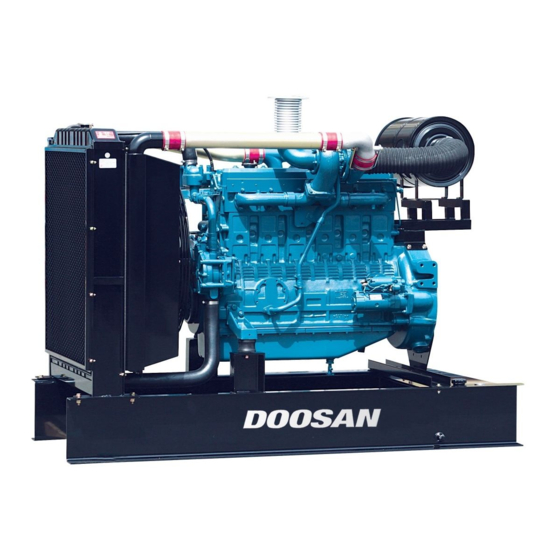
- Manuals
- Brands
- Doosan Manuals
- Engine
- DE12T
- Operation & maintenance manual
-
Contents
-
Table of Contents
-
Bookmarks
Quick Links
Related Manuals for Doosan DE12T
Summary of Contents for Doosan DE12T
-
Page 2
/P126TI /P126TI-1/DE12T. The POLUS means ‘Power Plus’ that is represented more powerful Doosan generating-set engines and it is marked on engine name as an initial P. On the other hand, intial D stands for standard engine prior to POLUS version. -
Page 3: Table Of Contents
CONTENTS <Operation> 1. Safety Regulations ……………………1 1.1. General Notes 1.4. Regulations Designed to Prevent Pollution 1.2. Regulations Designed to Prevent Accidents 1.5. Notes on Safety in Handling Used Engine Oil 1.3. Regulations Designed to Prevent Damage to Engine and Premature Wear 2.
-
Page 4
9.4. Breaking-in 10. Maintenance of Major Components ……………… 113 10.1. Cooling System 10.3. Fuel Injection Pump 10.2. Lubricating System 10.4. Turbocharger 11. Special Tool List ……………………163 • Appendix • Part & After service center • Applications for Doosan Engine… -
Page 5: General Notes
1. Safety Regulations 1.1. General Notes Handling diesel engines and the necessary resources is no problem when the personnel com- missioned with operation and maintenance are trained accordingly and use their common sense. This summary is a compilation of the most important regulations. These are broken down into main sections which contain the information necessary for preventing injury to persons, damage to property and pollution.
-
Page 6
1.2.2. During maintenance and care ¥ Always carry out maintenance work when the engine is switched off. If the engine has to be maintained while it is running, e.g. changing the elements of change-over filters, remember that there is a risk of scalding. Do not get too close to rotating parts. ¥… -
Page 7
2) If faults occur, find the cause immediately and have it eliminate in order to prevent more serious of damage. 3) Use only genuine DAEWOO spare parts. DAEWOO will accept no responsibility for damage resulting from the installation of other parts which are supposedly Òjust as goodÓ. 4) In addition to the above, note the following points. -
Page 8
Health precautions ¥ Avoid prolonged or repeated skin contact with used engine oil. ¥ Protect your skin by means of suitable agents (creams etc.) or wear protective gloves. ¥ Clean skin which has been in contact with engine oil. — Wash thoroughly with soap and water, A nailbrush is an effective aid. — Certain products make it easier to clean your hands. -
Page 9: Engine Assembly
2. General Information 2.1. Engine Assembly 2.1.1. Engine sectional view (Longitudinal) 14 15 EA8M1002 1. Cooling fan 7. Piston pin 13. Crankshaft 2. Exhaust valve 8. Piston 14. Oil pan 3. Valve spring 9. Combustion chamber 15. Connecting rod 4. Oil filter 10.
-
Page 10
2.1.2. Engine sectional view (Cross) EA8M1003 1. Intake manifold 7. Injection nozzle assembly 2. Fuel filter 8. Rocker arm 3. Oil cooler 9. Cylinder head cover 4. Injection pump 10. Exhaust manifold 5. Cylinder block 11. Piston ring 6. Oil filter 12. -
Page 11
2.1.3. Engine assembly views 1) DE12T 3 12 4 13 18 11 10 20 21 26 EA8M1004 1. Cooling fan 10. Flywheel housing 19. Thermostat 2. Cooling water pipe 11. Flywheel 20. Injection pump 3. Oil filler cap 12. Exhaust manifold 21. -
Page 12
2) P126TI / P126TI- 9 10 14 15 16 17 18 20 21 EA8M1005 1. Cooling fan 8. Oil pan 18. Injection pipe 2. Cooling water pipe 9. Starter 19. Thermostat 3. Air pipe 10. Flywheel housing 20. Injection pump (Intercooler Intake manifold) 11. -
Page 13
2.2. Engine Specification Engine Model DE12T P126TI P126TI-1 P126TI- Items Water-cooled, 4 cycle in-line Water-cooled, 4 cycle in-line type Engine type type Turbo charged Turbo charged & intercooled Combustion chamber type Direct injection type Cylinder liner type Replaceable dry liner… -
Page 14: Engine Model And Serial Number
They are also referred to as engine model and serial number because of their location. EA8O3001 ¥ Engine serial No. (example 1 : DE12T) EBHOA300001 MODEL BORE Serial No. SPEED 1500/1800…
-
Page 15: Engine Type
3.2. Engine Type The Engines DE12T/ P126TI / P126TI- are in-line vertical water-cooled 6-cylinder four-stroke diesel engines with direct injection. DE12T is turbo-charged engine, and P126TI / P126TI- models are turbo-charged and inter-cooled engine. 3.2.1. Cylinder block The cylinder block is a single piece of alloy cast iron. To increase its stiffness, it is extended to a level below the crankshaft center line.
-
Page 16: Engine Timing
3.3. Engine Timing Camshaft, oil pump and injection pump are driven by a gear train arranged at the front end. Injection pump gear Camshaft gear Water pump gear (Z = 72) (Z = 72) (Z = 29) Idle gear (Z = 52) Crankshaft gear (Z = 36) Oil pump idle gear…
-
Page 17: Lubrication System
3.5. Lubrication System The engine is equipped with force-feed lubrication. The pressure is produced by a gear pump whose drive gear is in direct mesh with the crankshaft gear at the front end of cylinder block. The oil pump draws the oil from the oil sump and delivers it through the oil cooler and oil filter to the main distributor gallery and from there to the main bearings, big-end bearings and camshaft bearings as well as to the small-end bearings and the rocker arms.
-
Page 18: Air Cleaner
3.5.1. Oil cooler An oil cooler is provided between the oil filter and the cylinder block. This cooler is a flat tube type with turbulence inserts and operated by the coolant. 3.5.2. Oil filter Check for oil pressure and oil leaks, and repair or replace the oil filter if necessary.
-
Page 19
3.7.1. Fuel filter This fuel filter has two functions not only oil filtering but also water separating. Before entering the suction chamber of the injection pump, the fuel is cleaned in a strainer of fuel feed pump and a fuel filter. Drain water in cartridge with loosening the cock under filter manually (6) from time to time. -
Page 20
Fuel oil selection chart General Fuel ASTM No. 1 No. 2 DIN 51601 Classification Test ASTM 1-D ASTM 2-D Gravity, û D 287 40 ~ 44 33 ~ 37 0.815 ~ 0.855 Flash Point D 93 100 (38) 125 (52) 131 (55) û… -
Page 21
3.8. Cooling System The engine has a liquid-cooling system. The fresh water pump is a maintenance-free by gear from the crankshaft. Depending on the agreed extent of delivery and the design of the engine, the coolant circuit can be equipped with temperature monitors which, in the event of loss of coolant, shut the engine down. -
Page 22
For the improper control might give the fatal damage to the cooling water pump and cylinder liners, detail care is needed. ¥ Since DE12T , P126TI and P126TI- cylinder liner is dry type, particularly the cooling water control should be applied thoroughly. -
Page 23
Note : In taking the cooling water sample, if the water in auxiliary tank were taken, it is hard to measure the accurate density. Take the cooling water sample necessarily loosen- ing the cooling water discharge plug. 2) At the state of a test paper soaked in the sampled water, after taking the paper out through water agitation, shake off the water. -
Page 24
3.9. V-belt Tension Check and Adjust By the finger-pressure the belt is pressed by Press hear here 10mm ~ 15mm between the fan pulley and 15mm the alternator pulley in normal condition. For Alternator the adjustment of the tension, loosen the Pulley Pulley adjusting bolts which support the alternator,… -
Page 25: Electrical Equipment
3.11. Electrical Equipment 3.11.1. Alternator The alternator is fitted with integral silicon rectifiers. A transistorized regulator mounted on the alternator body interior limits the alternator voltage. The alternator should not be operated except with the regulator and battery connected in circuit to avoid damage to the rectifier and regulator.
-
Page 26
3.11.2. Starter motor The sliding-gear starter motor is flanged to the rear of the flywheel housing on the left-hand side. When the starting key switch is turned on, the starter motor pinion flies out and engages the ring gear of the flywheel. Then the main contact is closed, current flows, and the engine is started. -
Page 27: Preparation
4. Commissioning and Operation 4.1. Preparation At the time of initial commissioning of a new or overhauled engine make sure to have observed the ÒTechnical Information for the installation DAEWOO generator enginesÓ. ¥ Oil filler neck on cylinder head cover Before daily starting of the engine, check the fuel, coolant and oil level, replenish if necessary.
-
Page 28
At the end of the break-in period, remove break-in oil and replace the oil filter. Fill oil pan with recommended engine oil. Refer to following table. <Engine Oil capacity> Oil pan (only) DE12T 23 liter P126TI/P126TI- 23 liter 4.2.3. Operating after break-in When starting a cold engine, always allow the engine to warm up gradually. -
Page 29: Inspection After Starting
4.3. Inspections after Starting During operation the oil pressure in the engine lubrication system must be monitored. If the mon- itoring devices register a drop in the lube oil pressure, switch off the engine immediately. And the charge warning lamp of the alternator should go out when the engine is running. ¥…
-
Page 30
4.5. Tuning the Engine The purpose of an engine tune-up is to restore power and performance thatÕs been lost through wear, corrosion or deterioration of one or more parts or components. In the normal operation of an engine, these changes can take place gradually at a number of points, so that itÕs seldom advisable to attempt an improvement in performance by correction of one or two items only. -
Page 31: Periodical Inspection And Maintenance
5. Maintenance and Care 5.1. Periodical Inspection and Maintenance In order to insure maximum, trouble-free engine performance at all times, regular inspection, adjustment and maintenance are vital. ¥ Daily inspections in below figure should be checked every day. ¥ The maintenance should be executed thoroughly at regular intervals. (Refer to «…
-
Page 32
5.2.3. Oil exchange procedure While the oil is still hot, exchange oil as fol- lows: ¥ Take out the oil dip dipstick. ¥ Remove the drain valve from oil pan and the drain plug form oil filter head, then drain out the engine oil into a container. Drain Plug EA8O5001 ¥… -
Page 33
¥ Recommend of lubricating oil Initial factory filling is high quality break-in oil (API Service CH-4 grade). During the break- in period (50 hours), check the oil level frequently. Somewhat higher oil consumption is nor- mal until piston rings are seated. The oil level should be maintained in the safe range between Min. -
Page 34: Cooling System
5.2.4. Replacement of oil filter cartridge At the same times of oil exchanges, replace the oil filter cartridge. ¥ Drain engine oil by loosening the drain Cartridge plug on the filter head. Caution : DonÕt forget tightening the drain plug after having drained engine oil.
-
Page 35
c) Loosen the coolant drain plug. Loosen the coolant drain plug of the cylinder block. EAMD001I Caution : When removing the pressure filler cap while the engine is still hot, cover the cap with a rag, then turn it slowly to release the internal steam pressure This will pre- vent a person from scalding with hot steam spouted out from the filler port. -
Page 36
5.3.3. Intercooler The intercooler is air to air type and has a large cooling fan capacity. The intercooler life and performance depends on the intake air condition greatly. Fouled air pollutes and clogs the air fins of intercooler. As a result of this, the engine output is decreased and engine malfunction is occurred. -
Page 37: Air Intake System
5.4. Air Intake System 1. Connection port, fouling indicator 2. Cleaner housing 3. Clamp 4. Element 5. Hexagon nut 6. Cover 7. Dust bowl EA6O5012 5.4.1. Maintenance (only when engine is switched off) Empty the dust bowl (7) regularly. The bowl should never be filled more than halfway with dust. On slipping off the two clamps (3), the dust bowl can be removed.
-
Page 38
5.4.3. Cleaning filter elements ¥ By compressed air (Wear goggles) For the purpose, the air gun should be fit- ted with a nozzle extension which is bent û at the discharge end and which is long enough to reach down inside to the bottom of the element. -
Page 39: Fuel System
5.5. Fuel System 5.5.1. Fuel filter ¥ After every 200 hour of operation, drain the water and sediment from the fuel- water separator. ¥ Shut off the engine. Use your hand to open the drain valve ¥ Turn the valve counter clockwise approxi- mately 2 ~ 3 turns until draining occurs.
-
Page 40
5.5.3. Fuel system checks Fill the tank with the recommended fuel. Keeping tanks full reduces water condensation and helps keep fuel cool, which is important to engine performance. Make sure fuel supply valves (if used) are open. To insure prompt starting and even running, the fuel system must be primed with the fuel feed pump manually before starting the engine the first time, or after a fuel filter change. -
Page 41
5.5.5. Priming pump strainer cleaning Clean the priming pump strainer every 200 operation hours. The strainer is incorporated in the priming pump inlet side joint bolt. Clean the strainer with the compressed air and rinse it in the fuel oil. Strainer(Inner) EA7O5009 5.5.6. -
Page 42
¥ Check injection pressure, and adjust the nozzle using the adjusting shim if the pressure does not meet the specified limit. ¥ Check nozzle spray patterns and replace if damaged. DE12T P126TI / P126TI- 1st : 160kg/cm Opening pressure 220kg/cm… -
Page 43
5.7. Turbocharger 5.7.1. Maintenance (by authorized specialist personnel) The turbochargers do not call for any specific maintenance. The only points to be observed are the oil pipes which should be checked at every oil change for leakage and restrictions. The air cleaners should be carefully serviced. Furthermore, a regular check should be kept on charge air exhaust gas pipes. -
Page 44
Dial gauge Magnetic vise Outlet Move the turbine shaft Radial play in both directions Limit of wear : 0.57mm simultaneously Oil inlet EA4M2018 — 40 -… -
Page 45: Adjustment Of Valve Clearance
6. Checking and Setting 6.1. Adjustment of Valve Clearance 6.1.1. General information The valve clearances are to be adjusted at the times of the following situations. ¥ After initial 50 hourÕs operation. ¥ When the engine is overhauled and the cylinder heads are disassembled. ¥…
-
Page 46
Loosen the lock nuts of the rocker arm adjusting screws and push the specified feeler gauge and adjust the valve clearance with adjusting screw respectively. Model Intake Valve Exhaust Valve DE12T 0.3 mm 0.3 mm P126TI / P126TI- 6.1.3 Method of adjusting the valve clearance… -
Page 47: Adjustment Of Injection Timing
Check hole flywheel clockwise until showing the notch mark of the right figure corresponding to the injection timing is aligned with the pointer ( ) on the flywheel housing. DE12T P126TI/P126TI- Fuel injection timing 12¡ 16¡ (B.T.D.C static) Injection timing…
-
Page 48
¥ Tighten the coupling fixing bolts and nuts to specified torque. 6.0 kg . m Torque EAMD021I ¥ Tighten the drive shaft connecting flange fixing bolts to specified torque. 7.5 ~ 8.5 kg . m Torque ¥ Install the oil delivery pipe and return pipe. 6.3. -
Page 49
6.4. V-belts The tension of the V-belts should be checked after every 2,000 hours of operation. (1) Change the V-belts if necessary If in the case of a multiple belt drive, wear or differing tensions are found, always replace the complete set of belts. -
Page 50
75 kg 70 kg 60 kg 20.2 mm 75 kg 70 kg 60 kg : Adopted in DE12T and P126TI / P126TI- (5) Tensioning and changing V-belt ¥ Remove fixing bolts. (1) ¥ Remove lock nut. (2) ¥ Adjust nut (3) until V-belts have correct tensions. -
Page 51: Periodic Inspection Cycle
7. Operation Tip 7.1. Periodic Inspection Cycle : Check & adjust : Replace Every Every Every Every Every Inspection Daily Remark 50hrs 200hrs 400hrs 800hrs 1200hrs Check for leakage(hoses, clamp) Check the water level Cooling Change the coolant water System Every Adjust the V-belt tension 2,000hrs…
-
Page 52: Trouble Shooting
7.2. Trouble Shooting 1. Engine Starting Impossible Starting motor operation poor Starting motor revolution Inspection of battery electorlytic Engine Fuel Ilquid amount & gravity Inspect air cleaner Inspect amount of fuel Normal Too low Normal None Normal Polluted Ajustment Recharging Replace or Replenish clean element…
-
Page 53
2. Engine Overheated Operating state 1. Overload 2. Radiator core clogged Fuel unit Cooling unit 3. Continuous over-run Check coolant Fuel excessive supply Inspect fuel quality Normal Too low Poor Check fan belt Clean and replace Repair Check injection nozzle tension wear with specilied fuel Replace… -
Page 54
3. Output Insufficient Engine Installation improper Check for coupling Fuel unit Others alignemnt Check for air mixing Inspect air cleaner Adjust or replace in fuel coupling Normal Clean Relpace Inspect fuel supply pump Inspect air leakage Inspect engine control Normal Clean Replace of air piping line rod, link, cable, etc. -
Page 55
4. Oil pressure lowered Check if oil pressure gauge indicates wrongly Check oil amount Too low Normal Use recommended oil Check cooling (replenish) temperature Too high Normal Refer to engine overhea Inspect oil quality Normal Check oil relief Water & fuel mixed Improper valve in oil… -
Page 56
5. Fuel Consumption Excessive Causes according to Use Conditions 1. Overload 2. Govemor’s Arbitrary Adjustment 3. Full Speed Operation for Long time 4. Sudden Speed Change from Low to Inspect fuel leakage High Speed Normal Oil leakage Inspect injection nozzle (injection pressure Adjust Replace atomizing state etc.) -
Page 57
6. Oil Consumption Excessive Cause according to use conditions 1. Excessive oil infusing 2. Continuous operation in low or extremely cold state Inspect oil leakage Inspect air cleaner Clean Replace Normal Oil leakage Check oil quality Internal External Retighten Check compressed Replace with Replace pressure… -
Page 58
8. Battery Discharge Generator Wiring Switch Battery Inspect cut wire Check fan belt Check electrolytic shorts and loose tension & damage liquid amount connections Repair Replace Normal Battery over Battery self Battery room Electrolytic charging discharge damage liquid’s standard Inspect generator Charging Voltage regulator Replace… -
Page 59
7.3. Causes and Remedies Condition Causes Remedies ¥ ValveÕs poor shut, stem distortion Repair or replace 1) Starting difficult ¥ (1) Compression pressure Valve spring damage Replace valve spring ¥ Cylinder head gasketÕs leak Replace gasket ¥ Wear of piston, piston ring or liner Adjust ¥… -
Page 60
Condition Cause Remedies 5) Engine noisy For noises arise compositely such asrota ting parts, lapping parts etc., there is nec essity to search the cause of noises accu rately. ¥ (1) Crankshaft As the wear of bearing or crankshaft Replace bearing & progress, the oil clearances increase. -
Page 61
Condition Cause Remedies 7) Oil Consumption Excessive ¥ (1) Oil level elevated Clearance between cylinder iner & Replace piston ¥ Wear of piston ring, ring groove Replace piston, piston ring ¥ Piston ringÕs damage, stick, wear Replace piston ring ¥ Piston ring openingÕs disposition Correct position improper… -
Page 62: General Information
8. General Information 8.1. General Repair Instructions 1. Before Performing service operation, disconnect the grounding cable from the battery for reducing the chance of cable damage and burning due to short-circuiting. 2. Use covers for preventing the components from damage or pollution. 3.
-
Page 63
POLUS P126TI, P126TI- DE12T (DE12 series) generator diesel engines discharge very low level of haz- ardous exhaust gases such as smoke, nitro- gen oxide, hydrocarbon, or carbon monoxide and thus ensure high performance and low fuel consumption. -
Page 64
9. Disassembly and Reassembly of Major Components 9.1. Disassembly 9.1.1. General precautions ¥ Maintenance operation should be carried out in a bright and clean place. ¥ Before disassembly, provide parts racks for storage of various tools and disassembled parts. ¥ Arrange the disassembled parts in the disassembly sequence and use care to prevent any damage to them. -
Page 65
9.1.3. Engine oil ¥ Take out the oil dipstick. ¥ Remove the oil drain valve of oil pan and drain out the engine oil into a prepared container. Drain valve EA8O5001 9.1.4. Alternator belt ¥ Loosen the tension adjusting nut installed on the alternator bracket, and take off the alternator belt. -
Page 66
9.1.7. Guide tube of oil level gauge ¥ Loosen the flange nut installed on the oil pan to remove the guide tube. EQM3005I 9.1.8. Fuel filter ¥ Remove fuel hoses connected to the fuel injection pump, take off the bracket fixing bolts, then disassemble the fuel filter. -
Page 67
9.1.11. Injection pipe ¥ Unscrew the hollow screws to disassem- ble the fuel return pipe. ¥ Remove the nuts installed on the fuel injection pump and nozzles, then disas- semble the injection pipe. EQM3009I 9.1.12. Intake manifold ¥ Remove the air hose connected to the fuel injection pump. -
Page 68
9.1.14. Exhaust manifold ¥ Release the exhaust manifold fixing bolts, disassemble the exhaust manifold, then remove the heat shield and gasket. NOTE : Make sure to release the nuts one after another because the exhaust manifold will removed if you unscrew two nuts simultaneously. -
Page 69
9.1.17. Water pump ¥ Remove the water pipe connected to the expansion tank. ¥ Remove the water pipe and hoses con- nected to the water pump. ¥ Unscrew the water pump fixing bolts and remove the water pump. 9.1.18. Injection pump ¥… -
Page 70
9.1.20. Fan drive pulley ¥ Remove the bolts and disassemble the fan drive pulley. 9.1.21. Vibration damper ¥ Unscrew the pulley fixing bolts and dis- assemble the pulley-vibration damper assembly. ¥ Unscrew the vibration damper fixing bolts and disassemble the damper from the pulley. -
Page 71
9.1.24. Fuel injection pump drive assembly ¥ Unscrew the injection pump drive shaft bearing housing fixing bolts and remove the injection pump drive assembly which the shaft, gear, bearings, and housing are put together. EAMD027I 9.1.25. Cylinder head cover ¥ Unscrew the cover fixing bolts and dis- assemble the cover. -
Page 72
9.1.28. Cylinder head ¥ Unscrew the cylinder head fixing bolts and take off the cylinder head. ¥ Remove the cylinder head gasket. EAMD031I 9.1.29. Valve and valve stem seal ¥ Compress the valve spring retainer using a jig and take off the valve cotter pins. ¥… -
Page 73
9.1.31. Oil pan ¥ Stand the engine with the flywheel hous- ing facing the bottom. ¥ Release the oil pan fixing bolts, remove the stiffeners then disassemble the oil pan. EAMD034I 9.1.32. Oil pump and oil pipe ¥ Unscrew the oil suction pipe bracket bolts, releasing the pipe fixing bolts, then disassemble the oil suction pipe assem- bly. -
Page 74
¥ Remove the piston pin snap rings, take off the piston pin, then disconnect the connecting rod from the piston. ¥ Disassemble the piston rings using ring pliers. ¥ Use care not to interchange the disas- sembled parts and keep them in the sequence of cylinder No. -
Page 75
9.1.37. Oil seal ¥ Take off the rear oil seal using an oil seal disassembling jig. ¥ If only the inside guide ring is removed, use a special tool to take off the outside seal. 9.1.38. Flywheel housing ¥ Loosen the housing fixing bolts disas- semble the flywheel housing. -
Page 76
9.1.41. Timing gear case ¥ Unscrew the case fixing bolts and disas- semble the timing gear case. EAMD046I 9.1.42. Crankshaft ¥ Remove the bolts from bearing caps. ¥ Remove the main bearing cap fixing bolts in the order of assembling. ¥… -
Page 77
9.2. Inspection 9.2.1. Cylinder block 1) Clean the cylinder block thoroughly and make a visual inspection for cracks or damage. 2) Replace if cracked or severely damaged, and correct if slightly damaged. 3) Check oil and water flow lines for restriction or corrosion. 4) Make a hydraulic test to check for any cracks or air leaks.(Hydraulic test) : Stop up each outlet port of water/oil passages in the cylinder block, apply air pressure of about 4kg/cm… -
Page 78
3) flatness Measure flatness of the intake/exhaust manifolds fitting surfaces on the cylinder head using a straight edge and a feeler gauge. Standard Limit 0.05 mm 0.2 mm 4) Hydraulic test Hydraulic test method for the cylinder head is same as that for cylinder block. 9.2.3. -
Page 79
• Valve head thickness Measure the valve head thickness, and replace the valve if the measured value is beyond the limit. Dimension Standard Limit Description Intake valve 1.5 mm 1 mm or less Exhaust valve 1.5 mm 0.9 mm or less EFM2037I 2) Valve guide Install the valve into the valve guide and… -
Page 80
3) Valve seat • Contacting face amount Measure the contacting face between intake valve and exhaust valve seat for valve seat wear, and replace if the mea- sured value exceeds the specified limit. Valve contact width Contact width ✝✞✟✏❆☛✌ Standard Limit 1.5 mm 2.0 mm… -
Page 81
For assembling of a new valve seat, by putting it among the dry ices of an ice box previ- • ously for about 2 hours for the cold shrinkage, and press it in the cylinder head by a special tool. (bench press) Apply the valve lapping compound on the valve head seating face and lap the valve seat by •… -
Page 82
• Valve spring tension Use a spring tester to measure the valve spring tension if the measured value is less than the specified limit, the valve spring must be replaced. Spring Set Length Limit force Spring tester Valve Spring Intake 61.8 ~ Tension at 37mm 61.8 kg… -
Page 83
2) Rocker arm • Visual check Visually check the face of the rocker arm in contact with the valve stem end for scores and step wear. If the wear is small, correct it with an oil stone or grind- ing paper of fine grain size. Rocker arm with a considerable amount of step wear should be replaced. -
Page 84
• Visual check of tappet Visually check the face of the tappets in contact with the cam for pitting, scores or cracks, and replace if severely damaged. If the amount of cracks or pitting is small, Unevenness Crack Normal correct with an oil stone or grinding ❘❏❆✔✠✟☛… -
Page 85
9.2.5. Cam shaft 1) Cam • Cam lobe height Standard Limit Cam journal diameter(A,B) 59.86 ~ 59.88 mm 59.52 mm Use a micrometer to measure the cam journal diameter. I II If the measured number is less than the I II specified limit, camshaft… -
Page 86
• Run-out Support the camshaft on two V blocks and check for run-out using a dial indi- cator. Correct or replace the cam shaft if the amount of run-out is beyond the value indicating need for servicing. Standard Limit 0.05 mm 0.2 mm EA0M4066 3) Cam shaft end play… -
Page 87
2) Wear With an outside micrometer measure the • diameter of the crankshaft journals and pins in the directions as shown, and compare the measured values to deter- mine the amount of wear. If the amount of wear is beyond the limit, •… -
Page 88
3) Crankshaft run-out Support the crankshaft on V blocks. • Turn the crankshaft with a dial indicator • placed on the surface plate and take the amount of crankshaft run-out. Standard Limit 0.05 mm 0.1 mm 9.2.7. Crank shaft bearing and connection rod bearing 1) Visual check Visually check the crankshaft bearing and connecting rod bearing for scores, uneven… -
Page 89
• Connecting rod bearing clearance Install the connecting rod bearing in the connecting rod bearing cap, tighten the connecting rod cap bolts to the specified torque, then measure the inside diame- ter. • 28 kg Torque 83.02 ~ 83.092 mm Standard Dia. -
Page 90
Spread = O A — O B EDM2047I • Crankshaft bearing crush Install the bearing and cap in the cylinder block, retighten the bolts to specified torque, unscrew out one bolt completely, then measure the clearance between the bearing cap and cylinder block using a feeler gauge. -
Page 91
9.2.8. Piston 1) Visual check Visually check the pistons for cracks, scuff or wear, paying particular attention to the ring groove. 2) Clearance between the piston and cylinder liner With an outside micrometer, measure • the piston outside diameter at a point 18mm away from the lower end of pis- ton skirt in a direction at a right angle to the piston pin hole. -
Page 92
9.2.9. Piston rings 1) Visual check Replace the piston rings with new ones if detected worn or broken when the engine is overhauled. 2) Piston ring gap Insert the piston ring into the upper por- • tion of the cylinder liner bore so that it is held at a right angle to the cylinder liner wall. -
Page 93
4) Piston ring tension With a tension tester, measure piston ring tension. Replace the piston ring if the measured value is beyond the limit. Standard Top ring 2.27 ~ 3.41 kg 2nd ring 2.0 ~ 3.0 kg Oil ring 4.03 ~ 5.57 kg 9.2.10. -
Page 94
9.2.11. Connecting rod 1) Distorsion Check the connecting rod for distortion. As shown in the figure below, install the connecting rod to the connecting rod tester, and check for distortion using a feeler gauge. If the connecting rod is found distorted, never re-use it but replace with a new one. -
Page 95
9.3. Reassembly 9.3.1. General precautions ¥ Wash clean all the disassembled parts, particularly oil and water ports, using compressed air, then check that they are free from restrictions. ¥ Arrange the general and special tools in order for engine assembly operation. ¥… -
Page 96
¥ Apply engine oil to the entire face of the tappets and slide them into the tappet holes on the cylinder block. ¥ Wet the cam bush inside diameter and camshaft with oil, and carefully assem- ble them while turning the camshaft. ¥… -
Page 97
¥ Semi-tighten a bolt at both sides of the crankshaft, apply engine oil to journals and pins, then assemble the crankshaft with the cylinder block by tightening the fixing bolts. ¥ Install the oiled thrust washers with the oil groove facing outward. ¥… -
Page 98
¥ Apply oil to the entire part of the bearing cap bolts, then tighten in tightening sequence to specified torque. ¥ Torque 30 kg ¥ After semi-tightening both bolts evenly, tighten them diagonally specified torque using a torque wrench as follows. EQM3059I <Tightening order>… -
Page 99
9.3.8. Flywheel ¥ Install a guide bar into a bolt hole on the crank shaft, and lift the flywheel to align the dowel pin with the pin hole on the fly- wheel for temporary assembly opera- tion. ¥ Install bolts in the remaining holes, take out the guide bar, then install a bolt in the hole where the guide bar had been inserted. -
Page 100
9.3.11. Timing gear ¥ Install the oil pump idle gear onto the No.7 bearing cap. ¥ Install a thrust washer over the camshaft Idle gear pin and assemble the cam gear by aligning it with camshaft key groove. Torque 3.1 kg ¥… -
Page 101
9.3.12. Timing gear case cover ¥ Install dowel pin on the timing gear case. ¥ Mount a gasket by aligning the fixing bolt holes with those on the gasket. ¥ Align the dowel pin with the cover pin hole, then install the cover with light tap. ¥… -
Page 102
9.3.15. Piston and connecting rod ¥ Use a piston heater to heat the piston approximately 100 ûC (212 ûF ) for 5 min- utes. ¥ Align the piston pin hole with the oiled connecting rod small end and press the piston pin (by lightly tapping with a rub- ber hammer) to assemble the connect- ing rod with the piston. -
Page 103
¥ Identify the mark «Y» or «TOP» on the ring end to prevent the top and bottom of the piston ring is interchanged each other and make the marked top face upward. Note : Be sure to make the piston ring end marked face(«Y»… -
Page 104
¥ Wet the fixing bolts with oil, semi-tighten them with hand, tighten them to specified torque using a torque wrench as follows. <Tightening order> (1) First stage : Coat engine oil over bolts (2) Second stage : Temporary screw the bolt about 1 ~ 2 threads (3) Third stage : With torque wrench, tighten at about 15 kg.m (4) Fourth stage : With torque wrench, tighten up to about 22 kg.m (5) Fifth stage : Finally, tighten in the specified torque 28kg.m with torque wrench . -
Page 105
9.3.18. Oil pan ¥ Mount gasket and put the oil pan there- ¥ Place stiffeners and tighten bolts. ¥ Align the bolt holes with gasket holes to prevent damage to the gasket and tight- en to specified torque. Torque 2.2 kg ¥… -
Page 106
9.3.20. Nozzle tube ¥ Apply sealant (LOCTITE # 620) to the nozzle tube and place the O-ring over the cylinder head fitting face on the nozzle tube, then install the nozzle tube in the cylinder head. ¥ Install a guider of the nozzle tube insert assÕy (Guider + Expander) the cylinder Guider head, then tighten the nozzle fixing nuts. -
Page 107
¥ Check the inside of combustion chamber for foreign substances, and carefully mount the cylinder head assembly in the block by aligning the dowel pin with the dowel pin hole. Be careful not to damage the head gasket. If the dowel pin is not in alignment, lift the cylinder head again and then remount it. -
Page 108
As for the valve clearance, adjust it when in cold, as follow. Model Intake Valve Exhaust Valve DE12T 0.3 mm 0.3 mm P126TI / P126TI- — By cranking the engine, let #6 cylinderÕs valves overlap. -
Page 109
¥ Adjust valve clearance with a feeler Valve clearance adjust gauge and tighten the fixing nuts to specified torque. 4.4 kg . m Torque EA8M3007 9.3.22. Rocker arm assembly ¥ Apply lubricating oil to the rocker arm bush and shaft, and assemble the inter- mediate bracket with the rocker arm using fixing bolts. -
Page 110
9.3.24. Oil cooler ¥ Install the oil cooler onto the oil cooler cover. ¥ Carefully apply the gasket to prevent oil leakage. ¥ Do not damage the gasket and install the cover onto the cylinder block. ¥ Connect a connection pipe between the water pump and oil cooler. -
Page 111
( ) on the fly- wheel housing. DE12T P126TI/P126TI- Fuel injection timing 12¡ 16¡ (B.T.D.C… -
Page 112
¥ Tighten the Coupling fixing bolts and nuts to specified torque. Torque 6.0 kg ¥ Tighten the drive shaft connecting flange fixing bolts to specified torque Torque 7.5 ~ 8.5 kg EAMD021I ¥ Install the oil delivery pipe and return pipe. -
Page 113
9.3.30. Power take-off ¥ Assemble the power take-off sub assem- bly. EA8M3010 9.3.31. Exhaust manifold ¥ Install the exhaust manifold gasket over the stud bolts by aligning the gasket with the exhaust port on the cylinder head so that the face and back of the gasket can be positioned correctly. -
Page 114
9.3.33. Starter ¥ Assemble the starter in position on the flywheel housing. ED5OM009 9.3.34. Intake manifold ¥ Fit a gasket on the intake manifold before assembling the intake manifold. EQM3011I 9.3.35. Injection pipe & fuel return pipe ¥ Assemble the injection pipe according to specified torque as blow Nut size Torque… -
Page 115
9.3.36. Fuel filter ¥ Assemble the fuel filter with the intake manifold. ¥ Assemble the fuel feed hose according to the direction of an arrow impressed on the fuel filter head so that fuel can be fed in the sequence of FUEL FEED PUMP FUEL FILTER FUEL INJECTION PUMP. -
Page 116
9.3.39. Cooling fan ¥ Install the cooling fan and flange, then tighten the fixing boltd. EQM3106I 9.3.40. V- belt ¥ Install the V-belt on the crank pulley, Press here alternator pulley and fan drive pulley. 15mm ¥ Adjust the V-belt tension using the ten- Alternator sion adjusting bolt. -
Page 117
10. Maintenance of Major Components 10.1. Cooling System 10.1.1. General information This engine is water-cooling type. Heat from the combustion chamber and engine oil heat are cooled down by coolant and radiated to the outside, resulting in the normal operation of the engine. -
Page 118
10.1.2. Water pump ¥ Loosen the bolt (16) to disassemble the housing cover (15). ¥ Heat the impeller (6) slightly, then remove it using a puller jig. ¥ Remove the mechanical seal. ¥ Unscrew the socket bolt (12) and remove the shaft and bearing assembly from the housing. ¥… -
Page 119
10.1.3. Thermostat ¥ General descriptions and main data To radiator The thermostat maintains a constant tem- û perature of coolant (71 ~ 85 C) and improves thermal efficiency of the engine by preventing heat loss. Namely, when the temperature of coolant Bypass is low, the thermostat valve is closed to valve… -
Page 120
10.1.4. Diagnostics and troubleshooting Complaints Possible causes Corrections ¥ ¥ 1. Engine overheating Lack of coolant Replenish coolant ¥ ¥ Radiator cap pressure Replace cap valve spring weakened ¥ ¥ Fan belt loosened or Adjust or replace fan belt broken ¥… -
Page 121: Lubricating System
10.2. Lubricating System 10.2.1. General descriptions and main data ¥ General descriptions All the engine oil pumped up from the oil pan by the gear type oil pump is filtrated through the oil cooler and oil filter, and this filtrated oil is forced through the main oil gallery in the cylinder block from where it is distributed to lubricate the various sliding parts, and fuel injection pump in order to ensure normal engine performance.
-
Page 122
10.2.2. Oil pump ¥ Disassembly (1) Disassembly of oil pump drive gear a .Unscrew the screw and disassem- ble the oil relief valve. b. Unfold the washer for the oil pump drive gear fixing nut and remove the nut. c. Disassemble the drive gear. EQM4006I (2) Remove the oil pump cover fixing nuts and disassemble the oil pump cover. -
Page 123
(3) Measuring clearance between drive shaft and bushing a. Measure the outside diameters of the drive shaft and driven shaft, and replace if the measured values are less than the limit. Limit 16.95 mm b. Measure the inside diameter of the pump body bushing to determine the clearance between the bushing and shaft, and compare the measured value with the standard value to determine whether to replace or not. -
Page 124
10.2.4. Diagnostics and troubleshooting Complaints Possible causes Corrections ¥ ¥ 1. Oil consumption Poor oil Use suggested oil ¥ ¥ excessive Oil seal or packing leaky Replace ¥ ¥ Pistons or piston rings worn Replace pistons and/or pis ton rings ¥… -
Page 125: Fuel System
10.3. Fuel Injection Pump 10.3.1. General information of fuel system The fuel system consists of the fuel tank, injection pump, injection nozzle, fuel filter, and fuel lines such as pipes and hoses necessary to connect those components. EA8O3004 1. Fuel filter 7.
-
Page 126
Make sure that servicing should be performed at the professional maintenance shop as authorized by Bosch or Zexel Company. For adjustment of fuel injection volume, refer to the ÔSpecifications of fuel injection pumpÕ described on the following pages. 1) DE12T (1) Main data and specifications Part No. : 65.11101-7222(106672-9920) -
Page 127
(8) Governor adjustment Rack limit over 14 11.0 10.8 Idle spring Set : 6.5 -0.5 +5 _ 250 400 PUMP SPEED (rpm) EA8M4001 — 123 -… -
Page 128
2) P126TI / P126TI- (1) Main data and specifications Part No. : 65.11101 -7310 (106674-4130 ZEXEL) Model : NP-PE6P120/700RS3S (106067-6020) Governor : Ghana Control (DWA-2000) Plunger & barrel 12, right hand double helix 30 lead Delivery valve : 90mm /st ( 7 x 2.35mm) Fuel feed pump : NP-FP/KD-PS (105237-5470) Pre-stroke… -
Page 129
10.3.3. Governor System (P126TI/ P126TI- ) Governor system for fuel injection pump consists of ÒIntegral ActuatorÓ and ÒSpeed Control UnitÓ. 10.3.3.1. Integral actuator EC2OM316 <Dimension View> Fig. No. Description QÕty Remark Frame Bearing retainer kit AssÕy Mounting bar SWP connector Mg610320 Front cover T3.2… -
Page 130
10.3.3.2. Speed Control Unit for Governor System (DWC-2000 SERIES SPEED CONTROL UNIT) <Introduction> This speed control unit performs the electronic function of the engine governing system. The speed control unit senses the pulses from the magnetic speed sensor, compares them with the speed control unit’s set point and supplies the appropriate current output to the actuator to control the engine’s fuel system. -
Page 131
The engine speed signal is usually obtained from a magnetic speed sensor mounted in close prox- imity to the teeth of a ferrous ring gear that is driven by the engine. The frequency of the speed sen- sor signal is proportional to the engine speed. The speed control unit will accept any signal if the fre- quency is proportional to engine signal, and in the frequency range of the speed control unit (1K to 7.5K Hz.). -
Page 132
1) Specification ¥ Performance Isochronous Operation / Steady State Stability ……….±0.25% or better Speed Range/Governor …………….. 1K~7.5 K Hz continuous Speed Drift with Temperature …………….±0.5% Maximum Idle Adjust CW ………………..60% of set speed Idle Adjust CCW ………….É.É……..Less than 1200Hz Droop Range …………É..ÉÉ…… -
Page 133
Reset Crank Overspeed Crank Test Speed Gain : DWC-2000 Stability : DC24V : 65.11220-7006 Starting GHANA CONTROL Fuel 826-1 Kuro 3-Dong, Duro-Gu Seoul 152-053 KOREA(DONG-IL TECKNO-TOWN) MADE IN KOREA Speed Ramping Idle Idle Speed Trim Droop Droop Autuator Pic-up Battery AUX 10V 10V POWER AUX. -
Page 134
2) Application and installation information The speed control unit is rugged enough for mounting in a control cabinet or engine mounted enclo- sure or in a remote console up to 20 meters(65ft.) from the engine. Care should be taken to insure that the speed control unit, mount it vertically so that condensation will not accumulate in the speed control unit. -
Page 135
¥ Start engine The speed control unit governed speed setting is factory set at approximately engine idle speed. Crank the engine with DC power applied to the governor system. The actuator will energize to the maximum fuel position until the engine starts. The governor system should control the engine at a low idle speed. -
Page 136
Method 2 : Start the engine and control at an idle speed for a period of time prior to accelerating to the operating speed. This method separates the starting process so that each may be optimized for the lowest smoke emissions. Replace the connection between Terminals M &… -
Page 137
¥ Accessory input The AUXiliary Terminal N accepts input signals from load sharing units, auto synchronizers, and other governor system accessories, DWC accessories are directly connected to this terminal. It is recommended that this connection from accessories be shielded as it is a sensitive input terminal. If the auto synchronizer is used alone, not in conjunction with a load sharing module, a 3M ohm resistor should be connected between Terminals N and P. -
Page 138
¥ OVERSPEED shutdown setting DWC-2000 has a Test switch to determine the OVERSPEED set point and test the engine shut- down function. If you want to adjust the OVERSPEED set point at the speed about 10% higher than the RUN set speed, use the Test switch. When the engine is operating at the Run set speed in pushing the Test switch, rotate the Overspeed Adjust. -
Page 139
¥ Unsatisfactory performance If the governing system functions poorly, perform the following tests. SYMPTOM TEST PROBABLE FAULT Actuator goes to full fuel. then, disconnect speed sensor at Terminals C & D. ¥ Do not crank. Apply If actuator still at full fuel speed control DC power to the gov- unit deffective. -
Page 140
¥ Electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) EMI SUSCEPTIBILITY — The governor system can be adversely affected by large inter- fering sig- nals that are conducted through the cabling or through direct radiation into the control circuits. All DWC-2000 speed control units contain filters and shielding designed to protect the units sensi- tive circuits from moderate external interfering sources. -
Page 141
10.3.4. Fuel feed pump 1) General descriptions and construction Priming pump Check valve Check valve Outlet Inlet side side Tappet Piston Cam shaft EQM4019I The P-type injection pump is mounted with K-ADS or KP type feed pump. These pumps have the same basic construction and operation, and the general descriptions of the KP type pump are given below: The figures show its construction (right figure) and operation (below figure). -
Page 142
Inlet side Outlet side Interruption EQM4020I This feed pump is mounted with a priming pump designed to permit manual feeding of fuel from the fuel tank with the injection pump mounted in the engine. During the manual feeding operation, air must be bled from the fuel lines. -
Page 143
2) disassembly ¥ Clamp the feed pump with a vise and disassemble the plugs (30, 32), strainer (31) and gaskets (35, 36). ¥ Take off the priming pump (25), plug (16), both gaskets (18), spring (15), and check valve (14). ¥… -
Page 144
5) Testing (1) Suction capacity test Connect one end of a hose to the inlet Outlet hose side of the feed pump and immerse the other end of it into the fuel tank as illus- Feed pump trated. Hold the feed pump in position about 1m above the level of fuel in the fuel tank. -
Page 145
10.3.5. Injection nozzle 1) General descriptions Pressurized fuel delivered from the fuel injection pump is sprayed into the combustion chamber past the injection nozzle at proper spray pressure and spray angle, then burnt completely to achieve effective engine performance. (1) At valve closed (2) At valve opened EQM4024I 2) 1-spring type… -
Page 146
(2) Reassembly ¥ After removing carbon deposit, sub- merge the nozzle in diesel oil and clean ¥ Replace all the gaskets with new ones. ¥ Assemble the parts and tighten them to specified torque. (3) Adjustment ¥ Remove the cap nut and assemble a nozzle to a nozzle tester. -
Page 147
3) 2-spring type (1) Disassembly EQM4029I 1. Nozzle holder body 13. Lift pin 2. Push rod 14. Pin 3. Primary spring 15. Spacer 4. Adjusting screw 16. Pin 6. Gasket 17. Retaining nut 7. Cap nut 30. Gasket 10. Adjusting shim 31. -
Page 148
(2) Inspection and adjustment a. Adjusting the primary opening pres- sure. Install the plate of plate assembly (157944-9520) onto a vise. Note : Use the plate assembly (157944-9520) in fixing a nozzle holder having a flange. A nozzle holder without flange should be EQM4030I directly installed onto a vise. -
Page 149
f. Install the pin (16) and nozzle (A) onto the spacer. EQM4034I g. After installing the gasket (6:157892-1500) on the nozzle, use the cap nut (7:157892- 4000 : SW22mm) to fix the nozzle onto the nozzle holder. Note : While tightening nut, keep checking to see if the lock pin… -
Page 150
j. Assemble the push rod (2), primary spring (3), and adjusting screw (4) on the nozzle holder in the order described. k. Install the gasket (6) and cap nut (7) onto the adjusting screw(4). l. Assemble the nozzle and nozzle holder assembly to the nozzle tester (105785- 1010). -
Page 151
¥ Inspecting the needle valve for full lift a. Install gasket (026508-1140) and plug (157892-1600 : SW12mm) onto the adjusting retaining nut (157892-1400). EQM4042I b. Install the nozzle holder on the plate with the cap nut facing upward. c. Install the holder(157892-4100: SW12 mm) into the cap nut. -
Page 152
f. Install the dial gauge on the holder assem- bly so that the pin is brought into contact with the upper end of the push rod, then fix the pin with the nut. Note 1 : Fix the dial gauge so that a stroke of 2 mm or so can be mea- sured. -
Page 153
¥ Inspection of pre-lift a. If the nozzle tester handle is released with the needle valve engaged in a full lift condition, the tester pressure drops, being accompanied by decrease in the needle valve lift value (indicated value on the dial gauge). kgf / cm EQM4049I Tester pressure… -
Page 154
c. If the measured pre-lift value deviates from the specified limit, replace the pin (14, 16), lift piece (13), spacer (15), and nozzle assembly (A) with a new Ònozzle service kitÓ. EQM4053I ¥ Inspection of secondary opening pressure a. After confirming the pre-lift, operate the nozzle tester and increase the internal pressure up to 350 ~ 450 kgf/cm to fully… -
Page 155
¥ Adjusting secondary opening pressure a. In the event that the measured value deviates from the specified limit, readjust the primary opening pressure if the amount of deviation is small. (to the stan- dard range of the primary opening pres- sure) — If the secondary opening pressure is lower than the standard value: Adjust the… -
Page 156
¥ Retaining nut a. Take out the dial gauge, nut, holder and gasket from the cap nut (7). b. Remove the adjusting retaining nut and gasket, and install the original retaining nut(SW 19mm). Cap nut 6.0 ~ 8.0 kg . m Tightening torque EQM4036I ¥… -
Page 157
10.3.6. Diagnostics and troubleshooting Complaints Possible causes Corrections 1. Engine wonÕt start (1) Fuel pipes clogged or air into pipe line Correct 1) Fuel not being pumped (2) Feed pump valve defective Replace out from feed pump (3) Feed pump piston or push rod sticking Disassemble, correct 2) Fuel not being injected (1) Fuel filter element restricted… -
Page 158
Complaints Possible causes Corrections 6. Engine output (1) Supply of fuel insufficient Check feed pump unstable (2) Air in fuel Bleed (3) Water in fuel Replace fuel (4) Operation of plungers unsmooth Disassemble, correct (5) Movement of control rack sluggish Disassemble, correct (6) Nozzles defective Disassemble, correct… -
Page 159: Turbocharger
10.4. Turbocharger 10.4.1. Main data and specifications 1) Main data and specifications Specification DE12T P126TI/P126TI- Turbocharger Model Allied Signal T45 Allied Signal TV51 50Hz: Approx. 1.1 kg/cm 50Hz: Approx. 1.5 kg/cm Air pressure at compressor outlet 60Hz: Approx. 1.2 kg/cm 60Hz: Approx.
-
Page 160
3) Construction Turbine housing Retainer ring Bolt Plug Bearing O-ring Crank Thrust collar Compressor wheel V-band Screw Wheel Thrust bearing Bolt Piston ring Thrust space Clamp Wheel shroud Piston ring Compressor housing Center housing Seal ring Elbow Retainer ring Seal ring Retainer Bearing Rear plate… -
Page 161
10.4.2. General descriptions The engine output is determined by the fuel delivery volume and engine efficiency. To burn the supplied fuel completely to change into effective power for the engine, the volume of air enough to burn the fuel completely should be supplied into the cylinders. Therefore, the engine output is determined substantially by the cylinder capacity, and a greater volume of compressed air is charged into cylinders of given capacity, the greater engine output can be obtained as a greater volume of air charged into the cylinders burns so… -
Page 162
10.4.4. Precautions for operation 1) Precautions for operation of engine The following precautions should be observed when starting, operating, or stopping the engine: Operations Precautions Reasons When starting 1) Check oil level 2) Crank the engine with starter to 2) Abrupt starting of the engine the engine check the increase in oil pres- causes the engine to rotate with… -
Page 163
10.4.5. Walk-around check and servicing As the condition of turbocharger depends greatly on how well the engine is serviced, it is very important to maintain the engine in accordance with the specified maintenance procedure. 1) Intake system Pay particular attention to the air cleaner when servicing the intake system. In the case of wet-type air cleaner, if the level of oil surface is lower than specified, clean- ing effect is poor;… -
Page 164
10.4.6. Periodical checking and servicing Make it a rule to check the turbocharger assembly for condition and contamination periodically. 1) Guide for checking the rotor for rotating condition The inspection of the rotor assembly for rotating condition should be performed by the degree of unusual sound. -
Page 165
(3) If the measured axial and radial plays are beyond the limit of wear, replace or repair the turbocharger. 3) Guide for disassembling/cleaning and checking the turbocharger First, disassemble the turbocharger from the engine and clean/check it with the oil inlet and outlet plugged with tape and so on. -
Page 166
10.4.7. Diagnostics and troubleshooting Complaints Possible causes Corrections 1. Excessive black 1) Air cleaner element clogged Replace or clean smoke 2) Restrictions in air duct Check and correct 3) Leakage at intake manifold Check and correct 4) Turbocharger seized up and not rotating Disassemble/repair or replace 5) Turbine blades and compressor blades Disassemble/repair or replace… -
Page 167: Special Tool List
11. Special Tool List Part No. Figure Tool Name DPN-5337 Nozzle tube insert assÕy EF.123-082 Nozzle tube extractor EF.123-015 Injection pump setting assÕy EF.123-173 Oil seal(NOK) insert assÕy (FR) EF.123-194A Oil seal(NOK) insert assÕy (RR) EF.123-317A Oil seal(NOK)puller assÕy (FR) EF.123-316A Oil seal(NOK) puller assÕy (RR) EF.123-347…
-
Page 168
Part No. Figure Tool Name EF.123-066 Valve stem seal punch EU.2-0131 Valve clearance adjust assÕy EF.123.-065 Valve spring press EU.2-0647 Crankshaft gear punch 60.99901-0027 Feeler gauge T7610001E Snap ring plier T7621010E Piston ring plier EF.120-208 Piston Ring Compressor — 164 -… -
Page 169
Appendix ¥ Tightening torque for major parts Screw Strength Major Parts Tightening Torque Remarks (Diameter x pitch) (grade) 1st : 6kg.m 2nd : 90û Cylinder head bolt M14 x 1.5 10.9T 3rd: 90û Dodecagon Finished : 90û (angle torque) Cylinder head cover bolt 8.8T 1.2 kg.m 1st : 15 kg.m… -
Page 170
¥ Standard bolt tightening torque table Refer to the following table for bolts other than described above. Degree of strength 10.9 12.9 Diameter (4A) (4D) (4S) (5D) (5S) (6D) (6S) (6G) (8G) (10K) (12K) pitch Limit value for elasticity (kg/mm (mm) Tightening torque (kg . -
Page 171
— 167 -… -
Page 172
— 168 -… -
Page 173
— 169 -… -
Page 174
— 170 -… -
Page 175
— 171 -…
Skip to content
Запчасти – Сервис – Ремонт двигателей Doosan
Инструкции / руководства
- Home
- Инструкции / руководства
© Copyright 2023. Все права защищены. DSEngine. Developed By Alex

#ПСМ
ТАКОЙ УВЛЕКАТЕЛЬНЫЙ ДЕНЬ
Сегодня вторую половину дня, как и собирался, провёл на выставке Нефтегаз-2023
Делюсь главными впечатлениями:
1. 70 % участников выставки — китайцы ????????.
2. Запомнилась история китайского завода. Не буду тыкать здесь известного российского производителя бурового оборудования, но часто производство даже у бывших советских заводов полного цикла выглядит именно так: китайский завод попросили российскими буквами нанести название и логотип.
3. У нас основная тема сегодня — это производители буровых насосов. Сейчас доля китайцев на рынке в России близка к 100 %. Задача правильно выбрать китайцев.
4. Американский CAT просит китайцев не продавать двигатели в Россию. Так что хочешь купить мотор, возьми у нагрузки китайский суповой набор.
5. Ключевые компоненты много какого китайского оборудования американские (автоматические трансмиссии, механизмы отбора мощности, контроллеры и т.д.).
6. В Китае 30-40 производителей. От шильдиковтирателей до огромных завод полного цикла.
7. Производителей из других дружественных стран — Турция, Иран на выставке 0.0…1 % условно.
8. Все китайцы просят после встречи сфоткаться. Видно нужен отчёт что не зря съездили.
9. Все взяли русских переводчиков, но, блин, они ничего не понимают в предмете разговора. Так что наша тактика на найм собственного «китайца» точно оправдана.
10. Каждый раз смотришь сайт и ролик за день до выставки и думаешь: «Почему мы решили не участвовать ????♂️». Выходишь с выставки и думаешь, что участие в выставках — это ????
24.04.2023 07:27:14

#ПСМ
НЕФТЕГАЗ-2023
Завтра (один день) планирую быть на выставке в Экспоцентре. Пишите, кто хочет пересечься.
Андрей Медведев
23.04.2023 11:10:15

#БИЗНЕС
ЗОЛОТАЯ КОНУРА vs. ЗАВОД
Ради интереса решил погуглить стоимость этого помещения конкрного типа на Остоженке рядом с Храмом Христа Спасителя в Москве (начало так называемой «Золотой Мили»). Оказалась, что мы примерно за такую же стоимость собираемся построить новый завод ПСМ Прайм 2.
Думаю для большинства инвесторов в России выбор очевиден.
Андрей Медведев
23.04.2023 05:40:53

#БИЗНЕС
ДЕЛО МОЕЙ ЖИЗНИ
В четверг к нам приезжал очень важный клиент и спросил моего коллегу (сам я был в Москве и Питере в этот день): «Зачем Андрей занимается этим бизнесом. Его же в десятки раз не масштабируешь и в Forbes так не попадешь».
Вот кратко мой ответ:
1. Я горжусь, чем я занимаюсь. И это все же про быть, а не про казаться. Очень рад, что я продаю не воздух, а крутое железо. И с каждым годом мы делаем всё более сложный и качественный продукт.
2. Я кайфую от того, что я делаю. У нас крутая команда и люди, с которыми приятно каждый день общаться, иногда 24/7. Классные офисы и заводы, где рад проводить большую часть своего жизненного времени.
3. Я каждый день развиваюсь. Новые проекты, новые навыки, новое общение, новые путешествия и т.д. И всё это в огромном количестве каждый день.
4. Я за почти 18 лет абсолютно не устал это делать, а наоборот, иногда даже жалко, что время летит так быстро.
5. Я уверен, что если ты каждый день херачишь, как сумасшедший с головой, то в один прекрасный момент ты вытащишь лотерейный билет на несколько десятков, а может и сотен миллиардов (ставки с каждым годом растут, и это не может не радовать). И это будет заслуженно.
P.S. В Forbes я обязательно попаду. Иначе зачем всё это ????????
Андрей Медведев
22.04.2023 10:07:24

#ПСМ
ИНЖИНИРИНГОВЫЙ ЦЕНТР
В итоге выбрали такой вариант. Дальше разработаем свою уникальную картинку на стену в виде кода (ASCII-графика, например).
Отвечаю на замечания из предыдущего поста на эту тему:
1. Что open space (в ПСМ, как я писал, это не обсуждается).
2. Также у нас принципиальная позиция, что инженеры должны быть в близком контакте с производством, а не в изолированном мире.
Андрей Медведев
21.04.2023 04:34:32
#БИЗНЕС
УРОВЕНЬ ОБЩЕНИЯ
Почему-то принято считать, что чем человек занимает более высокий пост, тем он более надменный и пафосный индюк ????. Возможно, так иногда и бывает, но из моего опыта в большинстве случаев всё наоборот.
У некоторых заказчиков мы общаемся на уровне собственников, первых и вторых лиц. И в 90 % случаях в крупных компаниях вице-президенты, генеральные директора — крайне адекватные люди, с хорошим культурным уровнем. Всё по делу, с взаимоуважением и интересом к теме.
Помню обратную ситуацию в Новом Уренгое, когда механик мне, генеральному директору системообразующей компании России в области Энергетического Машиностроения, который специально приехал вместе с продажником к нему на Север на встречу, говорит: «Э, ну давай там быстрее вещай, чё там тебе надо от меня».
Или ещё более забавную ситуацию на заводе шампанских вин в Питере. Меня одного продажник попросила заехать на встречу, а там сидит энергетик и заявляет: «У тебя есть 15 минут, продавай мне скорее, а то таких как ты у меня дохе***».
Андрей Медведев
20.04.2023 12:06:34
#ПРОМЫШЛЕННОСТЬ
ВСЁ ХОРОШО, НО НАДОЛГО ЛИ
Удивительная вещь, конечно, встречаюсь с многими производителями оборудования, и все загружены сейчас работой по самое не балуйся. Т.е. в моменте у многих всё очень хорошо, при этом никто не знает, что будет дальше. Это краткосрочный всплеск, а дальше медленное угасание или как?
К сожалению, такая неопределенность сказывается на инвестиционном настроения бизнеса. Казалось бы, пока ушли крупные мировые производители, есть уникальная возможность воспользоваться шансом и построить новые заводы и пароходы. Но любые вложения в долгую без стабильности мало кто рискует делать.
Поэтому нужны промышленности государственные деньги, гарантии, проекты и, главное, диалог про будущее.
Андрей Медведев
19.04.2023 09:25:01

#ПСМ
НАШИ НОВЫЕ ДРУЗЬЯ ????????
Вчера за ужином наши китайские партнеры сказали (правда после нескольких настоек и пару бокалов пива) что Си Цзиньпин, когда вернулся со встречи с Путиным в России, собрал крупнейшие китайские государственные компании производителей двигателей. На этом собрании он сказал, что надо помочь нашим российским партнерам, а им параллельно захватить российский рынок.
Мы активно строим работу сейчас с китайскими партнерами, и у меня запланировано 2 визита туда — в мае и в июне. Меня только несколько беспокоит их понимание, что деваться нам здесь некуда и надо использовать ситуацию по полной.
Например, российско-китайскому СП Волжский индустриальный двигатель, когда только всё начиналось, китайская сторона неплохо подняла цены. И сейчас китайский газовый Baudouin на 500 кВт стоит почти как раньше немецкий MAN.
Главное всё же сейчас — выстроить ВЗАИМОВЫГОДНОЕ сотрудничество ???????? ???????? win-win ????????????, а так я за дружбу и жвачку.
Андрей Медведев
18.04.2023 09:00:49

#ПСМ
ИНЖИНИРИНГ
Одним из главных фундаментов бизнеса ПСМ несомненно является инжиниринг. В нашей структуре есть Управление Главного Конструктора, в котором работает около 30 человек. Они находятся на одной из наших производственных площадок — ПСМ Красный Бор.
Наша задача существенно нарастить свои компетенции в этом блоке бизнеса (новые группы и специалисты), чтобы мы как в производственных возможностях были не досягаемы для конкурентов. ????
Кроме того, я уже транслировал на годовом собрании сотрудникам компании важную вещь. За 2 года мы должны достичь такой среды в компании, что не важно, где человек работает — в офисе ПСМ Сити в Башне Федерация или на производстве в Тутаеве или Ярославле, условия труда должны быть одинаковые.
В этом году у нас в плане инвестиций куча всего, но дизайн-проекта и ремонта Инжинирингового центра не было. Но в январе мы решили, что надо это сделать как можно быстрее за счет других статей расходов.
Сейчас план такой: в апреле утвердить визуализацию, дальше рабочая документация и в июне начать ремонт, чтобы край в августе сдать коллегам новое, красивое и современное рабочее пространство.
У нас было в работе 4 таких варианта. Угадайте, на каком мы остановились и уже прорабатываем детали.
МЫ РАЗВИВАЕМ РОССИЙСКОЕ ЭНЕРГЕТИЧЕСКОЕ МАШИНОСТРОЕНИЕ И ДЕЛАЕМ ЭТО КРАСИВО ????
Андрей Медведев
16.04.2023 01:22:24
#ЖИЗНЬ
БАСКЕТБОЛ ⛹️
До сегодня я один раз в жизни был на баскетболе и это был плей-офф НБА Вашингтон Уизардс — Бостон Селтикс. Это было топ-шоу ????, пример мощнейшей коммерциализации спорта и звезда.
Сегодня тоже была довольно эмоционально и постарались сделать шоу (Баста исполнил гимн ЦСКА).
Что удивительно и тогда Айзея Томас и сегодня Каспер Уэйр самые маленькие игроки (175 и 177 см) на площадке набрали больше всего очков и сделали игру. Сегодня вообще интересно у ЦСКА были лучшими самый маленький американец ???????? и самый высокий серб ???????? (213 см).
Не все так просто в этом мире: маленькие и большие, американцы, русские и сербы бьются за одну победу.
Андрей Медведев
15.04.2023 08:21:20


65.99892-8051
Operation Manual
GENERATOR DIESEL ENGINE
DE12T
POLUS
P126TI
FOREWORD
This manual has been prepared to help you use and maintain the DE12T/ P126TI generator diesel engines in a safe and correct manner.
These economical and high-performance diesel engines (OMEGA combustion system) have been designed and manufactured for generator application. They meet all the requirements such as low noise, fuel economy, high engine speed, and durability.
Nonetheless, to obtain the best performance and long life of an engine, it is essential to operate it appropriately and to carry out periodic checks as instructed in this manual. We strongly urge you to thoroughly read this manual from cover to cover and to acquaint yourself fully with all the information contained in this manual.
Please contact your authorized DAEWOO dealer for the answers to any questions you may have about your DE12T/ P126TI generator engine’s features, operation, or manuals.
In order to operate the engine in the optimal conditions and to maintain its best performances, the contents in this instruction are to be thoroughly understood and observed.
In addition refer to the INSTALLATION manual about DAEWOO generator engine installation instructions.
All warranty claims to be addressed to;
Engine Export Team,
DAEWOO Heavy Industries LTD.
DAEWOO Center 541
Namdaemun-ro 5-ga, Chung-gu
Seoul, Korea
TEL : (82-2-726-3205~8), FAX: (82-2-726-3168)
Or to your local DEALER or DISTRIBUTOR.
DAEWOO Heavy Industries LTD.
July. 1999
CONTENTS
|
1. |
General information ……………………………………………………………………………………………………. |
1 |
|
1.1. Engine specification |
1.2. Engine assembly |
|
|
2. |
Safety regulations………………………………………………………………………………………………………. |
6 |
|
2.1. General notes |
2.4. Regulations designed to prevent pollution |
|
|
2.2. Regulations designed to prevent accidents |
2.5. Notes on safety in handling used engine oil |
|
|
2.3. Regulations designed to prevent damage |
||
|
3. |
Technical information ……………………………………………………………………………………………….. |
10 |
3.1.Engine model and serial number
3.2.Engine type
3.3.Engine timing
3.4.Valves
3.5.Lubrication system
3.6.Air cleaner
3.7.Intercooler
3.8.Fuel system
3.9.Cooling system
3.10.V-belt tension check and adjust
3.11.Turbocharger
3.12.Electrical equipment
|
4. |
Commissioning and operation ………………………………………………………………………………….. |
26 |
|
4.1. Preparation |
4.4. Operation in winter |
|
|
4.2. Breaking-in |
4.5. Tuning the engine |
|
|
4.3. Inspection after starting |
||
|
5. |
Inspection and maintenance …………………………………………………………………………………….. |
30 |
|
5.1. Periodical inspection and maintenance |
5.5. Fuel system |
|
|
5.2. Lubrication system |
5.6. Injection nozzle maintenance |
|
|
5.3. Cooling system |
5.7. Turbocharger |
|
|
5.4. Air intake system |
||
|
6. |
Checking and setting ……………………………………………………………………………………………….. |
42 |
|
6.1. Adjustment of valve clearance |
6.4. Cylinder compression pressure |
|
|
6.2. Adjustment of injection timing |
6.5. V-belts |
|
|
6.3. Tightening the cylinder head bolts |
|
Appendix…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… |
49 |
WORLDWIDE NETWORK

1. General information
1.1. Engine specification
|
Engine Model |
DE12T |
P126TI |
P126TI-I |
|||||
|
Items |
||||||||
|
Engine type |
Water-cooled, 4 cycle in-line |
Water-cooled, 4 cycle in-line |
||||||
|
type |
||||||||
|
type Turbo charged |
||||||||
|
Turbo charged & intercooled |
||||||||
|
Combustion chamber type |
Direct injection type |
|||||||
|
Cylinder liner type |
Replaceable dry liner |
|||||||
|
Timing gear system |
Gear driven type |
|||||||
|
No. of piston ring |
Compression ring 2, oil ring 1 |
|||||||
|
No. of cylinder-bore x stroke |
(mm) |
4 — 123 x 155 |
||||||
|
Total piston displacement |
(cc) |
11,051 |
||||||
|
Compression ratio |
17.1 : 1 |
|||||||
|
Engine dimension (length x width x height) |
(mm) |
1,365.5 x 870 x 1,046 |
1,383 x 870 x 1,207 |
|||||
|
Engine weight |
(kg) |
910 |
||||||
|
Rotating direction (from flywheel) |
Counter clockwise |
|||||||
|
Fuel injection order |
1 — 5 — 3 — 6 — 2 — 4 |
|||||||
|
Fuel injection timing (B.T.D.C static) |
12° |
|||||||
|
Injection pump type |
Zexel in-line “P” type |
|||||||
|
Governor type |
Mechanical governor type(RSV) |
Electric governor type(GAC) |
||||||
|
Injection nozzle type |
Multi-hole type (5 hole) |
Multi-hole type (5 hole) |
||||||
|
Fuel injection pressure |
(kg/cm2) |
220 |
1st : 160, 2nd : 220 |
|||||
|
Compression pressure |
(kg/cm2) |
28 (at 200 rpm) |
||||||
|
Condition |
50Hz |
60Hz |
50Hz |
60Hz |
60Hz |
|||
|
(1,500rpm) |
(1,800rpm) |
(1,500rpm) |
(1,800rpm) |
(1,800rpm) |
||||
|
Continuous |
— |
— |
280PS |
336PS |
— |
|||
|
(206kW) |
(247kW) |
|||||||
|
Power (ISO 3046) |
||||||||
|
Prime |
205PS |
245PS |
328PS |
378PS |
356PS |
|||
|
(151kW) |
(180kW) |
(241kW) |
(278kW) |
(262kW) |
||||
|
Stand by |
226PS |
270PS |
370PS |
405PS |
392PS |
|||
|
(166kW) |
(199kW) |
(272kW) |
(298kW) |
(288kW) |
||||
|
Intake and exhaust valve clearance (at cold) |
(mm) |
0.3 |
||||||
|
Intake valve |
Open at |
18° (B.T.D.C) |
||||||
|
Close at |
34° (A.B.D.C) |
|||||||
|
Exhaust valve |
Open at |
46° (B.B.D.C) |
||||||
|
Close at |
14° (A.T.D.C) |
|||||||
|
Lubrication method |
Full forced pressure feed type |
|||||||
|
Oil pump type |
Gear type driven by crankshaft |
|||||||
|
Oil filter type |
Full-flow, Cartridge type |
|||||||
|
Lubricating oil capacity (max./min.) |
(lit) |
23/20 |
||||||
|
Oil cooler type |
Water cooled |
|||||||
|
Water pump |
Gear driven impeller type |
|||||||
|
Cooling Method |
Pressurized circulation |
|||||||
|
Cooling water capacity (engine only) |
(lit) |
19 |
||||||
|
Thermostat type |
Wax pallet type (83 ~ 95 °C) |
|||||||
|
Alternator voltage — capacity |
(V — A) |
24 — 45 |
||||||
|
Starting Motor voltage — output |
(V — kW) |
24 — 6.0 |
||||||
|
— 1 — |

1.2. Engine assembly
1.2.1. Engine sectional view (Longitudinal)
|
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
6 |
7 |
8 |
9 |
1
|
10 |
11 |
12 |
13 |
14 |
15 |
16 |
17 |
18 |
EA8M1002
|
1. |
Cooling fan |
7. |
Piston pin |
13. |
Crankshaft |
|
2. |
Exhaust valve |
8. |
Piston |
14. |
Oil pan |
|
3. |
Valve spring |
9. |
Combustion chamber |
15. |
Connecting rod |
|
4. |
Oil filter |
10. |
Crankshaft pulley |
16. |
Camshaft |
|
5. Tappet |
11. |
Vibration damper |
17. |
Flywheel housing |
|
|
6. |
Push rod |
12. |
Oil pump |
18. |
Flywheel |
— 2 —

1.2.2. Engine sectional view (Cross)
7 8 9
2
11
3
12
4
5
6
EA8M1003
|
1. |
Intake manifold |
7. |
Injection nozzle assembly |
|
2. |
Fuel filter |
8. |
Rocker arm |
|
3. |
Oil cooler |
9. |
Cylinder head cover |
|
4. |
Injection pump |
10. |
Exhaust manifold |
|
5. |
Cylinder block |
11. |
Piston ring |
|
6. |
Oil filter |
12. |
Turbocharger |
— 3 —

1.2.3.Engine assembly views
1)DE12T
|
1 |
2 |
3 |
12 |
4 |
27 |
13 |
18 |
5
22
|
23 |
8 |
6 |
9 |
11 10 |
|
|
16 |
17 |
15 |
7 |
19 |
25
24
EA8M1004
|
1. |
Cooling fan |
10. |
Flywheel housing |
19. Thermostat |
|
|
2. |
Cooling water pipe |
11. Flywheel |
20. |
Injection pump |
|
|
3. |
Oil filler cap |
12. |
Exhaust manifold |
21. |
Oil level gauge |
|
4. |
Cylinder head cover |
13. |
Injection nozzle assembly |
22. |
Mounting bracket |
|
5. Turbocharger |
14. |
Oil filter |
23. |
Vibration damper |
|
|
6. |
Oil drain valve |
15. |
Fuel filter |
24. |
Water pump |
|
7. Alternator |
16. |
Oil cooler |
25. |
Fan drive |
|
|
8. |
Oil pan |
17. |
Intake manifold |
26. |
Crankshaft pulley |
|
9. |
Starter |
18. |
Injection pipe |
27. |
Breather |
— 4 —
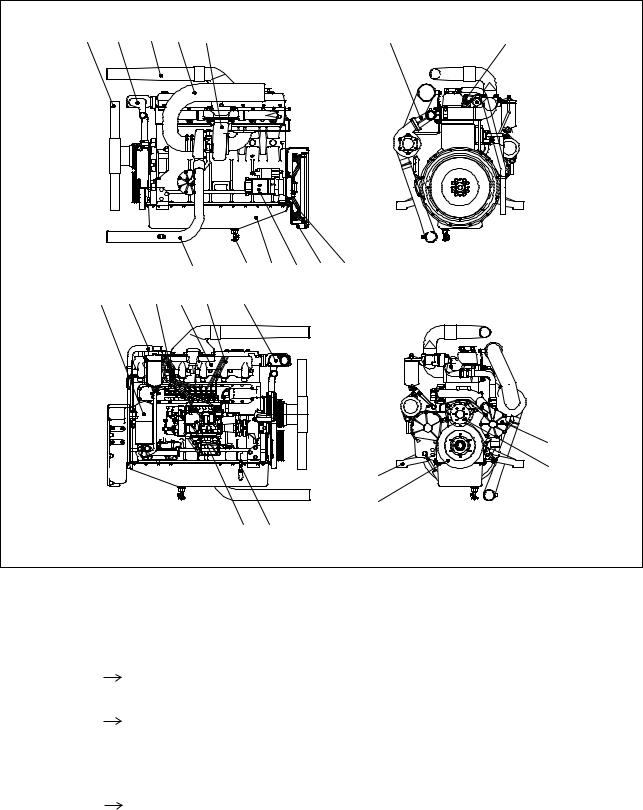
2) P126TI
|
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
12 |
13 |
|
7 |
6 |
8 |
9 |
10 |
11 |
||||
|
14 |
15 |
16 |
17 |
18 |
19 |
20 21
EA8M1005
|
1. |
Cooling fan |
8. Oil pan |
18. |
Injection pipe |
||
|
2. |
Cooling water pipe |
9. |
Starter |
19. Thermostat |
||
|
3. Air pipe |
10. |
Flywheel housing |
20. |
Injection pump |
||
|
(Intercooler |
Intake manifold) |
11. Flywheel |
21. |
Oil level gauge |
||
|
4. Air pipe |
12. |
Exhaust manifold |
22. |
Mounting bracket |
||
|
(Air cleaner |
Turbocharger) |
13. |
Injection nozzle assembly |
23. |
Vibration damper |
|
|
5. Turbocharger |
14. |
Oil filter |
24. |
Water pump |
||
|
6. |
Oil drain valve |
15. |
Breather hose |
25. |
Fan drive |
|
|
7. Air pipe |
16. |
Oil cooler |
||||
|
(Intercooler |
Intake manifold) |
17. |
Intake manifold |
— 5 —

2. Safety regulations
2.1. General notes
Day-to-day use of power engines and the service products necessary for running them presents no problems if the persons occupied with their operation, maintenance and care are given suitable training and think as they work.
This summary is a compilation of the most important regulations. These are broken down into main sections which contain the information necessary for preventing injury to persons, damage to property and pollution. In addition to these regulations those dictated by the type of engine and its site are to be observed also.
Important :
If, despite all precautions, an accident occurs, in particular through contact with caustic acids, fuel penetrating the skin, scalding from oil, antifreeze being splashed in the eyes etc., consult a doctor immediately.
2.2. Regulations designed to prevent accidents
2.2.1.During commissioning, starting and operation
Before putting the engine into operation for the first time, read the operating instructions carefully and familiarize yourself with the “critical” points, If you are unsure, ask your DAEWOO representative.
•For reasons of safety we recommend you attach a notice to the door of the engine room prohibiting the access of unauthorized persons and that you draw the attention of the operating personal to the fact that they are responsible for the safety of persons who enter the engine room.
•The engine must be started and operated only by authorized personnel. Ensure that the engine cannot be started by unauthorized persons.
•When the engine is running, do not get too close to the rotating parts. Wear close-fitting clothing.
•Do not touch the engine with bare hands when it is warm from operation risk of burns.
•Exhaust gases are toxic. Comply with the installation instructions for the installation of DAEWOO generator diesel engines which are to be operated in enclosed spaces. Ensure that there is adequate ventilation and air extraction.
•Keep vicinity of engine, ladders and stairways free of oil and grease.
Accidents caused by slipping can have serious consequences.
— 6 —

2.2.2.During maintenance and care
•Always carry out maintenance work when the engine is switched off. If the engine has to be maintained while it is running, e.g. changing the elements of change-over filters, remember that there is a risk of scalding. Do not get too close to rotating parts.
•Change the oil when the engine is warm from operation.
Caution :
There is a risk of burns and scalding. Do not touch oil drain valve or oil filters with bare
hands.
•Take into account the amount of oil in the sump. Use a vessel of sufficient size to ensure that the oil will not overflow.
•Open the coolant circuit only when the engine has cooled down. If opening while the engine is still warm is unavoidable, comply with the instructions In the chapter entitled “Cooling”.
•Neither tighten up nor open pipes and hoses (lube oil circuit, coolant circuit and any additional hydraulic oil circuit) during the operation. The fluid which flow out can cause injury.
•Fuel is inflammable. Do not smoke or use naked lights in its vicinity. The tank must be filled only when the engine is switched off.
•Keep service products (anti-freeze) only in containers which can not be confused with drinks containers.
•Comply with the manufacturer’s instructions when handling batteries.
Caution :
Accumulator acid is toxic and caustic. Battery gases are explosive.
2.2.3.When carrying out checking, setting and repair work
•Checking, setting and repair work must be carried out by authorized personnel only.
•Use only tools which are in satisfactory condition. Slip caused by the worn open-end wrench could lead to Injury.
•When the engine is hanging on a crane, no-one must be allowed to stand or pass under it. Keep lifting gear in good condition.
•When checking injectors, do not put your hands under the jet of fuel.
Do not inhale at atomized fuel.
•When working on the electrical system disconnect the battery earth cable first. Connect it up again last in prevent short circuits.
2.3.Regulations designed to prevent damage to engine and premature wear
1)Never demand more of the engine than it was designed to yield for its intended purpose. Detailed information on this can be found in the sales literature. The injection pump must not be adjusted without prior written permission of DAEWOO.
—7 —
2)If faults occur, find the cause immediately and have it eliminate in order to prevent more serious of damage.
3)Use only genuine DAEWOO spare parts. DAEWOO will accept no responsibility for damage resulting from the installation of other parts which are supposedly “just as good”.
4)In addition to the above, note the following points.
•Never let the engine run when dry, i.e. without lube oil or coolant. Use only DAEWOOapproved service products (engine oil, anti-freeze and anticorrosion agent).
•Pay attention to cleanliness, The Diesel fuel must be free of water. See “Maintenance and care”.
•Have the engine maintained at the specified intervals.
•Do not switch off the engine immediately when it is warm, but let it run without load for about 5 minutes so that temperature equalization can take place.
•Never put cold coolant into an overheated engine. See “Maintenance and care”.
•Do not add so much engine oil that the oil level rises above the max. marking on the dipstick. Do not exceed the maximum permissible tilt of the engine. Serious damage to the engine may result if these instructions are not adhered to.
•Always ensure that the testing and monitoring equipment (for battery charge, oil pressure, and coolant temperature) function satisfactorily.
•Comply with instructions for operation of the alternator. See “Commissioning and operation”.
•Do not let the water pump run dry. If there is a risk of frost, drain the water when the engine switched off.
2.4. Regulations designed to prevent pollution
2.4.1.Engine oil, filter element, fuel filter
•Take old oil only to an oil collection point. Take strict precautions to ensure that oil does not get into the drains or into the ground.
•The drinking water supply may be contaminated.
•Oil and fuel filter elements are classed as dangerous waste and must be treated as such.
2.4.2.Coolant
•Treat undiluted anti-corrosion agent and / or antifreeze as dangerous waste.
•When disposing of spent coolant comply with the regulations of the relevant local authorities.
2.5. Notes on safety in handling used engine oil
Prolonged or repeated contact between the skin and any kind of engine oil decreases the skin. Drying, irritation or inflammation of the skin may therefore occur. Used engine oil also contains dangerous substances which have caused skin cancer in animal experiments. If the basic rules of hygiene and health and safety at work are observed, health risks are not to the expected as a result of handling used engine oil.
— 8 —

Health precautions
•Avoid prolonged or repeated skin contact with used engine oil.
•Protect your skin by means of suitable agents (creams etc.) or wear protective gloves.
•Clean skin which has been in contact with engine oil.
—Wash thoroughly with soap and water, A nailbrush is an effective aid.
—Certain products make it easier to clean your hands.
—Do not use petrol, Diesel fuel, gas oil, thinners or solvents as washing agents.
•After washing apply a fatty skin cream to the skin.
•Change oil-soaked clothing and shoes.
•Do not put oily rags into your pockets.
Ensure that used engine oil is disposed of properly. — Engine oil can endanger the water supply —
For this reason do not let engine oil get into the ground, waterways, the drains or the sewers. Violations are punishable. Collect and dispose of used engine oil carefully.
For information on collection points please contact the seller, the supplier or the local authorities.
— 9 —

3. Technical information
3.1. Engine model and serial number
The engine model and serial number is located on the engine as illustrated. These numbers are required when requesting warranty and ordering parts. They are also referred to as engine model and serial number because of their location.
•Engine serial No. (example 1 : DE12T)
EBHGA900001
Serial No.
Production Year(19×9)
Engine Model Suffix
•Engine serial No. (example 2 : P126TI)
EDIGA900001
Serial No.
Production Year(1999)
Engine Model Suffix
Engine Number
|
EA8O3001 |
||||
|
MODEL |
BORE |
mm |
||
|
SPEED |
1500/1800 |
rpm |
STROKE |
mm |
|
STAND-BY |
VOLUME |
cc |
||
|
PRIME |
YEAR |
|||
|
SERIAL NUMBER |
||||
|
DAEWOO HEAVY INDUSTRIES LTD. |
||||
|
EA9O2002 |
< Name Plate : General >
|
IMPORTANT ENGINE INFORMATION |
DAEWOO HEAVY INDUSTRIES LTD. |
|
|
ENGINE AND MATERIAL DIV. |
||
|
6, MANSECOK-DONG, DONG-GU |
||
|
INCHEON, KOREA |
||
|
THIS DAEWOO HEAVY-DUTY DIESEL MODEL |
IS CERTIFIED TO OPERATE ON |
TYPE 2-D DIESEL FUEL. |
|
EPA AND CARB STANDARDIZED ENGINE FAMILY DESIGNATION IS |
||
|
TUNE-UP SPECIFICATIONS AND ADJUSTMENTS |
EA9O2003
< Name Plate : EPA & CARB >
— 10 —
3.2. Engine type
The Engines DE12T/ P126TI are in-line vertical water-cooled 6-cylinder four-stroke diesel engines with direct injection. DE12T is turbo-charged engine, and P126TI model is turbocharged and inter-cooled engine.
3.2.1.Cylinder block
The cylinder block is a single piece of alloy cast iron. To increase its stiffness, it is extended to a level below the crankshaft center line. The engine has replaceable dry cylinder liners and individual cylinder heads with struck-in valve seat rings and replaceable valve guides,
3.2.2.Piston con-rod / crankshaft
The forged crankshaft is a ingrate type (Counterweight is integrated with crank shaft body). Radial oil seal on crankshaft and flywheel are provided to seal the flywheel housing inside penetrations.
The con-rods (connecting rods) are die-forged, diagonally split and can be removed through the top of the cylinders together with the pistons. Crankshaft and connecting rods run in steel-backed lead bronze ready-to fit type bearings.
— 11 —

3.3. Engine timing
Camshaft, oil pump and injection pump are driven by a gear train arranged at the front end.
|
Injection pump gear |
Camshaft gear |
Water pump gear |
|
(Z = 72) |
(Z = 72) |
(Z = 29) |
|
Idle gear |
||
|
(Z = 52) |
||
|
Crankshaft gear |
||
|
(Z = 36) |
||
|
Oil pump idle gear |
||
|
(Z = 31) |
||
|
Oil pump drive gear |
||
|
(Z = 32) |
||
|
EA8O3002 |
3.4. Valves
The overhead valves are actuated via chilled cast iron tappets, push rods and rocker arms
from the camshaft.
— 12 —

3.5. Lubrication system
The engine is equipped with force-feed lubrication.
The pressure is produced by a gear pump whose drive gear is in direct mesh with the crankshaft gear at the front end of cylinder block.
The oil pump draws the oil from the oil sump and delivers it through the oil cooler and oil filter to the main distributor gallery and from there to the main bearings, big-end bearings and camshaft bearings as well as to the small-end bearings and the rocker arms.
The injection pump and the turbocharger are also connected to the engine lubricating system. The cylinder walls and timing gears are splash-lubricated.
Each cylinder has an oil jet provided for cooling the underside of the pistons. The lube oil is cleaned in a full-flow oil filter.
|
OPENING PRESSURE |
|||||
|
4.0 ~ 5.0 kg/cm2 |
|||||
|
RELIEF VALVE |
CYLINDER BLOCK MAIN GALLERY |
TURBO CHARGER |
|||
|
BY — PASS VALVE |
OIL FILTER |
CAM SHAFT BEARING |
|||
|
1.8 ~ 2.3 kg/cm2 |
|||||
|
IDLE GEAR SHAFT |
ROCKER ARM SHAFT |
||||
|
BY — PASS VALVE |
OIL SPRAY VALVE |
||||
|
1.5 ~ 1.8 kg/cm2 |
|||||
|
5.0 ~ 6.0 kg/cm2 |
OIL COOLER |
||||
|
SPRAY NOZZLE |
CRANK JOURNAL |
INJECTION PUMP |
|||
|
IDLE GEAR FACE |
VALVE ROCKER ARM |
||||
|
RELIEF VALVE |
|||||
|
10 + 1.5 kg/cm2 |
CRANK PIN |
||||
|
OIL PUMP |
|||||
|
TAPPET |
VALVE |
||||
|
OIL STRAINER |
|||||
|
EA8O3003 |
3.5.1.Recommend of lubricating oil
Initial factory fill is high quality break-in oil for API Service CD. During the break-in period (50 hours), frequently check the oil level. Somewhat higher oil consumption is normal until piston rings are seated. The oil level should be maintained in the safe range between the Min. and Max. marks on the dipstick. The safe range between the marks represents approximately 3 liters. To obtain the best engine performance and engine life, grade of engine oil is recommended. Engine oils are specified by API Service, letter designations and SAE viscosity numbers. If the specified motor oil is not available, use a reputable brand of engine oil labeled for API Service CD and SAE viscosity 30 or 15w40. Refer to oil identification symbol on the container.
Engine oil should be changed at the specified intervals. (800hr)
—13 —

|
Engine oil viscosity — ambient temperature |
||||||
|
SAE 20, 20W |
SAE 40, 50 |
|||||
|
Single |
SAE 10W |
SAE 30 |
||||
|
grade |
||||||
|
Ambient |
-30 C |
-15 C |
-0 C |
15 C |
25 C |
30 C |
|
temp |
(-20 F) |
(-0 F) |
(-32 F) |
(60 F) |
(80 F) |
(90 F) |
|
Multi |
SAE 10W — 30 |
|||||
|
grade |
||||||
|
SAE 15W — 40 |
||||||
|
SAE 10W — 40, 20W — 40, 20W — 50 |
||||||
|
SAE 5W — 20 |
||||||
|
EA4M1008 |
3.5.2.Oil cooler
An oil cooler is provided between the oil filter and the cylinder block. This cooler is a flat tube type with turbulence inserts and operated by the coolant.
3.5.3.Oil filter
Check for oil pressure and oil leaks, and repair or replace the oil filter if necessary. Change the oil filter cartridge simultaneously at every replacement of engine oil.
Oil filter (Cartridge)
Oil filter head
EQM4010I
— 14 —

3.6. Air cleaner
In case that elements are deformed, damaged or if the air cleaner has a crack, replace it. By the definite interval, the elements must be cleaned and replaced.
— Cleaning of air cleaner element: Every 200 hours.
— Changing of air cleaner element: Every 600
hours.
EFM1002I
3.7. Intercooler
The intercooler is air to air type and has a large cooling fan capacity. The intercooler life and performance depends on the intake air condition greatly. Fouled air pollutes and clogs the air fins of intercooler. As a result of this, the engine output is decreased and engine malfunction is occurred. So you always check whether the intake air systems like air filter element are worn or polluted.
Air/air intercooler with downstream radiator (Combined radiator)
Cooling air
Hot charge air from compressor
Recooled charge air
to intake pipe (max. 50 C)
EA5O4003
— Cleaning of intercooler fins: Every 600 hours.
— 15 —

3.8. Fuel system
The fuel is delivered by the fuel feed pump via the fuel filter to the injection pump and from there to the injection nozzles.
The fuel is sprayed into the cylinders through nozzles fitted in screw-fit injection nozzle holders in the cylinder heads.
Excessively delivered fuel and leak fuel from the nozzle flow through the return pipe back to the tank.
A strainer is arranged ahead of the fuel feed pump.
|
1 |
2 |
5 |
||
4
6
13
8
12
10
EA8O3004
|
1. |
Fuel filter |
7. Delivery pipe |
|
|
1a. Full water drain plug |
8. Fuel pipe (manual pump filter) |
||
|
2. Air bleeding screw (for fuel filter) |
9. Fuel tank |
||
|
3. |
Injection nozzle |
10. |
Fuel return pipe |
|
4. |
Overflow tube |
11. Suction pipe |
|
|
5. |
Fuel pipe (filter injection pump) |
12. |
Feed pump |
|
6. |
Overflow valve |
13. |
Injection pump |
— 16 —

3.8.1.Injection pump
The in-line injection pump is driven via gears from the crankshaft. It is connected to the force feed lubricating system of the engine and consequently maintenance-free. The governor flange-mounted on the pump casing is a variable range governor designed to keep the speed set by the speed control unit constant under conditions of varying load.
Governor system for fuel injection pump consists of “Integral Actuator” and “ Speed Control Unit”.
1) Integral Actuator
2)Speed control unit for governor system
The ESD5550 Series speed control unit is an all electronic device designed to control engine speed with fast and precise response to transient load changes. This closed loop control, when connected to a proportional electric actuator and supplied with a magnetic speed sensor signal, will control a wide variety of engines in an isochronous or droop mode. It is designed for high reliability and built ruggedly to withstand the engine environment.
Simplicity of installation and adjustment was foremost in the design. Non-interacting performance controls allow near optimum response to be easily obtained.
The primary features of the ESD5550 Series speed control unit are the engine STARTING FUEL and SPEED RAMPING adjustments. The use of these features will minimize engine exhaust smoke experienced prior to attaining engine operating speed.
Other features include adjustable droop and idle operation, inputs for accessories used in multiengine or special applications, protection against reverse battery voltage, transient voltages, accidental short circuit of the actuator and fail safe design in the event of loss of speed sensor signal or battery supply.
|
Engine model |
P126TI |
|
GAC governor model |
ACE 175A |
|
Speed control unit model |
ESD5550 |
— 17 —

6.00 (152)
5.25 (133)

|
C1 OFF |
ON |
C2 |
|||
|
LEAD CIRCUIT |
SOFT COUPLING |
||||
|
ON |
OFF |
||||
|
OVERSPEED |
|||||
|
G |
OVERNORS |
1 2 |
3 |
RESET TEST |
|
|
MERICA |
|||||
|
A CORP |
OVERSPEED |
||||
|
SPEED CONTROL UNIT |
|||||
|
MODEL : ESD5550 |
SPEED |
||||
|
S/N |
GAIN |
||||
|
MADE IN AGAWAM, MA U.S.A |
|||||
|
STABILITY |
|||||
|
STARTING |
SPEED |
E2 |
|||
|
FUEL |
RAMPING |
||||
|
E1 |
E3 |
||||
|
CAUTION |
|||||
|
DROOP |
DEAD TIME |
||||
|
COMPENSATION |
|||||
|
ENGINE SPEED CONTROL |
|||||
|
COMPONENT WHEN INSTALLING |
JUMPER |
||||
|
OR SERVICING REFER TO |
|||||
|
PRODUCT PUBLICATION |
|||||
|
PICK-UP |
_ + |
IDLE |
10V |
||
|
ACTUATOR |
BATTERY |
||||
|
AUX |
OUTPUT |
||||
|
A B C D E F G H J K L M N P |
OPTIONAL ACTUATOR CABLE SHELDING TO 
*
ACTUATOR
|
MAGNETIC |
CW |
||
|
PICK-UP |
|||
|
_ |
SPED TRIM |
||
|
+ |
S1 |
CONTROL — 5K |
|
|
FUSE |
|||
|
BATTERY |
|||
|
15A MAX |
|
ACCESSORY POWER |
1.03 (26) |
|
SUPPLY |
ACCESSORY INPUT
ADD JUMPER FOR 12V
BATTERY OR ACTUATOR
CURRENTS ABOVE 5A

CLOSE FORDROOP
CLOSE FOR IDLE
*SEE SPECIFIC ACTUATOR PUBLICATION FOR PROPER WIRING OF ACTUATOR BASED ON BATTERY VOLTAGE
EA6M4004
— 18 —

3.8.2.Fuel filter
This fuel filter has two functions not only oil filtering but also water separating.
Before entering the suction chamber of the injection pump, the fuel is cleaned in a strainer of fuel feed pump and a fuel filter.
Drain water in cartridge with loosening the cock under filter manually (6) from time to time.
The fuel filter should be replaced at every 1,200 hours.
3.8.3.Fuel requirements
DAEWOO marine diesel engines was designed to use Number 2-D diesel fuel or equivalent that meets specification DIN 51601-DK. For maximum fuel economy, Number 2-D fuel whenever possible. When temperatures are below -7˚C(20˚F), use Number 1-D fuel. If Number 1-D fuel is not available, the mixture of one kerosene to two gallons of Number 2-D fuel can be used. Once kerosene has been added, the engine should be run for several minutes to mix the fuel.
3.8.4.How to select fuel oil
Fuel quality is an important factor in obtaining satisfactory engine performance, long engine life, and acceptable exhaust emission levels. DAEWOO engines are designed to operate on most diesel fuels marketed today. In general, fuels meeting the properties of ASTM Designation D975 (grades 1-D and 2-D) have provided satisfactory performance.
The ASTM 975 specification, however, does not in itself adequately define the fuel characteristics needed for assurance of fuel quality.
The properties listed in the fuel oil selection chart below have provided optimum engine performance. Grade 2-D fuel is normally available for generator service. Grade 1-D fuel should not be used in pleasure craft engines, except in an emergency.
— 19 —

Fuel oil selection chart
|
General Fuel |
ASTM |
No. 1 |
No. 2 |
DIN 51601 |
|
|
Classification |
Test |
ASTM 1-D |
ASTM 2-D |
||
|
Gravity,˚API #) |
D 287 |
40 ~ 44 |
33 ~ 37 |
0.815 ~ 0.855 |
|
|
Flash Point |
|||||
|
Min. ˚F (˚C) |
D 93 |
100 (38) |
125 (52) |
131 (55) |
|
|
Viscosity, Kinematic |
|||||
|
CST 100 ˚F (40 ˚C ) |
D 445 |
1.3 ~ 2.4 |
1.9 ~ 4.1 |
1.8 ~ 10 |
|
|
Cloud Point ˚F #) |
D 2500 |
See Note 1) |
See Note 1) |
See Note 1) |
|
|
Sulfur Content |
|||||
|
wt%, Max. |
D 129 |
0.5 |
0.5 |
0.15 |
|
|
Carbon Residue |
D 524 |
0.15 |
0.35 |
0.1 |
|
|
on 10%, wt%, Max. |
|||||
|
Accelerated Stability |
|||||
|
Total Insolubles |
D 2274 |
1.5 |
1.5 |
||
|
mg/100 ml, Max. #) |
|||||
|
Ash, wt%, Max. |
D 482 |
0.01 |
0.01 |
||
|
Cetane Number, Min. +) |
D 613 |
45 |
45 |
> 45 |
|
|
Distillation |
D 86 |
||||
|
Temperature, ˚F(˚C) |
|||||
|
IMP, Typican #) |
350(177) |
375(191) |
|||
|
10% Typical #) |
385(196) |
430(221) |
|||
|
50% Typical #) |
45(218) |
510(256) |
680(360) |
||
|
90% +) |
500 (260) Max. |
625(329) Max. |
|||
|
End Point #) |
550(288) Max. |
675(357) Max. |
|||
|
Water & Sediment |
D 1796 |
0.05 |
0.05 |
0.05 |
|
|
%, Max. |
|||||
#) Not specified In ASTM D 975 +) Differs from ASTM D 975
Note : 1.The cloud point should be 6˚C(10˚F) below the lowest expected fuel temperature to prevent clogging of fuel fitters by crystals.
— 20 —

3.9. Cooling system
The engine has a liquid-cooling system. The fresh water pump is a maintenance-free by gear from the crankshaft.
Depending on the agreed extent of delivery and the design of the engine, the coolant circuit can be equipped with temperature monitors which, in the event of loss of coolant, shut the engine down.
•Check the coolant level of the expansion tank by removing the expansion tank filler cap, and add coolant if necessary.
•When injecting antifreeze solution, first drain out the old coolant from the cylinder block and radiator, and then clean them with cleaning solution.
•Be sure to mix soft water with antifreeze solution.
Water pipe
Thermostat
|
R |
Cylinder head |
||
|
a |
|||
|
d |
|||
|
i |
|||
|
a |
|||
|
Reserve tank |
t |
||
|
o |
|||
|
r |
|||
|
Water pump |
Cylinder block |
||
EJM4001I
— 21 —

3.9.1. Coolant pressure cap
Check the pressure valve opening pressure using a expansion tank cap tester. Replace the filler cap assembly if the measured valve does not reach the specified limit. (pressure valve opening pressure : 0.9 kg/cm2)
Note : Because it is dangerous to open the pressure cap quickly when coolant is hot, after lowering the inside pressure of the tank by slow-opening at first open it fully.
|
Rediater Cap |
|
Rediater |
|
EA5O3002 |
3.9.2.Anti-freeze
The anti-freeze, 50% of the whole coolant,
is always to be used to prevent the cooling system from the corrosion. And in winter the amount of anti-freeze shown in the following table should be used in accordance with the ambient temperature.
As the individual freezing points corresponding to the proportions of antifreeze in the table are subject to change slightly according to the kind of antifreeze, you must follow the specifications provided by the antifreeze manufacturer.
|
Ambient |
Cooling water (%) |
Anti-freeze (%) |
|
|
Temperature (˚C) |
|||
|
Over -10 |
85 |
15 |
|
|
-10 |
80 |
20 |
|
|
-15 |
73 |
27 |
|
|
-20 |
67 |
33 |
|
|
-25 |
60 |
40 |
|
|
-30 |
56 |
44 |
|
|
-40 |
50 |
50 |
|
As the ratio of antifreeze in the mixture decrease each time new coolant is added to make up for the loss coolant resulting from engine operation, Check the mix ratio with every replenishment of coolant, and top up as necessary.
— 22 —

3.10. V-belt tension check and adjust
By the finger-pressure the belt is pressed by 10mm ~ 15mm between the fan pulley and the alternator pulley in normal condition. For the adjustment of the tension, loosen the adjusting bolts which support the alternator, adjust the tension and tighten the bolts again.
|
Press hearre |
||
|
15mm |
||
|
Alternator |
Fan |
|
|
Pulley |
Pulley |
|
|
V-belt |
||
|
Crank Pulley |
EA8O3005 |
|
3.11. Turbocharger
The exhaust gases of the engine are passed through the turbine rotor of the turbocharger. Air compressor impeller mounted on the same shaft draws in fresh air and delivers it at a higher pressure to the cylinders.
The turbocharger is naturally air-cooled. Lubrication of the main bearing is by oil under pressure from the engine lubricating system.
5
C
EA6O3004
|
1. |
Compressor casing |
A. Air inlet |
|
2. |
Turbine casing |
B. Gas outlet |
|
3. |
Compressor wheel |
C. Gas inlet |
|
4. |
Impeller |
D. Oil supply |
|
5. |
Turbine |
E. Oil return |
— 23 —

3.12. Electrical equipment
3.12.1.Alternator
The alternator is fitted with integral silicon rectifiers. A transistorized regulator mounted on the alternator body interior limits the alternator voltage. The alternator should not be operated except with the regulator and battery connected in circuit to avoid damage to the rectifier and regulator.
24V x 45A
|
P-TAB : KET GP 890545 |
|
|
TACHOMETER CHARGE INDICATOR |
|
|
M6 x 1.0 THREAD |
ALDO SYSTEM FREQUENCY = RPM10 |
|
BATTERY TERMINAL |
«L» Terminal
«R» Terminal
CONNECTOR HOUSING
KET MG 620042
TERMINAL
KET ST 740254
|
EA8O3006 |
||||
|
The |
alternator |
is |
maintenance-free, |
|
|
nevertheless, it must be protected against |
To Battery + |
|||
|
dust and, above all, against moisture and |
Regulator |
|||
|
water. |
||||
|
RL = 150~250 OHM |
||||
|
Operate the alternator according to the |
||||
|
instructions given in the chapter. |
||||
|
EA8O3007 |
— 24 —

3.12.2.Starter motor
The sliding-gear starter motor is flanged to the rear of the flywheel housing on the left-hand side. As parts of every engine overhaul, the starter pinion and ring gear should be cleaned with a brush dipped in fuel and then a coat of grease should be applied again.
|
24V x 6.0kW |
||
|
TERMINAL «B» |
TERMINAL S/W |
24V x 6.0kW |
|
M10 x P1.5 |
M5 x P0.8 |
|
|
EA8O3008 |
Always protect starter motor against moisture.
Warning : Always disconnect the battery earth cable before starting work on the electrical system. Connect up the earth cable last, as there is otherwise a risk of shortcircuits.
|
S/W |
B |
W |
|
|
Motor |
B |
S |
|
|
S/W |
|||
|
S/W |
M |
||
|
KS |
|||
|
2.5A(20oC 24V) |
|||
|
EA8O3009 |
— 25 —

4. Commissioning and operation
4.1. Preparation
At the time of initial commissioning of a new or overhauled engine make sure to have
observed the “Technical Information for the installation DAEWOO generator engines”.
•Oil filler neck on cylinder head cover
Before daily starting of the engine, check the fuel, coolant and oil level, replenish if necessary.
The notches in the dipstick indicate the highest and lowest permissible oil levels The oil required in the sump is specified in the “Engine Specification”.
Note : The oil required to fill the oil fillers and pipes depends upon the engine and use and must be determined individually at the time of initial commissioning. (Make the Max and Min. marks of the determined quantity on the oil level gauge.)
•Cleanliness
Ensure outmost cleanliness when handling fuels, lubricants and coolants.
4.2.Breaking-in
4.2.1.Operation of a new engine (Break-In)
Because the sliding surfaces of a new engine are not lapped enough, the oil film can be destroyed easily by overload or overspeed and the engine life-time may be shortened. Therefore the following things must be obeyed by all means.
Up to the first 2,000km (150 hours)
•Engine should be run at fast idling until the temperature of the engine becomes normal operating condition.
•Overload or continuous high speed operation should be avoided.
•High speed operation with no load should be prevented.
•Abrupt start and stop of the engine should be avoided.
•Engine speed must be under 70% of its maximum speed.
•Maintenance and inspection must be accomplished thoroughly.
— 26 —

4.2.2.Check points for break-in
During the break-in (the initial running of the engine) period, be particularly observant as follows:
a)Check engine oil level frequently. Maintain oil level in the safe range, between the “min.” and “max.” marks on dipstick.
Note : If you have a problem getting a good oil level reading on dipstick, rotate dipstick 180˚
and re-insert for check.
b)Watch the oil pressure warning lamp. If the lamp blinks, it may be the oil pick-up screen is not covered with oil. Check oil dipstick. Add oil to the oil pan, if required. Do not overfill. If level is correct and the status still exists, see your DEALER for possible switch or oil pump and line malfunction.
Note : Oil pressure will rise as RPM increases, and fall as RPM decreases. In addition, cold oil will generally show higher oil pressure for any specific RPM than hot oil. Both of these conditions reflect normal engine operation.
c)Watch the engine water temperature gauge and be sure there is proper water circulation. The water temperature gauge needle will fluctuate if water level in expansion tank is too low.
At the end of the break-in period, remove break-in oil and replace the oil filter. Fill oil pan with recommended engine oil. Refer to following table.
<Engine Oil capacity>
|
Oil pan (only) |
|
|
DE12T |
23 liter |
|
P126TI |
23 liter |
4.2.3.Operating after break-in
When starting a cold engine, always allow the engine to warm up gradually. Never run the engine at full throttle until the engine is thoroughly warmed up. Be sure to check the oil level frequently during the first 50 hours of operation, since the oil consumption will be high until the piston rings are properly seated.
— 27 —
4.3. Inspections after starting
During operation the oil pressure in the engine lubrication system must be monitored. If the monitoring devices register a drop in the lube oil pressure, switch off the engine immediately. And the charge warning lamp of the alternator should go out when the engine is running.
•Do not disconnect the battery or pole terminals or the cables!
•If, during operation, the battery charge lamp suddenly lights up, stop the engine immediately and remedy the fault in the electrical system!
•Engine should be stopped if the color, the noise or the odor of exhaust gas is not normal.
•Confirm the following things through warning lamps and gauge panel.
4.3.1.Pressure of lubricating oil
The normal pressure comes up to 1 kg/cm2 (1.0 bar) at idling and 3 ~ 5 kg/cm2 (3.0 ~ 4.9 bar) at maximum speed. If the pressure fluctuates at idling or does not reach up to the expected level at high speed, shut down the engine immediately and check the oil level and the oil line leakage.
4.3.2.Temperature of cooling water
The cooling water temperature should be 78 ~ 85˚C in normal operating conditions. Abnormally high cooling water temperature could cause the overheating of engine and the sticking of cylinder components. And excessively low cooling water temperature increases the fuel consumption, accelerates the wears of cylinder liners and shortens the engine lifetime.
4.4. Operation in winter time
Pay special attention to the freezing of cooling water and the viscosity of lubricating oil.
4.4.1.Prevention against the freeze of cooling water
When not using anti-freeze, completely discharge the whole cooling water after engine running. The freeze of cooling water causes the fatal damages of the engine. Because the anti-freeze is used to prevent cooling water from freeze, consult “The amount of anti-freeze”.
4.4.2.Prevention against excessive cooling
Drop of thermal efficiency caused by excessive cooling increases fuel consumption, therefore prevent the engine from excessive cooling. If the temperature of coolant does not reach to normal condition (78 ~ 85˚C) after continuous operation, examine the thermostat or the other cooling lines.
4.4.3.Lubricating oil
As cold weather leads to the rise of oil viscosity, engine speed becomes unstable after starting. Therefore the lubricating oil for winter should be used to prevent this unstability. Refer to “Lubricating System section”.
—28 —
4.5. Tuning the engine
The purpose of an engine tune-up is to restore power and performance that’s been lost through wear, corrosion or deterioration of one or more parts or components. In the normal operation of an engine, these changes can take place gradually at a number of points, so that it’s seldom advisable to attempt an improvement in performance by correction of one or two items only. Time will be saved and more lasting results will be obtained by following a definite and thorough procedure of analysis and correction of all items affecting power and performance.
Economical, trouble-free operation can better be ensured if a complete tune-up is performed once every years, preferably in the spring. Components that affect power and performance to be checked are:
•Components affecting fuel injection ;
Nozzle, delivery valve, fuel filter, water separator, etc.
•Components affecting Intake & exhaust ; Air filter, inter-cooler, turbo, silencer, etc.
•Components affecting lubrication & cooling ; Air & oil filter, antifreeze, etc.
— 29 —

5. Maintenance and care
5.1. Periodical inspection and maintenance
In order to insure maximum, trouble-free engine performance at all times, regular inspection,
adjustment and maintenance are vital.
•Daily inspections in below figure should be checked every day.
•The maintenance should be executed thoroughly at regular internals. (refer to appendix “General Engine Inspection Cycle”.)
5.2.Lubrication system
5.2.1.Exchanging of lubrication oil
Engine oil and the oil filter are important factors affecting engine life. They affect ease of starting, fuel economy, combustion chamber deposits and engine wear. Refill and drain oil pan every 50 hours of operation or 6 months whichever occurs first. At the end of the breakin period (50 hours), change the oil sump oil and replace the oil filter.
5.2.2.Oil level
Check the oil level in the engine sump daily
|
with a dipstick. |
|||
|
• The notches in dipstick must indicate the |
|||
|
oil level between the max. and the min. |
|||
|
permissible. |
|||
|
• The oil level should be checked with the |
|||
|
engine horizontal and only after it has |
|||
|
been shut down for about 5 minutes. |
|||
|
• Examining the |
viscosity and |
the |
EA4O4001 |
|
contamination of the oil smeared at the |
|||
|
dipstick replace |
the engine oil |
if |
necessary.
Caution : Do not add so much engine oil that the oil level rises above the max. marking on the dipstick. Over lifting will result in damage to the engine.
— 30 —

5.2.3. Oil exchange procedure
While the oil is still hot, exchange oil as follows:
•Take out the oil dip dipstick.
•Remove the drain valve from oil pan and the drain plug form oil filter head, then drain out the engine oil into a container.
•Reassemble the drain valve with the oil pan and the drain plug with oil filter head after draining out the engine oil.
•Refill with new engine oil at the oil filler neck on the head cover and the lubricating oil in accordance with the oil capacity of the engine through oil filler. Be careful about the mixing of dust or contaminator during the supplement of oil. Then confirm that oil level gauge indicates the vicinity of its maximum level.
•For a few minutes, operate the engine at idling in order to circulate oil through lubrication system.
|
EA2O4001 |
|
EA2O4001 |
|
EA7O5003 |
•Thereafter shut down the engine. After waiting for about 10 minutes measure the quantity of oil and refill the additional oil if necessary.
— 31 —

5.2.4. Replacement of oil filter cartridge
|
At the same times of oil exchanges, replace |
|
|
the oil filter cartridge. |
|
|
• Drain engine oil by loosening the drain |
|
|
plug on the filter head. |
Cartridge |
Caution : Don’t forget tightening the drain plug after having drained engine oil.
|
• Loosen the oil filter by turning it counter- |
|
|
clockwise with a filter wrench. |
|
|
• With a rag wipe clean the fitting face of the |
|
|
filter body and the oil filter body so that |
|
|
new oil filter cartridge can be seated |
|
|
properly. |
Drain plug |
EA7O5004
•Lightly oil the O-ring and turn the oil filter
until sealing face is fitted against the O-ring. Turn 1-1/4 turns further with the filter wrench.
Note : It is strongly advisable to use DAEWOO genuine oil filter cartridge for replacement.
5.3. Cooling system
The coolant must be changed at intervals of 1,200 hours operation or six months whichever comes first. If the coolant is being fouled greatly, it will lead an engine overheat or coolant blow off from the expansion tank.
5.3.1.Coolant draining
a)Remove the pressure cap.
b) Open the drain valve at the radiator lower part to drain the coolant as the right figure.
Drain Valve
EA5O4002
— 32 —

c) Loosen the coolant drain plug.
Loosen the coolant drain plug of the cylinder
block.

Caution : When removing the pressure filler cap while the engine is still hot, cover the cap with a rag, then turn it slowly to release the internal steam pressure This will prevent a person from scalding with hot steam spouted out from the filler port.
5.3.2.Cleaning of the cooling inside system circuit (by authorized specialist personnel)
When the cooling system circuit are fouled with water scales or sludge particles, the cooling efficiency will be lowered.
Investigations have shown that in many cases the poor condition of the coolant and /or the cooling system accounts for damage to the water pump mechanical seal, The poor condition of the cooling system is normally due to use of unsuitable or no anti-freezing agents and corrosion inhibitor or defect, not early enough replaced covers for filler neck and working valves.
If twice in a short time the water pump of an engine develops leases or the coolant is heavily contaminated (dull, brown, mechanically contaminated, grey or black sings of a leakage on the water pump casing) clean the cooling system prior to removing that water pump as follows.
a)Drain coolant.
b)Remove thermostats, so that the whole cooling system is immediately flown through when cleaned.
c)Fill the cooling system with a mixture of potable water and 1.5% by volume of cleaner. (Henkel P3T5175)
d)Warm up engine under load. After a temperature of 60˚C is reached, run engine for a further 15 minutes.
e)Drain cleaning fluid.
f)Repeat steps c) and d).
g)Flush cooling system.
h)Replace drain plug by drain plug with a bore of 8mm diameter.
i)Fill cooling system with hot water.
j)Run engine at idle for 30 minutes. At the same time continuously replenish the water leaking from the bore in drain plug by adding fresh water.
Periodically clean the circuit interior with a cleaner.
— Cooling system cleaning interval: Every 1,200 hours.
— 33 —

5.3.3.Intercooler
The intercooler is air to air type and has a large cooling fan capacity. The intercooler life and performance depends on the intake air condition greatly. Fouled air pollutes and clogs the air fins of intercooler. As a result of this, the engine output is decreased and engine malfunction is occurred. So you always check whether the intake air systems like air filter element are worn or polluted.
Air/air intercooler with downstream radiator (Combined radiator)
Cooling air
Hot charge air from compressor
Recooled charge air
to intake pipe (max. 50 C)
EA5O4003
•Cleaning
In order to maintain the heat transfer efficiency of the intercooler, it is necessary to clean it at regular intervals.
Cleaning of intercooler fins : Every 600 hours.
— 34 —

5.4.Air intake system
1.Connection port, fouling indicator
|
2. |
Cleaner housing |
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 6 |
7 |
|
3. |
Clamp |
||||||
|
4. |
Element |
||||||
|
5. |
Hexagon nut |
||||||
|
6. |
Cover |
||||||
|
7. |
Dust bowl |
EA6O5012
5.4.1.Maintenance (only when engine is switched off)
Empty the dust bowl (7) regularly. The bowl should never be filled more than halfway with dust.
On slipping off the two clamps (3), the dust bowl can be removed. Take off the cover (6) of the dust bowl and empty.
Be careful to assemble cover and bowl correctly.
There is a recess in the cover rim and a lug on the collector which should register. Where the filter is installed horizontally, watch for “top” mark on cleaner bowl.
5.4.2.Changing filter element
Caution : Do not allow dirt to get into the clean air end.
On removing the hexagon nut, take out the dirty cartridge and renew or clean.
Wipe the cleaner housing with a damp cloth, in particular the sealing surface for the element.
EA6O5013
Notice : Unless the maximum number of cleanings (up to 5 x) have been done, the filter cartridge should be renewed every two years or 4,000 hours operation.
— 35 —

5.4.3. Cleaning filter elements
|
• By compressed air (Wear goggles) |
|
|
For the purpose, the air gun should be |
|
|
fitted with a nozzle extension which is bent |
|
|
90˚ at the discharge end and which is long |
|
|
enough to reach down inside to the bottom |
|
|
of the element. |
|
|
Moving the air gun up and down, blow out |
|
|
the element from the inside (maximum |
|
|
500kPa — 5 bar) until no more dust comes |
EA6O5014 |
|
out of the filter pleats. |
•By washing
Before washing, the element should be precleaned by means of compressed air,
|
as described above. |
|
|
Then allow the element to soak in |
|
|
lukewarm washing solvent for 10 minutes, |
|
|
and then move it to and for in the solvent |
|
|
for about 5 minutes. |
|
|
Rinse thoroughly in clean water, shake out |
EA6O5015 |
|
and allow drying at room temperature. The |
cartridge must be dry before it is reinstalled.
Never use steam sprayers, petrol (gasoline), alkalis or hot liquids etc. to clean the filter elements.
•Knocking out dirt by hand
In emergencies, when no compressed air or cleaning agent is available, it is possible to clean the filter cartridge provisionally by hitting the end disk of the cartridge with the ball of one’s thumb.
Under no circumstances should the element be hit with a hard object or knocked against a hard surface to loosen dirt deposits.
•Checking the filter cartridge
|
Before reinstalling the cartridge, it must be |
|
|
checked for damage e.g. to the paper |
|
|
pleats and rubber gaskets, or for bulges |
|
|
and dents etc. in the metal jacket. |
|
|
Cracks and holes in the paper pleating can |
|
|
be established by inspecting the cartridge |
|
|
with a flashlight. |
|
|
Damaged cartridges should not be reused |
|
|
under any circumstances. In cases of doubt, |
EA6O5016 |
|
discard the cartridge and install a new one. |
— 36 —

5.5. Fuel system
5.5.1.Fuel filter
•After every 1,200 hour of operation, drain the water and sediment from the fuelwater separator.
•Shut off the engine. Use your hand to
open the drain valve 6 .
•Turn the valve counter clockwise approximately 2 ~ 3 turns until draining occurs. Drain the filter sump of water until close fuel is visible.
•Turn the valve clockwise to close the drain valve. Do not over tighten the valve, overtightening can damage the threads.
5.5.2.Replacement of fuel filter
|
• Clean the area around the fuel filter head |
||||||||
|
3 . |
||||||||
|
• Remove the fuel filter |
2 |
by |
turning |
it |
||||
|
counter-clockwise with filter wrench. |
||||||||
|
(Discard the used filter.) |
||||||||
|
• Remove the fuel filter thread adapter seal |
||||||||
|
ring |
4 . |
|||||||
|
• Use a clean lint free cloth to clean the |
||||||||
|
gasket surface of the fuel filter head |
3 . |
EA7O5008 |
||||||
|
• Install the new thread |
adapter |
seal |
ring |
|||||
|
4 supplied with the new filter. |
||||||||
|
• Use clean oil to lubricate the filter seal |
5 |
, and fill the new filter with clean fuel. |
||||||
|
• Install the filter on the filter head |
3 . |
•Tighten the filter until the gasket contacts the filter head surface.
•Tighten the filter on additional one-half to three-fourths of a turn with the filter wrench, on as specified by the filter manufacturer.
Notice : Mechanical over tightening of the filter can distort the thread or damage the filter
element seal.
— 37 —

5.5.3.Fuel system checks
Fill the tank with the recommended fuel. Keeping tanks full reduces water condensation and helps keep fuel cool, which is important to engine performance.
Make sure fuel supply valves (if used) are open.
To insure prompt starting and even running, the fuel system must be primed with the fuel feed pump manually before starting the engine the first time, or after a fuel filter change. Refill at the end of each day’s operation to prevent condensation from contaminating the fuel. Condensation formed in a partially filled tank promotes the growth of microbial organisms that can clog fuel filters and restrict fuel flow.
If the engine is equipped with a fuel water separator, drain off any water that has accumulated. Water in fuel can seriously affect engine performance and may cause engine damage. DAEWOO recommends installation of a fuel water separator on generator units.
5.5.4.Fuel Contamination and water trap
In the generator environment, the most likely fuel contaminants are water and microbial growth (black “slime”). Generally, this type of contamination is the result of poor fuel handling practices.
Black “slime” requires water in the fuel to form and grow, so the best prevention is to keep water content to a minimum in storage tanks.
If diesel fuel which contains moisture is used the injection system and the cylinder liners / pistons will be damaged. This can be prevented to same extent by filling the tank as soon as the engine is switched off while the fuel tank is still warm (formation of condensation is prevented). Drain moisture from storage tanks regularly. Installation of a water trap upstream of the fuel filter is also advisable.
Notice : A galvanized steel tank should never be used for fuel storage, because the fuel oil reacts chemically with the zinc coating to form powdery flakes which can quickly clog the fuel filters and damage the fuel pump and injection nozzles.
|
5.5.5. Priming pump strainer cleaning |
|
|
Clean the priming pump strainer every 200 |
|
|
operation hours. |
|
|
The strainer is incorporated in the priming |
|
|
pump inlet side joint bolt. |
|
|
Clean the strainer with the compressed air |
|
|
and rinse it in the fuel oil. |
Strainer(Inner) |
EA7O5009
— 38 —

5.5.6. Bleeding the fuel system
|
After the cleaning of the fuel filter or after the |
||
|
engine stop by the lack of fuel, the bleeding |
||
|
of the fuel system must be executed by all |
||
|
means. |
||
|
Bleed the system by manually operating the |
||
|
priming pump with fuel filter outlet joint bolt |
Priming pump |
|
|
and injection pump bleeder screw loosened. |
||
|
• Press the feed pump cap repetitively until |
||
|
the fuel without bubbles comes out from |
EA9O4005 |
|
|
the bleeding valves. |
•After the whole air is pulled out, close the valve of the filter.
•Confirm the resistance of fuel delivery by the repetition pressing of the feed pump cap, Pressure and turn the feed pump cap simultaneously to close it.
5.5.7.Injection pump
•Check the fuel injection pump housing for cracks or breaks, and replace if damaged.
•Check and see if the lead seal for idling control and speed control levers have not been removed.
•No alterations must be made to the injection pump. If the lead seal is damaged the warranty on the engine will become null and void.
•We strongly recommended that any faults developing in the injection pump should be taken care of by authorized specialist personnel.
5.6. Injection Nozzle Maintenance (by authorized specialist personnel)
The injectors are designed to spray the fuel
delivered by the injection pump directly into the spherical combustion chamber in the piston crown.
The injector consists of the nozzle and the nozzle holder.
A copper seal fitted to the injector ensures gas-tight seating and good heat dissipation.
The opening pressure of the nozzle is
EA0M3003
adjusted by means of shims at the compression spring.
— 39 —

|
Normal |
Abnormal |
Abnormal |
EFM1006I |
|||
•Install a nozzle to a nozzle tester.
•Check injection pressure, and adjust the nozzle using the adjusting shim if the pressure does not meet the specified limit.
•Check nozzle spray patterns and replace if damaged.
|
DE12T |
P126TI |
||
|
Injection Nozzle pressure |
220kg/cm2 |
1st : 160kg/cm2 |
|
|
2nd : 220kg/cm2 |
|||
Caution : The injection lines are designed for high operating pressures and should thus be
handled with particular care.
•When mounting the pipes to the engine take care of good fitness.
•Do not bend pipes to permanent deformation (not for replacing the nozzles either).
•Do not mount any heavily bent pipes.
•Avoid bending the pipes at the ends by more than 2 to 3 degrees.
In case of faults in the injection system which might have resulted in excessive operating pressures, not only the failed part but also the injection line has to be replaced.
5.7. Turbocharger
5.7.1. Maintenance (by authorized specialist personnel)
The turbochargers do not call for any specific maintenance.
The only points to be observed are the oil pipes which should be checked at every oil change for leakage and restrictions.
The air cleaners should be carefully serviced.
Furthermore, a regular check should be kept on charge air exhaust gas pipes. Any leakages should be attended to at once because they are liable to cause overheating of the engine. When operating in highly dust or oil-laden atmospheres, cleaning of the air impeller may be necessary from time to time. To this end, remove compressor casing (Caution : Do not skew it!) and clean in a non-acid solvent, if necessary using a plastic scraper.
If the air compressor should be badly fouled, it is recommended that the wheel be allowed to
— 40 —

soak in a vessel with solvent and to clean it then with a stiff brush. In doing so, take care to see that only the compressor wheel is immersed and that the turbocharger is supported on the bearing casing and not on the wheel.
5.7.2. Special hints
It is recommended that the radial and axial clearances of the rotor be checked after every 3,000 hours operation.
This precaution will enable any wear of the Measuring of axial clearance bearings to be detected in good time before serious damage is caused to the rotor and bearings.
• Measuring rotor axial clearance
Turbine wheel chamber
Magnetic vise
Move the turbine shaft to axial direction
Dial gauge
Wear limit : 0.20mm
EA4M2017
• Measuring radial clearance
Dial gauge
Magnetic vise
Oil
Outlet
|
Radial play |
Move the turbine shaft |
|
Limit of wear : 0.57mm |
in both directions |
|
simultaneously |
Oil inlet
EA4M2018
— 41 —

6. Checking and setting
6.1. Adjustment of valve clearance
6.1.1.General information
The valve clearances are to be adjusted at the times of the following situations.
•After initial 50 hour’s operation.
•When the engine is overhauled and the cylinder heads are disassembled.
•When severe noise comes from valve train.
•When the engine is not normally operated, even though there is no trouble in the fuel system. The valve clearance of the cold engine are as follows.
— Intake valves : 0.3mm
—Exhaust valves : 0.3mm
6.1.2.Adjusting order of the valve clearance
1)After letting the #1 cylinder’s piston come at the compression top dead center by turning the crankshaft, adjust the valve clearances.
2)Loosen the lock nuts of rocker arm adjusting screws and push the feeler gauge of specified value between a rocker arm and a valve stem and adjust the clearance with adjusting screw respectively and then tighten with the lock nut.
3)As for the valve clearance, adjust it when in cold, as follow.
|
Model |
Intake Valve |
Exhaust Valve |
|||
|
DE12T |
0.3 mm |
0.3 mm |
|||
|
P126TI |
|||||
|
— By cranking the engine, let #6 cylinder’s valves overlap. |
|||||
|
— In time, adjust the valve clearance corresponding to “ |
”of lower lists. |
||||
|
— Adjust the valve clearance corresponding to “ |
” of lower lists. |
—After reinsuring the valve clearances, retighten if necessary.
4)No. 1 Cylinder is located at the side where flywheel was installed.
— 42 —

|
Flywheel |
Intake Valve |
Exhaust Valve |
Cylinder No. |
CoolingylinderFan |
|
|
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
6 |
|
EA8O6001 |
6.1.3 Method of adjusting the valve clearance
|
1) |
Loosen the lock-nuts |
1 |
using a ring |
||
|
spanner. |
4 |
||||
|
2) |
Insert a thickness gauge of 0.3mm |
||||
|
between valve stem 2 |
and rocker arm |
||||
|
3 . |
1 |
||||
|
3) Turn the adjusting bolts |
4 |
using a screw |
|||
|
driver until the gauge can be pulled out |
3 |
||||
|
with some restriction. |
|||||
|
4) After the adjustment fix the adjusting bolt |
2 |
||||
|
EA0O4014 |
|||||
|
not to rotate and tighten the lock-nut at the |
|||||
|
same time. |
5)Measure the clearance one more time and if necessary adjust again.
— 43 —

6.2. Adjustment of injection timing
6.2.1.Method of adjusting injection timing
•Turn the flywheel until No. 1 piston is placed in the “OT” position of notch marks on the flywheel, and then turn again the flywheel clockwise until showing the notch mark of the right figure corresponding to the injection timing is aligned with the pointer ( ) on the flywheel housing.
|
DE12T |
P126TI |
||
|
Fuel injection timing |
12° |
12° |
|
|
(B.T.D.C static) |
|||
•Turn the timer until the notch mark of the indicator plate attached to the fuel injection pump is aligned with the notch mark of the timer.
|
Timing |
|
|
Check hole |
|
|
Injection timing |
Flywheel |
|
notch mark |
ring gear |
|
EA8O6002 |
|
|
Notch |
|
|
mark |
|
|
EA9O5002 |
— 44 —

•Tighten the coupling fixing bolts and nuts to specified torque.
• Tighten the drive shaft connecting flange fixing bolts to specified torque.
• Install the oil delivery pipe and return pipe.
6.3.Tightening the cylinder head bolts
•The cylinder head bolts are to be tightened in the sequence shown in the illustrations, First tighten the bolts slightly, then slightly more again and finally tighten with a torque wrench.
<Cylinder Head Bolts>
|
Type 1 |
Type 2 |
|||
|
TY |
TY |
|||
|
Specification |
12.9T |
10.9T |
||
|
M14x1.5×153 |
M14x1.5×150 |
|||
|
Torque |
24.5 kg.m |
6 kg.m +180°+150° |
||
|
8 |
2 |
3 |
9 |
|
12 |
13 |
||
|
1 |
4 |
||
|
11 |
14 |
7 6 5 10
EAMD103I
•The tightening by excessive torque may cause the damages of the cylinder head gaskets, the flanges of cylinder liners and the cylinder head bolts, therefore obey the regular torque.
—45 —

6.4.Cylinder compression pressure
1)Stop the engine after warming it up, then remove the nozzle assemblies.
EA9O5003
2) Install a special tool (gauge adapter) in nozzle holder hole and connect the compression pressure gauge to the adapter.
3) Cut off fuel circulation, rotate the starter, then measure compression pressure of each cylinder.
EA9O5004
|
Standard |
24~28 kg/cm2 |
|
Limit |
24 kg/cm2 or less |
|
Allowance among cylinders |
L10% or less |
— Testing conditions : at water temperature of 20 °C and speed of 200 rpm (10 turns)
— 46 —

6.5. V-belts
The tension of the V-belts should be checked after every 2,000 hours of operation.
(1)Change the V-belts if necessary
If in the case of a multiple belt drive, wear or differing tensions are found, always replace the complete set of belts.
(2)Checking condition
Check V-belts for cracks, oil, overheating and wear.
(3)Testing by hand
|
The tension is correct if the V-belts can be |
Press here |
|||
|
pressed in by about the thickness of the V- |
15mm |
|||
|
belt. (no more midway between the belt |
Alternator |
Fan |
||
|
Pulley |
Pulley |
|||
|
pulleys) |
||||
|
A more precise check of the V-belt tension is |
V-belt |
|||
|
possible only by using a V-belt tension tester. |
||||
|
Crank Pulley |
EA8O3005 |
|||
|
(4) Measuring tension |
||||
|
1 Lower indicator arm (1) into the scale. |
||||
|
• Apply tester to belt at a point midway |
||||
|
between two pulleys so that edge of |
1 |
|||
|
contact surface (2) is flush with the V- |
||||
|
belt. |
||||
|
• Slowly depress pad (3) until the spring |
||||
|
can be heard to disengage. This will |
||||
|
cause the indicator to move upwards. |
||||
|
If pressure is maintained after the spring |
EA6O6011 |
|||
|
has disengaged a false reading will be |
||||
|
obtained! |
||||
|
2 |
Reading of tension |
|||
|
• Read of the tensioning force of the belt |
3 |
|||
|
at the point where the top surface of |
||||
|
the indicator arm (1) intersects with the |
||||
|
scale. |
||||
|
• Before taking readings make ensure |
||||
|
that the indicator arm remains in its |
||||
|
position. |
2 |
|||
|
EA6O6012 |
— 47 —
- Manuals
- Brands
- Doosan Manuals
- Engine
- DE12T
- Operation & maintenance manual
-
Contents
-
Table of Contents
-
Bookmarks
Quick Links
Related Manuals for Doosan DE12T
Summary of Contents for Doosan DE12T
-
Page 2
/P126TI /P126TI-1/DE12T. The POLUS means ‘Power Plus’ that is represented more powerful Doosan generating-set engines and it is marked on engine name as an initial P. On the other hand, intial D stands for standard engine prior to POLUS version. -
Page 3: Table Of Contents
CONTENTS <Operation> 1. Safety Regulations ……………………1 1.1. General Notes 1.4. Regulations Designed to Prevent Pollution 1.2. Regulations Designed to Prevent Accidents 1.5. Notes on Safety in Handling Used Engine Oil 1.3. Regulations Designed to Prevent Damage to Engine and Premature Wear 2.
-
Page 4
9.4. Breaking-in 10. Maintenance of Major Components ……………… 113 10.1. Cooling System 10.3. Fuel Injection Pump 10.2. Lubricating System 10.4. Turbocharger 11. Special Tool List ……………………163 • Appendix • Part & After service center • Applications for Doosan Engine… -
Page 5: General Notes
1. Safety Regulations 1.1. General Notes Handling diesel engines and the necessary resources is no problem when the personnel com- missioned with operation and maintenance are trained accordingly and use their common sense. This summary is a compilation of the most important regulations. These are broken down into main sections which contain the information necessary for preventing injury to persons, damage to property and pollution.
-
Page 6
1.2.2. During maintenance and care ¥ Always carry out maintenance work when the engine is switched off. If the engine has to be maintained while it is running, e.g. changing the elements of change-over filters, remember that there is a risk of scalding. Do not get too close to rotating parts. ¥… -
Page 7
2) If faults occur, find the cause immediately and have it eliminate in order to prevent more serious of damage. 3) Use only genuine DAEWOO spare parts. DAEWOO will accept no responsibility for damage resulting from the installation of other parts which are supposedly Òjust as goodÓ. 4) In addition to the above, note the following points. -
Page 8
Health precautions ¥ Avoid prolonged or repeated skin contact with used engine oil. ¥ Protect your skin by means of suitable agents (creams etc.) or wear protective gloves. ¥ Clean skin which has been in contact with engine oil. — Wash thoroughly with soap and water, A nailbrush is an effective aid. — Certain products make it easier to clean your hands. -
Page 9: Engine Assembly
2. General Information 2.1. Engine Assembly 2.1.1. Engine sectional view (Longitudinal) 14 15 EA8M1002 1. Cooling fan 7. Piston pin 13. Crankshaft 2. Exhaust valve 8. Piston 14. Oil pan 3. Valve spring 9. Combustion chamber 15. Connecting rod 4. Oil filter 10.
-
Page 10
2.1.2. Engine sectional view (Cross) EA8M1003 1. Intake manifold 7. Injection nozzle assembly 2. Fuel filter 8. Rocker arm 3. Oil cooler 9. Cylinder head cover 4. Injection pump 10. Exhaust manifold 5. Cylinder block 11. Piston ring 6. Oil filter 12. -
Page 11
2.1.3. Engine assembly views 1) DE12T 3 12 4 13 18 11 10 20 21 26 EA8M1004 1. Cooling fan 10. Flywheel housing 19. Thermostat 2. Cooling water pipe 11. Flywheel 20. Injection pump 3. Oil filler cap 12. Exhaust manifold 21. -
Page 12
2) P126TI / P126TI- 9 10 14 15 16 17 18 20 21 EA8M1005 1. Cooling fan 8. Oil pan 18. Injection pipe 2. Cooling water pipe 9. Starter 19. Thermostat 3. Air pipe 10. Flywheel housing 20. Injection pump (Intercooler Intake manifold) 11. -
Page 13
2.2. Engine Specification Engine Model DE12T P126TI P126TI-1 P126TI- Items Water-cooled, 4 cycle in-line Water-cooled, 4 cycle in-line type Engine type type Turbo charged Turbo charged & intercooled Combustion chamber type Direct injection type Cylinder liner type Replaceable dry liner… -
Page 14: Engine Model And Serial Number
They are also referred to as engine model and serial number because of their location. EA8O3001 ¥ Engine serial No. (example 1 : DE12T) EBHOA300001 MODEL BORE Serial No. SPEED 1500/1800…
-
Page 15: Engine Type
3.2. Engine Type The Engines DE12T/ P126TI / P126TI- are in-line vertical water-cooled 6-cylinder four-stroke diesel engines with direct injection. DE12T is turbo-charged engine, and P126TI / P126TI- models are turbo-charged and inter-cooled engine. 3.2.1. Cylinder block The cylinder block is a single piece of alloy cast iron. To increase its stiffness, it is extended to a level below the crankshaft center line.
-
Page 16: Engine Timing
3.3. Engine Timing Camshaft, oil pump and injection pump are driven by a gear train arranged at the front end. Injection pump gear Camshaft gear Water pump gear (Z = 72) (Z = 72) (Z = 29) Idle gear (Z = 52) Crankshaft gear (Z = 36) Oil pump idle gear…
-
Page 17: Lubrication System
3.5. Lubrication System The engine is equipped with force-feed lubrication. The pressure is produced by a gear pump whose drive gear is in direct mesh with the crankshaft gear at the front end of cylinder block. The oil pump draws the oil from the oil sump and delivers it through the oil cooler and oil filter to the main distributor gallery and from there to the main bearings, big-end bearings and camshaft bearings as well as to the small-end bearings and the rocker arms.
-
Page 18: Air Cleaner
3.5.1. Oil cooler An oil cooler is provided between the oil filter and the cylinder block. This cooler is a flat tube type with turbulence inserts and operated by the coolant. 3.5.2. Oil filter Check for oil pressure and oil leaks, and repair or replace the oil filter if necessary.
-
Page 19
3.7.1. Fuel filter This fuel filter has two functions not only oil filtering but also water separating. Before entering the suction chamber of the injection pump, the fuel is cleaned in a strainer of fuel feed pump and a fuel filter. Drain water in cartridge with loosening the cock under filter manually (6) from time to time. -
Page 20
Fuel oil selection chart General Fuel ASTM No. 1 No. 2 DIN 51601 Classification Test ASTM 1-D ASTM 2-D Gravity, û D 287 40 ~ 44 33 ~ 37 0.815 ~ 0.855 Flash Point D 93 100 (38) 125 (52) 131 (55) û… -
Page 21
3.8. Cooling System The engine has a liquid-cooling system. The fresh water pump is a maintenance-free by gear from the crankshaft. Depending on the agreed extent of delivery and the design of the engine, the coolant circuit can be equipped with temperature monitors which, in the event of loss of coolant, shut the engine down. -
Page 22
For the improper control might give the fatal damage to the cooling water pump and cylinder liners, detail care is needed. ¥ Since DE12T , P126TI and P126TI- cylinder liner is dry type, particularly the cooling water control should be applied thoroughly. -
Page 23
Note : In taking the cooling water sample, if the water in auxiliary tank were taken, it is hard to measure the accurate density. Take the cooling water sample necessarily loosen- ing the cooling water discharge plug. 2) At the state of a test paper soaked in the sampled water, after taking the paper out through water agitation, shake off the water. -
Page 24
3.9. V-belt Tension Check and Adjust By the finger-pressure the belt is pressed by Press hear here 10mm ~ 15mm between the fan pulley and 15mm the alternator pulley in normal condition. For Alternator the adjustment of the tension, loosen the Pulley Pulley adjusting bolts which support the alternator,… -
Page 25: Electrical Equipment
3.11. Electrical Equipment 3.11.1. Alternator The alternator is fitted with integral silicon rectifiers. A transistorized regulator mounted on the alternator body interior limits the alternator voltage. The alternator should not be operated except with the regulator and battery connected in circuit to avoid damage to the rectifier and regulator.
-
Page 26
3.11.2. Starter motor The sliding-gear starter motor is flanged to the rear of the flywheel housing on the left-hand side. When the starting key switch is turned on, the starter motor pinion flies out and engages the ring gear of the flywheel. Then the main contact is closed, current flows, and the engine is started. -
Page 27: Preparation
4. Commissioning and Operation 4.1. Preparation At the time of initial commissioning of a new or overhauled engine make sure to have observed the ÒTechnical Information for the installation DAEWOO generator enginesÓ. ¥ Oil filler neck on cylinder head cover Before daily starting of the engine, check the fuel, coolant and oil level, replenish if necessary.
-
Page 28
At the end of the break-in period, remove break-in oil and replace the oil filter. Fill oil pan with recommended engine oil. Refer to following table. <Engine Oil capacity> Oil pan (only) DE12T 23 liter P126TI/P126TI- 23 liter 4.2.3. Operating after break-in When starting a cold engine, always allow the engine to warm up gradually. -
Page 29: Inspection After Starting
4.3. Inspections after Starting During operation the oil pressure in the engine lubrication system must be monitored. If the mon- itoring devices register a drop in the lube oil pressure, switch off the engine immediately. And the charge warning lamp of the alternator should go out when the engine is running. ¥…
-
Page 30
4.5. Tuning the Engine The purpose of an engine tune-up is to restore power and performance thatÕs been lost through wear, corrosion or deterioration of one or more parts or components. In the normal operation of an engine, these changes can take place gradually at a number of points, so that itÕs seldom advisable to attempt an improvement in performance by correction of one or two items only. -
Page 31: Periodical Inspection And Maintenance
5. Maintenance and Care 5.1. Periodical Inspection and Maintenance In order to insure maximum, trouble-free engine performance at all times, regular inspection, adjustment and maintenance are vital. ¥ Daily inspections in below figure should be checked every day. ¥ The maintenance should be executed thoroughly at regular intervals. (Refer to «…
-
Page 32
5.2.3. Oil exchange procedure While the oil is still hot, exchange oil as fol- lows: ¥ Take out the oil dip dipstick. ¥ Remove the drain valve from oil pan and the drain plug form oil filter head, then drain out the engine oil into a container. Drain Plug EA8O5001 ¥… -
Page 33
¥ Recommend of lubricating oil Initial factory filling is high quality break-in oil (API Service CH-4 grade). During the break- in period (50 hours), check the oil level frequently. Somewhat higher oil consumption is nor- mal until piston rings are seated. The oil level should be maintained in the safe range between Min. -
Page 34: Cooling System
5.2.4. Replacement of oil filter cartridge At the same times of oil exchanges, replace the oil filter cartridge. ¥ Drain engine oil by loosening the drain Cartridge plug on the filter head. Caution : DonÕt forget tightening the drain plug after having drained engine oil.
-
Page 35
c) Loosen the coolant drain plug. Loosen the coolant drain plug of the cylinder block. EAMD001I Caution : When removing the pressure filler cap while the engine is still hot, cover the cap with a rag, then turn it slowly to release the internal steam pressure This will pre- vent a person from scalding with hot steam spouted out from the filler port. -
Page 36
5.3.3. Intercooler The intercooler is air to air type and has a large cooling fan capacity. The intercooler life and performance depends on the intake air condition greatly. Fouled air pollutes and clogs the air fins of intercooler. As a result of this, the engine output is decreased and engine malfunction is occurred. -
Page 37: Air Intake System
5.4. Air Intake System 1. Connection port, fouling indicator 2. Cleaner housing 3. Clamp 4. Element 5. Hexagon nut 6. Cover 7. Dust bowl EA6O5012 5.4.1. Maintenance (only when engine is switched off) Empty the dust bowl (7) regularly. The bowl should never be filled more than halfway with dust. On slipping off the two clamps (3), the dust bowl can be removed.
-
Page 38
5.4.3. Cleaning filter elements ¥ By compressed air (Wear goggles) For the purpose, the air gun should be fit- ted with a nozzle extension which is bent û at the discharge end and which is long enough to reach down inside to the bottom of the element. -
Page 39: Fuel System
5.5. Fuel System 5.5.1. Fuel filter ¥ After every 200 hour of operation, drain the water and sediment from the fuel- water separator. ¥ Shut off the engine. Use your hand to open the drain valve ¥ Turn the valve counter clockwise approxi- mately 2 ~ 3 turns until draining occurs.
-
Page 40
5.5.3. Fuel system checks Fill the tank with the recommended fuel. Keeping tanks full reduces water condensation and helps keep fuel cool, which is important to engine performance. Make sure fuel supply valves (if used) are open. To insure prompt starting and even running, the fuel system must be primed with the fuel feed pump manually before starting the engine the first time, or after a fuel filter change. -
Page 41
5.5.5. Priming pump strainer cleaning Clean the priming pump strainer every 200 operation hours. The strainer is incorporated in the priming pump inlet side joint bolt. Clean the strainer with the compressed air and rinse it in the fuel oil. Strainer(Inner) EA7O5009 5.5.6. -
Page 42
¥ Check injection pressure, and adjust the nozzle using the adjusting shim if the pressure does not meet the specified limit. ¥ Check nozzle spray patterns and replace if damaged. DE12T P126TI / P126TI- 1st : 160kg/cm Opening pressure 220kg/cm… -
Page 43
5.7. Turbocharger 5.7.1. Maintenance (by authorized specialist personnel) The turbochargers do not call for any specific maintenance. The only points to be observed are the oil pipes which should be checked at every oil change for leakage and restrictions. The air cleaners should be carefully serviced. Furthermore, a regular check should be kept on charge air exhaust gas pipes. -
Page 44
Dial gauge Magnetic vise Outlet Move the turbine shaft Radial play in both directions Limit of wear : 0.57mm simultaneously Oil inlet EA4M2018 — 40 -… -
Page 45: Adjustment Of Valve Clearance
6. Checking and Setting 6.1. Adjustment of Valve Clearance 6.1.1. General information The valve clearances are to be adjusted at the times of the following situations. ¥ After initial 50 hourÕs operation. ¥ When the engine is overhauled and the cylinder heads are disassembled. ¥…
-
Page 46
Loosen the lock nuts of the rocker arm adjusting screws and push the specified feeler gauge and adjust the valve clearance with adjusting screw respectively. Model Intake Valve Exhaust Valve DE12T 0.3 mm 0.3 mm P126TI / P126TI- 6.1.3 Method of adjusting the valve clearance… -
Page 47: Adjustment Of Injection Timing
Check hole flywheel clockwise until showing the notch mark of the right figure corresponding to the injection timing is aligned with the pointer ( ) on the flywheel housing. DE12T P126TI/P126TI- Fuel injection timing 12¡ 16¡ (B.T.D.C static) Injection timing…
-
Page 48
¥ Tighten the coupling fixing bolts and nuts to specified torque. 6.0 kg . m Torque EAMD021I ¥ Tighten the drive shaft connecting flange fixing bolts to specified torque. 7.5 ~ 8.5 kg . m Torque ¥ Install the oil delivery pipe and return pipe. 6.3. -
Page 49
6.4. V-belts The tension of the V-belts should be checked after every 2,000 hours of operation. (1) Change the V-belts if necessary If in the case of a multiple belt drive, wear or differing tensions are found, always replace the complete set of belts. -
Page 50
75 kg 70 kg 60 kg 20.2 mm 75 kg 70 kg 60 kg : Adopted in DE12T and P126TI / P126TI- (5) Tensioning and changing V-belt ¥ Remove fixing bolts. (1) ¥ Remove lock nut. (2) ¥ Adjust nut (3) until V-belts have correct tensions. -
Page 51: Periodic Inspection Cycle
7. Operation Tip 7.1. Periodic Inspection Cycle : Check & adjust : Replace Every Every Every Every Every Inspection Daily Remark 50hrs 200hrs 400hrs 800hrs 1200hrs Check for leakage(hoses, clamp) Check the water level Cooling Change the coolant water System Every Adjust the V-belt tension 2,000hrs…
-
Page 52: Trouble Shooting
7.2. Trouble Shooting 1. Engine Starting Impossible Starting motor operation poor Starting motor revolution Inspection of battery electorlytic Engine Fuel Ilquid amount & gravity Inspect air cleaner Inspect amount of fuel Normal Too low Normal None Normal Polluted Ajustment Recharging Replace or Replenish clean element…
-
Page 53
2. Engine Overheated Operating state 1. Overload 2. Radiator core clogged Fuel unit Cooling unit 3. Continuous over-run Check coolant Fuel excessive supply Inspect fuel quality Normal Too low Poor Check fan belt Clean and replace Repair Check injection nozzle tension wear with specilied fuel Replace… -
Page 54
3. Output Insufficient Engine Installation improper Check for coupling Fuel unit Others alignemnt Check for air mixing Inspect air cleaner Adjust or replace in fuel coupling Normal Clean Relpace Inspect fuel supply pump Inspect air leakage Inspect engine control Normal Clean Replace of air piping line rod, link, cable, etc. -
Page 55
4. Oil pressure lowered Check if oil pressure gauge indicates wrongly Check oil amount Too low Normal Use recommended oil Check cooling (replenish) temperature Too high Normal Refer to engine overhea Inspect oil quality Normal Check oil relief Water & fuel mixed Improper valve in oil… -
Page 56
5. Fuel Consumption Excessive Causes according to Use Conditions 1. Overload 2. Govemor’s Arbitrary Adjustment 3. Full Speed Operation for Long time 4. Sudden Speed Change from Low to Inspect fuel leakage High Speed Normal Oil leakage Inspect injection nozzle (injection pressure Adjust Replace atomizing state etc.) -
Page 57
6. Oil Consumption Excessive Cause according to use conditions 1. Excessive oil infusing 2. Continuous operation in low or extremely cold state Inspect oil leakage Inspect air cleaner Clean Replace Normal Oil leakage Check oil quality Internal External Retighten Check compressed Replace with Replace pressure… -
Page 58
8. Battery Discharge Generator Wiring Switch Battery Inspect cut wire Check fan belt Check electrolytic shorts and loose tension & damage liquid amount connections Repair Replace Normal Battery over Battery self Battery room Electrolytic charging discharge damage liquid’s standard Inspect generator Charging Voltage regulator Replace… -
Page 59
7.3. Causes and Remedies Condition Causes Remedies ¥ ValveÕs poor shut, stem distortion Repair or replace 1) Starting difficult ¥ (1) Compression pressure Valve spring damage Replace valve spring ¥ Cylinder head gasketÕs leak Replace gasket ¥ Wear of piston, piston ring or liner Adjust ¥… -
Page 60
Condition Cause Remedies 5) Engine noisy For noises arise compositely such asrota ting parts, lapping parts etc., there is nec essity to search the cause of noises accu rately. ¥ (1) Crankshaft As the wear of bearing or crankshaft Replace bearing & progress, the oil clearances increase. -
Page 61
Condition Cause Remedies 7) Oil Consumption Excessive ¥ (1) Oil level elevated Clearance between cylinder iner & Replace piston ¥ Wear of piston ring, ring groove Replace piston, piston ring ¥ Piston ringÕs damage, stick, wear Replace piston ring ¥ Piston ring openingÕs disposition Correct position improper… -
Page 62: General Information
8. General Information 8.1. General Repair Instructions 1. Before Performing service operation, disconnect the grounding cable from the battery for reducing the chance of cable damage and burning due to short-circuiting. 2. Use covers for preventing the components from damage or pollution. 3.
-
Page 63
POLUS P126TI, P126TI- DE12T (DE12 series) generator diesel engines discharge very low level of haz- ardous exhaust gases such as smoke, nitro- gen oxide, hydrocarbon, or carbon monoxide and thus ensure high performance and low fuel consumption. -
Page 64
9. Disassembly and Reassembly of Major Components 9.1. Disassembly 9.1.1. General precautions ¥ Maintenance operation should be carried out in a bright and clean place. ¥ Before disassembly, provide parts racks for storage of various tools and disassembled parts. ¥ Arrange the disassembled parts in the disassembly sequence and use care to prevent any damage to them. -
Page 65
9.1.3. Engine oil ¥ Take out the oil dipstick. ¥ Remove the oil drain valve of oil pan and drain out the engine oil into a prepared container. Drain valve EA8O5001 9.1.4. Alternator belt ¥ Loosen the tension adjusting nut installed on the alternator bracket, and take off the alternator belt. -
Page 66
9.1.7. Guide tube of oil level gauge ¥ Loosen the flange nut installed on the oil pan to remove the guide tube. EQM3005I 9.1.8. Fuel filter ¥ Remove fuel hoses connected to the fuel injection pump, take off the bracket fixing bolts, then disassemble the fuel filter. -
Page 67
9.1.11. Injection pipe ¥ Unscrew the hollow screws to disassem- ble the fuel return pipe. ¥ Remove the nuts installed on the fuel injection pump and nozzles, then disas- semble the injection pipe. EQM3009I 9.1.12. Intake manifold ¥ Remove the air hose connected to the fuel injection pump. -
Page 68
9.1.14. Exhaust manifold ¥ Release the exhaust manifold fixing bolts, disassemble the exhaust manifold, then remove the heat shield and gasket. NOTE : Make sure to release the nuts one after another because the exhaust manifold will removed if you unscrew two nuts simultaneously. -
Page 69
9.1.17. Water pump ¥ Remove the water pipe connected to the expansion tank. ¥ Remove the water pipe and hoses con- nected to the water pump. ¥ Unscrew the water pump fixing bolts and remove the water pump. 9.1.18. Injection pump ¥… -
Page 70
9.1.20. Fan drive pulley ¥ Remove the bolts and disassemble the fan drive pulley. 9.1.21. Vibration damper ¥ Unscrew the pulley fixing bolts and dis- assemble the pulley-vibration damper assembly. ¥ Unscrew the vibration damper fixing bolts and disassemble the damper from the pulley. -
Page 71
9.1.24. Fuel injection pump drive assembly ¥ Unscrew the injection pump drive shaft bearing housing fixing bolts and remove the injection pump drive assembly which the shaft, gear, bearings, and housing are put together. EAMD027I 9.1.25. Cylinder head cover ¥ Unscrew the cover fixing bolts and dis- assemble the cover. -
Page 72
9.1.28. Cylinder head ¥ Unscrew the cylinder head fixing bolts and take off the cylinder head. ¥ Remove the cylinder head gasket. EAMD031I 9.1.29. Valve and valve stem seal ¥ Compress the valve spring retainer using a jig and take off the valve cotter pins. ¥… -
Page 73
9.1.31. Oil pan ¥ Stand the engine with the flywheel hous- ing facing the bottom. ¥ Release the oil pan fixing bolts, remove the stiffeners then disassemble the oil pan. EAMD034I 9.1.32. Oil pump and oil pipe ¥ Unscrew the oil suction pipe bracket bolts, releasing the pipe fixing bolts, then disassemble the oil suction pipe assem- bly. -
Page 74
¥ Remove the piston pin snap rings, take off the piston pin, then disconnect the connecting rod from the piston. ¥ Disassemble the piston rings using ring pliers. ¥ Use care not to interchange the disas- sembled parts and keep them in the sequence of cylinder No. -
Page 75
9.1.37. Oil seal ¥ Take off the rear oil seal using an oil seal disassembling jig. ¥ If only the inside guide ring is removed, use a special tool to take off the outside seal. 9.1.38. Flywheel housing ¥ Loosen the housing fixing bolts disas- semble the flywheel housing. -
Page 76
9.1.41. Timing gear case ¥ Unscrew the case fixing bolts and disas- semble the timing gear case. EAMD046I 9.1.42. Crankshaft ¥ Remove the bolts from bearing caps. ¥ Remove the main bearing cap fixing bolts in the order of assembling. ¥… -
Page 77
9.2. Inspection 9.2.1. Cylinder block 1) Clean the cylinder block thoroughly and make a visual inspection for cracks or damage. 2) Replace if cracked or severely damaged, and correct if slightly damaged. 3) Check oil and water flow lines for restriction or corrosion. 4) Make a hydraulic test to check for any cracks or air leaks.(Hydraulic test) : Stop up each outlet port of water/oil passages in the cylinder block, apply air pressure of about 4kg/cm… -
Page 78
3) flatness Measure flatness of the intake/exhaust manifolds fitting surfaces on the cylinder head using a straight edge and a feeler gauge. Standard Limit 0.05 mm 0.2 mm 4) Hydraulic test Hydraulic test method for the cylinder head is same as that for cylinder block. 9.2.3. -
Page 79
• Valve head thickness Measure the valve head thickness, and replace the valve if the measured value is beyond the limit. Dimension Standard Limit Description Intake valve 1.5 mm 1 mm or less Exhaust valve 1.5 mm 0.9 mm or less EFM2037I 2) Valve guide Install the valve into the valve guide and… -
Page 80
3) Valve seat • Contacting face amount Measure the contacting face between intake valve and exhaust valve seat for valve seat wear, and replace if the mea- sured value exceeds the specified limit. Valve contact width Contact width ✝✞✟✏❆☛✌ Standard Limit 1.5 mm 2.0 mm… -
Page 81
For assembling of a new valve seat, by putting it among the dry ices of an ice box previ- • ously for about 2 hours for the cold shrinkage, and press it in the cylinder head by a special tool. (bench press) Apply the valve lapping compound on the valve head seating face and lap the valve seat by •… -
Page 82
• Valve spring tension Use a spring tester to measure the valve spring tension if the measured value is less than the specified limit, the valve spring must be replaced. Spring Set Length Limit force Spring tester Valve Spring Intake 61.8 ~ Tension at 37mm 61.8 kg… -
Page 83
2) Rocker arm • Visual check Visually check the face of the rocker arm in contact with the valve stem end for scores and step wear. If the wear is small, correct it with an oil stone or grind- ing paper of fine grain size. Rocker arm with a considerable amount of step wear should be replaced. -
Page 84
• Visual check of tappet Visually check the face of the tappets in contact with the cam for pitting, scores or cracks, and replace if severely damaged. If the amount of cracks or pitting is small, Unevenness Crack Normal correct with an oil stone or grinding ❘❏❆✔✠✟☛… -
Page 85
9.2.5. Cam shaft 1) Cam • Cam lobe height Standard Limit Cam journal diameter(A,B) 59.86 ~ 59.88 mm 59.52 mm Use a micrometer to measure the cam journal diameter. I II If the measured number is less than the I II specified limit, camshaft… -
Page 86
• Run-out Support the camshaft on two V blocks and check for run-out using a dial indi- cator. Correct or replace the cam shaft if the amount of run-out is beyond the value indicating need for servicing. Standard Limit 0.05 mm 0.2 mm EA0M4066 3) Cam shaft end play… -
Page 87
2) Wear With an outside micrometer measure the • diameter of the crankshaft journals and pins in the directions as shown, and compare the measured values to deter- mine the amount of wear. If the amount of wear is beyond the limit, •… -
Page 88
3) Crankshaft run-out Support the crankshaft on V blocks. • Turn the crankshaft with a dial indicator • placed on the surface plate and take the amount of crankshaft run-out. Standard Limit 0.05 mm 0.1 mm 9.2.7. Crank shaft bearing and connection rod bearing 1) Visual check Visually check the crankshaft bearing and connecting rod bearing for scores, uneven… -
Page 89
• Connecting rod bearing clearance Install the connecting rod bearing in the connecting rod bearing cap, tighten the connecting rod cap bolts to the specified torque, then measure the inside diame- ter. • 28 kg Torque 83.02 ~ 83.092 mm Standard Dia. -
Page 90
Spread = O A — O B EDM2047I • Crankshaft bearing crush Install the bearing and cap in the cylinder block, retighten the bolts to specified torque, unscrew out one bolt completely, then measure the clearance between the bearing cap and cylinder block using a feeler gauge. -
Page 91
9.2.8. Piston 1) Visual check Visually check the pistons for cracks, scuff or wear, paying particular attention to the ring groove. 2) Clearance between the piston and cylinder liner With an outside micrometer, measure • the piston outside diameter at a point 18mm away from the lower end of pis- ton skirt in a direction at a right angle to the piston pin hole. -
Page 92
9.2.9. Piston rings 1) Visual check Replace the piston rings with new ones if detected worn or broken when the engine is overhauled. 2) Piston ring gap Insert the piston ring into the upper por- • tion of the cylinder liner bore so that it is held at a right angle to the cylinder liner wall. -
Page 93
4) Piston ring tension With a tension tester, measure piston ring tension. Replace the piston ring if the measured value is beyond the limit. Standard Top ring 2.27 ~ 3.41 kg 2nd ring 2.0 ~ 3.0 kg Oil ring 4.03 ~ 5.57 kg 9.2.10. -
Page 94
9.2.11. Connecting rod 1) Distorsion Check the connecting rod for distortion. As shown in the figure below, install the connecting rod to the connecting rod tester, and check for distortion using a feeler gauge. If the connecting rod is found distorted, never re-use it but replace with a new one. -
Page 95
9.3. Reassembly 9.3.1. General precautions ¥ Wash clean all the disassembled parts, particularly oil and water ports, using compressed air, then check that they are free from restrictions. ¥ Arrange the general and special tools in order for engine assembly operation. ¥… -
Page 96
¥ Apply engine oil to the entire face of the tappets and slide them into the tappet holes on the cylinder block. ¥ Wet the cam bush inside diameter and camshaft with oil, and carefully assem- ble them while turning the camshaft. ¥… -
Page 97
¥ Semi-tighten a bolt at both sides of the crankshaft, apply engine oil to journals and pins, then assemble the crankshaft with the cylinder block by tightening the fixing bolts. ¥ Install the oiled thrust washers with the oil groove facing outward. ¥… -
Page 98
¥ Apply oil to the entire part of the bearing cap bolts, then tighten in tightening sequence to specified torque. ¥ Torque 30 kg ¥ After semi-tightening both bolts evenly, tighten them diagonally specified torque using a torque wrench as follows. EQM3059I <Tightening order>… -
Page 99
9.3.8. Flywheel ¥ Install a guide bar into a bolt hole on the crank shaft, and lift the flywheel to align the dowel pin with the pin hole on the fly- wheel for temporary assembly opera- tion. ¥ Install bolts in the remaining holes, take out the guide bar, then install a bolt in the hole where the guide bar had been inserted. -
Page 100
9.3.11. Timing gear ¥ Install the oil pump idle gear onto the No.7 bearing cap. ¥ Install a thrust washer over the camshaft Idle gear pin and assemble the cam gear by aligning it with camshaft key groove. Torque 3.1 kg ¥… -
Page 101
9.3.12. Timing gear case cover ¥ Install dowel pin on the timing gear case. ¥ Mount a gasket by aligning the fixing bolt holes with those on the gasket. ¥ Align the dowel pin with the cover pin hole, then install the cover with light tap. ¥… -
Page 102
9.3.15. Piston and connecting rod ¥ Use a piston heater to heat the piston approximately 100 ûC (212 ûF ) for 5 min- utes. ¥ Align the piston pin hole with the oiled connecting rod small end and press the piston pin (by lightly tapping with a rub- ber hammer) to assemble the connect- ing rod with the piston. -
Page 103
¥ Identify the mark «Y» or «TOP» on the ring end to prevent the top and bottom of the piston ring is interchanged each other and make the marked top face upward. Note : Be sure to make the piston ring end marked face(«Y»… -
Page 104
¥ Wet the fixing bolts with oil, semi-tighten them with hand, tighten them to specified torque using a torque wrench as follows. <Tightening order> (1) First stage : Coat engine oil over bolts (2) Second stage : Temporary screw the bolt about 1 ~ 2 threads (3) Third stage : With torque wrench, tighten at about 15 kg.m (4) Fourth stage : With torque wrench, tighten up to about 22 kg.m (5) Fifth stage : Finally, tighten in the specified torque 28kg.m with torque wrench . -
Page 105
9.3.18. Oil pan ¥ Mount gasket and put the oil pan there- ¥ Place stiffeners and tighten bolts. ¥ Align the bolt holes with gasket holes to prevent damage to the gasket and tight- en to specified torque. Torque 2.2 kg ¥… -
Page 106
9.3.20. Nozzle tube ¥ Apply sealant (LOCTITE # 620) to the nozzle tube and place the O-ring over the cylinder head fitting face on the nozzle tube, then install the nozzle tube in the cylinder head. ¥ Install a guider of the nozzle tube insert assÕy (Guider + Expander) the cylinder Guider head, then tighten the nozzle fixing nuts. -
Page 107
¥ Check the inside of combustion chamber for foreign substances, and carefully mount the cylinder head assembly in the block by aligning the dowel pin with the dowel pin hole. Be careful not to damage the head gasket. If the dowel pin is not in alignment, lift the cylinder head again and then remount it. -
Page 108
As for the valve clearance, adjust it when in cold, as follow. Model Intake Valve Exhaust Valve DE12T 0.3 mm 0.3 mm P126TI / P126TI- — By cranking the engine, let #6 cylinderÕs valves overlap. -
Page 109
¥ Adjust valve clearance with a feeler Valve clearance adjust gauge and tighten the fixing nuts to specified torque. 4.4 kg . m Torque EA8M3007 9.3.22. Rocker arm assembly ¥ Apply lubricating oil to the rocker arm bush and shaft, and assemble the inter- mediate bracket with the rocker arm using fixing bolts. -
Page 110
9.3.24. Oil cooler ¥ Install the oil cooler onto the oil cooler cover. ¥ Carefully apply the gasket to prevent oil leakage. ¥ Do not damage the gasket and install the cover onto the cylinder block. ¥ Connect a connection pipe between the water pump and oil cooler. -
Page 111
( ) on the fly- wheel housing. DE12T P126TI/P126TI- Fuel injection timing 12¡ 16¡ (B.T.D.C… -
Page 112
¥ Tighten the Coupling fixing bolts and nuts to specified torque. Torque 6.0 kg ¥ Tighten the drive shaft connecting flange fixing bolts to specified torque Torque 7.5 ~ 8.5 kg EAMD021I ¥ Install the oil delivery pipe and return pipe. -
Page 113
9.3.30. Power take-off ¥ Assemble the power take-off sub assem- bly. EA8M3010 9.3.31. Exhaust manifold ¥ Install the exhaust manifold gasket over the stud bolts by aligning the gasket with the exhaust port on the cylinder head so that the face and back of the gasket can be positioned correctly. -
Page 114
9.3.33. Starter ¥ Assemble the starter in position on the flywheel housing. ED5OM009 9.3.34. Intake manifold ¥ Fit a gasket on the intake manifold before assembling the intake manifold. EQM3011I 9.3.35. Injection pipe & fuel return pipe ¥ Assemble the injection pipe according to specified torque as blow Nut size Torque… -
Page 115
9.3.36. Fuel filter ¥ Assemble the fuel filter with the intake manifold. ¥ Assemble the fuel feed hose according to the direction of an arrow impressed on the fuel filter head so that fuel can be fed in the sequence of FUEL FEED PUMP FUEL FILTER FUEL INJECTION PUMP. -
Page 116
9.3.39. Cooling fan ¥ Install the cooling fan and flange, then tighten the fixing boltd. EQM3106I 9.3.40. V- belt ¥ Install the V-belt on the crank pulley, Press here alternator pulley and fan drive pulley. 15mm ¥ Adjust the V-belt tension using the ten- Alternator sion adjusting bolt. -
Page 117
10. Maintenance of Major Components 10.1. Cooling System 10.1.1. General information This engine is water-cooling type. Heat from the combustion chamber and engine oil heat are cooled down by coolant and radiated to the outside, resulting in the normal operation of the engine. -
Page 118
10.1.2. Water pump ¥ Loosen the bolt (16) to disassemble the housing cover (15). ¥ Heat the impeller (6) slightly, then remove it using a puller jig. ¥ Remove the mechanical seal. ¥ Unscrew the socket bolt (12) and remove the shaft and bearing assembly from the housing. ¥… -
Page 119
10.1.3. Thermostat ¥ General descriptions and main data To radiator The thermostat maintains a constant tem- û perature of coolant (71 ~ 85 C) and improves thermal efficiency of the engine by preventing heat loss. Namely, when the temperature of coolant Bypass is low, the thermostat valve is closed to valve… -
Page 120
10.1.4. Diagnostics and troubleshooting Complaints Possible causes Corrections ¥ ¥ 1. Engine overheating Lack of coolant Replenish coolant ¥ ¥ Radiator cap pressure Replace cap valve spring weakened ¥ ¥ Fan belt loosened or Adjust or replace fan belt broken ¥… -
Page 121: Lubricating System
10.2. Lubricating System 10.2.1. General descriptions and main data ¥ General descriptions All the engine oil pumped up from the oil pan by the gear type oil pump is filtrated through the oil cooler and oil filter, and this filtrated oil is forced through the main oil gallery in the cylinder block from where it is distributed to lubricate the various sliding parts, and fuel injection pump in order to ensure normal engine performance.
-
Page 122
10.2.2. Oil pump ¥ Disassembly (1) Disassembly of oil pump drive gear a .Unscrew the screw and disassem- ble the oil relief valve. b. Unfold the washer for the oil pump drive gear fixing nut and remove the nut. c. Disassemble the drive gear. EQM4006I (2) Remove the oil pump cover fixing nuts and disassemble the oil pump cover. -
Page 123
(3) Measuring clearance between drive shaft and bushing a. Measure the outside diameters of the drive shaft and driven shaft, and replace if the measured values are less than the limit. Limit 16.95 mm b. Measure the inside diameter of the pump body bushing to determine the clearance between the bushing and shaft, and compare the measured value with the standard value to determine whether to replace or not. -
Page 124
10.2.4. Diagnostics and troubleshooting Complaints Possible causes Corrections ¥ ¥ 1. Oil consumption Poor oil Use suggested oil ¥ ¥ excessive Oil seal or packing leaky Replace ¥ ¥ Pistons or piston rings worn Replace pistons and/or pis ton rings ¥… -
Page 125: Fuel System
10.3. Fuel Injection Pump 10.3.1. General information of fuel system The fuel system consists of the fuel tank, injection pump, injection nozzle, fuel filter, and fuel lines such as pipes and hoses necessary to connect those components. EA8O3004 1. Fuel filter 7.
-
Page 126
Make sure that servicing should be performed at the professional maintenance shop as authorized by Bosch or Zexel Company. For adjustment of fuel injection volume, refer to the ÔSpecifications of fuel injection pumpÕ described on the following pages. 1) DE12T (1) Main data and specifications Part No. : 65.11101-7222(106672-9920) -
Page 127
(8) Governor adjustment Rack limit over 14 11.0 10.8 Idle spring Set : 6.5 -0.5 +5 _ 250 400 PUMP SPEED (rpm) EA8M4001 — 123 -… -
Page 128
2) P126TI / P126TI- (1) Main data and specifications Part No. : 65.11101 -7310 (106674-4130 ZEXEL) Model : NP-PE6P120/700RS3S (106067-6020) Governor : Ghana Control (DWA-2000) Plunger & barrel 12, right hand double helix 30 lead Delivery valve : 90mm /st ( 7 x 2.35mm) Fuel feed pump : NP-FP/KD-PS (105237-5470) Pre-stroke… -
Page 129
10.3.3. Governor System (P126TI/ P126TI- ) Governor system for fuel injection pump consists of ÒIntegral ActuatorÓ and ÒSpeed Control UnitÓ. 10.3.3.1. Integral actuator EC2OM316 <Dimension View> Fig. No. Description QÕty Remark Frame Bearing retainer kit AssÕy Mounting bar SWP connector Mg610320 Front cover T3.2… -
Page 130
10.3.3.2. Speed Control Unit for Governor System (DWC-2000 SERIES SPEED CONTROL UNIT) <Introduction> This speed control unit performs the electronic function of the engine governing system. The speed control unit senses the pulses from the magnetic speed sensor, compares them with the speed control unit’s set point and supplies the appropriate current output to the actuator to control the engine’s fuel system. -
Page 131
The engine speed signal is usually obtained from a magnetic speed sensor mounted in close prox- imity to the teeth of a ferrous ring gear that is driven by the engine. The frequency of the speed sen- sor signal is proportional to the engine speed. The speed control unit will accept any signal if the fre- quency is proportional to engine signal, and in the frequency range of the speed control unit (1K to 7.5K Hz.). -
Page 132
1) Specification ¥ Performance Isochronous Operation / Steady State Stability ……….±0.25% or better Speed Range/Governor …………….. 1K~7.5 K Hz continuous Speed Drift with Temperature …………….±0.5% Maximum Idle Adjust CW ………………..60% of set speed Idle Adjust CCW ………….É.É……..Less than 1200Hz Droop Range …………É..ÉÉ…… -
Page 133
Reset Crank Overspeed Crank Test Speed Gain : DWC-2000 Stability : DC24V : 65.11220-7006 Starting GHANA CONTROL Fuel 826-1 Kuro 3-Dong, Duro-Gu Seoul 152-053 KOREA(DONG-IL TECKNO-TOWN) MADE IN KOREA Speed Ramping Idle Idle Speed Trim Droop Droop Autuator Pic-up Battery AUX 10V 10V POWER AUX. -
Page 134
2) Application and installation information The speed control unit is rugged enough for mounting in a control cabinet or engine mounted enclo- sure or in a remote console up to 20 meters(65ft.) from the engine. Care should be taken to insure that the speed control unit, mount it vertically so that condensation will not accumulate in the speed control unit. -
Page 135
¥ Start engine The speed control unit governed speed setting is factory set at approximately engine idle speed. Crank the engine with DC power applied to the governor system. The actuator will energize to the maximum fuel position until the engine starts. The governor system should control the engine at a low idle speed. -
Page 136
Method 2 : Start the engine and control at an idle speed for a period of time prior to accelerating to the operating speed. This method separates the starting process so that each may be optimized for the lowest smoke emissions. Replace the connection between Terminals M &… -
Page 137
¥ Accessory input The AUXiliary Terminal N accepts input signals from load sharing units, auto synchronizers, and other governor system accessories, DWC accessories are directly connected to this terminal. It is recommended that this connection from accessories be shielded as it is a sensitive input terminal. If the auto synchronizer is used alone, not in conjunction with a load sharing module, a 3M ohm resistor should be connected between Terminals N and P. -
Page 138
¥ OVERSPEED shutdown setting DWC-2000 has a Test switch to determine the OVERSPEED set point and test the engine shut- down function. If you want to adjust the OVERSPEED set point at the speed about 10% higher than the RUN set speed, use the Test switch. When the engine is operating at the Run set speed in pushing the Test switch, rotate the Overspeed Adjust. -
Page 139
¥ Unsatisfactory performance If the governing system functions poorly, perform the following tests. SYMPTOM TEST PROBABLE FAULT Actuator goes to full fuel. then, disconnect speed sensor at Terminals C & D. ¥ Do not crank. Apply If actuator still at full fuel speed control DC power to the gov- unit deffective. -
Page 140
¥ Electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) EMI SUSCEPTIBILITY — The governor system can be adversely affected by large inter- fering sig- nals that are conducted through the cabling or through direct radiation into the control circuits. All DWC-2000 speed control units contain filters and shielding designed to protect the units sensi- tive circuits from moderate external interfering sources. -
Page 141
10.3.4. Fuel feed pump 1) General descriptions and construction Priming pump Check valve Check valve Outlet Inlet side side Tappet Piston Cam shaft EQM4019I The P-type injection pump is mounted with K-ADS or KP type feed pump. These pumps have the same basic construction and operation, and the general descriptions of the KP type pump are given below: The figures show its construction (right figure) and operation (below figure). -
Page 142
Inlet side Outlet side Interruption EQM4020I This feed pump is mounted with a priming pump designed to permit manual feeding of fuel from the fuel tank with the injection pump mounted in the engine. During the manual feeding operation, air must be bled from the fuel lines. -
Page 143
2) disassembly ¥ Clamp the feed pump with a vise and disassemble the plugs (30, 32), strainer (31) and gaskets (35, 36). ¥ Take off the priming pump (25), plug (16), both gaskets (18), spring (15), and check valve (14). ¥… -
Page 144
5) Testing (1) Suction capacity test Connect one end of a hose to the inlet Outlet hose side of the feed pump and immerse the other end of it into the fuel tank as illus- Feed pump trated. Hold the feed pump in position about 1m above the level of fuel in the fuel tank. -
Page 145
10.3.5. Injection nozzle 1) General descriptions Pressurized fuel delivered from the fuel injection pump is sprayed into the combustion chamber past the injection nozzle at proper spray pressure and spray angle, then burnt completely to achieve effective engine performance. (1) At valve closed (2) At valve opened EQM4024I 2) 1-spring type… -
Page 146
(2) Reassembly ¥ After removing carbon deposit, sub- merge the nozzle in diesel oil and clean ¥ Replace all the gaskets with new ones. ¥ Assemble the parts and tighten them to specified torque. (3) Adjustment ¥ Remove the cap nut and assemble a nozzle to a nozzle tester. -
Page 147
3) 2-spring type (1) Disassembly EQM4029I 1. Nozzle holder body 13. Lift pin 2. Push rod 14. Pin 3. Primary spring 15. Spacer 4. Adjusting screw 16. Pin 6. Gasket 17. Retaining nut 7. Cap nut 30. Gasket 10. Adjusting shim 31. -
Page 148
(2) Inspection and adjustment a. Adjusting the primary opening pres- sure. Install the plate of plate assembly (157944-9520) onto a vise. Note : Use the plate assembly (157944-9520) in fixing a nozzle holder having a flange. A nozzle holder without flange should be EQM4030I directly installed onto a vise. -
Page 149
f. Install the pin (16) and nozzle (A) onto the spacer. EQM4034I g. After installing the gasket (6:157892-1500) on the nozzle, use the cap nut (7:157892- 4000 : SW22mm) to fix the nozzle onto the nozzle holder. Note : While tightening nut, keep checking to see if the lock pin… -
Page 150
j. Assemble the push rod (2), primary spring (3), and adjusting screw (4) on the nozzle holder in the order described. k. Install the gasket (6) and cap nut (7) onto the adjusting screw(4). l. Assemble the nozzle and nozzle holder assembly to the nozzle tester (105785- 1010). -
Page 151
¥ Inspecting the needle valve for full lift a. Install gasket (026508-1140) and plug (157892-1600 : SW12mm) onto the adjusting retaining nut (157892-1400). EQM4042I b. Install the nozzle holder on the plate with the cap nut facing upward. c. Install the holder(157892-4100: SW12 mm) into the cap nut. -
Page 152
f. Install the dial gauge on the holder assem- bly so that the pin is brought into contact with the upper end of the push rod, then fix the pin with the nut. Note 1 : Fix the dial gauge so that a stroke of 2 mm or so can be mea- sured. -
Page 153
¥ Inspection of pre-lift a. If the nozzle tester handle is released with the needle valve engaged in a full lift condition, the tester pressure drops, being accompanied by decrease in the needle valve lift value (indicated value on the dial gauge). kgf / cm EQM4049I Tester pressure… -
Page 154
c. If the measured pre-lift value deviates from the specified limit, replace the pin (14, 16), lift piece (13), spacer (15), and nozzle assembly (A) with a new Ònozzle service kitÓ. EQM4053I ¥ Inspection of secondary opening pressure a. After confirming the pre-lift, operate the nozzle tester and increase the internal pressure up to 350 ~ 450 kgf/cm to fully… -
Page 155
¥ Adjusting secondary opening pressure a. In the event that the measured value deviates from the specified limit, readjust the primary opening pressure if the amount of deviation is small. (to the stan- dard range of the primary opening pres- sure) — If the secondary opening pressure is lower than the standard value: Adjust the… -
Page 156
¥ Retaining nut a. Take out the dial gauge, nut, holder and gasket from the cap nut (7). b. Remove the adjusting retaining nut and gasket, and install the original retaining nut(SW 19mm). Cap nut 6.0 ~ 8.0 kg . m Tightening torque EQM4036I ¥… -
Page 157
10.3.6. Diagnostics and troubleshooting Complaints Possible causes Corrections 1. Engine wonÕt start (1) Fuel pipes clogged or air into pipe line Correct 1) Fuel not being pumped (2) Feed pump valve defective Replace out from feed pump (3) Feed pump piston or push rod sticking Disassemble, correct 2) Fuel not being injected (1) Fuel filter element restricted… -
Page 158
Complaints Possible causes Corrections 6. Engine output (1) Supply of fuel insufficient Check feed pump unstable (2) Air in fuel Bleed (3) Water in fuel Replace fuel (4) Operation of plungers unsmooth Disassemble, correct (5) Movement of control rack sluggish Disassemble, correct (6) Nozzles defective Disassemble, correct… -
Page 159: Turbocharger
10.4. Turbocharger 10.4.1. Main data and specifications 1) Main data and specifications Specification DE12T P126TI/P126TI- Turbocharger Model Allied Signal T45 Allied Signal TV51 50Hz: Approx. 1.1 kg/cm 50Hz: Approx. 1.5 kg/cm Air pressure at compressor outlet 60Hz: Approx. 1.2 kg/cm 60Hz: Approx.
-
Page 160
3) Construction Turbine housing Retainer ring Bolt Plug Bearing O-ring Crank Thrust collar Compressor wheel V-band Screw Wheel Thrust bearing Bolt Piston ring Thrust space Clamp Wheel shroud Piston ring Compressor housing Center housing Seal ring Elbow Retainer ring Seal ring Retainer Bearing Rear plate… -
Page 161
10.4.2. General descriptions The engine output is determined by the fuel delivery volume and engine efficiency. To burn the supplied fuel completely to change into effective power for the engine, the volume of air enough to burn the fuel completely should be supplied into the cylinders. Therefore, the engine output is determined substantially by the cylinder capacity, and a greater volume of compressed air is charged into cylinders of given capacity, the greater engine output can be obtained as a greater volume of air charged into the cylinders burns so… -
Page 162
10.4.4. Precautions for operation 1) Precautions for operation of engine The following precautions should be observed when starting, operating, or stopping the engine: Operations Precautions Reasons When starting 1) Check oil level 2) Crank the engine with starter to 2) Abrupt starting of the engine the engine check the increase in oil pres- causes the engine to rotate with… -
Page 163
10.4.5. Walk-around check and servicing As the condition of turbocharger depends greatly on how well the engine is serviced, it is very important to maintain the engine in accordance with the specified maintenance procedure. 1) Intake system Pay particular attention to the air cleaner when servicing the intake system. In the case of wet-type air cleaner, if the level of oil surface is lower than specified, clean- ing effect is poor;… -
Page 164
10.4.6. Periodical checking and servicing Make it a rule to check the turbocharger assembly for condition and contamination periodically. 1) Guide for checking the rotor for rotating condition The inspection of the rotor assembly for rotating condition should be performed by the degree of unusual sound. -
Page 165
(3) If the measured axial and radial plays are beyond the limit of wear, replace or repair the turbocharger. 3) Guide for disassembling/cleaning and checking the turbocharger First, disassemble the turbocharger from the engine and clean/check it with the oil inlet and outlet plugged with tape and so on. -
Page 166
10.4.7. Diagnostics and troubleshooting Complaints Possible causes Corrections 1. Excessive black 1) Air cleaner element clogged Replace or clean smoke 2) Restrictions in air duct Check and correct 3) Leakage at intake manifold Check and correct 4) Turbocharger seized up and not rotating Disassemble/repair or replace 5) Turbine blades and compressor blades Disassemble/repair or replace… -
Page 167: Special Tool List
11. Special Tool List Part No. Figure Tool Name DPN-5337 Nozzle tube insert assÕy EF.123-082 Nozzle tube extractor EF.123-015 Injection pump setting assÕy EF.123-173 Oil seal(NOK) insert assÕy (FR) EF.123-194A Oil seal(NOK) insert assÕy (RR) EF.123-317A Oil seal(NOK)puller assÕy (FR) EF.123-316A Oil seal(NOK) puller assÕy (RR) EF.123-347…
-
Page 168
Part No. Figure Tool Name EF.123-066 Valve stem seal punch EU.2-0131 Valve clearance adjust assÕy EF.123.-065 Valve spring press EU.2-0647 Crankshaft gear punch 60.99901-0027 Feeler gauge T7610001E Snap ring plier T7621010E Piston ring plier EF.120-208 Piston Ring Compressor — 164 -… -
Page 169
Appendix ¥ Tightening torque for major parts Screw Strength Major Parts Tightening Torque Remarks (Diameter x pitch) (grade) 1st : 6kg.m 2nd : 90û Cylinder head bolt M14 x 1.5 10.9T 3rd: 90û Dodecagon Finished : 90û (angle torque) Cylinder head cover bolt 8.8T 1.2 kg.m 1st : 15 kg.m… -
Page 170
¥ Standard bolt tightening torque table Refer to the following table for bolts other than described above. Degree of strength 10.9 12.9 Diameter (4A) (4D) (4S) (5D) (5S) (6D) (6S) (6G) (8G) (10K) (12K) pitch Limit value for elasticity (kg/mm (mm) Tightening torque (kg . -
Page 171
— 167 -… -
Page 172
— 168 -… -
Page 173
— 169 -… -
Page 174
— 170 -… -
Page 175
— 171 -…
Contact Us
NO.6 Gulouyuan, Juyuanzhou Industrial Zone, Jinshan Development Area, Fuzhou, Fujian, China.
008613705041170
008613705041170
sales@primepowergenset.com
Working hour: Monday — Saturday (9am — 6pm)
В настоящее время вы находитесь на странице с руководствами . Выберите один из продуктов, чтобы сразу перейти к руководству по этому продукту. Не можете найти ? Тогда попробуйте вбить в поле поиска и модель, чтобы найти нужное руководство . На ManualsPDF.ru в настоящее время имеется 4 руководств . Самые популярные :
- Doosan L136
- Doosan AD136
- Doosan L136TI
Последнее добавленное руководство было добавлено 2020-08-17, и это Doosan AD136.