MaxPlant
Все статьи раздела SIEMENS
Содержание
- Краткий обзор TIA Portal
- Шаговый ПИД-регулятор PID_ES (Step Controller)
- Введение в HMI Faceplate
- Управление дискретной задвижкой
- Создание фейсплаты дискретной задвижки (продолжение урока 4)
- Программирование дискретной задвижки (продолжение урока 5)
- Обработка аналоговых сигналов в TIA Portal
- Создание фейсплаты аналогового датчика, авторизация пользователя SIMATIC Comfort Panel (продолжение урока 7)
-
Разработка функционального блока обработки аналогового сигнала в STEP7 Professional (продолжение уроков 7 и
-
Адаптация проекта для панели оператора SIMATIC Comfort Panel в проект WinCC Advanced для ПК
(продолжение уроков 7-9) - Аварии и тренды, оперативные и исторические данные в WinCC Advanced (продолжение уроков 7-10)
-
Установка TIA Portal V15.1. Конвертация проекта, разработанного в TIA Portal V14,
в проект TIA Portal V15.1 - Контроль присутствия устройств в сети PROFINET или PROFIBUS для S7-1200 и S7-1500
-
Программирование в TIA Portal обмена данными по сети PROFINET между преобразователем частоты ATV630 и
контроллером SIMATIC S7-1500 - Счётчик моточасов (времени наработки)
- Управление светозвуковой сигнализацией
- Управление режимами работы насосных агрегатов
- Управление электроприводом насосных агрегатов
- Групповое квитирование аварийных сообщений в операторских панелях
SIMATIC HMI Panels - Настройка преобразователя частоты Altivar Process ATV600
- Обновление прошивки контроллера S7-1500
- Загрузка проекта в S7-1500 и ET200SP
- Создание резервной копии S7-1500: выгрузка проекта из ПЛК, архивирование проекта
- Уставки (Setpoints) в TIA Portal STEP7 или как не потерять
настройки ПИД-регуляторов после пусконаладки - Общее устройство (Shared Device) или как в TIA Portal несколько контроллеров делят между
собой одну станцию распределённого ввода-вывода - MRP домен + IRT домен = MRPD домен или введение в технологии
Media Redundancy и Real-time communication - Конфигурирование доменов IRT и MRPD (продолжение урока 26)
- Time-based IO или
как управлять быстрым дискретным технологическим процессом строго по времени - Как загрузить программу ПЛК SIMATIC S7-1500, если нет связи между программатором и ПЛК
- Как загрузить две программы ПЛК SIMATIC S7-1500 в S7-PLCSIM Advanced V2.0
на локальной и удалённой машинах и подключить к ним WinCC по TCP - SIMATIC Automation Tool
- Как установить связь между онлайн симулятором панели Weintek и S7-PLCSIM для отладки программ HMI-PLC
без панели оператора и ПЛК - Как протестировать программу контроллера S7-1200 с ПИД-регулятором PID_Compact в симуляторе S7-PLCSIM с помощью HMI, разработанного на панели оператора Weintek
- Как связать LOGO! с WinCC
- …
Время на прочтение
4 мин
Количество просмотров 426K
Добрый день, хабровчане! Полазив по Хабру, мною было обнаружено всего несколько топиков, в котором упоминалось бы словосочетание «Simatic Step 7». Хочу поделиться с Вами небольшой частью информации, накопленной мною за все время работы с программируемыми логическими контроллерами, и показать, что из себя представляют ПЛК, оболочка и что мне приходилось на них строить.
Данный пост содержит общую ознакомительную информацию о программировании ПЛК Siemens.
Введение
Устроилась я в эту фирму еще на 5м курсе института. К слову, образование мое к программированию относится весьма косвенно и было это больше увлечением. Познания мои на тот момент ограничивались курсом Delphi и весьма базовым Ассемблером. Компания занималась (да и занимается) проектированием, строительством и обслуживанием грузоподъемных машин, таких как погрузчики, портальные, козловые, мостовые и прочие краны. К ГП машинам мое образование имело еще меньше отношения. Поэтому я решила попробовать. 
Программируемые логические контроллеры Siemens
ПЛК фирмы Siemens — это промышленные контроллеры и используются для автоматизации технологических процессов. У нас, в частности, использовались для автоматизации работы грузоподъемных машин.
Simatic включает в себя несколько линеек ПЛК — Simatic S5 и Simatic S7. В свою очередь линейка Simatic S7 содержит семейства S7-200, S7-300, S7-400 и S7-1200.
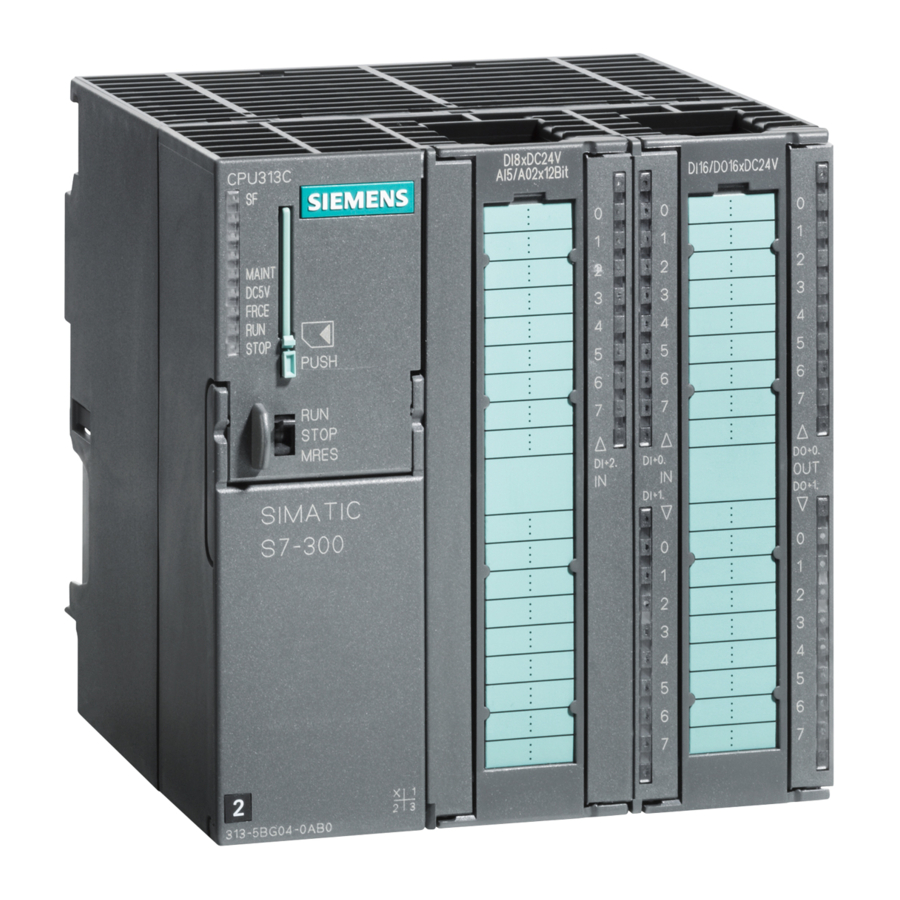
Чаще всего мы использовали ПЛК семейств S7-300 и S7-400, для которых компанией Siemens было разработано собственное программное обеспечение Simatic Step 7.
ПЛК включали в себя:
- модуль центрального процессора (CPU);
- блоки питания (PS) для питания контроллера от сети переменного или постоянного тока;
- сигнальные модули (SM), предназначенные для ввода/вывода дискретных и аналоговых сигналов;
- коммуникационные процессоры (CP), выполняющие автономную обработку коммуникационных задач в промышленных сетях Profibus, Industrial Ethernet и др.;
- функциональные модули (FM), которые выполняли задачи автоматического регулирования, взвешивания, позиционирования и пр.;
- интерфейсные модули (IM) для подключения стоек расширения к базовому блоку контроллера.
Кроме этого, к ПЛК через сеть Profibus подключалось большое количество ведомых устройств, таких как частотные преобразователи, приводы, абсолютные/инкрементные энкодеры и пр.
Вся работа ГП машины по максимуму автоматизировалась и крановщику нужно применять минимум усилий для управления оной.
Что из себя представляет Simatic Step 7?
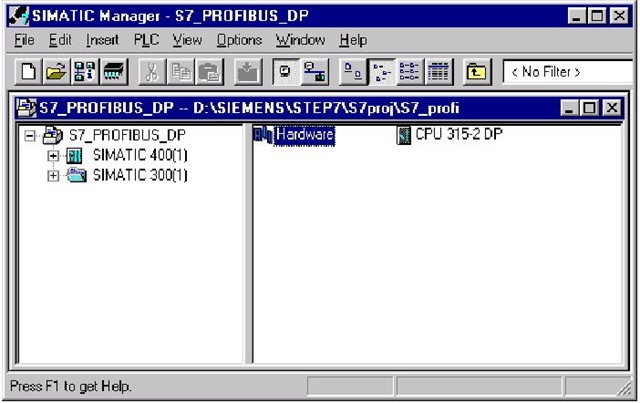
Главной утилитой является Step 7 — Simatic Manager, которая позволяет производить конфигурацию ПЛК и сетей (утилиты HWConfig и NetPro).
В процессе конфигурации определяется состав оборудования, способы подключения, используемые сети, адреса, выбираются настройки для используемых модулей. Готовая конфигурация загружается в ПЛК, что так же является настройкой оборудования.
Утилиты конфигурации позволяют осуществлять диагностику оборудования, обнаруживать аппаратные ошибки или неправильный монтаж.
Программирование ПЛК производится так же с помощью Simatic Manager, обеспечивающий написание программ в трех редакторах:
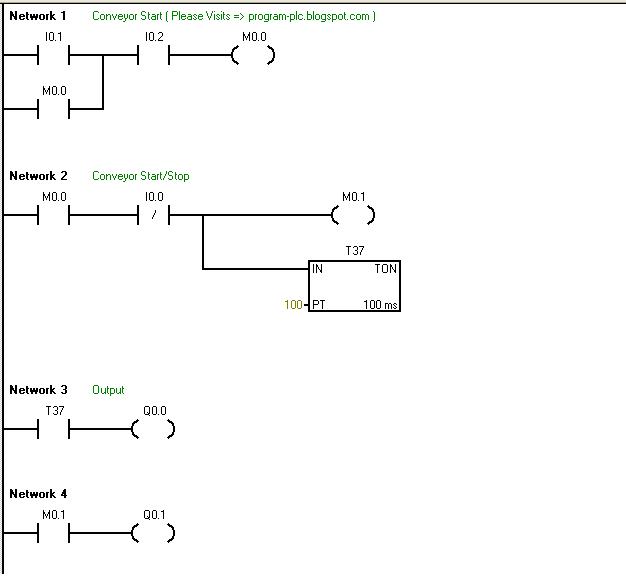
- LAD (Ladder Diagram) — релейные диаграммы. Редактор отображает программу в графическом представлении, похожем на электрическую монтажную схему. Логические схемы позволяют программе имитировать протекание электрического тока от источника напряжения через ряд логических условий на входах, которые активизируют условия на выходах. Источником напряжения выступает шина, находящаяся слева.
Основными элементами являются нормально замкнутые и нормально разомкнутые контакты.Соответственно, замкнутые контакты позволяют потоку сигнала протекать через них к следующему элементу, разомкнутые контакты — препятствуют протеканию потока сигнала.
Логика делится на сегменты, т.н. нэтворки (Network), программа исполняется слева направо и сверху вниз.
Особенностями редактора LAD является простота в использовании и понимании для начинающих программистов. - FBD (Function Block Diagram) — функциональные блочные диаграммы. Этот редактор отображает программу в виде обычных логических схем. Контактов нет, но есть эквивалентные функциональные блоки. В данном редакторе не используется понятие «поток сигнала», как в LAD, его выражает аналогичное понятие потока управления через логические блоки FBD.
Потоком сигнала называется пусть состояния «1» через элементы FBD. Логика программы вытекает из связей между функциональными блоками, обозначающими команды.
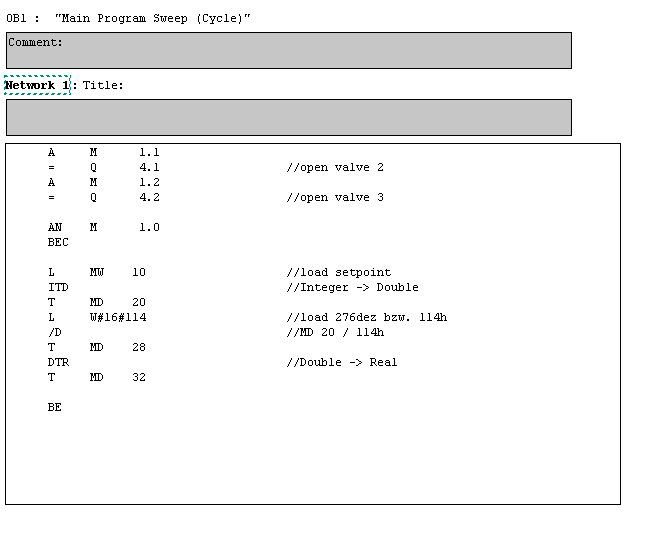
Графическое представление функционального плана хорошо отражает процесс выполнения программы. - STL (Statement List) — список инструкций. Данный редактор дает возможность создавать программы, вводя мнемонические обозначения команд. В этом редакторе можно создавать программы, которые невозможно создать в редакторах LAD и FBD. Программирование в STL очень похоже на программирование на Ассемблере, несколько специфическое.
ПЛК выполняет команды в порядке, определяемом программой, сверху вниз, затем начинает сначала.
С помощью редактора STL всегда можно посмотреть или отредактировать программы, созданные на LAD или FBD, обратное не всегда возможно.
Я работала с самого начала в STL, пробовала LAD, мне показался слишком непонятным и многие вещи таки не удавалась так просто в нем сделать, как в STL. Плюс еще в том, что при загрузке программы в ПЛК, она компилируется в STL и, соответственно, при выкачке ее из ПЛК на программатор она так же представлена в STL.
Вместо заключения
Программирование ПЛК занятие увлекательное, особенно когда это не стенд, а реальное оборудование.
Моя работа заключалась в создании программы на ПЛК для управления всей ГП машины либо отдельных ее частей, а так же загрузке программного обеспечения непосредственно в оборудование и его отладке.
Случалось разное, но работать с железом было очень интересно, хоть и не легко иногда.
А строили мы вот такие ГП машины:
-
Contents
-
Table of Contents
-
Bookmarks
Quick Links
Background and System Description 05/2017
Guide for Migrating SIMATIC
S7-300/S7-400 to SIMATIC
S7-1500 and TIA Portal
Boundary Conditions and Procedure for Migrating Hardware and
Software
https://support.industry.siemens.com/cs/ww/en/view/109478811
Related Manuals for Siemens SIMATIC S7-300
Summary of Contents for Siemens SIMATIC S7-300
-
Page 1
Background and System Description 05/2017 Guide for Migrating SIMATIC S7-300/S7-400 to SIMATIC S7-1500 and TIA Portal Boundary Conditions and Procedure for Migrating Hardware and Software https://support.industry.siemens.com/cs/ww/en/view/109478811… -
Page 2: Warranty And Liability
Application Examples at any time without prior notice. If there are any deviations between the recommendations provided in these Application Examples and other Siemens publications – e.g. Catalogs – the contents of the other documents have priority. We do not accept any liability for the information contained in this document.
-
Page 3: Table Of Contents
Partial or complete migration …………. 7 Planning the migration phases …………9 Advantages of modernization …………10 SIMATIC S7-300/S7-400 and SIMATIC S7-1500 System Architecture ..11 SIMATIC S7-300/S7-400 …………..11 3.1.1 Information on the SIMATIC S7-300 automation system ….12 3.1.2…
-
Page 4
Solution partner …………….79 References and online documents ……….. 80 6.4.1 Important information …………… 80 Appendix ………………….. 81 SIMATIC S7-300/S7-400, S7-1500 components and HMI in comparison ………………81 7.1.1 CPU modules ……………… 82 7.1.2 Comparison of the software/hardware properties ……84 7.1.3… -
Page 5: Introduction
TIA Portal, offers new and efficient programming and configuration options. This document contains recommendations and notes for users, regarding the new generation, who have so far been using SIMATIC S7-300/S7-400 automation systems and are planning to change to the new SIMATIC controller generation S7-1500.
-
Page 6: Planning Plant Migration
2 Planning Plant Migration Planning Plant Migration General procedure In the run-up to plant migration, there is considerable need for clarification. Therefore, it is all the more important to develop a detailed comprehensive concept for planning and implementing the pending migration. Each plant has different requirements for the migration process.
-
Page 7: Partial Or Complete Migration
2 Planning Plant Migration Plant operation after migration – Timely training of operating and maintenance staff – Implement changed/improved processes – Different cycle times of the plant – Schedule spare parts planning for future plant expansion and improvements Partial or complete migration What is decisive for the migration scope? Complexity of the control solution –…
-
Page 8
2 Planning Plant Migration In the end, all these influencing factors determine the decision on the type of migration that can be implemented: – Complete migration – Complete migration in phases – Partial migration – Rebuild Table 2-1 Type Cause Advantages Disadvantages Partial migration… -
Page 9: Planning The Migration Phases
2 Planning Plant Migration Planning the migration phases The transition to new technology requires careful planning to avoid problems and ensure maximum use of new functions and capabilities. For these reasons, it is important to the take time to plan the objectives and required steps before the start of the migration process.
-
Page 10: Advantages Of Modernization
Note More information can be found in the delivery release of the S7-1500 controllers: https://support.industry.siemens.com/cs/ww/en/view/67856446 Meanwhile, mechanisms and technologies have changed. A modern SIMATIC automation system such as the S7-1500 can offer you the following technical and…
-
Page 11: Simatic S7-300/S7-400 And Simatic S7-1500 System Architecture
3 SIMATIC S7-300/S7-400 and SIMATIC S7-1500 System Architecture SIMATIC S7-300/S7-400 and SIMATIC S7- 1500 System Architecture SIMATIC S7-300/S7-400 Figure 3-1 SIMATIC S7-300/S7-400 and S7-1500 automation systems Plant automation S7-400 Advanced Controller S7-1500 Factory automation S7-300 Basic Controller S7-1200 S7-200 Lower power range…
-
Page 12: Information On The Simatic S7-300 Automation System
3 SIMATIC S7-300/S7-400 and SIMATIC S7-1500 System Architecture 3.1.1 Information on the SIMATIC S7-300 automation system The SIMATIC S7-300 automation system is a programmable controller for factory automation/engineering in the OEM sector. The S7-300 system has a modular design and consists of the following components:…
-
Page 13: Information On The Simatic S7-400 Automation System
3 SIMATIC S7-300/S7-400 and SIMATIC S7-1500 System Architecture 3.1.2 Information on the SIMATIC S7-400 automation system Note This document is not valid for SIMATIC S7-400 in connection with PCS 7. The SIMATIC S7-400 automation system is a programmable controller for factory automation.
-
Page 14: Simatic S7-1500
3 SIMATIC S7-300/S7-400 and SIMATIC S7-1500 System Architecture SIMATIC S7-1500 3.2.1 Compared to the SIMATIC S7-300/S7-400 programmable controllers, the available CPU types of the new S7-1500 controller generation show considerable differences and functions. Features and functions of the available CPU types of the S7-1500:…
-
Page 15
3 SIMATIC S7-300/S7-400 and SIMATIC S7-1500 System Architecture The CPU executes the user program and the integrated system power supply supplies the electronics of the modules used via the backplane bus. The I/O modules form the interface between the controller and the process. -
Page 16: Hardware Migration
Change to current engineering (more efficient working, increased flexibility) Basis for future modifications Shorter product introduction times Reduced operational costs 4.1.2 Support, tools Siemens and its certified partners facilitate migration by providing: Check tool Readiness Check Tool (https://support.industry.siemens.com/cs/ww/en/view/60162195) Conversion tools –…
-
Page 17: Types Of Hardware Migration — Fallback Strategies
4 Hardware Migration 4.1.3 Types of hardware migration – fallback strategies For a hardware migration the implementation strategy has to be selected first. Resources, time and financial aspects as well as risks have to be evaluated very carefully. Table 4-1 Type Description Advantages…
-
Page 18: Selecting The Cpu
4 Hardware Migration Selecting the CPU Like SIMATIC S7-300/S7-400, SIMATIC S7-1500 provides a selection of CPUs with different performance levels. For reference, the appendix provides an overview table that compares the S7- 300/S7-400 CPUs recommended S7-1500 CPUs. (Chapter 7.1.1 CPU…
-
Page 19: Centralized And Distributed I/O
4.3.1 Centralized I/O The basic design of the centralized I/O of the SIMATIC S7-300/S7-400 differs only insignificantly from the one of the S7-1500. Both systems share the same design where the CPU and the centralized I/O are connected via an appropriate backplane bus.
-
Page 20: Distributed I/O
4 Hardware Migration Note Further information on the S7-400 automation system is available in the manual S7-400, M7-400 Automation System Module Data. https://support.industry.siemens.com/cs/ww/en/view/1117740 4.3.3 Distributed I/O For S7-300/S7-400 as well as S7-1500, distributed I/Os can be connected via PROFIBUS or PROFINET, for example, ET200SP, ET200MP, ET200AL, ET200pro, ET200eco or ET200iSP.
-
Page 21
4 Hardware Migration Complete migration of plants with ET 200 stations It is possible to fully retain the I/O during migration (provided it is compatible with the CPU). If the existing system is based on PROFIBUS, the interface connections could be exchanged for all stations to change to PROFINET. -
Page 22: Communication And Networks
4 Hardware Migration Communication and networks In SIMATIC S7-300/S7-400 there are a number of options for communication. These were expanded even further with S7-1500. The innovations comprise the following areas: System-internal communication Communication with external partners (numerous communications protocols) Below, some technical details between S7-300 and S7-1500 are compared with each other.
-
Page 23: Available Interfaces
4 Hardware Migration 4.4.2 Available interfaces The communication modules are an innovation in the system of the S7-1500 that provide the option to connect the internal interfaces of the CPU as well as the communication processors to the I/O. Table 4-8: Overview of available interfaces Interface S7-300 S7-1500…
-
Page 24: Number Of Internal Interfaces
4 Hardware Migration 4.4.4 Number of internal interfaces Similar to the S7-300, the number of interfaces for the S7-1500 depends on the type of CPU. Table 4-10 Overview of number of interfaces S7-1500 Number Type Number Interfaces Ports 1510SP(F) 1 x Profinet (3 x with BUS adapter) 1st interface->…
-
Page 25: Functions Of The Profinet/Ethernet Interfaces
4 Hardware Migration 4.4.5 Functions of the PROFINET/Ethernet interfaces Some CPUs (depending on type) of the S7-1500 were provided with more than one interface, this makes it possible to distribute several functions in the CPU to the different interfaces. Table 4-11 Excerpt of the functions available of the PROFINET/Ethernet interfaces Function S7-300 S7-1500…
-
Page 26: Interfaces For Point-To-Point Connections
1511(C/F/T) 1512C 1513(F) 1515(F/T) 1516(F) 1517(F/T) 1518(F) The “CPU-CPU Communication” compendium gives you an overview. https://support.industry.siemens.com/cs/ww/en/view/78028908 Note Communication will be discussed in greater detail in a later version of this guide. Migration S7-300/S7-400 nach S7-1500 Entry ID: 109478811, V1.1, 05/2017…
-
Page 27: Operator Control And Monitoring
Type/number of interfaces (MPI, PROFIBUS, PROFINET, USB) Data storage/storage options/memory size Note A detailed guideline for migrating older panels to Comfort Panels is available at: https://support.industry.siemens.com/cs/ww/en/view/49752044 4.5.2 HMI software Migrating the project which is part of the panel is possible. To do this, the project has to be available for WinCC flexible 2008 SP2/SP3, otherwise migration is not possible.
-
Page 28: Technological Function
4 Hardware Migration Technological function Note When migrating the technological functions of S7-300/S7-400 to S7-1500, in most cases it will not be possible to migrate the components one-to-one, instead a solution-based approach is used, i.e. hardware and software reproduce the function together.
-
Page 29
4 Hardware Migration Counter modules (FM 350-1/FM450-1) Table 4-15 Function in S7-300/S7-400 Solution in S7-1500 Comment Pulse encoder 24V TM Count 2x24V 200kHz input frequency Input (Counter Incremental encoder 24V TM Count 2x24V 200kHz input frequency signal) Incremental encoder 5V TM PosInput2 1MHz input frequency Internal 1 MHz reference… -
Page 30
4 Hardware Migration Counter module (FM350-2) Table 4-16 Function in S7-300 Solution in S7-1500 Comment Pulse encoder 24V + direction TM Count 2x24V 200kHz counter signal Input Pulse encoder 24V without TM Count 2x24V, 200kHz counter signal/ Counter direction TM Timer DIDQ 16x24V 50kHz counter signal signal Incremental encoder 24V… -
Page 31
4 Hardware Migration Cam control unit (FM352/FM452) Table 4-18 Function in S7-300/S7-400 Solution in S7-1500 Comment Input Incremental 24V TM Count 2x24V 200kHz input frequency Position Incremental 5V TM PosInput2 1MHz input frequency Absolute SSI TM PosInput2 Internal position value of Saves costs and space TO Axis Function… -
Page 32
4 Hardware Migration Positioning for stepper drives (FM353) Table 4-19 Function in S7-300 Solution in S7-1500 Comment Input DI for reference point TM PTO4 CPU 151xC Function Speed axes TO Speed_Axis Positioning TO Positioning_Axis Traversing programs Technology Template On request “S7-1500 MotionList”… -
Page 33
4 Hardware Migration Positioning for stepper and servo drives (FM453) Table 4-21 Function in S7-400 Solution in S7-1500 Comment Input Incremental 5V TM PosInput2 Absolute SSI TM PosInput2 Measuring the actual value via PROFIdrive Function Speed axes TO Speed_Axis Positioning TO Positioning_Axis Traversing programs Technology template… -
Page 34
4 Hardware Migration Highly functional, programmable modules FM 352-5, FM 357-2, FM 458-1DP Table 4-23 High-speed Boolean processor 4-axis interpolation Configurable application FM 352-5 FM 357-2 module FM 458-1DP Solution of the application based on: CPU 1518 for short cycle times TM Count for incremental encoder TM Count for incremental encoder… -
Page 35: Control
4 Hardware Migration 4.6.2 Control Figure 4-3 The following 3 control types are integrated and available for the S7-1500 in the TIA Portal. General description of the PID blocks Table 4-24 Name Function Advantages PID_Temp *) Temperature control for active heating Included in firmware and cooling with control and two Self-tuning (automatic…
-
Page 36
4 Hardware Migration Function in S7-300/S7-400 Solution in S7-1500 Comment (per channel) required; no wiring effort Dead band TO PID_Temp Split range TO_PID_temp Two parameter records Ramp/linearization Blocks in preparation Cascade control TO PID_Temp Application example (SIOS: 103526819) Other controller structures User-specific expansion Backup operation (CPU stop) Separate CPU to… -
Page 37
4 Hardware Migration Temperature/controller module (FM355-2 C/S) Table 4-27 Function in S7-300 Solution in S7-1500 Comment Input As FM355 C/S Function Heating controller TO PID_Compact, Alternative: Basic TO PID_Temp/TO PID_3Step PID_Controller: TCONT_CP/TCONT_S Cooling controller TO PID_Compact/TO PID 3Step Heating/cooling controller TO PID_Temp Two parameter records Self-tuning integrated… -
Page 38
4 Hardware Migration Modular PID Control Table 4-30 Function in S7-300/S7-400 Solution in S7-1500 Comment Function Actual value preparation TO PID_Compact, Error monitoring TO PID_Temp, PID control TP PID_3Step Control value processing Pulse generator, split range Standardization, scaling, User-specific expansion STEP 7 Standard switching functions (scale,… -
Page 39: Software Conversion
Migration effort same as or higher than rebuilding Achievement of higher throughputs due to increase in performance And many more Note For a general programming guide for SIMATIC S7-1500, refer to the following entry ID: https://support.industry.siemens.com/cs/ww/en/view/81318674 Migration S7-300/S7-400 nach S7-1500 Entry ID: 109478811, V1.1, 05/2017…
-
Page 40: Programming Languages
S7-SCL when migrating from STEP 7 V5.x to STEP 7 (TIA Portal). Note For an overview of the statements available to you for S7-1500, please use the following link: https://support.industry.siemens.com/cs/ww/en/view/86630375 Migration S7-300/S7-400 nach S7-1500 Entry ID: 109478811, V1.1, 05/2017…
-
Page 41: Option Packages And Expansions
5 Software Conversion 5.1.2 Option packages and expansions There are various expansions or option packages for STEP 7 V5.x, some of which are listed below. The TIA Portal provides a broad basis for the engineering, since many expansions that had to be installed separately as options in STEP 7 V5.x are now available integrated.
-
Page 42: Variants Of The Tia Portal
Each other option that is subject to license, which is part of the STEP 7 V5.x project, also has be licensed. Note The TIA selection tool supports you with the migration of licenses and suggests the most economical variants: http://www.siemens.en/tia-selection-tool Migration S7-300/S7-400 nach S7-1500 Entry ID: 109478811, V1.1, 05/2017…
-
Page 43: Programming Environment
Microsoft Windows Server 2012 R2 Hyper-V Note Statements regarding compatibilities of the individual SIMATIC packages can be found at https://support.industry.siemens.com/cs/ww/en/view/64847781 As the hardware platform, we recommend: SIMATIC Field PG M4 Premium or Premium Plus (for example, article number: 6ES7716-1CB10-0CE4 or 6ES7716-2CB10-…
-
Page 44: Migration Of The Project
5 Software Conversion Note An action package for field PGs is available that is specifically designed for migrations, which can be performed with the migration tool: The package does not include STEP 7 V5.x or WinCC flexible licenses. The article number is: 6ES7716-2CA10-0CD4 Migration of the project 5.2.1…
-
Page 45
5 Software Conversion Step Instruction Check which alarm numbering procedure is used in the project. If project-wide is set, the migration is cancelled. Migration S7-300/S7-400 nach S7-1500 Entry ID: 109478811, V1.1, 05/2017… -
Page 46
Note For information on how to check your project for consistency, refer to the following entry: https://support.industry.siemens.com/cs/ww/en/view/5416540 Note The components in the TIA Portal are subject to the target date 01.10.2007. All products no longer released at this date, are not included. -
Page 47: Migration From Step 7 V5.X To Step 7 (Tia Portal)
5 Software Conversion 5.2.2 Migration from STEP 7 V5.X to STEP 7 (TIA Portal) Option 1: Migration with TIA Portal In order to migrate a project from STEP 7 V5.x to STEP 7 (TIA Portal) V13 SP1 (both software packages are located on a computer), perform the following steps: Table 5-6 Step Instruction…
-
Page 48
5 Software Conversion Step Instruction Check the result of the migration process with the migration protocol. If necessary, adapt the project. Compile the migrated project. If required, rectify the fault. If required, carry out further steps. Migration S7-300/S7-400 nach S7-1500 Entry ID: 109478811, V1.1, 05/2017… -
Page 49
Note The migration tool can be found on any installation DVD of STEP 7 (TIA Portal) or in the following entry (for the current version of the TIA Portal): https://support.industry.siemens.com/cs/ww/en/view/58638200 Table 5-7 Step Instruction Open the Migration Tool TIA V13. -
Page 50: Migrating Projects With Safety Program
5 Software Conversion Step Instruction Select the appropriate initial project. (Note the tick on “Include hardware configuration”) Check the result of the migration process with the migration protocol. If necessary, adapt the project. Compile the migrated project. If required, rectify the fault. 5.2.3 Migrating projects with safety program Without compilation…
-
Page 51
5 Software Conversion Safety project where the program structure of Distributed Safety and the overall signature has been preserved. Note The acceptance printout created with S7 Distributed Safety V5.4 SP5 remains valid! With compilation Only when the migrated project is recompiled with STEP 7 Safety Advanced V13 will it receive the new program structures and a new overall signature. -
Page 52
TWO_HAND – WR_FDB – RD_FDB – – SENDS7 – RCVS7 Note the block version when inserting them. Note More information on STEP 7 Safety can be found in the manual: https://support.industry.siemens.com/cs/en/en/view/54110126 Migration S7-300/S7-400 nach S7-1500 Entry ID: 109478811, V1.1, 05/2017… -
Page 53: Further Steps — Migrating The Cpu S7-300/S7-400 To S7-1500
5 Software Conversion 5.2.4 Further steps — migrating the CPU S7-300/S7-400 to S7-1500 Once the project is available in the TIA Portal, other adaptations have to be carried out as well. The CPU is not automatically changed to the S7-1500 during the migration process.
-
Page 54
5 Software Conversion Step Instruction Select the suitable CPU. Important: When changing to the CPU S7-1500 only the CPU is adjusted. If other modules are inserted in the central configuration of the S7-300, they have to added manually when changing to S7-1500. Note: You can import the HW configuration from your STEP 7 V5.x project into the TIA Selection Tool. -
Page 55: Optimization Of The Tia Portal Project
5 Software Conversion 5.2.5 Optimization of the TIA portal project The full migration is not yet completed with the created TIA Portal project. If there are no other messages in the migration protocol itself and if there are also no errors after compilation, in most cases it will still be necessary to carry out an optimization.
-
Page 56
5 Software Conversion Table 5-10 Block type S7-300/S7-400 S7-1500 64 Kbyte Optimized up to 10Mbyte (depending on the CPU type), non-optimized 64kbyte 64 Kbyte Optimized up to 512kbyte, depending on the CPU type 64 Kbytes Optimized up to 512kbyte, depending on the CPU type 64 Kbytes Optimized up to 512kbyte, depending… -
Page 57
5 Software Conversion New data types For the programming in TIA Portal some new data types have been introduced, among others also 64 bit data types. This makes it possible to process considerably larger and more precise values. Table 5-11 Data type Size Range of values… -
Page 58
5 Software Conversion New instructions New instructions make it very conveniently possible to configure the programming. Below, you can find a small selection of new instructions: Table 5-12 Name Usage Appearance CALCULATE Carry out calculations independent from data type MOVE Copy value Copy array MOVE_BLK… -
Page 59
Note Other recommendations of how the user program can be optimized can be found in programming guideline S7-1200/S7-1500. https://support.industry.siemens.com/cs/ww/en/view/90885040 Note Once hardware and software have been fully migrated, optimized and loaded, a test of all functions should be carried out! -
Page 60: Program Structure And Standard Functions
5 Software Conversion Program structure and standard functions 5.3.1 Organization blocks (OB) Organization blocks are located in the firmware of the SIMATIC CPU and called by the CPU’s operating system when specific events occur. They are the interface between the system program and the user program and can be programmed by the user.
-
Page 61
For information on system diagnostics, please refer to the following two entries: https://support.industry.siemens.com/cs/ww/en/view/68011497 https://support.industry.siemens.com/cs/ww/en/view/98210758 Figure 5-1 STEP 7 (TIA) -
Page 62: Function Blocks And Functions, Data Blocks, Plc Data Types
For reasons of compatibility STEP 7 V5.x and STEP 7 TIA Portal does not differ in the basic functions but in some details. They are explained in detail in the programming guideline. https://support.industry.siemens.com/cs/ww/en/view/81318674 Migration S7-300/S7-400 nach S7-1500 Entry ID: 109478811, V1.1,…
-
Page 63
5 Software Conversion Functions (FC) For functions in STEP 7 (FCs), appropriate input and output signals can be declared and transferred to the FC when they are called. In addition, the FC can provide a direct return value of the function. Temporary tags and constants can be declared in an FC. -
Page 64: Advantages Of Step 7 Tia Portal Compared To Step 7 V5.X
5 Software Conversion 5.3.3 Advantages of STEP 7 TIA Portal compared to STEP 7 V5.x The basic function in STEP 7 V5.x and STEP 7 TIA Portal are the same. However, there are some detailed improvements regarding handling and programming. Below, you find an excerpt of some functions that have been realized in STEP 7 TIA Portal.
-
Page 65
5 Software Conversion STEP 7 TIA Portal Description/advantage Motion functions are already Before, motion functions were not integrated in standard CPUs integrated in the standard CPU — > PLCopen Blocks Speed, positioning axis and synchronous axes are available PID integrated compact controller (PID_Compact, PID_3Step, PID_Temp) PID basic controllers are… -
Page 66
5 Software Conversion STEP 7 TIA Portal Description/advantage Recipes/archives as CSV file, Recipes as csv file previously did not exist on the CPU via the web server of the CPU Security Integrated – more There are only 2 protection levels for S7-300/S7-400. Now it is protection levels available possible to assign the access levels better. -
Page 67
5 Software Conversion STEP 7 TIA Portal Description/advantage Library concept Libraries have already been possible for STEP 7 V5.x but without versioning. Blocks, data types, screens and entire stations can be stored. System status list (SSL) has The diagnostic options for the S7-1500 and TIA Portal have been fully been replaced by a new system revised. -
Page 68
5 Software Conversion Programming Table 5-18 STEP 7 TIA Portal Description/advantage All instructions are available in In STEP 7 V5.x not all instructions were available in LAD/FBD all programming languages Same performance for all In TIA Portal all programming languages are directly compiled into programming languages machine code and therefore offer all the same performance. -
Page 69
5 Software Conversion STEP 7 TIA Portal Description/advantage Slicing possible – access to Slicing access can look as follows, e.g.,: .%X0 for Bool, .%B0 for elements of a larger data type byte, .%W0 for word, .%D0 for double word Slicing also possible in LAD/FBD SCL –… -
Page 70
5 Software Conversion STEP 7 TIA Portal Description/advantage Simplified handling of send/receive communication through wizard Simplified “Calculate” block Simplified mathematic functions (selectable data type) Migration S7-300/S7-400 nach S7-1500 Entry ID: 109478811, V1.1, 05/2017… -
Page 71
5 Software Conversion STEP 7 TIA Portal Description/advantage 64 bit data types available Short and unsigned data types available Variant instead of any pointer For more information and examples, refer to the TIA Portal Online Help. Migration S7-300/S7-400 nach S7-1500 Entry ID: 109478811, V1.1, 05/2017… -
Page 72
5 Software Conversion STEP 7 TIA Portal Description/advantage Integrated modbus blocks Modbus TCP blocks: Modbus RTU blocks: Migration S7-300/S7-400 nach S7-1500 Entry ID: 109478811, V1.1, 05/2017… -
Page 73
5 Software Conversion STEP 7 TIA Portal Description/advantage Program structuring For a good overview of the program design subgroups can be created in the “Program blocks” folder which enables a logic division of the program Benefits of known office When creating tags, the autofill function, which is known from features Office, can be used. -
Page 74
5 Software Conversion STEP 7 TIA Portal Description/advantage Grouping of devices in project Groups can be created in the project tree, to sort plant parts navigation Assigning several PROFINET Mass functions allow certain functions to be carried out for several devices to a controller in one devices, here, for example, assigning several IO devices to one step… -
Page 75
5 Software Conversion STEP 7 TIA Portal Description/advantage Global search The search is not only restricted to the currently open block but can also be carried out globally. This is how it is possible to find all places in the project. Creating/saving profiles When machines always have the same structure, they often also require the same components. -
Page 76
5 Software Conversion STEP 7 TIA Portal Description/advantage Creating or restoring backups A backup can be created directly on the CPU (via display). of the CPU via display (without additional software) Migration S7-300/S7-400 nach S7-1500 Entry ID: 109478811, V1.1, 05/2017… -
Page 77: Differences In The Hardware Of The S7-300/S7-400 And S7-1500
Windows card reader, or the storage medium becomes useless for the CPU. For more information regarding the SMC, please refer to the system manual for the S7-1500 in chapter “SIMATIC Memory Card” at: https://support.industry.siemens.com/cs/ww/en/view/59191792 Migration S7-300/S7-400 nach S7-1500 Entry ID: 109478811, V1.1,…
-
Page 78: Programming Of Sequential Controls — S7-Graph In Step 7 V5.X And Tia Portal
5 Software Conversion Programming of sequential controls – S7-GRAPH in STEP 7 V5.x and TIA Portal Note Programming sequential controls – S7-GRAPH will be described in a later version of this guide. Migration S7-300/S7-400 nach S7-1500 Entry ID: 109478811, V1.1, 05/2017…
-
Page 79: The Most Important Recommendations
Migration of obsolete control systems is the prerequisite for high availability over the entire life cycle of your plant. Siemens offers comprehensive migration support for typical fields of application. We support you from the idea stage to planning and implementation. The scope of services includes migration or temporary support of your migration projects.
-
Page 80: References And Online Documents
Link SIMATIC S7-300 CPU 31xC and CPU 31x: Technical data 12996906 SIMATIC S7-300 CPU 31xC and CPU 31x: Installation 13008499 SIMATIC S7-300 Instruction list S7-300 CPUs and ET 200 CPUs 31977679 SIMATIC S7-300 S7-300 Module Data 8859629 Table 6-3 S7-400 manuals…
-
Page 81: Appendix
This means: The respective listed SIMATIC S7-1500 hardware component must not automatically be regarded as an equivalent to the listed SIMATIC S7-300/S7- 400 component. It is the user’s responsibility to consider the technical characteristics (e.g., limits) of the SIMATIC S7 module and to check whether these parameters are relevant to the customer application (plant) and complied with.
-
Page 82: Cpu Modules
Note The content of the following table is for reference only! Please note the general information in this chapter: SIMATIC S7-300/S7-400, S7-1500 components and HMI in comparison. The TIA Selection Tool provides support for the implementation of S7-300/S7-400 to S7-1500: http://www.siemens.en/tia-selection-tool…
-
Page 83
7 Appendix S7-300 Description S7-1500 Description 6ES7 318-3EL00-0AB0 CPU 319-3PN/DP 6ES7 517-3AP00-0AB0 CPU 1517-3PN/DP 6ES7 318-3EL01-0AB0 CPU 319-3PN/DP 6ES7 517-3AP00-0AB0 CPU 1517-3PN/DP 6ES7 318-3FL00-0AB0 CPU 319F-3PN/DP 6ES7 517-3FP00-0AB0 CPU 1517F-3PN/DP 6ES7 318-3FL01-0AB0 CPU 319F-3PN/DP 6ES7 517-3FP00-0AB0 CPU 1517F-3PN/DP 6ES7 151-7AA20-0AB0 IM 151-7 CPU 6ES7 510-1DJ01-0AB0 CPU 1510SP-1PN… -
Page 84: Comparison Of The Software/Hardware Properties
7 Appendix 7.1.2 Comparison of the software/hardware properties The following tables below give an overview of the properties that are available in the individual CPU types. CPU hardware properties Table 7-3 Property S7-300/S7-400 S7-1500 Display Yes, for 1511, 1513-1518 Display for failsafe CPU shows — Safety mode enabled/disabled — Signature — Time stamp last change…
-
Page 85
7 Appendix CPU programming languages general Table 7-5 Properties S7-300/S7-400 S7-1500 Symbolic programming FBD/ F-FBD LAD/F-LAB S7-GRAPH HiGraph no, planned Same functions in all programming languages SFBs SFCs S7 timer S7 F timer ICE counter S7 counter Edge evaluation Global DBs Instance DB System status list (SSL) Totally new solution… -
Page 86
7 Appendix Property S7-300/S7-400 S7-1500 JMP_LIST Concept for libraries with versioning Concept for F libraries with versioning Data type D-WORD for safety program yes, with UDT D-INT data type for safety program CPU online functions Table 7-7 Property S7-300/S7-400 S7-1500 Consistent download of all modifications Download in run mode yes, simultaneous… -
Page 87
7 Appendix CPU diagnostics functions Table 7-10 Property S7-300/S7-400 S7-1500 Integrated system diagnostics Identical diagnostics on web server , HMI, display and engineering CPU web server Table 7-11 Property S7-300/S7-400 S7-1500 File explorer Archive and recipe handling via web server CPU technology functions Table 7-12 Property… -
Page 88: Digital Modules S7-300
7 Appendix 7.1.3 Digital modules S7-300 Note The content of this table is for reference only! Please note the general information in this chapter: SIMATIC S7-300/S7-400, S7-1500 components and HMI in comparison Table 7-13 S7-300 Description S7-1500 Description Digital input modules…
-
Page 89
7 Appendix S7-300 Description S7-1500 Description relais 6ES7 322-5GH00-0AA0 16DA, UC 24- 16DA, 24…125V 6ES7 522-5EH00-0AB0 48V/0.5A UC/2A HF 6ES7 322-1CF00-0AA0 8DA, DC 48- 16DA, 24…125V 6ES7 522-5EH00-0AB0 125V/1.5A UC/2A HF Digital input/output modules 16DI, 24VDC/16DA, 6ES7 323-1BL00-0AA0 16DE/16DA 6ES7 523-1BL00-0AA0 24VDC/0.5A BA 16DI, 24VDC/16DA, 6ES7 323-1BH01-0AA0… -
Page 90: Digital Modules S7-400
7 Appendix 7.1.4 Digital modules S7-400 Note The content of this table is for reference only! Please note the general information in this chapter: SIMATIC S7-300/S7-400, S7-1500 components and HMI in comparison Table 7-14 S7-400 Description S7-1500 Description Digital input modules…
-
Page 91: Analog Modules S7-300
7 Appendix 7.1.5 Analog modules S7-300 Note The content of this table is for reference only! Please note the general information in this chapter: SIMATIC S7-300/S7-400, S7-1500 components and HMI in comparison Table 7-15 S7-300 Description S7-1500 Description Analog input modules…
-
Page 92: Analog Modules S7-400
7 Appendix 7.1.6 Analog modules S7-400 Note The content of this table is for reference only! Please note the general information in this chapter: SIMATIC S7-300/S7-400, S7-1500 components and HMI in comparison Table 7-16 S7-400 Description S7-1500 Description Analog input modules…
-
Page 93: Communication Modules S7-300
7 Appendix 7.1.7 Communication modules S7-300 Note The content of this table is for reference only! Please note the general information in this chapter: SIMATIC S7-300/S7-400, S7-1500 components and HMI in comparison Table 7-17 Article number Description S7-1500 Article number…
-
Page 94: Technology Modules S7-300
7 Appendix 7.1.9 Technology modules S7-300 Note The content of this table is for reference only! Please note the general information in this chapter: SIMATIC S7-300/S7-400, S7-1500 components and HMI in comparison Table 7-19 Article number Description S7-1500 Description 6ES7 338-4BC01-…
-
Page 95: Technology Modules S7-400
7 Appendix 7.1.10 Technology modules S7-400 Note The content of this table is for reference only! Please note the general information in this chapter: SIMATIC S7-300/S7-400, S7-1500 components and HMI in comparison Table 7-20 Article number Description S7-1500 Description 6ES7 450-1AP00-…
-
Page 96: Operator Panels
7 Appendix 7.1.11 Operator panels Note The content of this table is for reference only! Extensive information can be found in the panels migration guide: https://support.industry.siemens.com/cs/ww/en/view/49752044 Table 7-21 Predecessor device MLFB/article number Replaced by MLFB/article number OP 77B 6AV6641-0CA01-0AX1 KP400 Comfort 6AV2124-1DC01-0AX0 TP 177B 4″…
-
Page 97: History
8 History History Table 8-1 Version Date Modifications V1.0 09/2015 First version V1.01 09/2015 Additional note in chapters 1.1, 3.1.2 and 7.1.1 V1.1 05/2017 Expansion of migration of technological functions + general revision Migration S7-300/S7-400 nach S7-1500 Entry ID: 109478811, V1.1, 05/2017…