal toprevent the entry of foreign material into the fuelsystem.
WSHK0166
2
1
WSHK0167
21
Fuel System 1C-35
4HK1
Name1. Fuel Leak Off Pipe
6HK1
Name1. Fuel Leak Off Pipe
9. Remove the common rail and the common railbracket.
Caution:• Do not grasp the pressure sensor, during the
common rail removal procedure.• Take care not to damage the connector unit of the
pressure sensor.
* 4HK1 is shown for illustration.
Name1. Common Rail Bracket (4HK1)2. Common Rail
Disassembly1. Remove the fuel pressure limiter.
4HK1
1
1C-36 Fuel System
6HK1
Name1. Common Rail2. Pressure Sensor3. Pressure Limiter
Reassembly1. Install the fuel pressure limiter.
4HK1
6HK1
Name1. Common Rail2. Pressure Sensor3. Pressure Limiter
Installation1. Tighten the common rail bracket to the specified
torque. (4HK1)
2. Tighten the common rail to the specified torque.
Caution:• Do not grasp the pressure sensor, during the
common rail reassembly procedure.• Take care not to damage the connector unit of the
pressure sensor.
Tightening torque: 172 N⋅m (17.5 kg⋅m/127 lb ft)
WSHK0168
2
3
1
Tightening torque: 19 N⋅m (1.9 kg⋅m/14 lb ft)
Tightening torque: 4HK1: 19 N⋅m (1.9 kg⋅m/14 lb ft)6HK1: 25 N⋅m (2.5 kg⋅m/18 lb ft)
WSHK0168
2
3
1
Fuel System 1C-37
* 4HK1 is shown for illustration.
Name1. Common Rail Bracket (4HK1)2. Common Rail
3. Tighten the fuel leak off pipe (1) using themounting eyebolt and the clip using the specifiedtorque.
4. Tighten the fuel pipe (5) using the mounting sleevenut and the specified torque.
4HK1
6HK1
5. Tighten the injection pipe and the clip using thespecified mounting torque.
Important:Replace the high-pressure pipe in fuel system with newone if it has been removed.
• Apply a thin coat of engine oil on the periphery ofthe sleeve nut on the fuel injector side andassemble.
Tightening torque4HK1 (2): 18 N⋅m (1.8 kg⋅m/13 lb ft)6HK1 (2): 10 N⋅m (1.0 kg⋅m/7.4 lb ft)4HK1 (3): 12 N⋅m (1.2 kg⋅m/106 lb in)6HK1 (3): 14.2 N⋅m (1.4 kg⋅m/126 lb in)4HK1 (4): 8 N⋅m (0.8 kg⋅m/71 lb in)4HK1 (7): 6 N⋅m (0.6 kg⋅m/53 lb in)6HK1 (7): 8.8 N⋅m (0.9 kg⋅m/78 lb in)
Tightening torque (6): 44 N⋅m (4.5 kg⋅m/32 lb ft)(8): 44 N⋅m (4.5 kg⋅m/32 lb ft)
Injection pipe sleeve nutTightening torque: 44 N⋅m (4.5 kg⋅m/32 lb ft)
Injection pipe clipTightening torque: 6 N⋅m (0.6 kg⋅m/53 lb in)
WSHK0169
8 52
6
3
1
7
1C-38 Fuel System
4HK1
6HK1
Name1. Fuel Injection Pipe2. Pipe Clip
6. Install the gasket to the EGR valve and tighten thebolts to the specified torque.
Tightening torque: 24 N⋅m (2.4 kg⋅m/18 lb ft)7. Install the gasket to the EGR adapter and tighten
the bolts to the specified torque.
Tightening torque: 24 N⋅m (2.4 kg⋅m/18 lb ft)
4HK1
6HK1
Name1. EGR Adapter2. EGR Valve
WSHK0167
21
WSHK0166
2
1
Fuel System 1C-39
Torque Specifications4HK1
1C-40 Fuel System
6HK1
WSHK0172
6 (0.6 / 4)44 (4.5 / 33)
25 (2.5 / 18.4)
24 (2.4 / 17)
24 17
19.6 (2.0 / 14.5)
10 (1.0 / 7.4)
8.8 (0.9 / 6.5)
44 33
N.m (lb ft)
39 (4.0 / 29)
44 (4.5 / 33)
24 (2.4 / 17)
N m(kg m/lb ft)
Engine Electrical
ENGINEEngine Electrical
TABLE OF CONTENTSService Precautions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1D-2
General Procedure. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1D-2Charging System. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1D-3
General Description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1D-3Generator (4HK1) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1D-5
Removal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1D-5Installation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1D-6Torque Specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1D-6Specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1D-7
Generator (6HK1) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1D-14Specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1D-14Charging Circuit . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1D-14Structure. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1D-15Disassembly and Inspection of Generator . . . .1D-16Inspection. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1D-20Assembly . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1D-22Bench Testing. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1D-23Trouble Diagnosis . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1D-24Specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1D-24
Starting System . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1D-25General Description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1D-25On-machine Service: Starting System . . . . . . .1D-26
Starter (4HK1) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1D-27Removal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1D-27Installation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1D-28Torque Specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1D-28Main Data and Specifications. . . . . . . . . . . . . .1D-29
Starter (6HK1) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1D-37Specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1D-37Sectional view (reference) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1D-38Output Characteristic (reference). . . . . . . . . . .1D-39Disassembly and Inspection of Starter. . . . . . .1D-40Assembly of Starter . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1D-46No Load Test . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1D-50Specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1D-50
Preheating System . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1D-51Glow Plug Replacement. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1D-51Precautions on Service Work. . . . . . . . . . . . . .1D-52A List of Defective Phenomena . . . . . . . . . . . .1D-52Main Data and Specifications. . . . . . . . . . . . . .1D-53
Engine Electrical
1D-1 Engine Electrical
1D-2 Engine Electrical
Service PrecautionsGeneral ProcedureWhen fasteners are removed, always reinstall them atthe same location from which they were removed. If afastener needs to be replaced, use the correct partnumber fastener for that application. If the correct partnumber fastener is not available, a fastener of equalsize and strength (or stronger) may be used. Fastenersthat are not reused, and those requiring thread lockingcompound will be called out. The correct torque valuemust be used when installing fasteners that require it. Ifthe above conditions are not followed, parts or systemdamage could result.
Engine Electrical 1D-3
Charging SystemGeneral DescriptionThe main charging system components are thebatteries, the generator and the battery dischargeindicator light circuit. The generator is a selfrectifyingtype with a built-in regulator.
Name1. Generator2. Lower Mount Bolt3. Nut4. Spring Washer5. Washer6. Bracket7. Bracket Mount Bolt
8. Plate9. Bolt
10. ACG Adjust Bolt11. Sliding Piece12. Washer13. Adjust Nut
ACG
12
54
2
13
11
10
3
1D-4 Engine Electrical
MaintenanceThe most common indication of charging systemtroubles is an undercharged or overcharged battery.Since the battery itself may be defective, the first stepshould be to check its condition. In the case of anundercharged battery, check for battery drain causedby grounds or by accessories left turned on.Keep the generator and all other electrical systemterminals clean and tight. A loose or badly corrodedterminal connection will create excessive resistance inthe system and result in hard starting, dim lights etc.Inspect the generator system at regular intervals andcorrect any potential causes of trouble before machineperformance is affected.Diagnosis of Charging SystemTrouble in the charging system will be evidenced asone or more of the following three conditions:
1. The battery discharge warning light will stay on.2. An undercharged battery as evidenced by slow
cranking.3. An overcharge, or overvoltage, condition.
Undercharged BatteryInspection
1. Accessories to be sure none were left on forextended periods.
2. Drive belt for proper tension.3. The ECM main relay has been ON stuck at the key
switch OFF position. (Battery voltage isconsumed.)
4. Wiring and connections for corrosion or looseness.Overcharge (or Overvoltage) conditionA charging rate in excess of 29.5-volts for a prolongedperiod may cause early electrical system failure.Blown fuses. light bulbs burned out, and even batteryfailure may result. If this condition exists, test thegenerator as described under “Generator Output Test”later in this section.
Noisy GeneratorInspection
1. Drive pulley for looseness.2. Mounting bolts for looseness.3. Bearings for dirt, damage, or wear.• Generator noise may also be caused by worn or
damaged diodes and/or starter.Electrical TestsBefore performing the following generator electricaltests on the vehicle, be certain that the system wiring isnot defective and generator belts are not slipping. Also,the battery must be fully charged for a valid test of thecharging system.
Notice:To avoid damage to the vehicle electrical system,always observe the following precautions:
• Do not polarize the generator.• Do not short across or ground any of the terminals
in the charging circuit except as specificallyinstructed herein.
• NEVER operate the generator with the outputterminal open-circuited.
• Be sure the generator and battery have the sameground polarity.
• When connecting a charger or booster battery tothe battery, connect negative to negative andpositive to positive.
1. With the engine control switch “ON” and engine notrunning, connect a voltmeter from terminal “E” toground. The voltmeter should show 0 volts.
2. With the engine control switch “ON,” and enginenot running, connect a voltmeter from terminal “B”to ground. The voltmeter should read at least 24volts.
3. With the engine control switch “ON” and the enginenot running, connect a voltmeter from white wireside of the connector to ground. The voltmetershould show 24 volts.
4. With the engine control switch “ON” and the enginenot running, the “charge” light should be on. Thisshows that the other circuit in the connection isworking.
5. With the engine running and the headlight highbeams (if equipped) turned on, read the voltage atthe “B” post on the generator. The voltmeter shouldread at least 24 volts.
6. If steps 1 through 4 are not OK, check connectorsin the harness for looseness or corrosion andretest.
7. If step 5 voltage is low, substitute a known goodregulator and test again. If the voltage is still low,bench test the generator.
Engine Electrical 1D-5
Generator (4HK1)
Removal• Battery negative cable.
1. Electrical wiring at the generator.2. Loosen the adjust nut.3. Loosen the ACG adjust bolt.4. Loosen the lower mount bolt.5. Drive belt
1D-6 Engine Electrical
6. Generator.
Installation1. Generator.
2. ACG Adjust bolt.3. Adjust nut.
4. Electrical wiring at the generator.• Battery negative cable.
Torque Specifications
Tightening torque:Lower Mount Bolt 127 N⋅m (13.0 kg⋅m/94 lb ft)
Tightening torque:Adjust Nut 68 N⋅m (6.9 kg⋅m/50 lb ft)
WSHK0054
ACG
52(5.3 / 38)
127(13 / 94)
68(6.9 / 50)
52(5.3 / 38)
N m(kg m/lb ft)
Engine Electrical 1D-7
Specifications Connector terminal
Name1. R Terminal2. L Terminal
Internal connections
Isuzu Part No. 8973750170
Nominal output (V-A) 24-50
Rated speed (rpm) 5000
Regulator-type IC type
Regulated voltage (V) 28.5±1
Weight (kg) 9.5
Terminal symbol Lead wire color Wire specifications
R R AEX 0.75f
L L AEX 0.75f
1 2
SG
ICREGULATOR
B
R
L
E
1D-8 Engine Electrical
Disassembly of generator
Disassembly Procedure1. Screw2. Cover3. Through Bolt4. Rotor, Front Bracket Assembly5. Nut, Washer6. Pulley7. Fan8. Collar9. Screw
10. Retainer11. Ball Bearing12. Front Bracket
13. Collar14. Ball Bearing15. Rotor Assembly16. Screw17. Field Coil Assembly18. Stator Assembly19. Holder20. Regulator Assembly21. Bolt (B terminal)22. Condenser23. Rectifier AssemblyAssembly is the reverse order of disassembly.
56
78 3
1110 9 13
18
1514
12
2021
23
2216
17
19
12
Engine Electrical 1D-9
Inspection and repair of generator1. Diode
Check the continuity of forward and inversedirections with a tester. Normal diodes show lowresistance in forward direction and high resistancein inverse one.Judge that they are faulty other than those above.
2. CondenserCharge the condenser with a tester (at Ω × 1000range), and connect a tester lead inversely. Judgeit as normal if the needle on a meter deflects a littleand returns to the original position.Judge that they are faulty other than those above.
3. Diode for initiating excitation, ResistorCheck the continuity between connector terminalsR and L with a tester (at Ω × 100 range). Normaldiodes and resistors show low resistance inforward direction and high resistance in inverseone.Judge that they are faulty other than those above.
4. Field coil• To judge the insulating condition of field coil,
measure between the protrusion portions and coreof the coil with a tester (at Ω × 1000 range). Judgeas faulty if it has continuity.
1D-10 Engine Electrical
• Measure between the protrusion portions of fieldcoil with a tester, and judge as normal if theresistance is about 6.7Ω (20°C 68°F).
5. Stator coil• To judge the insulating condition of stator coil,
measure between the stator coil and core with atester (at Ω × 1000 range). Judge as faulty if it hascontinuity.
• Judge as normal if there is continuity between Nlead of stator coil and three leads.
6. Bearing• Check if the bearing rotates smoothly or has no
noise.If the result of the inspection is unsatisfactory,replace the bearing.
Engine Electrical 1D-11
Performance testIn the performance test of generator, connect asfollows and measure the regulated voltage and outputcurrent.
Actual wiring diagram for performance test of IC regulator built-in generator
Disassembly Procedure1. Voltmeter2. R Terminal3. L Terminal4. Charging Lamp 24 V-3 W
5. Clamp Tester Ammeter6. Battery 24 V7. Variable Resistor
Regulated voltage measurement of regulatorClose SW1 switch, and warm-up five to ten minutes atapprox. 1500 rpm in generator until an ammeter shows6 A or less.After confirming that an ammeter shows between 2 and6 A, set the generator between approx. 3000 to 4000rpm. If an voltmeter shows between 27.5 and 29.5 V,the regulated voltage of regulator is normal.If the ammeter shows 6 A or more, charge the batteryfor a while or replace it with full-charged battery.Replace the regulator if the voltmeter shows out ofrange between 27.5 and 29.5 V.
Measurement of the output currentClose SW1 and SW2 switches, and raise the generatorspeed to 5000 rpm. While keeping the voltmetershowing 27 V, measure the maximum value of outputcurrent with a variable resistor.In this time, judge as normal if the output current is 50A or more.
Caution:• Do not cut off battery circuit during generator
rotating.• Do not connect to L terminal if the charging lamp
(24 V-3 W) is not used.Never connect L terminal and B circuit directly.Diode for excitation may be broken.
E
E
V
SW 2SW 1
1
2 3
4
5
76
Specified value of regulated voltage27.5 V — 29.5 V (+25°C 77°F)
1D-12 Engine Electrical
Handling of generatorBe careful with the following when handling agenerator.
• Connecting the polarities of battery inverselycauses generator diode to be broken.
• While the engine runs, NEVER disconnect thewiring of battery terminal and charging circuit.
• Wiring connection to terminal must be performedproperly according to terminal symbol.
• Do not perform megger test on semiconductordevice.
• Be sure to disconnect the battery terminal (−)before inspection on equipment.
• Do not open/close the battery relay switch whilethe engine runs.
• Disconnect the battery terminal when chargingfrom external source such as quick charge.
• Do not pour steam cleaner or water directly on it.• After connecting to B terminal and E terminal,
tighten them to the following torque.B terminal 4.9 N⋅m 50 kgf⋅cm/43 lb inE terminal 4.9 N⋅m 50 kgf⋅cm/43 lb in
• Refer to “Belt Adjustment” for tension adjustmentof V-belt.
Engine Electrical 1D-13
Trouble and Action
Trouble symptom Trouble location Trouble cause Action to be taken
Charging is impossible.
Wiring and ammeter
Open or short circuit, disconnection Repair
Generator. Open circuit, short to ground, short circuit in each coil Replace
Broken diode Replace
Regulator Defective regulator. Replace
Poor contact in terminal of regulator Repair
Insufficient charging
Wiring Open or short circuit, looseness in connection Repair
Generator. Looseness of generator driven belt Repair
Layer or short circuit in field coil Replace
Layer or short circuit in stator coil Replace
Defective diode Replace
Poor contact in each terminal Repair
Regulator Defective regulator. Replace
Poor contact in terminal of regulator Repair
Excessive charging
Regulator Defective regulator. Replace
Unstable charging current
Wiring Intermittent contact or nearly disconnected connection in wiring Repair
Generator. Looseness of generator driven belt Repair
Short circuit or nearly disconnected connection in field coil Repair
Short circuit or nearly disconnected connection in stator coil Repair
Poor contact in each terminal Repair
Regulator Defective regulator. Replace
Poor contact in terminal of regulator Repair
Noisy generator Generator. Improper installation of generator Repair
Defective bearing Replace
Contact of rotor core and stator core Repair
Defective diode Replace
Short circuit in stator coil Replace
1D-14 Engine Electrical
Generator (6HK1)Specifications
Charging Circuit
Name1. Field Coil2. Stator Coil3. Diode Trio4. Charging Lamp
5. Key Switch6. Battery 24 V7. IC Regulator8. Generator
Charging circuit and internal circuit are shown in the illustration above.Charging system consists of IC regulator built-in generator, battery, charging lamp and wires to connect them.
Manufacturer Mitsubishi Electric Co.
Isuzu Part No. 1-81200-633-0 1-81200-603-2
Model by manufacturer A009TU3782 A004TU6285
Nominal voltage (V) 24
Output current (A) 90 50
Rated speed (rpm) 5000
Output current/Voltage (A/V/rpm) 114/27/5000 50/27/5000
No load voltage (V/rpm) 24/900
Revolution direction Clockwise
Polarity (−)
Pulley diameter (P. C. D) (mm/in) 90/3.543 80/3.150
N
B
L
R
L
F
E
E
R
1
2
3 4 5
6
7
8
Engine Electrical 1D-15
Structure
Name1. Rear Bracket2. IC Regulator3. Bearing4. Rectifier5. Stator
6. Rotor7. Bearing8. Pulley9. Front Bracket
10. Coil Assembly (Field Coil)
This generator has no brush.Main parts are a rotor, stator, rectifier assembly, frontbracket, rear bracket, IC regulator, bearing, pulley andso on.Moving parts are a rotor and pulley. A field coil issecured to rear bracket.Six main diodes and two additional diodes are used toconvert three-phase alternating current, generated instator coil, into direct current. Among six main diodes,there are three positive diodes and three negativediodes.In addition, three tiny diodes, called trio diode, are usedto supply field current.This generator has three terminals, which are B
terminal (for direct current output), L terminal and Rterminal.The L terminal is connected to field coil. Therefore, aswell as R terminal, it becomes input terminal forinitiating excitation current until the generator starts togenerate electric power.It also provides function as output terminal. (Currentcapacity is 1 A.)The charging lamp will be off if the voltage on Lterminal reaches battery voltage.Both bearings are sealed, therefore periodic lubricant isnot necessary.IC regulator cannot be disassembled. Handle it asassembly.
78
9
10
1
2
3
4
5 6
1D-16 Engine Electrical
Disassembly and Inspection of Generator
Name1. Nut Washer2. Pulley, Fan3. Collar4. Through Bolt5. Front Bracket6. Ball Bearing7. Retainer8. Rotor Assembly
9. Ball Bearing10. Screw11. Cover12. Rectifier Assembly13. Regulator Assembly14. Stator Assembly15. Field Coil Assembly
1
2
4
3
56
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
Engine Electrical 1D-17
Name1. Nut Washer2. Pulley, Fan3. Key4. Collar5. Through Bolt6. Front Bracket7. Ball Bearing8. Retainer9. Rotor Assembly
10. Ball Bearing11. Field Coil Assembly12. Connector Set13. Screw14. Terminal Set15. Cover16. Rectifier Assembly17. Regulator Assembly18. Stator Assembly
Disassembly
Caution:To facilitate re-assembly, put alignment marks on frontbracket and rear bracket before disassembly.
1. Remove out the four through-bolts.Pry between stator and front bracket with a tip offlathead screwdriver and separate the front bracketpulley rotor assembly from stator rear bracketassembly carefully.
Caution:Take care not to damage the stator coil.
2. Hold the rotor with a vise without deforming therotor ball.Remove the nut which fixes pulley, and remove thepulley, fan, spacer and front bracket.
Caution:Do not lose a half-moon key when removing the pulley.
Caution:To hold the rotor with a vise, grip the portion A. PortionB is not strong enough to be gripped.
1
32
5
4
67
8
9
11
10
14
12
13
15
16
17
18
1D-18 Engine Electrical
Name1. Ball
3. If the front bearing needs to be removed, removethe screw which fixes retainer, and push out thebearing using appropriate socket.
Caution:Do not remove it if not necessary. Do not reuse theremoved bearing.
4. If the rotor bearing needs to be removed, it can bedone by a general bearing puller.
Caution:Do not remove it if not necessary. Do not reuse theremoved bearing.
5. To remove the coil assembly from rear bracket,firstly remove the screw A (which fixes coil terminalportion to IC regulator).Removing a screw B (which fixes the coil assemblyto rear bracket) prior to screw A may causedamage to terminal portion.Hold the coil assembly by hand not to damage toterminal portion.Then, remove the screw B and remove the coilassembly.
Name1. Connector
6. Disconnect the connector.7. Remove the cap and nut from terminal bolt of
rectifier.Pry between rear bracket and B terminal assemblyto remove the B terminal. A tube remains on rearbracket.
Caution:Do not lose the tube.
B
A A
1
1
A
B
Engine Electrical 1D-19
Name1. IC Regulator2. Rectifier3. B terminal4. Terminal Bolt5. B terminal6. Cap7. Nut
8. Cap9. Nut
10. Terminal Bolt11. Terminal Bolt12. Terminal Bolt13. Rectifier
1
2
3
4
12
13
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
1D-20 Engine Electrical
Name1. IC Regulator2. Terminal Bolt3. Nut
4. B terminal5. Tube6. Rectifier
8. Remove two screws which fix rectifier and twoscrews which fix regulator.Remove the stator and rectifier assembly from rearbracket as a unit.Then, remove the IC regulator.
9. Disconnect four lead wires of stator coil andremove the stator from rectifier.
Caution:Lead wires of stator coil are soldered (melting point:230°C 446°F) on rectifier terminal.Disconnect them quickly (within five seconds) not toheat the rectifier causing damage to diode.
Inspection1. Stator
Check visually for damage, loose connection anddiscoloration of coil.
• Check the continuity between two lead wires ofstator coil with a circuit tester. Replace the stator ifno continuity is present.
• Check the continuity between lead wire of statorcoil and core with a circuit tester. Replace thestator if continuity is present.
Name1. Stator Coil Lead
N
1
2
3
4
5
6
1
Engine Electrical 1D-21
2. Rotor• Check the bearings for noise, rattle or grease
leakage (wipe off if tiny amount of grease).Replace it if faulty. It is easier to check for noiseand rattle when it is press-fitted into shaft thanwhen it is a single unit.
Name1. Stator Coil Lead2. Core
3. Coil assemblyMeasure the resistance between terminal portionswith a circuit tester.Replace the coil assembly if the value is out ofspecified value.
Name1. Terminal2. Terminal Portion
4. Rectifier assembly• Check the continuity between positive diode,
additional diode positive heat sink on positive sideand four diode terminals with a circuit tester.The positive diode has short circuit if continuity ispresent in both directions. Replace the rectifierassembly.The positive diode has open circuit if no continuityis present in both directions. Replace the rectifierassembly.
• Negative diode and additional diode on negativesideCheck the continuity between negative heat sinkand four diode terminals with a circuit tester.The negative diode has short circuit if continuity ispresent in both directions. Replace the rectifierassembly.The negative diode has open circuit if no continuityis present in both directions. Replace the rectifierassembly.
• Diode trio (three tiny diodes)Check the continuity in both directions with a circuittester.The diode is faulty if continuity is present in bothdirections or no continuity is in both directions.Replace the rectifier assembly.
Name1. Diode Terminal Portion2. Positive Diode3. A Part of Negative Diode
5. Front bearingCheck the bearings for noise, rattle or greaseleakage (wipe off if tiny amount of grease).Replace them if faulty. It is easier to check fornoise and rattle when the bearing is press-fittedinto bracket than when it is a single unit.
1
2
2
1
2
31
1D-22 Engine Electrical
6. RegulatorThe regulator cannot be checked with a circuittester. After re-assembling the generator, check itto make sure that regulator controls the voltage forgenerator.
AssemblyAssembly can be performed in the reverse order ofdisassembly. However, be careful with the following.
1. Lubrication is not necessary. Bearing is filled withgrease and is sealed.
Caution:Keep a bearing with resin band for rotor shaft awayfrom oil. Wipe off oil on bearing box area of rearbracket. Oil may cause creep.
2. Use a high temperature solder (melting point:230°C 446°F).Using a soldering iron (with 180 — 270 watt),soldering must be performed quickly (within fiveseconds) not to heat the rectifier.
3. Tightening torque• Pulley fixing nut:
132 — 162 N⋅m 13.5 — 16.5 kg⋅m/97 — 119 lbft
• Through bolt:12.8 — 18.6 N⋅m 1.3 — 1.9 kg⋅m/9 — 14 lb ft
• Bearing retainer fixing screw:2 — 5.3 N⋅m 20 — 54 kgf⋅cm/18 — 47 lb in
• Coil assembly fixing screw:2 — 5.3 N⋅m 20 — 54 kgf⋅cm/18 — 47 lb in
• Rectifier fixing screw:2 — 5.3 N⋅m 20 — 54 kgf⋅cm/18 — 47 lb in
• Regulator fixing screw:2 — 5.3 N⋅m 20 — 54 kgf⋅cm/18 — 47 lb in
• Nut for B terminal bolt:4.9 — 8.7 N⋅m 50 — 88 kgf⋅cm/43 — 77 lb in
4. Assembly of rear bracket to stator assembly andfront bracket to rotor assembly
• The rotor bearing and rear bracket are engagedtightly. Heat the bearing box area of rear bracket to50 — 60°C (122 — 140°F) prior to assembly.
• After re-assembling the generator, rotate the pulleyto confirm that the rotor rotates smoothly.
Engine Electrical 1D-23
Bench TestingBench testing is performed as follows.
Regulated voltage check1. Wire as shown in the illustration.
Use an ammeter with 100 A rating and a voltmeterwith 30 V rating.
Name1. Voltmeter2. Ammeter3. Lamp (24 V, 3 W or less)4. Key Switch 15. Battery (24 V)6. Key Switch 27. Load Resistance
2. Close the switch 1. Leave the switch 2 open.In this time, the lamp comes on.If it does not, check the voltage on L terminal.If the voltage is almost the same as batteryvoltage, check the generator.If the voltage is low, lamp or the circuit is open.
3. Increase the generator speed gradually.Make sure that the lamp goes off before the speedreaches approx. 1300 rpm.Notice the voltage. If the voltage is not controlledand exceeds 30 V, the IC regulator may be faulty.If the voltage does not exceed battery voltage, thegenerator does not generate electric power.Check the generator again.If the lamp does not go off, check the generatoragain.
4. Set the generator speed to approx. 5000 rpm andread an ammeter. If the value is 5 A or less, readindication on a voltmeter. This is regulated voltage.If an ammeter shows 5 A or more, keep chargingfor a while until it shows below 5 A or replace thebattery with full-charged one.If regulated voltage is out of specified value,replace the regulator.
Output current testOutput current test is performed to check if thegenerator generates rated output.
1. After checking regulated voltage, decrease thegenerator speed until it stops.
2. Close the switch 1. The lamp should come on.3. Set the value of no load resistance to maximum
(minimum current) and close the switch 2.4. Increase the generator speed to 5000 rpm and
keep it. Adjust the load resistance so that outputcurrent becomes maximum.Keep this condition 15 minutes and increase intemperature of the generator.15 minutes later, set the generator speed to thespecified speed (2500 and 5000 rpm) and thenadjust the load resistance so that output currentbecomes maximum in this condition.In this time, if indication of ammeter is withinspecified value, the generator is normal.If it is less than specified value, check thegenerator again according to “Inspection” page.
B
8R
L
1
2
3
4
6
75V
A
1D-24 Engine Electrical
Trouble Diagnosis
Specifications
Symptom Trouble cause
No generation of electric power
a. Defective IC regulatorb. Open circuit in field coil
Low output a. Defective diodeb. Defective stator coilc. Defective rectifierd. Internal short circuit in field coil
Too high regulated voltage
a. Defective IC regulator
Noise a. Defective bearingb. Defective rectifierc. Foreign material in generator
Item Standard value and limit
Isuzu Part No. 1-81200-633-0 1-81200-603-2
Manufacturer code No. A009TU3782 A004TU6285
Rated output (V-A) 24-90 24-50
Output characteristic (hot)
Voltage (V) 27 27
Current (A) 105 or more 42 or more
Revolution speed (r/min) 2,500 2,500
Voltage (V) 27 27
Current (A) 114 or more 50 or more
Revolution speed (r/min) 5,000 5,000
Field coil resistance (Ω: at 20°C) 4.3-5.0 4.4-5.1
Regulated voltage by regulator (V) 28-29 28-29
Revolution direction (viewed from pulley side) Clockwise Clockwise
Engine Electrical 1D-25
Starting SystemGeneral Description
Starter and Glow Plug RelaysThe starter is a 5 kilowatt, reduction drive model.The gear housing and armature end bearing housingsare aluminum. The brush ASM has replaceablebrushes. The commutator bars are mica insulated andare undercut.
The starter circuit starts at the batteries. The batterycable goes to the large terminal on the starter.From that terminal wires lead to the engine controlswitch and the starter relay.
* 4HK1 is shown for illustration.
Name1. Starter2. Nut
3. Ground Cable4. Bolt
MaintenanceKeep the starter’s exterior clean. Remove corrosionfrom the terminals, leads, and connectors.Tighten the starter to engine mounting bolts and theelectrical cable retaining nuts.
1D-26 Engine Electrical
Diagnosis of Starting System
No Cranking, No Sound• Discharged batteries. Check for the cause of the
discharged batteries.• Sulfated battery terminals. Clean all the battery
terminals and cable ends.• A starter that draws too much current.• Starter relay won’t work. Attempt to start and listen
for a “click” at the starter relay. If there is no “click,”check the starter relay control terminals with a testlight. If the test light shows that power is getting tothe starter relay, check the ground circuit with thetest light. If the ground circuit is OK, replace thestarter relay.
• Engine control switch start circuit won’t close.With the engine control switch turned to start,check the starter relay with a test light. If the testlight doesn’t come on, check the starter circuit atthe engine control switch with the test light. If thetest light comes on, check the harness for an openand repair. If the test light does not come on,replace the engine control switch.
• Starter relay power circuit isn’t closing. Attempt tostart. The starter relay “clicks.” Check thesecondary terminals with a test light. If the test lightlights on the battery side only, replace the starterrelay. If the test light lights on both terminals, checkfor an open at the starter.
• Starter clicks when start is attempted. Check allpower connections for corrosion. Cleanconnections if corrosion is present. Terminal onstarter should have at least 18 volts on it whencranking the engine. If voltage is OK, replace thestarter.
Slow Cranking, Solenoid Clicks or Chatters• Discharged batteries. Check for cause of
discharged batteries.• Check the battery terminal for corrosion. Hint: Test
for warm terminals. Clean all the battery terminalsand connectors.
• Loose or dirty connections. Measure the crankingvoltage at the battery terminals. If the voltage isless than 18 volts, load test the battery. If thebattery is bad, replace the battery. If the battery isgood, repair the starter.
If the voltage is 18 volts or more, measure the voltagefrom the battery NEGATIVE terminal to the engineblock. If the voltage is 0.5 volt or more, repair theground cable and connections.If the voltage is less than 0.5 volt, measure the voltageat the battery cable terminal on the starter. If thevoltage is 18 volts or more, repair the starter. If thevoltage is less than 18 volts, clean and tighten thepositive cable connections. If the voltage is still lessthan 18 volts, replace the positive cable.
On-machine Service: Starting System
MaintenanceKeep starter terminals and all other terminals in theelectrical system clean tight. A loose or corrodedconnection or terminal will cause excessive resistancein the system that will result in hard starting. At regularintervals, inspect the starting system to locate andcorrect potential causes of trouble before the systemperformance is affected. Starting motors do not requirelubrication.
Engine Electrical 1D-27
Starter (4HK1)
Removal1. Battery negative cable from the battery.2. Cables and electrical leads from the starter.3. Two mount nuts.4. Starter.
1D-28 Engine Electrical
Installation1. Starter2. Two mount nuts.
3. Cables and electrical leads to the starter.4. Battery negative cable to the battery.
Torque Specifications
* 4HK1 is shown for illustration.
Tightening torque:Mount nuts 82.4 N⋅m (8.4 kg⋅m/61 lb ft)
Engine Electrical 1D-29
Main Data and Specifications
Model (Manufacturer) Nikko Electric Industry Co., Ltd
Rating Voltage V 24
Power output kw 5
Time Sec. 30
Number of pinion teeth 11
Revolution direction (viewed from pinion side) Clockwise
Weight (approx.) N kg 78.4 8
No load characteristic
Current/Voltage A/V 85 or less/24
Speed rpm 3300 or more
Load characteristic Current/Voltage A/V 500 or less/18.5
Torque N⋅m kgf⋅m 28.4 2.9 or more
Speed rpm 1250 or more
Locking characteristic
Current/Voltage A/V 1400 or less/9
Torque N⋅m kgf⋅m 88.2 9.0 or more
1D-30 Engine Electrical
Connections (Nikko Electric Industry Co., Ltd)
Name1. Starter Relay2. Battery
3. Motor4. Magnetic Switch
B
M
E
SS.S
B
C
P1
P2
C2 C1
C3
Fc
Ar
1 4 3
2
S.S Starter switchAr ArmatureFc Field coilC1 Pressure coilC2 Holding coilC3 Starter relay coilP1 Sub contactorP2 Main contactor
Engine Electrical 1D-31
Disassembly of starter24 V 5.0KW (Nikko Electric Industry Co., Ltd)
Name1. Clip Ring2. Pinion Stopper, Pinion, Spring3. Lead Wire4. Bolt5. Magnetic Switch6. Screw7. Bolt8. Rear Bracket9. Brush Holder ASM
10. Yoke ASM11. Armature12. Cover13. Packing14. Idle Gear
15. Ball16. Rubber Bushing17. Plate18. Spring19. Pin20. Holder21. Shift Lever22. E Clip23. Overrunning Clutch ASM24. Internal Gear25. Washer26. Drive Shaft ASM27. Front Bracket ASMAssembly is the reverse order of disassembly.
1 24
27
19
5
2120
1817
16
2524
22
233
26
1415
1312
11
10
9
8
6
7
1D-32 Engine Electrical
Inspection and repair of starter1. Magnetic switch
Never perform operational check on magneticswitch as single unit.
Inspection of coil• Check the pressure coil C1 and holding coil C2 for
open circuit using a tester.Check the continuity between magnetic switch andM terminal. It has open circuit if no continuity.(Resistance approx. 1.6Ω)
• Supply 24 V between M terminal of magneticswitch and case, push the plunger by hand, andthen release it. It is normal if it is not sucked. Coil isdefective if it is sucked.
Caution:Perform this while the magnetic switch is set up.
Contact Point CheckService limit of contact point is judged by damagedcondition on contact surface in the following procedure.Measure the load current on starter. Replace it ifvoltage drop between terminals B and M is 0.3 V ormore per 100 A.
Caution:Use a digital voltmeter to measure voltage drop. Usingan analog voltmeter may damage itself.
2. ArmatureBentness measurement of shaftMeasure with a dial gauge, and repair or replace ifbentness is 0.05 mm (0.0020 in) or more.
Engine Electrical 1D-33
Inspection of commutator• Check the surface of commutator. File the
surface smooth with No.400 to 600 sand paperif it is rough. Repair with a lathe if deflection is0.1 mm (0.004 in) or more.
• Measure the depth of undercut and repair if it is0.2 mm (0.008 in) or less.
Name1. Repair is needed2. Improper repair3. Good
Outside diameter of commutatorMeasure the outside diameter of commutator witha slide-caliper. If the measured value is less thanthe limit, replace it.
Inspection of armature coil• Using a growler tester, put probe on a armature
core. It is normal if probe does not vibrates.• Check with a tester. It is normal if there is no
continuity between commutator and shaft.
3. Field Coil• Check the field coil for open circuit with a tester. It
is open circuit if there is no continuity between Mterminal in field coil and lead wire on brush side.
• Check between field coil and yoke with a tester. Itis normal if there is no continuity between them.
4. Overrunning clutch• Rotate the pinion by hand. It is normal if it is
rotated smoothly in one direction only.Check the pinion tooth surface. Replace if it hasworn or damage.
Caution:If the entire overrunning clutch is soaked in liquid whenwashing it, internal grease flows out, causing seizure.
mm (in)Standard Limit
32.4 (1.276) 31.4 (1.236)
WSHK0120
mm(in)
0.5-0.8(0.02-0.03)
1
2
3
1D-34 Engine Electrical
5. Reduction gear• Check the reduction gear. It is normal if it has no
wear.
6. Bearing• Check if the bearing outer race rotates smoothly by
hand.
7. Brush height• Measure the brush height. If it is less than the limit,
replace the brush.
mm (in)Standard Limit
17 — 18 (0.669 — 0.709) 10 (0.394)
Engine Electrical 1D-35
Handling of starter1. Precautions on handling• Improper gap between pinion and ring gear causes
faulty mesh. (Gap 2 — 5 mm 0.079 — 0.197 in)• Also, the front bracket is installed on the engine
side securely.• Be sure to turn off the battery switch before
removal/installation of stater.• Tightening/inserting wiring must be performed
properly. Improper work causes starting troubledue to high contact resistance.
2. Precautions on starting• Be careful with charging status of battery.
Insufficiently-charged battery causes startingtrouble.
• After checking engine starting, turn off the staterswitch immediately.
• One continuous use should be less than 10seconds. If re-starting is needed, wait until thepinion stops completely.
• If the starter does not stop rotating when the starterswitch is turned off, turn off the battery switchimmediately. In this case, check the wiring, switch,etc.
1D-36 Engine Electrical
Trouble countermeasure
Trouble symptom Trouble cause
Starter does not operate when starter switch is turned on.
1. Full discharge of battery2. Open circuit, poor contact3. Poor contact in starter switch or improper tightening of terminal4. Poor contact in starter relay or plug terminal5. Short or open circuit in magnetic switch coil
Pinion moves forward but it does not engage with ring gear.
1. Insufficient capacity of battery2. Improper gap of pinion and ring gear3. Wear of pinion or ring gear tooth edge4. Dust on pinion shaft5. Insufficient auxiliary rotation of armature due to insufficient thrust gap
of motor
Pinion engages and rotates motor but it does not run engine.
1. Slippage of clutch2. Breakage of reduction gear
Pinion engages but it does not run engine.
1. Insufficient capacity of battery2. Too high rotational resistance of engine3. Improper tightening of wiring circuit terminal4. Short circuit of armature or field coil5. Contamination of commutator6. Fatigue or wear of brush spring7. Locking of bearing8. Poor contact in magnetic switch
When turning starter switch off, starter does not stop after engine starts.
1. Retuning failure of starter switch contact2. Retuning failure of starter relay contact3. Short circuit in magnetic switch coil
Engine Electrical 1D-37
Starter (6HK1)Specifications
Manufacturer Mitsubishi Electric Co.
Isuzu Part No. 181100-4140
Manufacturer code No. M008T60971
Power output (V-kw) 24-5.0
Rating (Sec) 30
Outside diameter of yoke (mm/in) 85/3.346
Revolution direction Right
Protection Dust-proof, drip-proof
Reduction mechanism Internal gear
Weight (kg) 7.2
Pinion Module 3
Pressure angle 14.5
The number of teeth 11
Gear ratio ring gear/pinion gear 12.8 129/11
No load Voltage (V) 23
Current (A) 85 or less
Revolution speed (rpm) 3,300 or more
Restraint Voltage (V) 9
Current (A) 1,400 or less
Torque N⋅m kgf⋅m 88 9 or more
Pinion engagement voltage (V) 16.0 or less
1D-38 Engine Electrical
Sectional view (reference)
Name1. Through Bolt2. Bearing3. Rear Bracket4. Brush Holder5. Magnetic Switch6. Shift Lever7. Gear Shaft
8. Pinion9. Bearing
10. Front Bracket11. Gear12. Yoke13. Armature
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10111213
Engine Electrical 1D-39
Output Characteristic (reference)
WSHK0070
0
0 200 400 600 800 1000 1200 1400 1500
4
8
12
16
20
24
V
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
kW
0
20
40
60
80
100
120
N.m
0
1000
2000
3000
4000
5000
6000
r/min
Rotationspeed
Rotationforce
Output Terminalvoltage
Rotationspeed
Rotation forceOutput
Terminal voltage
Current (A)
1D-40 Engine Electrical
Disassembly and Inspection of StarterDisassembly diagram: disassemble in the order of the numbers.
Name1. Snap Ring2. Stop Ring3. Pinion4. Pinion Spring5. Lead Wire with Terminal6. Screw7. Magnetic Switch8. Screw9. Through Bolt
10. Rear Bracket11. Yoke Assembly12. O-Ring13. Brush Holder14. Armature15. Ball
16. Plate17. Packing18. Packing19. Plate20. Planetary Gear21. Lever22. E-shaped Retaining Ring 23. Overrunning Clutch24. Internal Gear25. Washer26. Gear Shaft27. Front Bracket28. Bearing29. Washer30. Brush
12
34
23
2425
12
11
3012
13
10
8
22
2620
15 517
16
14
2928
6
27
7
1819
219
Engine Electrical 1D-41
Disassembly
Caution:• Before disassembling the starter, put alignment
marks on each magnet switch, yoke front bracketand rear bracket to facilitate re-assembly.
• In normal condition, if tap the pinion or stop ringtoward the front bracket side, the front bracket willbe broken. Therefore, tap the stop ring when thepinion come out to cranking position.
1. Connect the starter to battery as shown in theillustration.When closing the switches SW1 and SW2, thepinion move forward to the cranking position andthe armature rotates.Then, open the switch SW2 to stop the armaturerotating.
Caution:Remove the pinion within 10seconds since heat isgenerated during electric discharge.
2. Apply the pipe, which just fits the stop ring, on thering and tap the pipe with a hammer to remove thestop ring toward the pinion side once.Then, remove the snap ring and remove the stopring, pinion and pinion spring.
Caution:Do not reuse the snap ring.
Name1. Pinion2. Clutch Shaft3. Snap Ring4. Stop Ring5. Pipe6. Pinion Spring
3. Remove the nut on M terminal of magnet switchand remove the lead wire with terminal.
Caution:Tightening screw is tight. Use a shock driver to loosen.
4. Remove the brush holder-tightening screw andthrough bolt.Then, remove the rear bracket and O-ringtogether.
Caution:Do not reuse the removed O-ring.Also, do not reuse also O-ring on tightening screw.
5. Apply a socket (outside diameter 32 mm1.260 in) on a commutator of armature.Then, slide the brush on the socket to yokeassembly and O-ring.This facilitates to re-assemble.
Caution:Do not reuse the removed O-ring.
6. Remove the brush from brush holder by pulling upthe brush spring, and then remove the brushholder.
7. Remove the armature.Remove a bearing using a general puller.
8. Remove the plate in planetary gear and removethe packing.Then, remove the packing and plate on the leversupport.
9. Remove the internal gear, gearshift, overrunningclutch and lever as a unit from front bracket.
WSHK0072
M
B
S
SW 1
SW 2
Battery24V
Wiring diagram to move pinion forward
Disconnect the lead wire(attached with terminal)from the M terminal.
1
2
36
4
5
1D-42 Engine Electrical
10. Remove the lever.
Caution:Remember the direction of lever.11. Remove the two E-shaped retaining ring.
To remove the overrunning clutch, rotate the splineby one tooth to remove it from gearshift assembly.
Caution:Do not reuse removed E-shaped retaining ring.12. Remove the internal gear.
In this time, take out one washer which adjustsaxial play of gearshift.
Inspection and maintenance1. Armature• Check the armature coil for internal short circuit
with a growler tester.Replace the armature if internal circuit is present.
• Check the armature coil for grounding (faultyinsulating) with a circuit tester.Replace the armature if grounding is present.
• Check the outside of commutator for wear.Replace the armature if wear exceeds limit.
Engine Electrical 1D-43
• Check the depth (undercut) of insulating mold ofcommutator.Remove abrasion powder on brush, and repair iffaulty.
Name1. Good2. Insulating3. Commutator Segment4. Defective
• Check the gears for wear or damage.Replace the armature if fault is present.
• Check the bearings for noise, rattle or greaseleakage.
2. Field coil• Check the coil for open circuit with a circuit tester.
Replace the yoke assembly if open circuit ispresent.
• Check the coil for grounding (faulty insulating) witha circuit tester.Repair or replace the yoke assembly if groundingis present.
3. Brush• Measure the length of the brush.
If it is worn to the limit, replace the brush holderassembly on the brush holder as a unit and onlybrush on the yoke assembly side.
• Make sure the brush moves smoothly in the brushholder. Also, check the brush spring pressure.
1
2
3
4
1D-44 Engine Electrical
• Check the brush holder for grounding (faultyinsulating) with a circuit tester.Clean the brush holder before checking.Replace the brush holder assembly if thecontinuity is present when putting one probe ofcircuit tester to brush holder plate (metal part) andanother one to insulated holder.
Name1. Brush Length2. Insulated Holder
4. Overrunning clutch and pinionHold the housing of overrunning clutch by hand.Make sure that the pinion can be rotated by handwith a light resistance in one direction and cannotbe in the opposite direction. Replace theoverrunning clutch if faulty.Check the pinion, and replace it if wear or scratchis present.
Caution:Grease is present in overrunning clutch. Do not usewash oil or cleaning agent for cleaning.Wipe off stain on overrunning clutch with a cloth.
5. Front bracketCheck the bearing and oil seal, and replace thefront bracket assembly (including bearing, oil seal)if faulty.
6. Internal gear and planetary gearCheck the internal gear and planetary gear, andreplace them if excessive wear or damage ispresent.
7. LeverIt the portion which contacts the overrunningswitch is worn, the protruded position of pinion willbe faulty.(Refer to “4. Assembly” section to adjust theprotruded position of pinion.)
Name1. Worn Part
1
2
1
Engine Electrical 1D-45
8. Magnetic switchCheck the continuity between the M terminal andthe body, and replace the magnet switch if nocontinuity is present.Then, make sure that no continuity is presentbetween B terminal and M terminal. Replace themagnet switch if continuity is present.
Name1. M Terminal2. S Terminal3. B Terminal
1
2
3
1D-46 Engine Electrical
Assembly of StarterAssembly diagram: Assemble in the order of the numbers.
Name1. Brush2. Washer3. Bearing4. Front Bracket5. Gear Shaft6. Washer7. Internal Gear8. Overrunning Clutch9. E-shaped Retaining Ring
10. Lever11. Planetary Gear12. Plate13. Packing14. Packing15. Plate
16. Ball17. Armature18. Brush Holder19. O-Ring20. Yoke Assembly21. Rear Bracket22. Through Bolt23. Screw24. Magnetic Switch25. Screw26. Lead Wire with Terminal27. Pinion Spring28. Pinion29. Stop Ring30. Snap Ring
WSHK0084
3029
2827
8
76
19
20
119
18
21
23
9
511
16 2614
15
17
23
25
4
24
1312
1022
Engine Electrical 1D-47
1. Lubricant locations and tightening torque
Lubricant locations
2. Axial play of armature shiftAdjustment is unnecessary (assemble the ball intoa tip of shaft.)
3. Axial play of gear shaftAdjustment is unnecessaryAppropriate gap will be obtained automaticallywhen one washer (removed in step 12 ofdisassembly procedure) is inserted betweeninternal gear and gearshift.
4. Assembly of gearshift
Pass the gear shaft through washer, internal gearand overrunning clutch. Then move theoverrunning clutch by one tooth of spline to makesure that the clutch cannot be pulled out.Assemble the E-shaped retaining ring.
Caution:• Do not reuse removed E-shaped retaining ring.
WSHK0085
G
E
I
C B
H F
A D
(2.0~2.6 / 14.4~18.8)
N m(kg m/lb ft)
19.6~25.5
(0.25~0.45 / 1.8~3.2)2.4~4.4
(0.8~1.3 / 5.8~9.4)7.8~12.7
(0.5~0.9 / 3.6~6.5)4.9~8.8
Shown in the
illustrationLubricant locations Lubricant agent
A Sleeve bearing and ball Molycote AG650
B Clutch shaft sliding surface MULTEMP 6129
C Spline portion and sliding portion of gearshift MULTEMP 6129
D Sliding portion of lever and overrunning clutch Molycote AG650
E Armature shift gear, planetary gear, internal gear Molycote AG650
F Under pinion MULTEMP 6129
G Outer surface of armature bearing (tiny amount) MULTEMP 6129
H Oil seal MULTEMP 6129
I Surface of plunger (tiny amount) MULTEMP 6129
1D-48 Engine Electrical
• If assembling the E-shaped retaining ring prior tothe overrunning clutch, the clutch cannot beassembled. Be careful with it.
Name1. Overrunning Clutch2. Washer3. Gear Shaft4. E-shaped Retaining Ring 5. Internal Gear
5. Assembly of pinionAssemble the pinion spring, pinion and stop ring toclutch shaft in this order, then assemble the snapring to the groove of clutch shaft at the end.Then, pull strongly the stop ring toward the snapring side with a gear puller and fix both of them.
Caution:• Assemble the pinion before assembling the
magnet switch to front bracket.• Do not reuse the removed snap ring.
Name1. Pinion2. Clutch Shaft3. Snap Ring4. Stop Ring5. Pinion Spring
6. Check of the pinion protruded positionAfter assembling the starter, check the protrudedposition of pinion.How to measure and adjust• Connect the starter to battery.
When closing the switches SW1 and SW2, thepinion move forward to the cranking positionand the armature rotates.Then, open the switch SW2 to stop thearmature rotating.
1
5
4
2
3
4
3
25
1
Engine Electrical 1D-49
• Push into or pull back a tip of the crankshaftlightly by hand and measure the movingdistance of it.Adjust by using one or two packings (0.5 mm0.020 in) of magnet switch and front bracketso that this measurement value is between 0.5— 2.0 mm (0.020 — 0.079 in).If this adjustment cannot be done, replace thelever.
Name1. Battery 24 V
M
B
S
SW 1
SW 2
1
WSHK0089
Amount of shaft moved
Push back the clutchshaft lightly by hand.
Check of pinion moving out position
1D-50 Engine Electrical
No Load Test1. After adjusting the protruded position of pinion,
connect the starter as shown in the illustrationabove.
Caution:Use a thick electric wire and tighten the connectedportion securely.
2. Close the switch and read the speed, current andvoltage.If the measured values are out of specified value,disassemble and inspect again.
Name1. Battery 24 V2. Ammeter3. Voltmeter
Specifications
M
B
S
SW
1 V 3
A2
Item Standard value or limit
No load characteristic
Voltage (V) 23
Current (A) 85 or less
Speed (rpm) 3,300 or more
Commutator Outside diameter (mm/in) 32/1.260
Limit (mm/in) 31.4/1.236
Commutator Undercut (mm/in) 0.5/0.020
Limit (mm/in) 0.2/0.008
Brush Length (mm/in) 18/0.709
Limit (mm/in) 11/0.433
Brush spring Pressure (N) 29 — 39
Limit (N) 13.7
Protruded position of pinion (mm/in) 0.5 — 2.0/0.020 — 0.079
Engine Electrical 1D-51
Preheating SystemGlow Plug Replacement
Precautions during maintenanceAdequate care should be taken as over-tightening theglow plug could lead to damage.Removal Procedure
1. Remove the engine harness, the EGR valve, thepressure sensor, and all of the fuel injectorconnectors.
2. Remove the EGR valve and the EGR adapter.3. Tape the EGR case holes shut to prevent the entry
of foreign material.
* 4HK1 is shown for illustration.
Name1. EGR Adapter2. EGR Valve
4. Remove the glow plug connector.5. Remove the glow plug.
Installation Procedure1. Install the glow plug.
2. Install and tighten the glow connector with thedesignated torque.
3. Install the EGR valve and the EGR adapter.
Tightening torque: 24 N⋅m (2.4 kg⋅m/18 lb ft)
* 4HK1 is shown for illustration.
Name1. EGR Adapter2. EGR Valve
4. Attach the engine harness connectors. Eachcomposite connector should make a loud clickwhen it is securely attached.
Tightening torque: 20 N⋅m (2.0 kg⋅m/15 lb ft)
Tightening torque: 1.2 N⋅m (0.1 kg⋅m/11 lb in)
1D-52 Engine Electrical
Precautions on Service WorkAdequate care should be taken as over-tightening theglow plug could lead to damage.Explanations on functions and operationThe preheating system consists the ECM, the glowrelay, glow plugs and the glow indicator lamp. Thepreheating system is operated when the engine coolanttemperature is low, and make the engine easy to start.Glow plug check
• Use the circuit tester and measure the resistanceof the glow plug.
• If the measured value deviates from the specifiedvalue, then replace the glow plug.
• Resistance value of glow plug is approximatelyless than 5Ω.
Caution:Use glow plugs from the same manufacturer.
A List of Defective Phenomena• The glow indicator lamp does not light up.• Preheating does not work.• Preheating time is too long or too short.
Engine Electrical 1D-53
Trouble Shooting
The glow indicator lamp does not light up.
Preheating does not work.
Preheating time is too long or too short.
Main Data and Specifications
Condition Possible Cause CorrectionThe glow indicator lamp does not light up.
Slow blow fuse has blown. Replace the slow blow fuse.Fuse is unavailable. Replace the fuse.Indicator valve is burnt out. Replace the indicator valve.Engine control system is faulty. Refer to the “Engine Control
System”
Condition Possible Cause CorrectionPreheating does not work. Slow blow fuse has blown. Replace the slow blow fuse.
Defective or faulty glow plug relay connector contact.
Re-mount or replace the glow plug relay.
Engine control system is faulty. Refer to the “Engine Control System”
Condition Possible Cause CorrectionPreheating time is too long or too short.
Thermo-sensor fault and break in circuit or short circuit.
Replace the thermo-sensor. Repair the circuit.
Fault in glow plug. Replace or tighten the glow plug.Engine control system is faulty. Refer to the “Engine Control
System”
Item Model
Preheating device model Glow plug
Glow plug rated voltage/ current (V-A) 23 – 3.5
1D-54 Engine Electrical
Exhaust System
ENGINEExhaust System
TABLE OF CONTENTSEGR System . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1F-2
Precautions on Service Work. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1F-2Explanations on Functions and Operation . . . . . 1F-2
EGR Valve and EGR Cooler . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1F-3Components. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1F-3Removal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1F-3Inspection. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1F-4Installation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1F-4Torque Specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1F-5
Exhaust System . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1F-6A List of Defective Phenomena . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1F-6Troubleshooting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1F-6
Turbocharger (6HK1) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1F-7Table of Specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1F-7Turbocharger Structured Diagram . . . . . . . . . . . 1F-8Disassembly and Inspection of Turbocharger . . 1F-9Assembly of Turbocharger . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1F-15
Turbocharger (4HK1) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1F-20Measurement Tool. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1F-21Other Material . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1F-21
1F-2 Exhaust System and Turbocharger
Exhaust System and Turbocharger 1F-1
1F-2 Exhaust System
EGR SystemPrecautions on Service WorkPerform EGR related assembly according to the usualprocedure of temporarily fitting and then permanentlytightening the parts so that unnecessary stresses arenot applied on the parts.
Explanations on Functions and OperationRe-circulate a part of the exhaust gas of the EGRsystem in the intake manifold. Reduce the combustiontemperature and inhibit NOx generation since inertgases may be mixed up in the intake air.An electronic control system is used in this EGR tobalance the requirements of operability and lowemissions. A DC motor is operated using the controlcurrent of the Engine Control Module (ECM) to controlthe EGR.Refer to the chapter on Engine Control System fordetails on fault diagnosis of the EGR system.
Name1. EGR Cooler2. Engine Control Module (ECM)
3. EGR Valve DC Motor
Exhaust System 1F-3
EGR Valve and EGR CoolerComponents
Name1. EGR Adapter2. Cooling Water Pipe (out)3. EGR Cooler
4. EGR Pipe5. Cooling Water Pipe (in)6. EGR Valve
Removal1. Drain the coolant.2. Disconnect the EGR valve connector.3. Remove the EGR pipe.
1F-4 Exhaust System
* 4HK1 is shown for illustration.
Name1. EGR Adapter2. Cooling Water Pipe (out)3. EGR Cooler4. EGR Pipe5. Cooling Water Pipe (in)
4. Remove the cooling water pipes.5. Remove the EGR adapter.6. Remove the EGR cooler.7. Remove the EGR valve.
Caution:After removing the EGR valve and EGR adapter, sealso that foreign matter does not enter.
Inspection
Gas leak check• Check for gas leak in various parts of the EGR gas
line.If the results of the check show abnormalities, repair orreplace the defective parts.
EGR valve check• Refer to the chapter on Engine Control System for
details on the method of checking the EGR valve.
Installation1. Mount the EGR valve.• Insert the gasket and temporarily fit the EGR valve.
Notice:Temporarily tighten the bolts.
2. Install the EGR cooler.• Temporarily fit the EGR cooler to the bracket.
Notice:Temporarily tighten the bolts.
3. Install the EGR adapter.• Temporarily fit the EGR adapter between the EGR
cooler and exhaust manifold.
Notice:Temporarily tighten the bolts.
4. Install the EGR pipe.• Insert the gasket between the two ends of the EGR
pipe and temporarily fit it.
Notice:Temporarily tighten the bolts.
During temporary assembly, tighten the nutsand bolts to the specified torque in the ordershown in the illustration.
* 4HK1 is shown for illustration.
Name1 ~ 9 Show the Order of Tighten Bolts and Nuts.
Tightening torque1, 2: 28 N⋅m (2.9 kg⋅m/21 lb ft)3, 4, 5, 6: 24 N⋅m (2.4 kg⋅m/18 lb ft)
Exhaust System 1F-5
Torque Specifications
* 4HK1 is shown for illustration.
1F-6 Exhaust System
Exhaust SystemA List of Defective Phenomena
• Vibration or rattling noise from the exhaust system• Clogging of exhaust system• Exhaust leakage or noise
Troubleshooting
Vibration or rattling noise from the exhaust system
Clogging of exhaust system
Exhaust leakage or noise
Condition Possible Cause CorrectionVibration or rattling noisefrom the exhaust system
Loose or misaligned components Match the joints and then re-tighten.Or, check for damage in the hanger,mounting brackets and clamps.
Condition Possible Cause CorrectionClogging of exhaust system Clogging or deformation of the exhaust
pipingRepair or replace the exhaust piping.
Condition Possible Cause CorrectionExhaust leakage or noise Defect or misalignment in mounting Match the joints and then re-tighten.
Damage or burn-out of exhaust pipingor silencer
Replace the damaged part.
Defective components in the exhaustsystem (clamps, pipes, silencer)
Replace the defective part.
Internal damage to silencer Replace the silencer
Exhaust System 1F-7
Turbocharger (6HK1)
Table of Specifications
Item Assembly specifications Service limit
Turbine shaft Axial play mm (in) 0.06 — 0.09(0.00236 — 0.00354) 0.11 (0.00433)
Radial play mm (in) 0.10 — 0.17 (0.00394 — 0.00669) 0.205 (0.00807)
Journal outside diameter (A) mm (in) — 11.380 (0.44803)
Sealing groove width (B) mm (in) — 1.33 (0.05236)
Runout mm (in) — 0.11 (0.00433)
Sealinginsertion part
Turbine side (bearing housing) (F) mm (in) — 17.03 (0.67047)
Compressor side (seal plate) (H) mm (in) — 14.05 (0.55315)
Oil thrower Sealing groove width (G) mm (in) — 1.52 (0.05984)
Bearinghousing
Bearing housing inner diameter (B) mm (in) — 16.11 (0.63425)
Thrust bearing inside diameter for press-fit portion
(L) mm (in) — 23.020 (0.90630)
Thrust bearing
Bearing pad height at compressor side (J) mm (in) — 0.0 — 0.060(0.0 — 0.00236)
Thrust collar thickness (K) mm (in) — 2.950 (0.11614)
F
B
E
A
HL
J
K
G
1F-8 Exhaust System
Turbocharger Structured Diagram
Name1. Turbine Housing2. Heat Protector3. Floating Metal4. Oil Thrower5. Compressor Housing
6. Seal Plate7. Compressor Impeller8. Seal Ring9. Seal Ring
10. Turbine Shaft
7
81
10 9
2 3
4 5
6
Exhaust System 1F-9
Disassembly and Inspection of TurbochargerDisassembly diagram: disassemble in the order of the numbers.
Name1. Compressor Housing2. Nut3. Compressor Impeller4. Seal Plate5. Oil Thrower6. Seal Ring7. G Coupling8. Turbine Housing9. Turbine Shaft
10. Seal Ring11. Gasket12. Heat Protector13. Thrust Bearing14. Thrust Collar15. Snap Ring16. Floating Metal17. Thrust Bearing18. Bearing Housing
18
7
11
1210
9
15
8
1616
1714
135
6
4
1
32
1F-10 Exhaust System
Disassembly
Caution:If you perform inspection with the turbochargerremoved from the engine, plug the oil port openingbefore work.
Inspection Prior to Disassembly• Measurement of axial play of turbine shaft
If it exceeds the service limit, check the thrustmetal, the thrust bushing, and the oil thrower.
• Measurement of radial play of turbine shaft
If it exceeds the service limit, check the floatingmetal.
• Measurement on the machine of radial play ofturbine shaftInsert a thickness gauge into the gap between thecompressor impeller and housing, and measurethe clearance.The thickness gauge to be inserted must be 0.2mm (0.0078 in) or less.
1. Compressor housing• Put alignment marks between the compressor
housing and the seal plate, and tap thecompressor housing to drive it out.
• Liquid gasket is applied to the mating surfaces ofthe compressor and the seal plate.
Caution:Take care not to damage the impeller during removal ofthe compressor housing.
Name1. Alignment Mark
Axial play mm (in)
Assembly specifications 0.06 — 0.09(0.0024 — 0.0035)
Service limit 0.11 (0.0043)
Radial play mm (in)
Assembly specifications 0.10 — 0.17(0.00394 — 0.00669)
Service limit 0.205 (0.00807)
1
Exhaust System 1F-11
2. Compressor impeller• Attach the box spanner to the turbine-side shaft
end of the turbine shaft, and remove the nut. Thenut is left-hand screw.
• Remove the impeller from the turbine shaft.• Washing of impeller
Soak in the cleaning solvent until the foreignmatters soften, and clean it with a plastic scraperor hard brush.
Caution:Do not use a wire brush.
Name1. Left-hand Thread
3. Seal plate• Loosen the pot small screw.• Lightly tap the bearing housing in the seal plate
with a wooden hammer.• Liquid gasket is applied to the mating surfaces of
the seal plate and the bearing housing.
4. Oil thrower• Remove the oil thrower from the seal plate.
5. G coupling• Loosen the nut and remove the G coupling from
the turbine housing and the center housing.6. Turbine housing• Remove the center housing from the turbine
housing.• Washing of turbine housing
Soak in the cleaning solvent to remove the foreignmatters.
7. Turbine shaft• Hold the heat protector lightly by hand, and take
out the turbine shaft.• If it is hard to remove, lightly tap the compressor-
side shaft end with a wooden hammer. • Washing of turbine shaft
Soak in the cleaning solvent until the foreignmatters soften, and clean it with a plastic scraperor hard brush.
Caution:• Do not use a wire brush.• Foreign matters remaining on the surface causes
the unbalance of weight. Therefore, wash itthoroughly.
• Take care not to damage the floating metal contactsurface of the shaft and the seal ring groove.
1
1F-12 Exhaust System
8. Heat protector• Remove the heat protector from the bearing
housing.9. Thrust bearing (compressor side)• Loosen the Plate small screw with a screwdriver,
and remove the thrust bearing and the thrust collar.10. Floating metal
• Remove the turbine-side snap ring with snap ringpliers.
• Draw out the floating metal from the bearinghousing.
11. Thrust bearing (turbine side)• Using a brass bar, push out the compressor-side
floating metal from the turbine-side bearinghousing, together with the thrust bearing.
Caution:While pushing out with a bar, take care that they do notrun on to damage the snap ring.12. Snap ring
• Remove the 2 snap rings from the bearing housingwith snap ring pliers.
13. Seal ring• Remove the seal rings from turbine shaft and oil
thrower.
Inspection
Compressor housing• Check the compressor housing for crack or
damage, and replace if defective.
Turbine housing• Check the turbine housing for crack or damage,
and replace if defective.
Impeller• Check the impeller for scratch, dent or crack.
Exhaust System 1F-13
Heat protector• Check the heat protector for damage, thermal
deformation or corrosion.
Turbine shaft• Measure the journal outer diameter of the turbine
shaft, and the groove width of the seal ringinsertion part.
Name1. Journal outer diameter2. Ring groove width
• Measurement of turbine shaft runout
Seal plate• Inspection of damage on the seal plate,
measurement of inner diameter of the seal ringinsertion part
Oil thrower• Inspection of damage on the oil thrower sliding
surface, measurement of the seal ring groovewidth
Journal outer diameter mm (in)Service limit φ 11.38 (0.4480)
Groove width of the seal ring insertion part
mm (in)
Service limit 1.33 (0.0524)
1
2
Turbine shaft runout mm (in)Service limit 0.011 (0.00043)
Inner diameter of the seal ring insertion part
mm (in)
Service limitH 14.05 (0.5531)
H
1F-14 Exhaust System
Thrust collar• Measure the thrust collar thickness (K), and
replace with new one if it exceeds the service limit.
Thrust bearing• Replace the compressor-side and the turbine-side
thrust bearings with new ones.
Floating metal• Replace the floating metal with new one.
Bearing housing• Check the casting surface for peeling from
oxidation-deterioration, dent or crack. Replace withnew one if faulty.
G coupling• Replace with new one.
Seal ring• Replace with new one.
Others• Check the bolts for deformation, and replace with
new ones if faulty. Also, replace the Plate smallscrew with new one.
Seal ring groove width G mm (in)Service limit
G 1.52 (0.0598)
Thickness of thrust collar mm (in)Service limit
K 2.950 (0.11614)
mm (in)Location Service limit
Bearing housing inner diameter (B) 16.11 (0.6343)
Turbine-side seal ring insertionpart
(F) 17.03 (0.6705)
Turbine-side thrust bearingpress-fit part inner diameter
(L) 23.02 (0.9063)
K
G
F B L
Exhaust System 1F-15
Assembly of TurbochargerAssembly diagram: Assemble in the order of the numbers.
Assembly Procedure1. Bearing Housing2. Snap Ring3. Floating Metal4. Thrust Bearing5. Seal Ring6. Heat Protector7. Turbine Shaft8. Thrust Collar9. Thrust Bearing
10. Gasket11. Turbine Housing12. G Coupling13. Seal Ring14. Oil Thrower15. Seal Plate16. Compressor Impeller17. Nut18. Compressor Housing
1
12
10
65
7
2
11
33
48
914
13
15
18
1617
1F-16 Exhaust System
Assembly1. Bearing housing• Check that the bearing housing is free of damage
and foreign matters.2. Snap ring• Install the 2 snap rings to the bearing housing with
snap ring pliers.• After assembling the floating metal (turbine side),
install the snap ring at the position shown in thefigure.
Name1. Turbine-Side Floating Metal
3. Floating metal• Apply oil to the floating metal, and assemble it to
the bearing housing.After securing it with a snap ring, assemble thecompressor-side floating metal.
Caution:• Place the snap ring with its rounded-side facing to
the floating metal.• Assemble the inner snap ring with its end gap
facing to the oil outlet-direction of the housing, toprevent it from blocking the oil path.
• Assemble the turbine-side snap ring to the housingwith its end gap facing to the direction as shown inthe illustration.
• Apply oil to the floating metal before assembly.
Name1. Apply Oil.
4. Thrust bearinga. Press-fitting of turbine-side thrust bearing• Press-fit the turbine-side thrust bearing into the
bearing housing.• Position the pawl of the turbine-side thrust
bearing for more than 2 mm (0.0787 in) apartfrom the existing press-fitting part.
• Do not press the thrust bearing pad surfaceduring press-fitting.
• The press-fit pressure must be between 215.6N 22.0 kgf and 1862 N 190 kgf.
• After press-fitting, remove the dust powderusing vacuum.
Besco super engine oil
1
1
Exhaust System 1F-17
b. After press-fitting, check the depth and flatnessof the turbine-side thrust bearing.(Depth 3.08±0.02 mm 0.1213±0.0008 in,Flatness is below 0.01 mm 0.0004 in: Seeillustration)
Name1. Common Tolerance
5. Seal ring• Insert the seal ring to the turbine shaft.• Use new seal ring.
6. Heat protector• Install the heat protector to the bearing housing.
7. Turbine shaft• Apply engine oil to the journal portion of the turbine
shaft, and insert it from the turbine side of thebearing housing.
• Take care not to damage the floating metal with theturbine shaft. Also, insert with the end gap of theseal ring facing to the oil inlet side so that its corematches with the turbine shaft.
Name1. Apply Oil.
8. Thrust collar• Apply engine oil to the thrust collar, and install ti to
the turbine shaft.9. Thrust bearing• Apply engine oil to the metal portion of the thrust
bearing, and insert it to the bearing housing.• Apply Loctite to the Plate small screw threads, and
install it using torque screwdriver.
Name1. Apply Oil.
10. Gasket• Set the gasket to the turbine housing, and install it
to the bearing housing.
WSHK0147
120
120
1
3.08
0.
02(0
.121
3 0
.000

mm(in)
Tightening torque: 3.7 N⋅m (0.38 kgf⋅m/33 lb in)
1
1
1F-18 Exhaust System
11. Turbine housing• Assemble by aligning the phase of the turbine
housing and the bearing housing with the turbinehousing positioning pin and the bearing housinghole.
12. G couplinga. Check that it does not run on the turbine
housing or the bearing housing.b. Tighten temporarily to the specified torque
using a torque wrench.
c. Hammering: Perform the hammering of (1) to(6) in the numerical order, using the followingprocedure.
d. Tighten to the specified torque using a torquewrench.
e. Perform (c) and (d) of the above step again.
Name1. Approx. 60°2. Approx. 60°3. Torque Wrench
Hammering procedure1) Using a metal hammer (Approx. 250g in
weight), lightly tap 2 to 3 times (same place),from the outer portion toward the center.
2) Do not hammer the G coupling directly. Placebrass bar between as shown in the illustration.
Name1. Approx. φ 13 mm (0.5 in)2. Hammer3. G Coupling4. Bearing Housing5. Gasket6. Heat Shield Plate7. Turbine Housing
Tightening torque: 83 N⋅m (8.5 kgf⋅m/61 lb ft)
Tightening torque: 83 N⋅m (8.5 kgf⋅m/61 lb ft)
A
3
21
1
2
3
6
5
4
WSHK0153
150 ~ 200 mm3 4
5
67
2
1
(6 ~ 8 in)
Exhaust System 1F-19
13. Seal ring• Install the seal ring to the oil thrower.• Use new one.
14. Oil thrower• Insert the oil thrower into the seal plate.• Insert with the end gap of the seal ring facing to the
oil inlet side.15. Seal plate
• Apply liquid gasket to the turbine-side flangesurface. Application thickness 0.1 — 0.2 mm(0.004 — 0.008 in) (B)
• Install the seal plate to the bearing housing.• Apply Loctite (B) to the Pot small screw threads,
and install it using torque screwdriver.
16. Compressor impeller• Insert the compressor impeller to the turbine shaft.
17. Nut• Attach the box spanner to the turbine-side shaft
end of the turbine shaft, and tighten the nut.• The nut is left-hand thread. Make sure the turning
direction.
18. Compressor housing• Apply liquid gasket to the compressor-side flange
surface of the seal plate. Illustration shown in theprevious page (A)Application thickness 0.1 — 0.2 mm (0.004 —0.008 in)
• Align the alignment marks that marked during thedisassembly, and assemble the compressorhousing to the seal plate.
Check after assembly• Make sure that the axial play and radial play of
rotor are within the specified value.Refer to the section on inspection.
ThreeBond No. 1207
Tightening torque: 23 N⋅m (2.3 kgf⋅m/17 lb ft)
Tightening torque: 7.8 N⋅m (0.80 kgf⋅m/69 lb in)
ThreeBond No. 1207
BA
Tightening torque: 7.9 N⋅m (0.81 kgf⋅m/70 lb in)
1F-20 Exhaust System
Turbocharger (4HK1)
Inspection of TurbochargerInspection
Caution:Turbocharger on 4HK1 engine cannot be overhauledstructurally.
Perform only the following inspection.• Measurement of axial play of turbine shaft
• Inspection of radial play of turbine shaftInsert a thickness gauge into the gap between thecompressor impeller and housing, and measurethe clearance.The thickness gauge to be inserted must be 0.2mm (0.0078 in) or less.
Axial play mm (in)Service limit 0.11 (0.004)
Exhaust System 1F-21
Measurement Tool
Other Material
Shape Name Part number Usage
Caliper
—
Measurement of the seal ring groove widthMeasurement of inner diameter of the seal ringinsertion partMeasurement of turbine shaft journal outerdiameterMeasurement of thrust bushing grooveclearanceMeasurement of thrust bearing thicknessMeasurement of floating metal inner/outerdiameterMeasurement of inner diameters of the centerhousing metal portion and ring portion
Dial gauge
—
Measurement of turbine shaft axial gap, radialgap and runout
Name Usage
Besco super engine oil Floating metal sliding portionThrust bushing sliding portionThrust bearing sliding portionTurbine shaft journal portion
ThreeBond No. 1207 Housing installing surface of the seal plateFlange of the compressor housing
Loctite No. 242 Seal plate tightening screw thread
1F-22 Exhaust System and Turbocharger