This CSS Reference shows the basic syntax of a CSS rule; lists all standard CSS properties, pseudo-classes and pseudo-elements, @-rules, units, and selectors, all together in alphabetical order, as well as just the selectors by type and allows you to quickly access detailed information for each of them. It not only lists the CSS 1 and CSS 2.1 properties, but also is a CSS3 reference that links to any CSS3 property and concept standardized, or already stabilized. Also included is a brief DOM-CSS / CSSOM reference.
Note that CSS rule-definitions are entirely (ASCII) text-based, whereas DOM-CSS / CSSOM, the rule-management system, is object-based.
See also Mozilla CSS Extensions for Gecko-specific properties prefixed with -moz; and WebKit CSS Extensions for WebKit-specific properties. See Vendor-prefixed CSS Property Overview by Peter Beverloo for all prefixed properties.
Basic rule syntax
Be warned that any syntax error in a rule definition will invalidate the entire rule.
Style rules
selectorlist { property: value; [more property:value; pairs] }
...where selectorlist is: selector[:pseudo-class] [::pseudo-element] [, more selectorlists]
See selector, pseudo-element, pseudo-class lists below.
Examples
strong { color: red;}
div.menu-bar li:hover > ul { display: block; }
More about examples: #1, #2
@rules
As these have so many different structure-formats, see At-rule for syntax of the specific at-rule you want.
Keyword index
A
:activeadditive-symbols (@counter-style)::after (:after)align-contentalign-itemsalign-selfall<an-plus-b><angle>animationanimation-delayanimation-directionanimation-durationanimation-fill-modeanimation-iteration-countanimation-nameanimation-play-stateanimation-timing-function@annotationannotation()attr()
B
::backdropbackface-visibilitybackgroundbackground-attachmentbackground-blend-modebackground-clipbackground-colorbackground-imagebackground-originbackground-positionbackground-repeatbackground-size<basic-shape>::before (:before)<blend-mode>block-sizeblur()borderborder-block-endborder-block-end-colorborder-block-end-styleborder-block-end-widthborder-block-startborder-block-start-colorborder-block-start-styleborder-block-start-widthborder-bottomborder-bottom-colorborder-bottom-left-radiusborder-bottom-right-radiusborder-bottom-styleborder-bottom-widthborder-collapseborder-colorborder-imageborder-image-outsetborder-image-repeatborder-image-sliceborder-image-sourceborder-image-widthborder-inline-endborder-inline-end-colorborder-inline-end-styleborder-inline-end-widthborder-inline-startborder-inline-start-colorborder-inline-start-styleborder-inline-start-widthborder-leftborder-left-colorborder-left-styleborder-left-widthborder-radiusborder-rightborder-right-colorborder-right-styleborder-right-widthborder-spacingborder-styleborder-topborder-top-colorborder-top-left-radiusborder-top-right-radiusborder-top-styleborder-top-widthborder-widthbottom@bottom-center@bottom-left@bottom-left-corner@bottom-right@bottom-right-cornerbox-decoration-breakbox-shadowbox-sizingbreak-afterbreak-beforebreak-insidebrightness()
C
calc()caption-sidecaret-colorch@character-variantcharacter-variant()@charset:checkedcircle()clearclipclip-pathcm<color>colorcolumn-countcolumn-fillcolumn-gapcolumn-rulecolumn-rule-colorcolumn-rule-stylecolumn-rule-widthcolumn-spancolumn-widthcolumnscontentcontrast()<counter>counter-incrementcounter-reset@counter-stylecross-fade()cubic-bezier()::cuecursor<custom-ident>
D
:defaultdeg:dirdirection:disableddisplaydpcmdpidppxdrop-shadow()
E
element()ellipse()em:emptyempty-cells:enabledex
F
fallback (@counter-style)filter:first:first-child::first-letter (:first-letter)::first-line (:first-line):first-of-typefit-content()<flex>flex-basisflex-directionflex-flowflex-growflex-shrinkflex-wrapfloat:focusfont@font-facefont-familyfont-family (@font-face)font-feature-settingsfont-feature-settings (@font-face)@font-feature-valuesfont-kerningfont-language-overridefont-sizefont-size-adjustfont-stretchfont-stretch (@font-face)font-stylefont-style (@font-face)font-synthesisfont-variantfont-variant (@font-face)font-variant-alternatesfont-variant-capsfont-variant-east-asianfont-variant-ligaturesfont-variant-numericfont-variant-positionfont-weightfont-weight (@font-face)format()format() (@font-face)frframes()<frequency>:fullscreen
G
grad<gradient>grayscale()gridgrid-areagrid-auto-columnsgrid-auto-flowgrid-auto-rowsgrid-columngrid-column-endgrid-column-gapgrid-column-startgrid-gapgrid-rowgrid-row-endgrid-row-gapgrid-row-startgrid-templategrid-template-areasgrid-template-columnsgrid-template-rows
H
heightheight (@viewport)@historical-forms:hoverhsl()hsla()hue-rotate()hyphenshz
I
<ident><image>image()image-orientationimage-renderingimage-resolutionimage-set()ime-mode@importin:in-range:indeterminateinheritinitialinline-sizeinset()<integer>:invalidinvert()isolation
J
justify-content
K
@keyframeskhz
L
:lang:last-child:last-of-typeleader():leftleft@left-bottom@left-middle@left-top<length>letter-spacingline-breakline-heightlinear-gradient():linklist-stylelist-style-imagelist-style-positionlist-style-typelocal()
M
marginmargin-block-endmargin-block-startmargin-bottommargin-inline-endmargin-inline-startmargin-leftmargin-rightmargin-topmaskmask-clipmask-compositemask-imagemask-modemask-originmask-positionmask-repeatmask-sizemask-typematrix()matrix3d()max-heightmax-height (@viewport)max-widthmax-width (@viewport)max-zoom (@viewport)@mediamin-block-sizemin-heightmin-height (@viewport)min-inline-sizemin-widthmin-width (@viewport)min-zoom (@viewport)minmax()mix-blend-modemmms
N
@namespacenegative (@counter-style):not:nth-child:nth-last-child:nth-last-of-type:nth-of-type<number>
O
object-fitobject-positionoffset-block-endoffset-block-startoffset-inline-endoffset-inline-start:only-child:only-of-typeopacityopacity():optionalorderorientation (@viewport)@ornamentsornaments()orphans:out-of-rangeoutlineoutline-coloroutline-offsetoutline-styleoutline-widthoverflowoverflow-wrapoverflow-xoverflow-y
P
pad (@counter-style)paddingpadding-block-endpadding-block-startpadding-bottompadding-inline-endpadding-inline-startpadding-leftpadding-rightpadding-top@pagepage-break-afterpage-break-beforepage-break-insidepc<percentage>perspectiveperspective()perspective-originpointer-eventspolygon()<position>positionprefix (@counter-style)ptpx
Q
qquotes
R
radradial-gradient()range (@counter-style)<ratio>:read-only:read-writerect()remrepeat()repeating-linear-gradient()repeating-radial-gradient():requiredresize<resolution>revertrgb()rgba():rightright@right-bottom@right-middle@right-top:rootrotate()rotate3d()rotateX()rotateY()rotateZ()ruby-alignruby-mergeruby-position
S
ssaturate()scale()scale3d()scaleX()scaleY()scaleZ():scopescroll-behaviorscroll-snap-coordinatescroll-snap-destinationscroll-snap-type::selectionsepia()<shape>shape-image-thresholdshape-marginshape-outsideskew()skewX()skewY()speak-as (@counter-style)src (@font-face)steps()<string>@stylesetstyleset()@stylisticstylistic()suffix (@counter-style)@supports@swashswash()symbols (@counter-style)symbols()system (@counter-style)
T
tab-sizetable-layout:targettarget-counter()target-counters()target-text()text-aligntext-align-lasttext-combine-uprighttext-decorationtext-decoration-colortext-decoration-linetext-decoration-styletext-emphasistext-emphasis-colortext-emphasis-positiontext-emphasis-styletext-indenttext-justifytext-orientationtext-overflowtext-renderingtext-shadowtext-transformtext-underline-position<time><timing-function>top@top-center@top-left@top-left-corner@top-right@top-right-cornertouch-actiontransformtransform-box<transform-function>transform-origintransform-styletransitiontransition-delaytransition-durationtransition-propertytransition-timing-functiontranslate()translate3d()translateX()translateY()translateZ()turn
U
unicode-bidiunicode-range (@font-face):unresolvedunset<url>url()user-zoom (@viewport)
V
:validvar()vertical-alignvh@viewportvisibility:visitedvmaxvminvw
W
white-spacewidowswidthwidth (@viewport)will-changeword-breakword-spacingword-wrapwriting-mode
Z
z-indexzoom (@viewport)
Others
--*
Selectors
- Basic Selectors
- Type selectors
elementname - Class selectors
.classname - ID selectors
#idname - Universal selectors
* ns|* *|* - Attribute selectors
[attr=value]
- Type selectors
- Combinators (more info)
- Adjacent sibling selectors
A + B - General sibling selectors
A ~ B - Child selectors
A > B - Descendant selectors
A B
- Adjacent sibling selectors
- Pseudo-elements (more info)
::after::before::first-letter::first-line::selection::backdrop::placeholder::marker::spelling-error::grammar-error
- Standard pseudo-classes (more info)
:active:any:checked:default:dir():disabled:empty:enabled:first:first-child:first-of-type:fullscreen:focus:hover:indeterminate:in-range:invalid:lang():last-child:last-of-type:left:link:not():nth-child():nth-last-child():nth-last-of-type():nth-of-type():only-child:only-of-type:optional:out-of-range:read-only:read-write:required:right:root:scope:target:valid:visited
A complete list of selectors in the Selectors Level 3 specification.
CSS3 Tutorials
These small how-to pages describe new technologies appeared in CSS3, or in CSS2.1 but with low support until recently:
- Using CSS media queries
- Using CSS counters
- Using CSS gradients
- Using CSS transforms
- Using CSS animations
- Using CSS transitions
- Using CSS multiple backgrounds
- Using CSS flexible boxes
- Using CSS multi-column layouts
Concepts
- CSS syntax
- At-rule
- Comments
- Specificity
- Initial value
- Inheritance
- Specified value
- Computed value
- Used value
- Actual value
- Resolved value
- Box model
- Replaced element
- Value definition syntax
- Shorthand properties
- Mastering margin collapsing
- Visual formatting model
- Layout mode
DOM-CSS / CSSOM
Major object types:
- document.styleSheets
- styleSheets[i].cssRules
- cssRules[i].cssText (selector & style)
- cssRules[i].selectorText
- elem.style
- elem.style.cssText (just style)
- elem.className
- elem.classList
Important methods:
CSSStyleSheet.insertRuleCSSStyleSheet.deleteRule
Document Tags and Contributors
Contributors to this page:
mfluehr,
xfq,
Tigt,
teoli,
Igornorlin,
Sebastianz,
antorajees,
athagoras,
Jeremie,
pcat,
BychekRU,
avd-apps,
xiaolong,
amitabha197,
chrisdavidmills,
ziyunfei,
Jonathan_Watt,
phil_nist,
loptop,
jswisher,
HUBOGART,
Sheppy,
elkhote,
ethertank,
hade,
FredB,
jogo.obb,
bpartridge81,
deepak7275,
lmorchard,
tregagnon,
fscholz,
takahashi_yuki,
Manuel_Strehl,
McGurk,
sjltaylor,
inma_610,
BijuGC,
Jürgen Jeka,
jwalker,
Crash,
Brettz9,
Miken32,
Moacir Bispo,
TigerSoldier,
Nathymig,
Mgjbot,
Saurabhmathur,
Waldo,
Pastelgrim,
Michael2402,
Federico,
DBaron,
George3,
Nickolay,
Ptak82,
Dria
Last updated by:
mfluehr,
Jul 29, 2017, 3:56:08 AM
На чтение 2 мин. Просмотров 17 Опубликовано 08.12.2022
CSS расшифровывается как каскадная таблица стилей, это язык сценариев для управления представлением, потоком и стилем HTML-элементов. Честно говоря, освоить CSS не так-то просто, для этого требуется практика и практика, и в этой статье я покажу вам дорожную карту того, как вы можете начать свое путешествие по CSS.
Содержание
- Совсем новичок в CSS
- Знакомство с основами
- Практика и последовательность
- Основная дорожная карта CSS
- Хорошие ссылки
- Хорошие каналы Youtube, за которыми стоит следить
- Заключение
Совсем новичок в CSS
Если вы совсем новичок в CSS, я рекомендую вам одного из лучших учителей на youtube — Net ninja, он легко и непринужденно научит вас многим концепциям CSS, таким как основы, позиционирование, отзывчивый дизайн и т.д. Проверьте его.
Если вы предпочитаете читать, поищите freecodecamp.org или mdn в Google.
Знакомство с основами
После того как вы ознакомились с основами CSS, вам нужно будет применить эти знания и создать полезные вещи. Есть замечательный сайт https://frontendmentor.io, на котором можно найти задачи по дизайну, которые вы можете попробовать решить самостоятельно и получить обратную связь от сообщества, когда вы их отправляете. Если вы застряли в создании этих задач, посмотрите эти каналы youtube.
- Tech Upfront
- Tsbsankara
Практика и последовательность
Даже если вы можете создать одну или две задачи, нельзя останавливаться, нужно продолжать практиковаться и практиковаться, и именно поэтому я настоятельно рекомендую заглянуть на сайт frontendmentor.io. На Frontendmentor есть задания от уровня новичка до уровня Гуру, поэтому развивайте свои навыки с помощью заданий для новичков и постепенно переходите к заданиям для юниоров, затем к заданиям среднего уровня, затем к заданиям для продвинутых и, наконец, к заданиям для Гуру.
Основная дорожная карта CSS
- Первые шаги CSS (что такое css, зачем его использовать и т.д.)
- Строительные блоки CSS
- Селекторы CSS
- Модель коробки
- Фоны и границы
- переполняющий контент
- значения и единицы
- изображения, медиа и формы
- Стилизация таблиц
- CSS-макеты
- Flexbox
- CSS Grid
- Позиционирование
- Репонсивный дизайн и медиа-запросы
- Стилизация текста
- Основы стилизации текста и шрифтов
- стилизация списков
- Шрифты Google
- Отзывчивая типографика (типографика — это модное слово для шрифта).
Хорошие ссылки
- MDN
- css-tricks
- freecodecamp
- internetingishard
Хорошие каналы Youtube, за которыми стоит следить
- The Net Ninja
- tsbsankara
- Tech upfront
- Кевин Пауэлл
- Флорин Поп
Заключение
CSS требует практики и преданности, просто продолжайте создавать сайты, и рано или поздно вы станете профессионалом в CSS и узнаете некоторые важные концепции CSS. Не забудьте проверить список ссылок выше, спасибо за чтение, увидимся в следующий раз ✌🏽✌🏽.
Рассказываем о языке, благодаря которому интернет стал красивым.
Основы CSS
Аббревиатура CSS расшифровывается как Cascading Style Sheets, что в переводе означает «каскадные таблицы стилей». Это язык разметки, используемый для визуального оформления веб-сайтов.
Объекты, расположенные на странице, размещаются с помощью HTML. А вот CSS отвечает за то, как эти объекты выглядят. Их размер, цвет, фоновое изображение, степень прозрачности, расположение относительно других элементов, поведение при наведении курсора, визуальное изменение кнопок при нажатии и т.п.
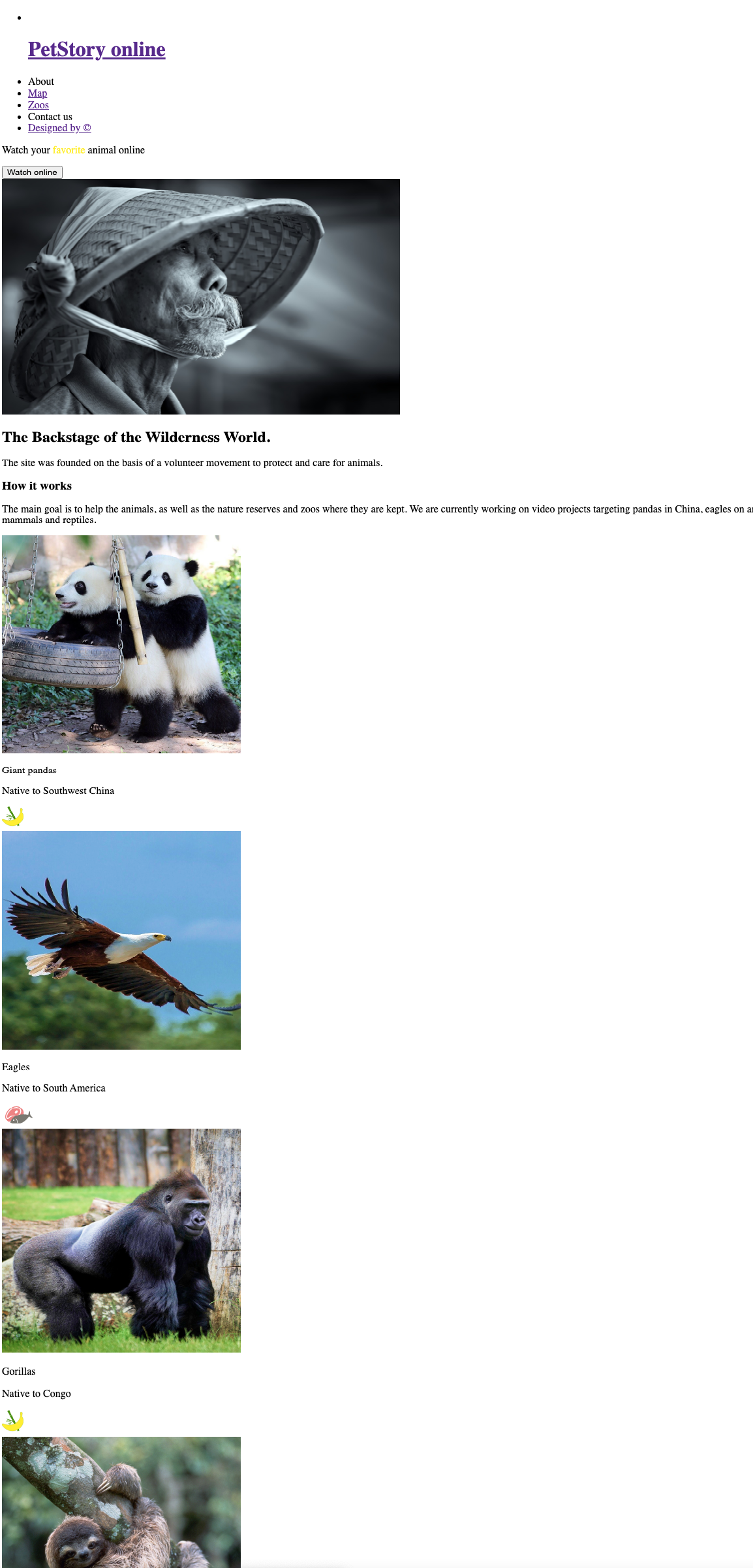
Вот сайт, сделанный с помощью одного лишь HTML:
А вот как выглядит та же страница после добавления CSS-разметки и оформления блоков с помощью каскадных таблиц стилей:
Практически любые «внешние проявления» сайта создаются с помощью CSS. Это стиль ваших страниц.
Синтаксис разметки
Язык CSS быстро стал стандартом в веб-разработке, потому что он позволяет быстро изменить визуальное оформление сайта, не прибегая к использованию более сложных языков программирования.
Достаточно ознакомиться с простейшими правилами CSS, и можно легко собрать вполне симпатичный сайт со всем необходимым контентом. «Простота» обеспечивается за счет понятного синтаксиса.
Синтаксис CSS в отдельном файле в соответствующем формате (.css) выглядит так:
селектор {
свойство: значение;
}
-
Селектор – это ссылка на элемент в HTML, над которым будет вестись работа (оформление).
-
Свойство – определенная характеристика элемента, которую нужно изменить. Например, размер или цвет.
-
Значение – цифровое или текстовое обозначение для выбранного свойства.
Попробуем поменять цвет текста в блоке section на красный:
section {
color: red;
}
Как видите, все понятно даже без знания разметки. Даже далекий от программирования человек поймет, что происходит в вышеописанном коде. Это самое лучшее в CSS. Все логично.
Медиазапросы и тег <style>
Выше был продемонстрирован базовый синтаксис, но он может быть куда более замысловатым. Например, для создания стилей под различные разрешения экранов используются запросы @media. Они выглядят так:
@media (max-width: 768px) {
section: {
color: red;
}
}
Такой код изменит цвет текста на красный в разделе section только для экранов с разрешением меньше 768 пикселей.
А еще CSS-разметку можно использовать прямо в HTML-файлах для тестирования стилей и внесения мелких изменений.
<html>
<body>
<section style= "color: red;"></section>
</body>
</html
С другими примерами оформления CSS можно ознакомиться в официальном руководстве MDN.
Что еще может CSS
Выше я уже сказал, что CSS используется для всего визуального оформления документов. Но чтобы стало яснее, посмотрим на примеры использования разметки в коде. Так вы поймете, что возможностей у CSS куда больше, чем кажется.
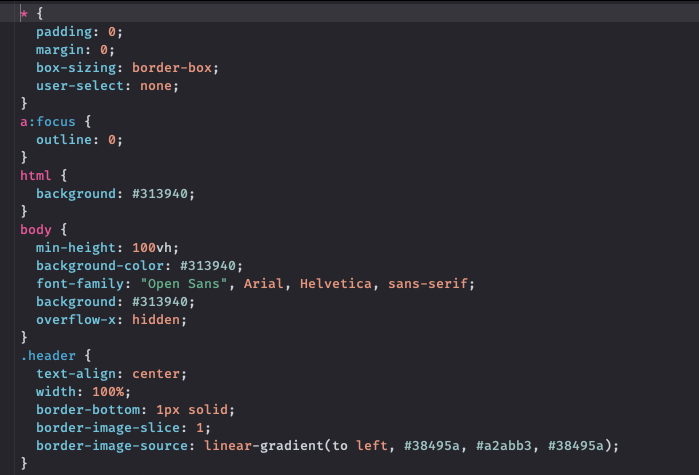
Например, с помощью CSS можно задать параметры для SVG-изображения:
svg {
width: 120px;
height: 68px;
fill: green;
}
Или создать блоки div любых размеров с SVG-изображением в качестве фона:
.block {
width: 220px;
height: 192px;
background-image: url("../path-to-image/image.svg");
}
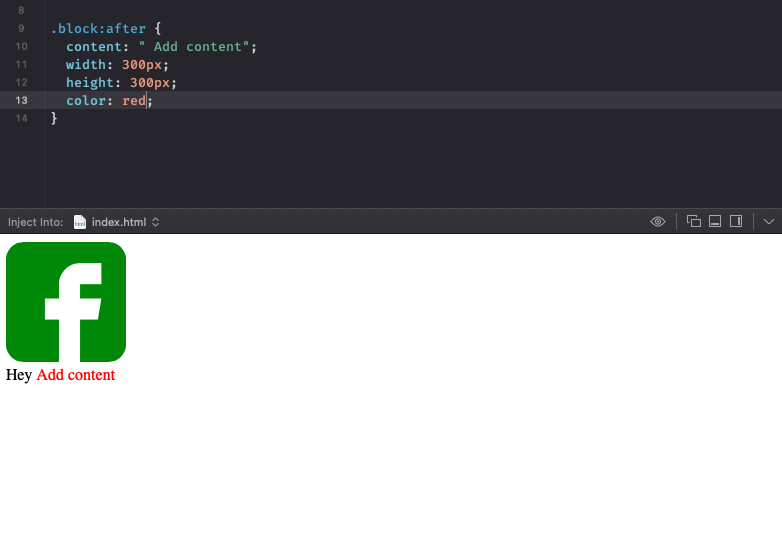
Или же вовсе добавить в блок информацию, которой изначально нет в HTML-документе:
.block:after {
content: "kakoy-to-text ";
}
Также можно добавлять контент или CSS-разметку на новые объекты, созданные вне HTML. Для этого в CSS есть псевдоселекторы :after и :before (они позволяют разместить новые элементы до или после выбранного объекта).
И даже это мелочи. С помощью CSS можно рисовать, создавать объекты любых форм, анимировать их и т.п.
Комьюнити теперь в Телеграм
Подпишитесь и будьте в курсе последних IT-новостей
Подписаться
Препроцессоры и другие варианты реализации CSS
По умолчанию стили прописываются в текстовом файле, но это не единственный вариант. Базовый CSS не обладает преимуществами сложных языков программирования, переменными или вложением свойств.
Поэтому разработчики создали препроцессоры наподобие LESS. Это механизм на базе JavaScript, позволяющий внедрить в работу со стилями синтаксис и некоторые примитивные функции из JavaScript. Если вам кажется, что у CSS недостаточно функциональности, то следует ознакомиться с препроцессорами.
Также CSS часто реализуется внутри фреймворков. Например, технология react-styled-components перенасыщает всю функциональность каскадных стилей напрямую в код на базе React. То есть можно в одном файле прописывать стили, структуру приложения и его логику.
Правда, такой стиль взаимодействия со стилями противоречит первоначальной идее CSS.
О концепции деления контента и его оформления
Сама идея разделить контент и его оформление на две части появилась в связи с необходимостью создавать сайты более сложных форматов – с уникальными стилевыми решениями, красивыми шрифтами, анимациями, произвольным порядком блоков и кучей других деталей, вынуждающих верстальщиков искать новые пути взаимодействия с HTML-документами.
Постепенно вебмастеры и разработчики отказались от стандартного оформления страниц с помощью таблиц (это встроенный в HTML синтаксис, не требующий дополнительных инструментов для оформления), потому что это усложняло структуру страниц. HTML-файлы сильно раздувались, ими было сложно управлять, а способов оформить хотя бы текст больше не становилось. Но всех спас CSS.
Правда, даже CSS может заметно увеличить размеры HTML и сделать его трудночитаемым, если применять каскадные таблицы прямо в основном документе. Поэтому за правило взято оформление CSS-разметки в отдельном файле, который затем подключается к условному index.html, а тот уже подтягивает нужные стили.
Т.е. файлы HTML и CSS живут раздельно.
Основные принципы построения макетов с помощью CSS
Одна из ключевых задач CSS в современной верстке – создание макетов сайта. HTML уже не играет такой важной роли в том, как будут размещены объекты. HTML-документ отвечает за структуру и вложенность элементов, что упрощает чтение сайтов скринридерами и дальнейшую разметку с использованием каскадных стилей.
Для расположения элементов на «полотне» сайта используются две основные методики:
-
Flex – позволяет автоматически распределить объекты в блоке за счет создания блоков-оберток со свойством flex.
-
Grid – позволяет отказаться от оберток и размещать объекты по сетке.
Оба метода позволяют создавать сайты, элементы которых всегда занимают корректную позицию и адаптируются под меняющееся разрешение экрана.
Как изучить и начать использовать CSS?
Каскадные таблицы стилей – на удивление интуитивная вещь. Даже новички успешно справляют с самостоятельным изучением разметки без обращения за помощью к профессиональным разработчикам и дизайнерам. Достаточно обращаться в Google за описанием свойств стилей и запоминать их.
Но есть загвоздки. В частности, они касаются методик создания макетов. С ходу понять их тяжело, поэтому нужно хорошее руководство.
Ну и нельзя забывать про великое множество курсов для веб-разработчиков. Они всегда покрывают углубленное знакомство с HTML, CSS и JavaScript, причем качество изучения стилей почти везде находится на одному уровне. Не нужно отдавать сумасшедшие деньги за дорогие курсы, можно выбрать какой-нибудь бюджетный вариант (если интересует именно CSS).
Где и как редактировать разметку?
Если вы уже сейчас хотите опробовать свои силы, то можно создать стили с помощью любого текстового редактора. Создаем файл в формате .css, а потом вписываем туда свойства и их значения в соответствии с синтаксисом разметки.
Лучше использовать специализированные редакторы и IDE. Они автоматически дополнят код, подскажут свойства и их значения, сообщат об обнаруженных ошибках, упростят выбор цветов и так далее. Рекомендую использовать редактор VS Code (своего рода стандарт). Он бесплатный и функциональный. Но есть и другие варианты.
Чтобы внесенные в CSS-файл изменения возымели эффект над HTML-документом, первый нужно подключить ко второму. Для этого в head-тег HTML-файла нужно добавить ссылку в формате:
<link rel="stylesheet" href="style.css">
Вместо заключения
На этом все. Как видите, CSS – это мощный инструмент для оформления сайтов, без которого невозможно сделать красивую страницу (даже если использовать какие-либо фреймворки типа React).
Глубокое изучение каскадных таблиц поможет сделать ваши сайты более стильными, при этом не перебарщивая с количеством JS-кода, что положительно скажется на производительности ресурса.
Use this CSS reference to browse an alphabetical index of all the standard CSS properties, pseudo-classes, pseudo-elements, data types, and at-rules. You can also browse a list of all the CSS selectors organized by type and a list of key CSS concepts. Also included is a brief DOM-CSS / CSSOM reference.
Basic rule syntax
Style rule syntax
style-rule ::=
selectors-list {
properties-list
}
… where :
selectors-list ::=
selector[:pseudo-class] [::pseudo-element]
[, selectors-list]
properties-list ::=
[property : value] [; properties-list]
See selector, pseudo-class, pseudo-element lists below. The syntax for each specified value depends on the data type defined for each specified property.
Style rule examples
strong {
color: red;
}
div.menu-bar li:hover > ul {
display: block;
}
For a beginner-level introduction to the syntax of CSS selectors, please see this tutorial. Be aware that any CSS syntax error in a rule definition invalidates the entire rule. Invalid rules are ignored by the browser. Note that CSS rule definitions are entirely (ASCII) text-based, whereas DOM-CSS / CSSOM (the rule management system) is object-based.
At-rule syntax
As the structure of at-rules varies widely, please see At-rule to find the syntax of the specific one you want.
Keyword index
Note: The property names in this index do not include the JavaScript names where they differ from the CSS standard names.
—
-webkit-line-clamp
A
:activeadditive-symbols (@counter-style)::after (:after)align-contentalign-itemsalign-selfall<an-plus-b><angle><angle-percentage>animationanimation-delayanimation-directionanimation-durationanimation-fill-modeanimation-iteration-countanimation-nameanimation-play-stateanimation-timing-function@annotationannotation()attr()
B
::backdropbackface-visibilitybackgroundbackground-attachmentbackground-blend-modebackground-clipbackground-colorbackground-imagebackground-originbackground-positionbackground-repeatbackground-size<basic-shape>::before (:before)<blend-mode>block-sizeblur()borderborder-blockborder-block-colorborder-block-endborder-block-end-colorborder-block-end-styleborder-block-end-widthborder-block-startborder-block-start-colorborder-block-start-styleborder-block-start-widthborder-block-styleborder-block-widthborder-bottomborder-bottom-colorborder-bottom-left-radiusborder-bottom-right-radiusborder-bottom-styleborder-bottom-widthborder-collapseborder-colorborder-end-end-radiusborder-end-start-radiusborder-imageborder-image-outsetborder-image-repeatborder-image-sliceborder-image-sourceborder-image-widthborder-inlineborder-inline-colorborder-inline-endborder-inline-end-colorborder-inline-end-styleborder-inline-end-widthborder-inline-startborder-inline-start-colorborder-inline-start-styleborder-inline-start-widthborder-inline-styleborder-inline-widthborder-leftborder-left-colorborder-left-styleborder-left-widthborder-radiusborder-rightborder-right-colorborder-right-styleborder-right-widthborder-spacingborder-start-end-radiusborder-start-start-radiusborder-styleborder-topborder-top-colorborder-top-left-radiusborder-top-right-radiusborder-top-styleborder-top-widthborder-widthbottom@bottom-centerbox-decoration-breakbox-shadowbox-sizingbreak-afterbreak-beforebreak-insidebrightness()
C
calc()caption-sidecaret-colorch@character-variantcharacter-variant()@charset:checkedcircle()clamp()clearclipclip-pathcm<color>colorcolor-adjustcolumn-countcolumn-fillcolumn-gapcolumn-rulecolumn-rule-colorcolumn-rule-stylecolumn-rule-widthcolumn-spancolumn-widthcolumnsconic-gradient()contentcontrast()<counter>counter-incrementcounter-resetcounter-set@counter-stylecounters()cross-fade()cubic-bezier()::cuecursor<custom-ident>
D
:defaultdeg<dimension>:dirdirection:disableddisplay<display-box><display-inside><display-internal><display-legacy><display-listitem><display-outside>dpcmdpidppxdrop-shadow()
E
element()ellipse()em:emptyempty-cells:enabledenv()ex
F
fallback (@counter-style)filter<filter-function>:first:first-child::first-letter (:first-letter)::first-line (:first-line):first-of-typefit-content()<flex>flexflex-basisflex-directionflex-flowflex-growflex-shrinkflex-wrapfloat:focusfont@font-facefont-familyfont-family (@font-face)font-feature-settingsfont-feature-settings (@font-face)@font-feature-valuesfont-kerningfont-language-overridefont-optical-sizingfont-sizefont-size-adjustfont-stretchfont-stretch (@font-face)font-stylefont-style (@font-face)font-synthesisfont-variantfont-variant (@font-face)font-variant-alternatesfont-variant-capsfont-variant-east-asianfont-variant-ligaturesfont-variant-numericfont-variant-positionfont-variation-settings (@font-face)font-weightfont-weight (@font-face)format()fr<frequency><frequency-percentage>:fullscreen
G
gapgrad<gradient>grayscale()gridgrid-areagrid-auto-columnsgrid-auto-flowgrid-auto-rowsgrid-columngrid-column-endgrid-column-startgrid-rowgrid-row-endgrid-row-startgrid-templategrid-template-areasgrid-template-columnsgrid-template-rows
H
Hzhanging-punctuationheightheight (@viewport)@historical-forms:hoverhsl()hsla()hue-rotate()hyphens
I
<ident><image>image()image-orientationimage-renderingimage-set()@importin:in-range:indeterminateinheritinitialinline-sizeinsetinset()inset-blockinset-block-endinset-block-startinset-inlineinset-inline-endinset-inline-start<integer>:invalidinvert()isolation
J
justify-contentjustify-itemsjustify-self
K
kHz@keyframes
L
:lang:last-child:last-of-typeleader():leftleft@left-bottom<length><length-percentage>letter-spacingline-breakline-heightlinear-gradient():linklist-stylelist-style-imagelist-style-positionlist-style-typelocal()
M
marginmargin-blockmargin-block-endmargin-block-startmargin-bottommargin-inlinemargin-inline-endmargin-inline-startmargin-leftmargin-rightmargin-top::markermaskmask-clipmask-compositemask-imagemask-modemask-originmask-positionmask-repeatmask-sizemask-typematrix()matrix3d()max()max-heightmax-height (@viewport)max-widthmax-width (@viewport)max-zoom (@viewport)@mediamin()min-block-sizemin-heightmin-height (@viewport)min-inline-sizemin-widthmin-width (@viewport)min-zoom (@viewport)minmax()mix-blend-modemmms
N
@namespacenegative (@counter-style):not:nth-child:nth-last-child:nth-last-of-type:nth-of-type<number>
O
object-fitobject-position:only-child:only-of-typeopacityopacity():optionalorderorientation (@viewport)@ornamentsornaments()orphans:out-of-rangeoutlineoutline-coloroutline-offsetoutline-styleoutline-widthoverflowoverflow-wrapoverflow-xoverflow-y
P
pad (@counter-style)paddingpadding-blockpadding-block-endpadding-block-startpadding-bottompadding-inlinepadding-inline-endpadding-inline-startpadding-leftpadding-rightpadding-top@pagepage-break-afterpage-break-beforepage-break-insidepc<percentage>perspectiveperspective()perspective-originplace-contentplace-itemsplace-self::placeholderpointer-eventspolygon()<position>positionprefix (@counter-style)ptpx
Q
Qquotes
R
radradial-gradient()range (@counter-style)<ratio>:read-only:read-writerect()remrepeat()repeating-linear-gradient()repeating-radial-gradient():requiredresize<resolution>revertrgb()rgba():rightright@right-bottom:rootrotaterotate()rotate3d()rotateX()rotateY()rotateZ()row-gap
S
ssaturate()scalescale()scale3d()scaleX()scaleY()scaleZ():scopescroll-behaviorscroll-marginscroll-margin-blockscroll-margin-block-endscroll-margin-block-startscroll-margin-bottomscroll-margin-inlinescroll-margin-inline-endscroll-margin-inline-startscroll-margin-leftscroll-margin-rightscroll-margin-topscroll-paddingscroll-padding-blockscroll-padding-block-endscroll-padding-block-startscroll-padding-bottomscroll-padding-inlinescroll-padding-inline-endscroll-padding-inline-startscroll-padding-leftscroll-padding-rightscroll-padding-topscroll-snap-alignscroll-snap-stopscroll-snap-typescrollbar-colorscrollbar-width::selectionselector()sepia()<shape>shape-image-thresholdshape-marginshape-outsideskew()skewX()skewY()::slottedspeak-as (@counter-style)src (@font-face)steps()<string>@stylesetstyleset()@stylisticstylistic()suffix (@counter-style)@supports@swashswash()symbols (@counter-style)symbols()system (@counter-style)
T
tab-sizetable-layout:targettarget-counter()target-counters()target-text()text-aligntext-align-lasttext-combine-uprighttext-decorationtext-decoration-colortext-decoration-linetext-decoration-styletext-emphasistext-emphasis-colortext-emphasis-positiontext-emphasis-styletext-indenttext-justifytext-orientationtext-overflowtext-renderingtext-shadowtext-transformtext-underline-position<time><time-percentage><timing-function>top@top-centertouch-actiontransformtransform-box<transform-function>transform-origintransform-styletransitiontransition-delaytransition-durationtransition-propertytransition-timing-functiontranslatetranslate()translate3d()translateX()translateY()translateZ()turn
U
unicode-bidiunicode-range (@font-face)unset<url>url()user-zoom (@viewport)
V
:validvar()vertical-alignvh@viewportvisibility:visitedvmaxvminvw
W
white-spacewidowswidthwidth (@viewport)will-changeword-breakword-spacingword-wrapwriting-mode
X
x
Z
z-indexzoom (@viewport)
Others
--*
Selectors
The following are the various selectors, which allow styles to be conditional based on various features of elements within the DOM.
Simple selectors
Simple selectors are fundamental selectors; these are the most basic selectors that are frequently combined to create other, more complex selectors.
- Type selector
elementname - Class selector
.classname - ID selector
#idname - Universal selector
*,ns|*,*|*,|* - Attribute selectors
[attr=value]
Combinators
Combinators are selectors that establish a relationship between two or more simple selectors, such as «A is a child of B» or «A is adjacent to B.»
- Comma combinator
A, B - Specifies that both
AandBelements are selected. This is a grouping method to select several matching elements. - Adjacent sibling combinator
A + B - Specifies that the elements selected by both
AandBhave the same parent and that the element selected byBimmediately follows the element selected byAhorizontally. - General sibling combinator
A ~ B - Specifies that the elements selected by both
AandBshare the same parent and that the element selected byAcomes before—but not necessarily immediately before—the element selected byB. - Child combinator
A > B - Specifies that the element selected by
Bis the direct child of the element selected byA. - Descendant combinator
A B - Specifies that the element selected by
Bis a descendant of the element selected byA, but is not necessarily a direct child. - Column combinator
A || B - Specifies that the element selected by
Bis located within the table column specified byA. Elements which span multiple columns are considered to be a member of all of those columns.
Pseudo-classes
:active:any-linkÂ:blankÂ:checked:currentÂ:default:defined:dir()Â:disabled:dropÂ:empty:enabled:first:first-child:first-of-type:fullscreenÂ:futureÂ:focus:focus-visibleÂ:focus-within:has()Â:host:host():host-context()Â:hover:indeterminate:in-range:invalid:is()Â:lang():last-child:last-of-type:left:link:local-linkÂ:not():nth-child():nth-col()Â:nth-last-child():nth-last-col()Â:nth-last-of-type():nth-of-type():only-child:only-of-type:optional:out-of-range:pastÂ:placeholder-shownÂ:read-only:read-write:required:right:root:scope:target:target-withinÂ:user-invalidÂ:valid:visited:where()Â
Pseudo-elements
::after (:after)::backdropÂ::before (:before)::cue (:cue)::cue-region()::first-letter (:first-letter)::first-line (:first-line)::grammar-errorÂ::markerÂ::part()Â::placeholderÂ::selection::slotted()::spelling-errorÂ
See also: A complete list of selectors in the Selectors Level 3 specification.
Concepts
Syntax and semantics
- CSS syntax
- At-rules
- Cascade
- Comments
- Descriptor
- Inheritance
- Shorthand properties
- Specificity
- Value definition syntax
- CSS unit and value types
Values
- Actual value
- Computed value
- Initial value
- Resolved value
- Specified value
- Used value
Layout
- Block formatting context
- Box model
- Containing block
- Layout mode
- Margin collapsing
- Replaced elements
- Stacking context
- Visual formatting model
DOM-CSS / CSSOM
Major object types
DocumentOrShadowRoot.styleSheetsstyleSheets[i].cssRulescssRules[i].cssText(selector & style)cssRules[i].selectorTextHTMLElement.styleHTMLElement.style.cssText(just style)Element.classNameElement.classList
Important methods
CSSStyleSheet.insertRule()CSSStyleSheet.deleteRule()
See also
- Mozilla CSS extensions (prefixed with
-moz-) - WebKit CSS extensions (mostly prefixed with
-webkit-) - Microsoft CSS extensions (prefixed with
-ms-)
Document Tags and Contributors
Contributors to this page:
ramiy,
JonathanPool,
verdy_p,
Sheppy,
estelle,
SphinxKnight,
mdnwebdocs-bot,
Sebastianz,
Amarildo,
alattalatta,
JonHypersomniac,
ExE-Boss,
TrisTOON,
chrisdavidmills,
Malvoz,
yutzuch,
mfluehr,
jswisher,
Flinstone87,
Zectbumo,
leoo,
dublebuble,
xfq,
Tigt,
teoli,
Igornorlin,
antorajees,
athagoras,
Jeremie,
pcat,
BychekRU,
avd-apps,
xiaolong,
amitabha197,
ziyunfei,
Jonathan_Watt,
phil_nist,
loptop,
HUBOGART,
elkhote,
ethertank,
hade,
FredB,
jogo.obb,
bpartridge81,
deepak7275,
lmorchard,
tregagnon,
fscholz,
takahashi_yuki,
Manuel_Strehl,
McGurk,
sjltaylor,
inma_610,
BijuGC,
Jürgen Jeka,
jwalker,
Crash,
Brettz9,
miken32,
Moacir Bispo,
TigerSoldier,
Nathymig,
Mgjbot,
Saurabhmathur,
Waldo,
Pastelgrim,
Michael2402,
Federico,
DBaron,
George3,
Nickolay,
Ptak82,
Dria
Last updated by:
ramiy,
Sep 28, 2019, 6:32:00 AM