Просмотров 24к. Опубликовано 29.12.2021
Обновлено 26.01.2022
Активный пользователь всемирной паутины уже не раз использовал приложения для голосовой связи через мобильный интернет на основе протокола SIP. Этот протокол имеет широкую область применения: от видеоконференций вплоть до онлайн-игр.
SIP (Session Initiation Protocol)
С английского «протокол установления сеанса»
С помощью СИП-телефонии устройства настраивают корректную связь для обмена данными по следующей цепочке: клиент?сервер?клиент. Таким образом, устройства лучше взаимодействуют друг с другом и организовывают качественную коммуникацию по принципу чередования вопросов и ответов.
Содержание
- Технология SIP-телефонии
- Стандартные телефонные номера
- Оборудование для SIP-телефонии
- SIP- и IP-телефония: отличия
- Преимущества SIP-телефонии
- Программы для сип-телефонии
- Blink
- MicroSIP
- Zoiper
- Настройка SIP-телефонии
- Поставщики телефонии
- Что такое SIP-телефония в видео
Технология SIP-телефонии
После того как мы познакомились с SIP-телефонией, разберем ее принципы работы. Алгоритм обмена голосовыми сообщениями выглядит следующим образом:
- Происходит преобразование человеческого сигнала в цифровой с помощью специальных кодеков. Это позволяет снизить нагрузку на телефонную сеть и обеспечить высокую скорость коммуникаций.
- Преобразованный сигнал передается на устройство «на другом конце провода».
- Устанавливается связь между устройствами с помощью IP-адреса. Далее начинается соединение сеанса по SIP-протоколу.
- После соединения между устройствами сигнал расшифровывается в аналоговый сигнал. В итоге абонент, взявший трубку, слышит человеческий голос.
Стандартные телефонные номера
- Виртуальный номер. Это сотовый номер без физической АТС для переадресации вызовов.
- Прямой номер. Такая комбинация цифр используется для городских и междугородних номеров. Прямые звонки не отличаются от вызовов через обычные АТС. Однако есть существенное преимущество — высокое качество сигнала.
- Бесплатный номер. Такой номер имеют вид 8-800. Как правило, используется службами поддержки для работы с клиентами.
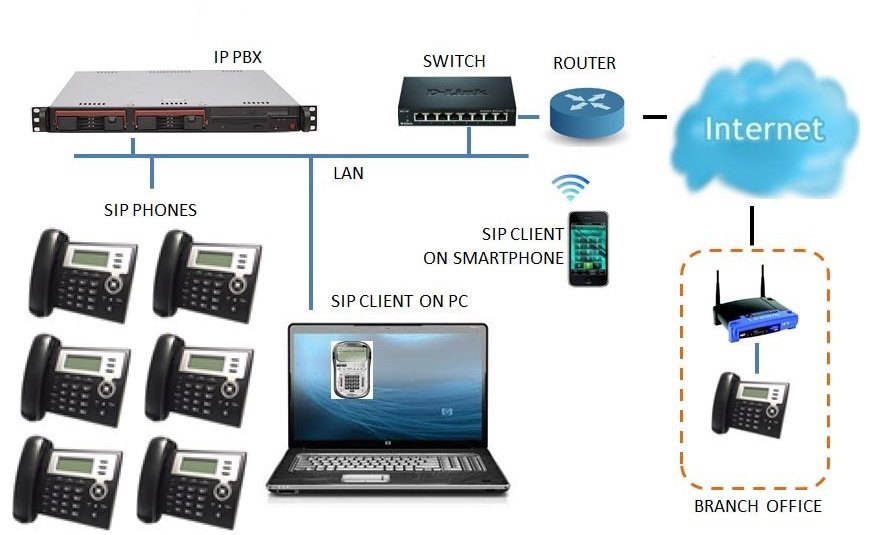
Оборудование для SIP-телефонии
После того как абонент набрал нужный номер, вызов автоматически поступает в облачный сервис. Далее вызов маршрутизируется на номер собеседника, с которым хочет связаться пользователь. В зависимости от способа организации связи вызов может быть направлен как на SIP, так и на IP номер.
Чтобы пользоваться SIP-телефонией, вам потребуется иметь хотя бы одно оборудование/приложение из этого списка:
- VoIP-телефон (Voice over IP). Он позволяет передавать голосовые сообщения через интернет-протоколы
- Аналоговый телефон, подключенный к IP-шлюзу и роутеру.
- ПК или ноутбук с доступом в интернет и установленным приложение для звонков.
- Мобильный телефон, подключенный к роутеру, на котором установлена специальная СИП-программа.
SIP- и IP-телефония: отличия
Мы уже немного разобрались в термине «SIP-телефония», поэтому сейчас детально рассмотрим IP-протокол.
IP (Internet Protocol)
с английского «межсетевой протокол»
Благодаря этому протоколу все устройства объединяются в глобальную сеть. У каждого абонента имеется персональный IP-адрес для обмена данными.
Основные отличия SIP- от IP-телефонии:
- IP-телефония позволяет совершать только голосовые звонки, в свою очередь, SIP-соединения обеспечивает обмен как аудиофайлами, так и видеороликами.
- Система IP приписывает каждой компьютерной сети уникальный адрес и осуществляет передачу данных с помощью специальных IP-протоколов. Стоит отметить, что SIP работает с разными технологиями для обмена мультимедийной информации.
Преимущества SIP-телефонии
Рассмотрим сильные стороны протокола установления сеанса:
ДЕШЕВИЗНА
Стоимость затрат на подключение SIP-телефонии значительно меньше по сравнению с аналоговыми АТС.
ЛЕГКАЯ НАСТРОЙКА И УСТАНОВКА
Ключевое качество такой технологии — простота установки и использования. Для связи вам потребуется либо ноутбук, либо смартфон с подключенным интернетом.
БАЗОВАЯ ТАРИФИКАЦИЯ
Услуги телефонной связи оплачиваются по базовым тарифам. Единая стоимость звонков позволяет крупным компаниям с филиалами в разных точках мира экономить на роуминге.
ПРОСТАЯ ИНТЕГРАЦИЯ С CRM-СИСТЕМАМИ
Благодаря интеграции с системами аналитики, есть возможность проверять эффективность работы операторов, отслеживать рекламные каналы и мониторить качество обслуживания.
ПОВЫШЕННАЯ ЗАЩИТА
В отличие от аналоговой связи SIP-телефония обладает повышенной защитой от внешнего прослушивания.
РАБОТАЕТ С ВИДЖЕТАМИ ОБРАТНОГО ЗВОНКА
В связи с этим показатели конверсии звонков увеличиваются в два раза.
Программы для сип-телефонии
Детально разберем популярные приложения для работы с СИП-телефонией.
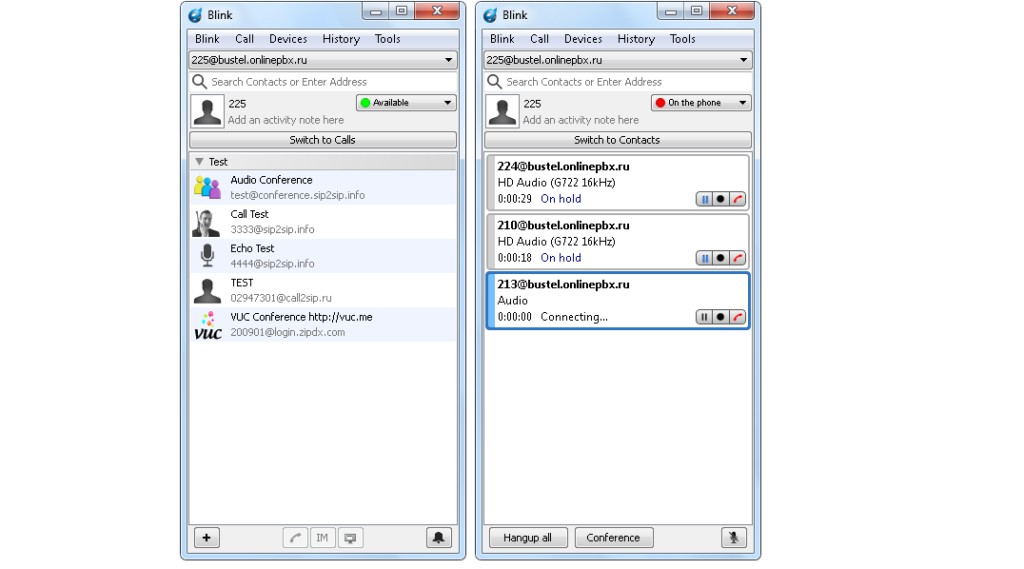
Blink
Blink является качественным клиентом связи в онлайн-режиме с использованием протокола SIP.
Приложение подходит для пользователей Windows, Mac OS и Linus. Софтфон предлагает бесплатную версию для тестирования программы. Поддерживает безлимитное количество аккаунтов, видео в разрешении HD и TLS шифрование. Умеет передавать и записывать голосовые файлы.
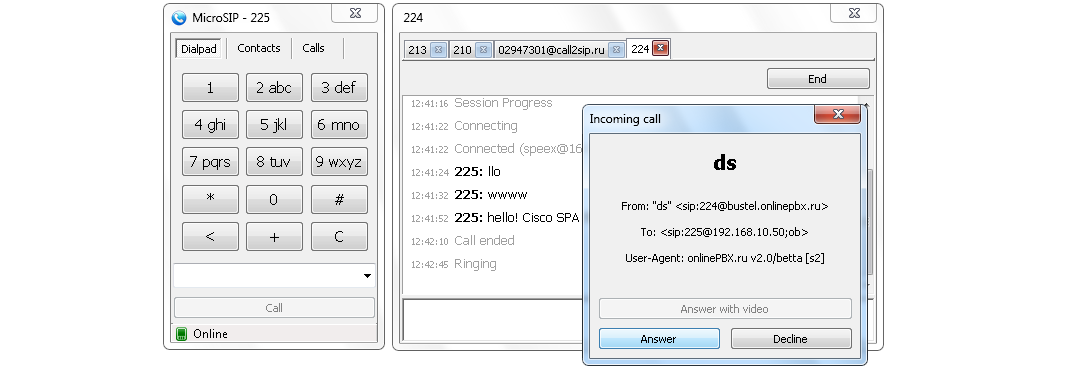
MicroSIP
Компактное решение с поддержкой видеозвонков.
Софтфон выпускается для Windows. Приложение весит 2,5 МБ и занимает оперативной памяти не более 5-12 МБ. Присутствует поддержка видео h264 и h263+. Простой интерфейс, разобраться с которым сможет каждый. Таким образом, MicroSIP — лучший вариант для привередливого пользователя.
Zoiper
Продвинутый мессенджер для SIP-телефонии.
Приложение оснащено программным шифрованием, поэтому можно больше не беспокоиться, что записи разговоров попадут не в те руки. Есть телефонная книга, содержащая данные абонентов. Присутствует текстовый чат для удобного общения с клиентами. Предсказуемый интерфейс.
Настройка SIP-телефонии
- Настольный SIP-телефон
Стационарный SIP-телефон используется для поддержки голосовой почты, переадресации и удержания вызова. Чтобы использовать аппарат, необходимо зарегистрироваться в личном кабинете поставщика.
- Wi-Fi SIP-телефон
Установка и настройка Wi-Fi телефона практически ничем не отличается от стационарного, только должно соблюдаться следующее условие — устройство с подключением роутера должно попадать в зону действия беспроводной сети.
- Программный SIP-телефон
Для использования программной телефонии нужно установить softphone на персональный компьютер, ноутбук или планшет. Чтобы проводить видеоконференции, необходимо подключить веб-камеру, микрофон и динамик. Приложение потребует зарегистрироваться и выполнить надлежащие настройки.
Поставщики телефонии
| Поставщик телефонии | Описание | Тарификация |
| МТС | Компания предоставляет продукт «СИП-телефония» для корпоративных клиентов. Провайдер обеспечивает круглосуточную техподдержку, быстрое подключение и низкие цены. | Для каждого бизнес-клиента предоставляет индивидуальные условия подключения. Поставщик не разглашает стоимость звонков. |
| Теле2 | У виртуальной АТС существует множество полезных функций для бизнеса: группировка контактов на подразделения и филиалы, создание внутренних номеров для быстрого дозвона, а также синхронизация записи разговоров. | Tele2 предоставляется 3 тарифных плана в зависимости от количества сотрудников. Самый дешевый пакет обойдется в 700 рублей за 1 многоканальный номер для 5 сотрудников. |
| Ростелеком | Оказывает услуги СИП-телефонии как для небольших офисов, так и для крупных компаний. Для подключения услуги не требуется дополнительных вложений на покупку оборудования. Можно звонить по всей России, даже в самые отдаленные точки страны. | Тарифный план начинается от 1200 рублей в месяц. В него входит 600 минут для 5 операторов. Для новых абонентов РТ при оформлении заявки по 30.04.2022 действует акция, и стоимость услуги составляет 1 рубль. |
| Билайн | Beeline помогает бизнесу повышать уровень продаж, благодаря многоканальной телефонии. Вдобавок у интернет-провайдера есть функция голосового меню (IVR) для уточнения нюансов или быстрой переадресации на менеджера. | Компания ВымпелКом предоставляет 5 тарифов на любой выбор. Минимальный счет составляет 0 рублей для входящих звонков. |
| Yota | SIP-телефония подходит не только для физических лиц, но и для компаний. Инновационное решение позволяет существенно сократить расходы на связь и улучшить качество ее. | Йота не предоставляет информацию в открытом виде. Узнать стоимость услуги можно напрямую у менеджеров. |
| Белтелеком | Компания предлагает услугу «Максифон» для обработки голосовых вызовов по России, формирования адресной книжки и создания видеозвонков между абонентами провайдера. | Beltelecom предоставляет 3 различных пакета в зависимости от задач клиента. Например, у тарифного плана «Свободный» не списывается абонентская плата. |
| YouMagic | Это сервис IP-телефонии, осуществляющий звонки на фиксированные и мобильные номера в любую точку мира. Кроме того, провайдер предлагает пользователям услуги облачной атс и MFC-телефонии. | Подключение и использование тарифа «Базовый» у Юмеджик составляет 1 рубль за первый месяц. Далее взимается плата в размере 1900 рублей в месяц. |
| Дом.ру | ЭР-Телеком предоставляет услугу голосовой связи по СИП-шлюзу. Такое решение дает возможность оптимизировать расходы на связь и экономить на общении в роуминге. | Стоимость минуты вызова по России составляет 3,6 рубля с учетом НДС. Одинаковая цена как для домашних, так и для мобильных номеров. |
| SIPNET | Платформа позволяет автоматически соединяться с клиентами, мониторить переговоры с абонентами и обеспечивать стабильную связь. | Минимальный пакет услуг у Сипнет начинается от 590 рублей в месяц. Такой тариф подходит тем, кому важно поддерживать качественное общение с клиентами. Для большого потока звонков подойдет тариф «Максимум» от 2390 рублей в месяц. |
| Манго | Популярный инструмент с функцией SIP-телефонии. Многоканальный номер позволяет параллельно вести до 100 разговоров с клиентами. Облачная телефонная станция дает возможность сэкономить средства на дополнительном оборудовании. | Тарификация у MANGO OFFICE начинается от 750 рублей в месяц. В пакет входит: 3 многоканальных номера, распределение вызовов и прием звонков в автоматическом режиме. |
Что такое SIP-телефония в видео
SIP – это актуальный вектор развития, продиктованный потребностями рынка. Как думаете, такая телефони укрепится и будет доминировать над GSM при учете скорости глобальной интернетизации?
Session Initiation Protocol — Introduction
Session Initiation Protocol (SIP) is one of the most common protocols used in VoIP technology. It is an application layer protocol that works in conjunction with other application layer protocols to control multimedia communication sessions over the Internet.
VoIP Technology
Before moving further, let us first understand a few points about VoIP.
-
VOIP is a technology that allows you to deliver voice and multimedia (videos, pictures) content over the Internet. It is one of the cheapest way to communicate anytime, anywhere with the Internet’s availability.
-
Some advantages of VOIP include −
-
Low cost
-
Portability
-
No extra cables
-
Flexibility
-
Video conferencing
-
-
For a VOIP call, all that you need is a computer/laptop/mobile with internet connectivity. The following figure depicts how a VoIP call takes place.
With this much fundamental, let us get back to SIP.
SIP – Overview
Given below are a few points to note about SIP −
-
SIP is a signalling protocol used to create, modify, and terminate a multimedia session over the Internet Protocol. A session is nothing but a simple call between two endpoints. An endpoint can be a smartphone, a laptop, or any device that can receive and send multimedia content over the Internet.
-
SIP is an application layer protocol defined by IETF (Internet Engineering Task Force) standard. It is defined in RFC 3261.
-
SIP embodies client-server architecture and the use of URL and URI from HTTP and a text encoding scheme and a header style from SMTP.
-
SIP takes the help of SDP (Session Description Protocol) which describes a session and RTP (Real Time Transport Protocol) used for delivering voice and video over IP network.
-
SIP can be used for two-party (unicast) or multiparty (multicast) sessions.
-
Other SIP applications include file transfer, instant messaging, video conferencing, online games, and steaming multimedia distribution.
Where Does SIP Fit In?
Basically SIP is an application layer protocol. It is a simple network signalling protocol for creating and terminating sessions with one or more participants. The SIP protocol is designed to be independent of the underlying transport protocol, so SIP applications can run on TCP, UDP, or other lower-layer networking protocols.
The following illustration depicts where SIP fits in in the general scheme of things −
Typically, the SIP protocol is used for internet telephony and multimedia distribution between two or more endpoints. For example, one person can initiate a telephone call to another person using SIP, or someone may create a conference call with many participants.
The SIP protocol was designed to be very simple, with a limited set of commands. It is also text-based, so anyone can read a SIP message passed between the endpoints in a SIP session.
SIP — Network Elements
There are some entities that help SIP in creating its network. In SIP, every network element is identified by a SIP URI (Uniform Resource Identifier) which is like an address. Following are the network elements −
- User Agent
- Proxy Server
- Registrar Server
- Redirect Server
- Location Server
User Agent
It is the endpoint and one of the most important network elements of a SIP network. An endpoint can initiate, modify, or terminate a session. User agents are the most intelligent device or network element of a SIP network. It could be a softphone, a mobile, or a laptop.
User agents are logically divided into two parts −
-
User Agent Client (UAC) − The entity that sends a request and receives a response.
-
User Agent Server (UAS) − The entity that receives a request and sends a response.
SIP is based on client-server architecture where the caller’s phone acts as a client which initiates a call and the callee’s phone acts as a server which responds the call.
Proxy Server
It is the network element that takes a request from a user agent and forwards it to another user.
-
Basically the role of a proxy server is much like a router.
-
It has some intelligence to understand a SIP request and send it ahead with the help of URI.
-
A proxy server sits in between two user agents.
-
There can be a maximum of 70 proxy servers in between a source and a destination.
There are two types of proxy servers −
-
Stateless Proxy Server − It simply forwards the message received. This type of server does not store any information of a call or a transaction.
-
Stateful Proxy Server − This type of proxy server keeps track of every request and response received and can use it in future if required. It can retransmit the request, if there is no response from the other side in time.
Registrar Server
The registrar server accepts registration requests from user agents. It helps users to authenticate themselves within the network. It stores the URI and the location of users in a database to help other SIP servers within the same domain.
Take a look at the following example that shows the process of a SIP Registration.
Here the caller wants to register with the TMC domain. So it sends a REGISTER request to the TMC’s Registrar server and the server returns a 200 OK response as it authorized the client.
Redirect Server
The redirect server receives requests and looks up the intended recipient of the request in the location database created by the registrar.
The redirect server uses the database for getting location information and responds with 3xx (Redirect response) to the user. We will discuss response codes later in this tutorial.
Location Server
The location server provides information about a caller’s possible locations to the redirect and proxy servers.
Only a proxy server or a redirect server can contact a location server.
The following figure depicts the roles played by each of the network elements in establishing a session.
SIP – System Architecture
SIP is structured as a layered protocol, which means its behavior is described in terms of a set of fairly independent processing stages with only a loose coupling between each stage.
-
The lowest layer of SIP is its syntax and encoding. Its encoding is specified using an augmented Backus-Naur Form grammar (BNF).
-
At the second level is the transport layer. It defines how a Client sends requests and receives responses and how a Server receives requests and sends responses over the network. All SIP elements contain a transport layer.
-
Next comes the transaction layer. A transaction is a request sent by a Client transaction (using the transport layer) to a Server transaction, along with all responses to that request sent from the server transaction back to the client. Any task that a user agent client (UAC) accomplishes takes place using a series of transactions. Stateless proxies do not contain a transaction layer.
-
The layer above the transaction layer is called the transaction user. Each of the SIP entities, except the Stateless proxies, is a transaction user.
SIP — Basic Call Flow
The following image shows the basic call flow of a SIP session.
Given below is a step-by-step explanation of the above call flow −
-
An INVITE request that is sent to a proxy server is responsible for initiating a session.
-
The proxy server sendsa 100 Trying response immediately to the caller (Alice) to stop the re-transmissions of the INVITE request.
-
The proxy server searches the address of Bob in the location server. After getting the address, it forwards the INVITE request further.
-
Thereafter, 180 Ringing (Provisional responses) generated by Bob is returned back to Alice.
-
A 200 OK response is generated soon after Bob picks the phone up.
-
Bob receives an ACK from the Alice, once it gets 200 OK.
-
At the same time, the session gets established and RTP packets (conversations) start flowing from both ends.
-
After the conversation, any participant (Alice or Bob) can send a BYE request to terminate the session.
-
BYE reaches directly from Alice to Bob bypassing the proxy server.
-
Finally, Bob sends a 200 OK response to confirm the BYE and the session is terminated.
-
In the above basic call flow, three transactions are (marked as 1, 2, 3) available.
The complete call (from INVITE to 200 OK) is known as a Dialog.
SIP Trapezoid
How does a proxy help to connect one user with another? Let us find out with the help of the following diagram.
The topology shown in the diagram is known as a SIP trapezoid. The process takes place as follows −
-
When a caller initiates a call, an INVITE message is sent to the proxy server. Upon receiving the INVITE, the proxy server attempts to resolve the address of the callee with the help of the DNS server.
-
After getting the next route, caller’s proxy server (Proxy 1, also known as outbound proxy server) forwards the INVITE request to the callee’s proxy server which acts as an inbound proxy server (Proxy 2) for the callee.
-
The inbound proxy server contacts the location server to get information about the callee’s address where the user registered.
-
After getting information from the location server, it forwards the call to its destination.
-
Once the user agents get to know their address, they can bypass the call, i.e., conversations pass directly.
SIP — Messaging
SIP messages are of two types − requests and responses.
-
The opening line of a request contains a method that defines the request, and a Request-URI that defines where the request is to be sent.
-
Similarly, the opening line of a response contains a response code.
Request Methods
SIP requests are the codes used to establish a communication. To complement them, there are SIP responses that generally indicate whether a request succeeded or failed.
These SIP requests which are known as METHODS make SIP message workable.
-
METHODS can be regarded as SIP requests, since they request a specific action to be taken by another user agent or server.
-
METHODS are distinguished into two types −
-
Core Methods
-
Extension Methods
-
Core Methods
There are six core methods as discussed below.
INVITE
INVITE is used to initiate a session with a user agent. In other words, an INVITE method is used to establish a media session between the user agents.
-
INVITE can contain the media information of the caller in the message body.
-
A session is considered established if an INVITE has received a success response(2xx) or an ACK has been sent.
-
A successful INVITE request establishes a dialog between the two user agents which continues until a BYE is sent to terminate the session.
-
An INVITE sent within an established dialog is known as a re-INVITE.
-
Re-INVITE is used to change the session characteristics or refresh the state of a dialog.
INVITE Example
The following code shows how INVITE is used.
INVITE sips:Bob@TMC.com SIP/2.0 Via: SIP/2.0/TLS client.ANC.com:5061;branch = z9hG4bK74bf9 Max-Forwards: 70 From: Alice<sips:Alice@TTP.com>;tag = 1234567 To: Bob<sips:Bob@TMC.com> Call-ID: 12345601@192.168.2.1 CSeq: 1 INVITE Contact: <sips:Alice@client.ANC.com> Allow: INVITE, ACK, CANCEL, OPTIONS, BYE, REFER, NOTIFY Supported: replaces Content-Type: application/sdp Content-Length: ... v = 0 o = Alice 2890844526 2890844526 IN IP4 client.ANC.com s = Session SDP c = IN IP4 client.ANC.com t = 3034423619 0 m = audio 49170 RTP/AVP 0 a = rtpmap:0 PCMU/8000
BYE
BYE is the method used to terminate an established session. This is a SIP request that can be sent by either the caller or the callee to end a session.
-
It cannot be sent by a proxy server.
-
BYE request normally routes end to end, bypassing the proxy server.
-
BYE cannot be sent to a pending an INVITE or an unestablished session.
REGISTER
REGISTER request performs the registration of a user agent. This request is sent by a user agent to a registrar server.
-
The REGISTER request may be forwarded or proxied until it reaches an authoritative registrar of the specified domain.
-
It carries the AOR (Address of Record) in the To header of the user that is being registered.
-
REGISTER request contains the time period (3600sec).
-
One user agent can send a REGISTER request on behalf of another user agent. This is known as third-party registration. Here, the From tag contains the URI of the party submitting the registration on behalf of the party identified in the To header.
CANCEL
CANCEL is used to terminate a session which is not established. User agents use this request to cancel a pending call attempt initiated earlier.
-
It can be sent either by a user agent or a proxy server.
-
CANCEL is a hop by hop request, i.e., it goes through the elements between the user agent and receives the response generated by the next stateful element.
ACK
ACK is used to acknowledge the final responses to an INVITE method. An ACK always goes in the direction of INVITE.ACK may contain SDP body (media characteristics), if it is not available in INVITE.
-
ACK may not be used to modify the media description that has already been sent in the initial INVITE.
-
A stateful proxy receiving an ACK must determine whether or not the ACK should be forwarded downstream to another proxy or user agent.
-
For 2xx responses, ACK is end to end, but for all other final responses, it works on hop by hop basis when stateful proxies are involved.
OPTIONS
OPTIONS method is used to query a user agent or a proxy server about its capabilities and discover its current availability. The response to a request lists the capabilities of the user agent or server. A proxy never generates an OPTIONS request.
Extension Methods
Subscribe
SUBSCRIBE is used by user agents to establish a subscription for the purpose of getting notification about a particular event.
-
It contains an Expires header field that indicates the duration of a subscription.
-
After the time period passes, the subscription will automatically terminate.
-
Subscription establishes a dialog between the user agents.
-
You can re-subscription again by sending another SUBSCRIBE within the dialog before the expiration time.
-
A 200 OK will be received for a subscription from User.
-
Users can unsubscribe by sending another SUBSCRIBE method with Expires value 0(zero).
NOTIFY
NOTIFY is used by user agents to get the occurrence of a particular event. Usually a NOTIFY will trigger within a dialog when a subscription exists between the subscriber and the notifier.
-
Every NOTIFY will get 200 OK response if it is received by notifier.
-
NOTIFY contain an Event header field indicating the event and a subscriptionstate header field indicating the current state of the subscription.
-
A NOTIFY is always sent at the start and termination of a subscription.
PUBLISH
PUBLISH is used by a user agent to send event state information to a server.
-
PUBLISH is mostly useful when there are multiple sources of event information.
-
A PUBLISH request is similar to a NOTIFY, except that it is not sent in a dialog.
-
A PUBLISH request must contain an Expires header field and a Min-Expires header field.
REFER
REFER is used by a user agent to refer another user agent to access a URI for the dialog.
-
REFER must contain a Refer-To header. This is a mandatory header for REFER.
-
REFER can be sent inside or outside a dialog.
-
A 202 Accepted will trigger a REFER request which indicates that other user agent has accepted the reference.
INFO
INFO is used by a user agent to send call signalling information to another user agent with which it has established a media session.
-
This is an end-to-end request.
-
A proxy will always forward an INFO request.
UPDATE
UPDATE is used to modify the state of a session if a session is not established. User could change the codec with UPDATE.
IF a session is established, a re-Invite is used to change/update the session.
PRACK
PRACK is used to acknowledge the receipt of a reliable transfer of provisional response (1XX).
-
Generally PRACK is generated by a client when it receive a provisional response containing an RSeq reliable sequence number and a supported:100rel header.
-
PRACK contains (RSeq + CSeq) value in the rack header.
-
The PRACK method applies to all provisional responses except the 100 Trying response, which is never reliably transported.
-
A PRACK may contain a message body; it may be used for offer/answer exchange.
MESSAGE
It is used to send an instant message using SIP. An IM usually consists of short messages exchanged in real time by participants engaged in text conversation.
-
MESSAGE can be sent within a dialog or outside a dialog.
-
The contents of a MESSAGE are carried in the message body as a MIME attachment.
-
A 200 OK response is normally received to indicate that the message has been delivered at its destination.
SIP — Response Codes
A SIP response is a message generated by a user agent server (UAS) or SIP server to reply a request generated by a client. It could be a formal acknowledgement to prevent retransmission of requests by a UAC.
-
A response may contain some additional header fields of info needed by a UAC.
-
SIP has six responses.
-
1xx to 5xx has been borrowed from HTTP and 6xx is introduced in SIP.
-
1xx is considered as a provisional response and the rest are final responses.
| S.No. | Function & Description |
|---|---|
| 1 | 1xx: Provisional/Informational Responses
Informational responses are used to indicate call progress. Normally the responses are end to end (except 100 Trying). |
| 2 | 2xx: Success Responses
This class of responses is meant for indicating that a request has been accepted. |
| 3 | 3xx: Redirect Responses
Generally these class responses are sent by redirect servers in response to INVITE. They are also known as redirect class responses. |
| 4 | 4xx: Client Failure Responses
Client error responses indicate that the request cannot be fulfilled as some errors are identified from the UAC side. |
| 5 | 5xx: Server Failure Response
This class response is used to indicate that the request cannot be processed because of an error with the server. |
| 6 | 6xx: Global Failure Response
This response class indicates that the server knows that the request will fail wherever it is tried. As a result, the request should not be sent to other locations. |
SIP — Headers
A header is a component of a SIP message that conveys information about the message. It is structured as a sequence of header fields.
SIP header fields in most cases follow the same rules as HTTP header fields. Header fields are defined as Header: field, where Header is used to represent the header field name, and field is the set of tokens that contains the information. Each field consists of a fieldname followed by a colon («:») and the field-value (i.e., field-name: field-value).
SIP Headers — Compact Form
Many common SIP header fields have a compact form where the header field name is denoted by a single lower case character. Some examples are given below −
| Header | Compact Form |
|---|---|
| To | T |
| Via | V |
| Call-ID | I |
| Contact | M |
| From | F |
| Subject | S |
| Content-Length | I |
SIP Header Format
The following image shows the structure of a typical SIP header.
Headers are categorized as follows depending on their usage in SIP −
- Request and Response
- Request Only
- Response Only
- Message Body
SIP — Session Description Protocol
SDP stands for Session Description Protocol. It is used to describe multimedia sessions in a format understood by the participants over a network. Depending on this description, a party decides whether to join a conference or when or how to join a conference.
-
The owner of a conference advertises it over the network by sending multicast messages which contain description of the session e.g. the name of the owner, the name of the session, the coding, the timing etc. Depending on these information, the recipients of the advertisement take a decision about participation in the session.
-
SDP is generally contained in the body part of Session Initiation Protocol popularly called SIP.
-
SDP is defined in RFC 2327. An SDP message is composed of a series of lines, called fields, whose names are abbreviated by a single lower-case letter, and are in a required order to simplify parsing.
Purpose of SDP
The purpose of SDP is to convey information about media streams in multimedia sessions to help participants join or gather info of a particular session.
-
SDP is a short structured textual description.
-
It conveys the name and purpose of the session, the media, protocols, codec formats, timing and transport information.
-
A tentative participant checks these information and decides whether to join a session and how and when to join a session if it decides to do so.
-
The format has entries in the form of <type> = <value>, where the <type> defines a unique session parameter and the <value> provides a specific value for that parameter.
-
The general form of a SDP message is −
x = parameter1 parameter2 … parameterN
-
The line begins with a single lower-case letter, for example, x. There are never any spaces between the letter and the =, and there is exactly one space between each parameter. Each field has a defined number of parameters.
Session Description Parameters
Session description (* denotes optional)
- v = (protocol version)
- o = (owner/creator and session identifier)
- s = (session name)
- i =* (session information)
- u =* (URI of description)
- e =* (email address)
- p =* (phone number)
- c =* (connection information — not required if included in all media)
- b =* (bandwidth information)
- z =* (time zone adjustments)
- k =* (encryption key)
- a =* (zero or more session attribute lines)
Protocol Version
The v= field contains the SDP version number. Because the current version of SDP is 0, a valid SDP message will always begin with v = 0.
Origin
The o= field contains information about the originator of the session and session identifiers. This field is used to uniquely identify the session.
-
The field contains −
o=<username><session-id><version><network-type><address-type>
-
The username parameter contains the originator’s login or host.
-
The session-id parameter is a Network Time Protocol (NTP) timestamp or a random number used to ensure uniqueness.
-
The version is a numeric field that is increased for each change to the session, also recommended to be a NTP timestamp.
-
The network-type is always IN for Internet. The address-type parameter is either IP4 or IP6 for IPv4 or IPv6 address either in dotted decimal form or a fully qualified host name.
Session Name and Information
The s= field contains a name for the session. It can contain any nonzero number of characters. The optional i= field contains information about the session. It can contain any number of characters.
URI
The optional u= field contains a uniform resource indicator (URI) with more information about the session
E-Mail Address and Phone Number
The optional e= field contains an e-mail address of the host of the session. The optional p= field contains a phone number.
Connection Data
The c= field contains information about the media connection.
-
The field contains −
c =<network-type><address-type><connection-address>
-
The network-type parameter is defined as IN for the Internet.
-
The address-type is defined as IP4 for IPv4 addresses and IP6 for IPv6 addresses.
-
The connection-address is the IP address or host that will be sending the media packets, which could be either multicast or unicast.
-
If multicast, the connection-address field contains −
connection-address=base-multicast-address/ttl/number-of-addresses
where ttl is the time-to-live value, and number-of-addresses indicates how many contiguous multicast addresses are included starting with the base-multicast address.
Bandwidth
The optional b= field contains information about the bandwidth required. It is of the form −
b=modifier:bandwidth − value
Time, Repeat Times, and Time Zones
The t= field contains the start time and stop time of the session.
t=start-time stop-time
The optional r= field contains information about the repeat times that can be specified in either in NTP or in days (d), hours (h), or minutes (m).
The optional z= field contains information about the time zone offsets. This field is used if are occurring session spans a change from daylight savings to standard time, or vice versa.
Media Announcements
The optional m= field contains information about the type of media session. The field contains −
m= media port transport format-list
-
The media parameter is either audio, video, text, application, message, image, or control. The port parameter contains the port number.
-
The transport parameter contains the transport protocol or the RTP profile used.
-
The format-list contains more information about the media. Usually, it contains media payload types defined in RTP audio video profiles.
Example: m = audio 49430 RTP/AVP 0 6 8 99
One of these three codecs can be used for the audio media session. If the intention is to establish three audio channels, three separate media fields would be used.
Attributes
The optional a= field contains attributes of the preceding media session. This field can be used to extend SDP to provide more information about the media. If not fully understood by a SDP user, the attribute field can be ignored. There can be one or more attribute fields for each media payload type listed in the media field.
Attributes in SDP can be either
- session level, or
- media level.
Session level means that the attribute is listed before the first media line in the SDP. If this is the case, the attribute applies to all the media lines below it.
Media level means it is listed after a media line. In this case, the attribute only applies to this particular media stream.
SDP can include both session level and media level attributes. If the same attribute appears as both, the media level attribute overrides the session level attribute for that particular media stream. Note that the connection data field can also be either session level or media level.
An SDP Example
Given below is an example session description, taken from RFC 2327 −
v = 0 o = mhandley2890844526 2890842807 IN IP4 126.16.64.4 s = SDP Seminar i = A Seminar on the session description protocol u = http://www.cs.ucl.ac.uk/staff/M.Handley/sdp.03.ps e = mjh@isi.edu(Mark Handley) c = IN IP4 224.2.17.12/127 t = 2873397496 2873404696 a = recvonly m = audio 49170 RTP/AVP 0 m = video 51372 RTP/AVP 31 m = application 32416udp wb a = orient:portrait
SIP — The Offer/Answer Model
The use of SDP with SIP is given in the SDP offer answer RFC 3264. The default message body type in SIP is application/sdp.
-
The calling party lists the media capabilities that they are willing to receive in SDP, usually in either an INVITE or in an ACK.
-
The called party lists their media capabilities in the 200 OK response to the INVITE.
A typical SIP use of SDP includes the following fields: version, origin, subject, time, connection, and one or more media and attribute.
-
The subject and time fields are not used by SIP but are included for compatibility.
-
In the SDP standard, the subject field is a required field and must contain at least one character, suggested to be s=- if there is no subject.
-
The time field is usually set to t = 00. SIP uses the connection, media, and attribute fields to set up sessions between UAs.
-
The origin field has limited use with SIP.
-
The session-id is usually kept constant throughout a SIP session.
-
The version is incremented each time the SDP is changed. If the SDP being sent is unchanged from that sent previously, the version is kept the same.
-
As the type of media session and codec to be used are part of the connection negotiation, SIP can use SDP to specify multiple alternative media types and to selectively accept or decline those media types.
The offer/answer specification, RFC 3264, recommends that an attribute containing a = rtpmap: be used for each media field. A media stream is declined by setting the port number to zero for the corresponding media field in the SDP response.
Example
In the following example, the caller Tesla wants to set up an audio and video call with two possible audio codecs and a video codec in the SDP carried in the initial INVITE −
v = 0 o = John 0844526 2890844526 IN IP4 172.22.1.102 s = - c = IN IP4 172.22.1.102 t = 0 0 m = audio 6000 RTP/AVP 97 98 a = rtpmap:97 AMR/16000/1 a = rtpmap:98 AMR-WB/8000/1 m = video 49172 RTP/AVP 32 a = rtpmap:32 MPV/90000
The codecs are referenced by the RTP/AVP profile numbers 97, 98.
The called party Marry answers the call, chooses the second codec for the first media field, and declines the second media field, only wanting AMR session.
v = 0 o = Marry 2890844526 2890844526 IN IP4 172.22.1.110 s = - c = IN IP4 200.201.202.203 t = 0 0 m = audio 60000 RTP/AVP 8 a = rtpmap:97 AMR/16000 m = video 0 RTP/AVP 32
If this audio-only call is not acceptable, then Tom would send an ACK then a BYE to cancel the call. Otherwise, the audio session would be established and RTP packets exchanged.
As this example illustrates, unless the number and order of media fields is maintained, the calling party would not know for certain which media sessions were being accepted and declined by the called party.
The offer/answer rules are summarized in the following sections.
Rules for Generating an Offer
An SDP offer must include all required SDP fields (this includes v=, o=, s=, c=,and t=). These are mandatory fields in SDP.
It usually includes a media field (m=) but it does not have to. The media lines contain all codecs listed in preference order. The only exception to this is if the endpoint supports a huge number of codecs, the most likely to be accepted or most preferred should be listed. Different media types include audio, video, text, MSRP, BFCP, and so forth.
Rules for Generating an Answer
An SDP answer to an offer must be constructed according to the following rules −
-
The answer must have the same number of m= lines in the same order as the answer.
-
Individual media streams can be declined by setting the port number to 0.
-
Streams are accepted by sending a nonzero port number.
-
The listed payloads for each media type must be a subset of the payloads listed in the offer.
-
For dynamic payloads, the same dynamic payload number does not need to be used in each direction. Usually, only a single payload is selected.
Rules for Modifying a Session
Either party can initiate another offer/answer exchange to modify a session. When a session is modified, the following rules must be followed −
-
The origin (o=) line version number must either be the same as the last one sent, which indicates that this SDP is identical to the previous exchange, or it may be incremented by one, which indicates new SDP that must be parsed.
-
The offer must include all existing media lines and they must be sent in the same order.
-
Additional media streams can be added to the end of the m= line list.
-
An existing media stream can be deleted by setting the port number to 0. This media line must remain in the SDP and all future offer/answer exchanges for this session.
Call Hold
One party in a call can temporarily place the other on hold. This is done by sending an INVITE with an identical SDP to that of the original INVITE but with a = sendonly attribute present.
The call is made active again by sending another INVITE with the a = sendrecv attribute present. The following illustration shows the call flow of a call hold.
SIP — Mobility
Personal mobility is the ability to have a constant identifier across a number of devices. SIP supports basic personal mobility using the REGISTER method, which allows a mobile device to change its IP address and point of connection to the Internet and still be able to receive incoming calls.
SIP can also support service mobility – the ability of a user to keep the same services when mobile
SIP Mobility During Handover(Pre-call)
A device binds its Contact URI with the address of record by a simple sip registration. According to the device IP address, registration authorizes this information automatically update in sip network.
During handover, the User agent routes between different operators, where it has to register again with a Contact as an AOR with another service provider.
For example, let’s take the example of the following call flow. UA which has temporarily received a new SIP URI with a new service provider. The UA then performs a double registration −
-
The first registration is with the new service operator, which binds the Contact URI of the device with the new service provider’s AOR URI.
-
The second REGISTER request is routed back to the original service provider and provides the new service provider’s AOR as the Contact URI.
As shown later in the call flow, when a request comes in to the original service provider’s network, the INVITE is redirected to the new service provider who then routes the call to the user.
For the first registration, the message containing the device URI would be −
REGISTER sip:visited.registrar1.com SIP/2.0 Via: SIP/2.0/UDP 172.22.1.102:5060;branch = z9hG4bK97a7ea349ce0fca Max-Forwards: 70 To: Tom <sip:UA1@registrar1.in> From: Tom <sip:UA1@registrar1.in>;tag = 72d65a24 Call-ID: 4e719d1c1fc9000803630373300@172.22.1.102 CSeq: 1 REGISTER Contact: <sip:Tom@172.22.1.102:5060> Expires: 600000 Content-Length: 0
The second registration message with the roaming URI would be −
REGISTER sip:home.registrar2.in SIP/2.0 Via: SIP/2.0/UDP 172.22.1.102:5060;branch = z9hG4bKah4vn2u Max-Forwards: 70 To: Tom <sip:UA1@registrar2.in> From: Tom <sip:UA1@registrar2.in>;tag = 45375 Call-ID:87nr43i@172.22.1.102 CSeq: 6421 REGISTER Contact: <sip:UA1@registrar2.in> Content-Length: 0
The first INVITE that is represents in the above figure would be sent to sip:registrar2.in; the second INVITE would be sent to sip: sip:Tom@registrar2.in, which would be forwarded to sip:Tom@172.22.1.102. It reaches Tom and allows the session to be established. Periodically both registrations would need to be refreshed.
Mobility During a Call(re-Invite)
User Agent may change its IP address during the session as it swaps from one network to another. Basic SIP supports this scenario, as a re-INVITE in a dialog can be used to update the Contact URI and change the media information in the SDP.
Take a look at the call flow mentioned in the figure below.
-
Here, Tom detects a new network,
-
Uses DHCP to acquire a new IP address, and
-
Performs a re-INVITE to allow the signalling and media flow to the new IP address.
If the UA can receive media from both networks, the interruption is negligible. If this is not the case, a few media packets may be lost, resulting in a slight interruption to the call.
The re-INVITE would appear as follows −
INVITE sip:Jerry@TTP.com SIP/2.0 Via: SIP/2.0/UDP 172.22.1.102:5060;branch = z9hG4bK918f5a84fe6bf7a Max-Forwards: 70 To: <sip:Harry@TTP.com> From: sip:Tom@PPT.com;tag = 70133df4 Call-ID: 76d4861c19c CSeq: 1 INVITE Accept: application/sdp Accept-Language: en Allow: INVITE,ACK,CANCEL,BYE,INFO,OPTIONS,REFER,NOTIFY,SUBSCRIBE Contact: <sip:172.22.1.102:5060>; Content-Type: application/sdp Content-Length: 168 v = 0 o = PPT 40467 40468 IN IP4 192.168.2.1 s = - c = IN IP4 192.168.2.1 b = AS:49 t = 0 0 b = RR:0 b = RS:0 a = rtpmap:97 AMR/8000/1 m = audio 6000 RTP/AVP 96 a = fmtp:102 0-15 a = ptime:20 a = maxptime:240
The re-INVITE contains Bowditch’s new IP address in the Via and Contact header fields and SDP media information.
Mobility in Midcall(With replace Header)
In midcall mobility, the actual route set (set of SIP proxies that the SIP messages must traverse) must change. We cannot use a re-INVITE in midcall mobility
For example, if a proxy is necessary for NAT traversal, then Contact URI must be changed — a new dialog must be created. Hence, it has to send a new INVITE with a Replaces header, which identifies the existing session.
Note − Suppose A & B both are in a call and if A gets another INVITE (let’s say from C) with a replace header (should match existing dialog), then A must accept the INVITE and terminate the session with B and transfer all resource to newly formed dialog.
The call flow is shown in the following Figure. It is similar to the previous call flow using re-INVITE except that a BYE is automatically generated to terminate the existing dialog when the INVITE with the Replaces is accepted.
Given below are the points to note in this scenario −
-
The existing dialog between Tom and Jerry includes the old visited proxy server.
-
The new dialog using the new wireless network requires the inclusion of the new visited proxy server.
-
As a result, an INVITE with Replaces is sent by Tom, which creates a new dialog that includes the new visited proxy server but not the old visited proxy server.
-
When Jerry accepts the INVITE, a BYE is automatically sent to terminate the old dialog that routes through the old visited proxy server that is now no longer involved in the session.
-
The resulting media session is established using Tom’s new IP address from the SDP in the INVITE.
Service Mobility
Services in SIP can be provided in either proxies or in UAs. Providing service mobility along with personal mobility can be challenging unless the user’s devices are identically configured with the same services.
SIP can easily support service mobility over the Internet. When connected to Internet, a UA configured to use a set of proxies in India can still use those proxies when roaming in Europe. It does not have any impact on the quality of the media session as the media always flows directly between the two UAs and does not traverse the SIP proxy servers.
Endpoint resident services are available only when the endpoint is connected to the Internet. A terminating service such as a call forwarding service implemented in an endpoint will fail if the endpoint has temporarily lost its Internet connection. Hence some services are implemented in the network using SIP proxy servers.
SIP — Forking
Sometime a proxy server forwards a single SIP call to multiple SIP endpoints. This process is known as forking. Here a single call can ring many endpoints at the same time.
With SIP forking, you can have your desk phone ring at the same time as your softphone or a SIP phone on your mobile, allowing you to take the call from either device easily.
Generally, in an office, suppose boss unable to pick the call or away, SIP forking allow the secretary to answer calls his extension.
Forking will be possible if there is a stateful proxy available as it needs to perform and response out of the many it receives.
We have two types of forking −
- Parallel Forking
- Sequential Forking
Parallel Forking
In this scenario, the proxy server will fork the INVITE to, say, two devices (UA2, UA3) at a time. Both the devices will generate 180 Ringing and whoever receives the call will generate a 200 OK. The response (suppose UA2) that reaches the Originator first will establish a session with UA2. For the other response, a CANCEL will be triggered.
If the originator receives both the responses simultaneously, then based on q-value, it will forward the response.
Sequential Forking
In this scenario, the proxy server will fork the INVITE to one device (UA2). If UA2 is unavailable or busy at that time, then the proxy will fork it to another device (UA3).
Branch — ID and Tag
Branch IDs help proxies to match responses to forked requests. Without Branch IDs, a proxy server would not be able to understand the forked response. Branch-id will be available in Via header.
Tags are used by the UAC to distinguish multiple final responses from different UAS. A UAS cannot resolve whether the request has been forked or not. Therefore, it need to add a tag.
Proxies also can add tags if it generates a final response, they never insert tags into requests or responses they forward.
It may be possible that a single request can be forked by multiple proxy servers also. So the proxy which would fork shall add its own unique IDs to the branches it created.
Call leg and Call ID
A call leg refers to one to one signalling relationship between two user agents. The call ID is a unique identifier carried in SIP message that refers to the call. A call is a collection of call legs.
A UAC starts by sending an INVITE. Due to forking, it may receive multiple 200 OK from different UAs. Each corresponds to a different call leg within the same call.
A call is thus a group of call legs. A call leg refers to end-to-end connection between UAs.
The CSeq spaces in the two directions of a call leg are independent. Within a single direction, the sequence number is incremented for each transaction.
Voicemail
Voicemail is very common now-a-days for enterprise users. It’s a telephone application. It comes to picture when the called party is unavailable or unable to receive the call, the PBX will announce to calling party to leave a voice message.
User agent will either get a 3xx response or redirect to voicemail server if the called party’s number is unreachable. However, some kind of SIP extension is needed to indicate to the voicemail system which mailbox to use—that is, which greeting to play and where to store the recorded message. There are two ways to achieve this −
-
By using a SIP header field extension
-
By using the Request-URI to signal this information
Suppose for the user sip:Tom@tutorialspoint.com has a voicemail system at sip:voicemail.tutorialspoint.com which is providing voicemail, the Request-URI of the INVITE when it is forwarded to the voicemail server could look like −
sip:voicemail.tutorialspoint.com;target = sip:Tom@tutorialspoint.com;cause = 486
The following illustration shows how the Request-URI carries the mailbox identifier and the reason (here 486).
SIP — Proxies and Routing
As we know, a proxy server can be either stateless or stateful. Here, in this chapter, we will discuss more on proxy servers and SIP routing.
Stateless Proxy Server
A stateless proxy server simply forwards the message it receives. This kind of server does not store any information of the call or transaction.
- Stateless proxies forget about the SIP request once it has been forwarded.
- Transaction will be fast via stateless proxies.
Stateful Proxy Server
A stateful proxy server keeps track of every request and response that it receives. It can use the stored information in future, if required. It can retransmit the request if it does not receive a response from the other side.
-
Stateful proxies remember the request after it has been forwarded, so they can use it for advance routing. Stateful proxies maintain transaction state. Transaction implies transaction state, not call state.
-
Transaction is not as fast with stateful proxies as stateless.
-
Stateful proxies can fork and retransmit if required.(e.g.: call forward busy, for example).
Via and Record-route
Record-Route
The Record-Route header is inserted into requests by proxies that wanted to be in the path of subsequent requests for the same call-id. It is then used by the user agent to route subsequent requests.
Via
Via headers are inserted by servers into requests to detect loops and to help responses to find their way back to the client. This is helpful for only responses to reach their destination.
-
A UA himself generate and add its own address in a Via header field while sending request.
-
A proxy forwarding the request adds a Via header field containing its own address to the top of the list of Via header fields.
-
A proxy or UA generating a response to a request copies all the Via header fields from the request in order into the response, then sends the response to the address specified in the top Via header field.
-
A proxy receiving a response checks the top Via header field and matches its own address. If it does not match, the response has been discarded.
-
The top Via header field is then removed, and the response forwarded to the address specified in the next Via header field.
Via header fields contain protocolname, versionnumber, and transport (SIP/2.0/UDP, SIP/2.0/TCP, etc.) and contain portnumbers and parameters such as received, rport, branch.
-
A received tag is added to a Via header field if a UA or proxy receives the request from a different address than that specified in the top Via header field.
-
A branch parameter is added to Via header fields by UAs and proxies, which is computed as a hash function of the Request-URI, and the To, From, Call-ID, and CSeq number.
SIP to PSTN
SIP (Softphone) and PSTN (Old telephone) both are different networks and speaks different languages. So we need a translator (Gateway here) to communicate between these two networks.
Let us take an example to show how a SIP phone places a telephone call to a PSTN through PSTN gateway.
In this example, Tom (sip:tom@tutorialspoint.com) is a sip phone and Jerry uses a global telephone number +91401234567.
SIP to PSTN through Gateways
The following illustration shows a call flow from SIP to PSTN through gateways.
Given below is a step-by-step explanation of all the process that takes place while placing a call from a SIP phone to PSTN.
-
First of all, (Tom)SIP phone dials the global number +91401234567 to reach Jerry. SIP user agent understands it as a global number and converts it into request-uri using DNS and trigger the request.
-
The SIP phone sends the INVITE directly to gateway.
-
The gateway initiates the call into the PSTN by selecting an SS7 ISUP trunk to the next telephone switch in the PSTN.
-
The dialled digits from the INVITE are mapped into the ISUP IAM. The ISUP address complete message (ACM) is sent back by the PSTN to indicate that the trunk has been created.
-
The telephone generates ringtone and it goes to telephone switch. The gateway maps the ACM to the 183 Session Progress response containing an SDP indicating the RTP port that the gateway will use to bridge the audio from the PSTN.
-
Upon reception of the 183, the caller’s UAC begins receiving the RTP packets sent from the gateway and presents the audio to the caller so they know that the callee progressing in the PSTN.
-
The call completes when the called party answers the telephone, which causes the telephone switch to send an answer message (ANM) to the gateway.
-
The gateway then cuts the PSTN audio connection through in both directions and sends a 200 OK response to the caller. As the RTP media path is already established, the gateway replies the SDP in the 183 but causes no changes to the RTP connection.
-
The UAC sends an ACK to complete the SIP signalling exchange. As there is no equivalent message in ISUP, the gateway absorbs the ACK.
-
The caller sends BYE to gateway to terminates. The gateway maps the BYE into the ISUP release message (REL).
-
The gateway sends the 200OK to the BYE and receives an RLC from the PSTN.
SIP — Codecs
A codec, short for coder-decoder, does two basic operations −
-
First, it converts an analog voice signal to its equivalent digital form so that it can be easily transmitted.
-
Thereafter, it converts the compressed digital signal back to its original analog form so that it can be replayed.
There are many codecs available in the market – some are free while others require licensing. Codecs vary in the sound quality and vary in bandwidth accordingly.
Hardware devices such as phones and gateways support several different codecs. While talking to each other, they negotiate which codec they will use.
Here, in this chapter, we will discuss a few popular SIP audio codecs that are widely used.
G.711
G.711 is a codec that was introduced by ITU in 1972 for use in digital telephony. The codec has two variants: A-Law is being used in Europe and in international telephone links, uLaw is used in the U.S.A. and Japan.
-
G.711 uses a logarithmic compression. It squeezes each 16-bit sample to 8 bits, thus it achieves a compression ratio of 1:2.
-
The bitrate is 64 kbit/s for one direction, so a call consumes 128 kbit/s.
-
G.711 is the same codec used by the PSTN network, hence it provides the best voice quality. However it consumes more bandwidth than other codecs.
-
It works best in local area networks where we have a lot of bandwidth available.
G.729
G.729 is a codec with low bandwidth requirements; it provides good audio quality.
-
The codec encodes audio in frames of 10 ms long. Given a sampling frequency of 8 kHz, a 10 ms frame contains 80 audio samples.
-
The codec algorithm encodes each frame into 10 bytes, so the resulting bitrate is 8 kbit/s in one direction.
-
G.729 is a licensed codec. End-users who want to use this codec should buy a hardware that implements it (be it a VoIP phone or gateway).
-
A frequently used variant of G.729 is G.729a. It is wire-compatible with the original codec but has lower CPU requirements.
G.723.1
G.723.1 is the result of a competition that ITU announced with the aim to design a codec that would allow calls over 28.8 and 33 kbit/s modem links.
-
We have two variants of G.723.1. They both operate on audio frames of 30 ms (i.e. 240 samples), but the algorithms differ.
-
The bitrate of the first variant is 6.4 kbit/s, while for the second variant, it is 5.3 kbit/s.
-
The encoded frames for the two variants are 24 and 20 bytes long, respectively.
GSM 06.10
GSM 06.10 is a codec designed for GSM mobile networks. It is also known as GSM Full Rate.
-
This variant of the GSM codec can be freely used, so you will often find it in open source VoIP applications.
-
The codec operates on audio frames 20 ms long (i.e. 160 samples) and it compresses each frame to 33 bytes, so the resulting bitrate is 13 kbit/.
SIP — B2BUA
A back-to-back user agent (B2BUA) is a logical network element in SIP applications. It is a type of SIP UA that receives a SIP request, then reformulates the request, and sends it out as a new request.
Unlike a proxy server, it maintains dialog state and must participate in all requests sent on the dialogs it has established. A B2BUA breaks the end-to-end nature of SIP.
B2BUA – How it Works?
A B2BUA agent operates between two endpoints of a phone call and divides the communication channel into two call legs. B2BUA is a concatenation of UAC and UAS. It participates in all SIP signalling between both ends of the call, it has established. As B2BUA available in a dialog service provider may implement some value-added features.
In the originating call leg, the B2BUA acts as a user agent server (UAS) and processes the request as a user agent client (UAC) to the destination end, handling the signalling between end points back-to-back.
A B2BUA maintains the complete state for the calls it handles. Each side of a B2BUA operates as a standard SIP network element as specified in RFC 3261.
Functions of B2BUA
A B2BUA provides the following functions −
-
Call management (billing, automatic call disconnection, call transfer, etc.)
-
Network interworking (perhaps with protocol adaptation)
-
Hiding of network internals (private addresses, network topology, etc.)
Often, B2BUAs are also implemented in media gateways to bridge the media streams for full control over the session.
Example of B2BUA
Many private branch exchange (PBX) enterprise telephone systems incorporate B2BUA logic.
Some firewalls have built in with ALG (Application Layer Gateway) functionality, which allows a firewall to authorize SIP and media traffic while still maintaining a high level of security.
Another common type of B2BUA is known as a Session Border Controller (SBC).
Наверняка, каждый знает о таком понятии, как IP, но слыша термин «SIP телефония» многие спрашивают, что это такое и зачем оно нужно.
А на самом деле это очень современный способ обмена голосовыми сообщениями, который позволяет общаться с помощью обычных компьютеров и специальных аппаратов.
Данный тип связи имеет множество преимуществ, которые касаются безопасности и удобства использования. Но обо всем лучше говорить по порядку. Этим и займемся.
Cодержание:
Общие понятия
Итак, рассматриваемая нами аббревиатура расшифровывается как «Session Initiation Protocol», что переводится «Протокол Установления Сеанса».
Если говорить просто, этот протокол отвечает за установление соединения между двумя или более пользователями.
То есть он поддерживает соединение, обеспечивает его безопасность (защищает от несанкционированного доступа – прослушки) и завершает его.
Протокол используется в конференциях, мгновенных сообщениях, онлайн-играх и, конечно же, в телефонии.
Чтобы понять, что такое SIP телефония, стоит начать с такого понятия, как IP, которое расшифровывается как «Internet Protocol» («Межсетевой протокол»).
Он отвечает за обмен данных в принципе. Чтобы передавать голос, существует разновидность IP, которая называется VoIP.
Это расшифровывается как «Voice Internet Protocol», то есть «Голос через межсетевой протокол».
Если сообщения не тестовые, а голосовые, то они передаются именно через VoIP. При этом такие голосовые сообщения могут передаваться через обычный телефон или же через компьютер, к которому подключены устройства для записи, передачи и приема голоса, то есть микрофон и наушники. Если они передаются через интернет, а не через традиционные телефонные связи, речь идет о VoIP.
Рис. 1. Разговор двух людей по телефону
Все понятно?
Если у вас остаются вопросы, смело задавайте их в комментариях ниже. Теперь перейдем непосредственно к тому, каким образом здесь замешан Session Initiation Protocol.
Все дело в том, что SIP, являясь разновидностью протокола IР, служит как раз для передачи данных, то есть голосовых сообщений в телефонии.
Существуют и другие протоколы, но рассматриваемый нами является одним из наиболее распространенных. Собственно, поэтому мы о нем говорим. Рассмотрим его более подробно.
к содержанию ↑
Алгоритм работы
Звонок, то есть обмен голосовыми сообщениями, проводится следующим образом:
1Сначала сообщение первого абонента записывается и сжимается. Делается это при помощи набора специальных кодеков, то есть небольших программ, выполняющих мелкие функции. Чаще всего они являются незаметными для пользователя. Благодаря сжатию нагрузка на Интернет-соединение значительно снижается. При этом качество голоса всегда остается достаточно высоким.
2Также кодеки преобразовывают сигнал из аналогового в цифровой.
3Сигнал передается на устройство, на котором работает второй абонент.
4Когда этот сигнал попадает на второе устройство, оно соединяется с первым именно при помощи рассматриваемого нами протокола. Первое, что он делает, так это позволяет найти обоим устройствам друг друга. Для этого они используют адреса IP друг друга.
5После установки соединения сигнал преобразовывается из цифрового в аналоговый, и второй абонент слышит своего собеседника в телефонной трубке или наушниках.
Если более детально, сначала голос первого абонента (который говорит) попадает в SIP-оператор, потом через интернет передается на такой же оператор второго абонента и через тот же интернет передается на устройство.
Если это обычный телефон, то дополнительно используется специальный шлюз, если компьютер или ноутбук, то гарнитура. Это показано на рисунке 2.
Там в качестве первого абонента выступает клиент, а в качестве второго – компания, в которую он обращается.
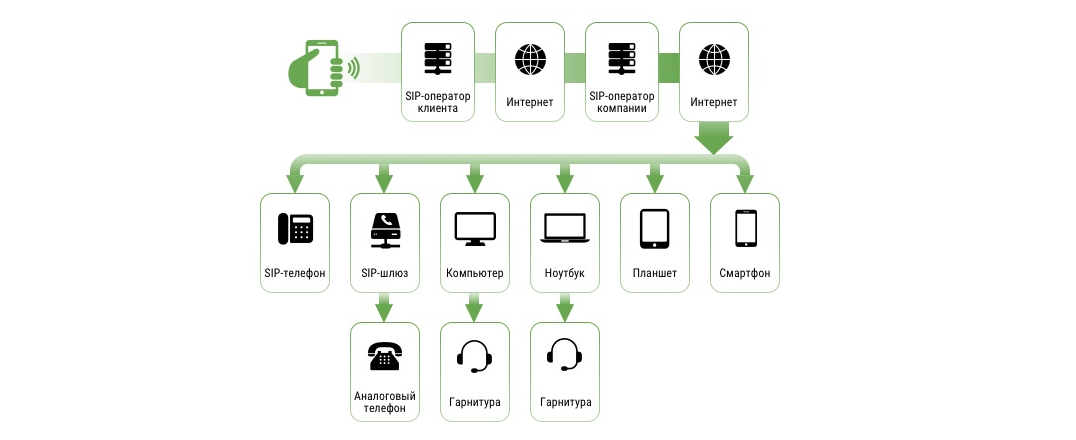
Рис. 2. Наглядное представление работы рассматриваемой технологии
Теперь рассмотрим более подробно то, с помощью чего, то есть каких устройств, можно использовать данную технологию.
к содержанию ↑
Как осуществляются звонки
В телефонии звонить можно при помощи таких устройств:
- специальный SIP-телефон;
- обычный аналоговый телефон с SIP-шлюзом;
- ПК или ноутбук с установленной специальной программой;
- планшет или смартфон с установленной специальной программой.
Он выглядит точно так же, как и обычный стационарный аппарат, который еще до недавних пор можно было увидеть в каждом доме.
Только на нем написано, что это устройство, которое использует Session Initiation Protocol.
Рис. 3. SIP-телефон Yealink SIP-T57V
Наиболее простой вариант использования рассматриваемой технологии состоит в том, чтобы скачать на компьютер соответствующее программное обеспечение и воспользоваться наушниками с гарнитурой.
Поэтому есть смысл рассмотреть несколько очень популярных и удобных программ для использования такой телефонии.
к содержанию ↑
Программы для работы с телефонией
Ниже приведен список ПО, которое является наиболее востребованным на сегодняшний день.
Blink
Как видно на рисунке 4, эта программа очень похожа на старую-добрую Аську, она же ICQ.
Здесь вверху есть строка поиска, благодаря которой можно найти собеседника по его номеру в программе или IP-адресу. Чтобы позвонить, нужно просто нажать на нужный контакт.
Во время разговора можно поставить беседу на паузу, записать на диктофон или положить трубку.
Для этого есть соответствующие кнопки небольшого размера. Одновременно можно общаться с несколькими людьми.
Рис. 4. Blink
Стоит сказать, что у данного ПО есть платная версия. Она более функциональна, чем бесплатная.
MicroSIP
Это очень легкий для оперативной памяти телефонный клиент, который также легок в использовании.
Кроме обмена голосовыми сообщениями, можно также отправлять своим контактам текстовые послания. В главном окне находится циферблат, который позволяет набрать номер нужного собеседника.
Также есть вкладка «Contаcts», которая позволяет увидеть список контактов, и «Calls» — список звонков, то есть история.
Рис. 5. MicroSIP
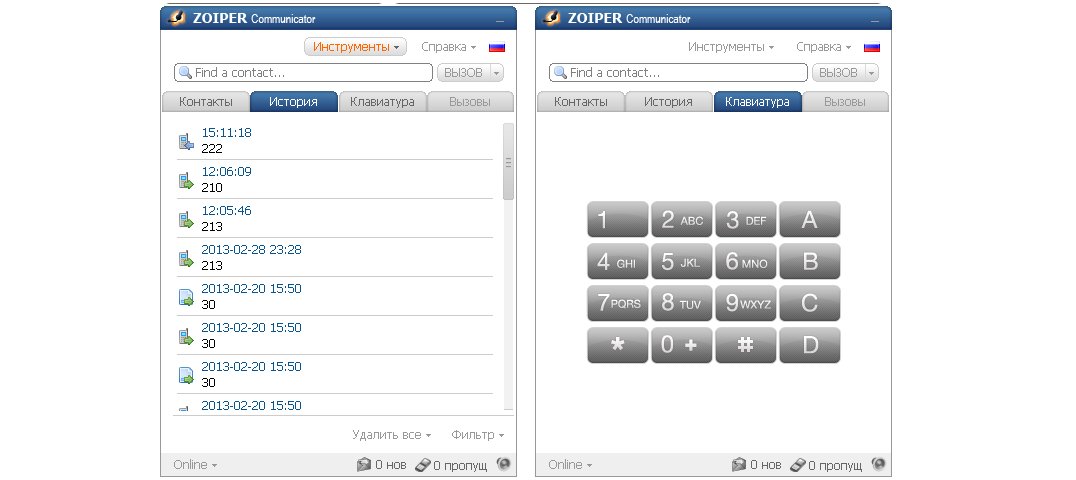
Zoiper
Zoiper отличает то, что у этой программы есть множество версий для различных операционных систем. Это ПО на русском языке, что весьма приятно.
На главной странице есть вкладки «Контакты», «История», «Клавиатура» и «Вызовы».
Любому пользователю будет понятно, что это за вкладки и что он увидит при переходе на них. Вверху есть строка поиска. Все сделано просто и очень удобно.
Рис. 6. Zoiper
У Zoiper есть платная и бесплатная версии. Вторая является ознакомительной и не дает возможности сделать звонок.
Это лишь некоторые программы, которые обеспечивают связь между абонентами при помощи протокола Session Initiation Protocol.
Но и приведенные выше три образца ПО могут дать представление о том, как используется. Теперь поговорим о преимуществах использования такой технологии.
к содержанию ↑
Как обеспечивается безопасность
Одной из главных положительных сторон СИП является безопасность. Она обеспечивает полноценную защиту от прослушки любого типа.
Это означает, что никто не сможет получить доступ к вашим разговорам и слушать их без вашего разрешения.
Примечательно, что осуществить несанкционированный доступ к обычным аналоговым телефонам достаточно легко.
Для этого даже не нужно иметь какие-то особые знания в данной области. Но этим так просто не получится.
Безопасность обеспечивается сразу тремя стандартами и протоколами:
- SRTP используется для шифрования любого вида мультимедиа.
- SIPS накладывает дополнительные соглашения на передачу данных.
- В RFC 3261 существует целый раздел, в котором говорится об обеспечении безопасности в рассматриваемой нами технологии. В частности, там говорится, что TLS шифрует сигнальный трафикповерх TCP/UDP.
Возможно, все это вам ни о чем не говорит, но поверьте, такой уровень безопасности можно встретить достаточно редко.
А теперь перейдем к другим преимуществам.
к содержанию ↑
Преимущества
Вот список положительных сторон использования SIP телефонии:
1Невысокая стоимость. Даже если покупать лицензию на программы, упомянутые выше или другие, подобные им, это будет стоить намного меньше, чем если использовать полноценную автоматическую телефонную станцию. При этом СИП является прекрасной альтернативой АТС в плане качества связи и других особенностей.
2Для обеспечения разговоров необходимо иметь только компьютер и наушники с гарнитурой. Опять же, если говорить об АТС, то понадобится намного больше устройств. Чтобы все их синхронизировать между собой, понадобится очень много времени и сил. Для компаний это весьма существенный фактор.
3В обычной телефонной линии вы будете платить разную цену за разговоры с разными людьми. Все будет зависеть от того, где находится абонент, и какое устройство он использует для разговоров. В случае с SIP цена всегда фиксированная и она не меняется через время.
4Возможность синхронизации и интеграции в систему 1С и другие аналитические программы. В компаниях обычно используется достаточно много такого ПО и возможность интеграции в них также будет огромным плюсом.
5С помощью данной технологии можно организовать колл-центр, сотрудники которого будут находиться в разных уголках мира. Это означает, что вам не нужно будет иметь огромный офис или арендовать большие помещения, где будут размещаться все сотрудники.
6При этом кроме самих звонков, можно использовать также автоответчик, кнопку связи для сайтов, голосовую почту, голосовое меню и много чего еще. Все это также очень удобно.
Качество связи здесь тоже очень высокое.
Фактически, у СИП телефонии нет существенных недостатков, поэтому руководителям компаний обязательно стоит обратить внимание на возможность использования этой технологии в бизнесе.
SIP (англ.: Session Initiation Protocol – протокол инициации сеанса) – дополняет VoIP, поскольку предоставляет функции безопасного подключения. Помимо VoIP, используется в других мультимедийных технологиях: онлайн-игры, видео. Был разработан вместе с протоколом – H.323, который использовался с VoIP до SIP.
Session Initiation Protocol работает с сеансами связи, которые представляют собой периоды времени, в течение которых стороны общаются. К ним относятся телефонные звонки через Интернет, мультимедийные конференции, рассылка и т. д.
SIP обеспечивает необходимое подключение для создания, изменения и завершения сеансов с одним или несколькими общающимися участниками. Осуществляет безопасную передачу данных, отправляя небольшие сообщения, состоящие из заголовка и тела.
Содержание страницы
- 1 Функции SIP
- 1.1 Структура сообщения SIP
- 1.2 Зачем использовать SIP?
- 1.3 Как работает SIP
- 1.4 Что требуется?
- 1.5 Зачем нужна учетная запись SIP?
- 1.6 Структура SIP-адреса
- 1.7 Как использовать SIP-адрес
- 2 SIP-клиен
- 2.1 OnSIP
- 2.1.1 Преимущества
- 2.1.2 Недостатки
- 2.2 IPtel
- 2.2.1 Преимущества
- 2.2.2 Недостатки
- 2.3 SIP2SIP
- 2.3.1 Достоинства
- 2.3.2 Недостатки
- 2.4 AntiSIP
- 2.4.1 Достоинства
- 2.4.2 Недостатки
- 2.1 OnSIP
- 3 Как получить SIP-аккаунт
- 3.1 Проверьте свою электронную почту
Функции SIP
SIP – это протокол безопасного подключения для VoIP и телефонии в целом, благодаря следующим функциям:
Перевод имени и местоположение пользователя: SIP преобразует адрес в имя и, таким образом, достигает вызываемого абонента в любом месте.
Согласование функций: не все взаимодействующие стороны (которых может быть более двух) имеют необходимые функции. Например, не у всех может быть поддержка видео. SIP позволяет группе согласовывать функции.
Управление участниками вызова: SIP позволяет участнику устанавливать или отменять подключения к другим пользователям во время вызова. Пользователи также могут быть переведены в режим ожидания.
Изменения в функции вызова: SIP позволяет пользователю изменять характеристики вызова. Например, как пользователь, вы можете захотеть отключить видео, особенно когда новый участник присоединяется к сеансу.
Согласование мультимедиа: этот механизм обеспечивает возможность выбора соответствующего кодека для установления вызова между различными устройствами.
Структура сообщения SIP
SIP работает, когда передающие устройства отправляют и получают сообщения. Сообщение SIP несет много информации, которая помогает идентифицировать сеанс, контролировать время и описывать мультимедиа. Ниже приведен список содержания сообщения:
- Информация о протоколе (например, версия)
- Информация о сеансе (создатель, имя и т. д.)
- Информация об участнике (электронная почта, телефон и т. д.)
- Информация о пропускной способности
- Информация о шифровании
- Описание времени (активное время и время повтора)
- Описание медиа (название, адрес и т. д.)
- Информация о пропускной способности медиа
- Медиа ключ шифрования
Зачем использовать SIP?
SIP позволяет людям во всем мире общаться с помощью компьютеров и мобильных устройств через Интернет. Это важная часть интернет-телефонии, позволяющая использовать преимущества VoIP (передача голоса по IP).
Самое интересное преимущество, которое мы получаем от SIP, – это сокращение расходов на связь. Звонки (голосовые или видео) между пользователями SIP бесплатны по всему миру. Даже SIP -приложение и SIP – адрес предоставляются бесплатно.
SIP как протокол также очень мощный и эффективный во многих отношениях. Многие организации используют SIP для внутренней и внешней связи, сосредоточенной вокруг АТС.
Как работает SIP
Вы получаете SIP-адрес, устанавливаете SIP-клиент на вашем компьютере, мобильном устройстве. Затем нужно настроить свой SIP-клиент. Есть множество технических функций и опций. Просто подготовьте свои учетные данные и заполните все необходимые поля. Настройка занимает 1-2 минуты.
Что требуется?
Если хотите общаться посредством SIP, вам необходимо:
- SIP-адрес / учетная запись. Предоставляется бесплатно многими поставщиками (список ниже).
- SIP-клиент. Это программа, которую вы устанавливаете на свой компьютер или мобильное устройство. Он содержит функции софтфона и предоставляет интерфейс для общения. Существуют разные типы клиентов SIP. Среди наиболее распространенных – приложения, предлагаемые поставщиками услуг VoIP.
Некоторые из них поддерживают SIP. Но у вас есть клиенты, которые созданы для SIP и не зависят от какой-либо услуги. Вы можете использовать их с любой учетной записью SIP и даже использовать их в среде УАТС. - Интернет соединение. С достаточной пропускной способностью для голосовой и видео связи. Для голосовой связи не требуется много, особенно если вы используете расширенные кодеки.
- Динамик и микрофон. Гарнитура, наушники, микрофон и веб-камера для видеосвязи.
- Друзья, с которыми можно поговорить. Друзьям также нужно использовать SIP, если вы хотите, чтобы звонки были бесплатными. Делитесь SIP-адресами точно так же, как телефонными.
Протокол инициации сеанса обезопасит звонки через Интернет и другие IP- сети. SIP-адрес – это уникальный идентификатор для каждого пользователя в сети. Как и номер телефона, он идентифицирует каждого пользователя в глобальной телефонной сети. Он также известен как унифицированный идентификатор ресурса.
Вы получаете SIP-адрес, когда регистрируетесь для учетной записи. Действует как дескриптор связи, который люди используют для связи с вами. SIP-адреса могут быть преобразованы в телефонные номера, которые легче отследить в качестве идентификаторов контактов.
Экономия, достижимая с помощью учетной записи SIP, составляет 40 процентов для внутренних звонков и 90 процентов для международных звонков.
Зачем нужна учетная запись SIP?
Вы используете учетную запись SIP для настройки настольных телефонов VoIP, программных телефонов и мобильных клиентов VoIP. Учетная запись SIP открывает двери для бесплатных видеозвонков и голосовых вызовов HD на многих платформах, включая компьютеры под управлением Windows и Mac, а также мобильные устройства iOS и Android. SIP-to-SIP звонки между любыми двумя SIP-адресами через Интернет почти всегда бесплатны.
Для компаний, которые имеют много международных контактов, SIP предлагает огромную экономию. Поскольку это услуга VoIP с меньшим количеством закупок оборудования и низкими затратами на техническое обслуживание.
Хотя это может показаться странным, SIP-вызов удобен только после короткого сеанса обучения. В большинстве случаев качество звука лучше, чем при использовании проводного телефона.
Малые предприятия и стартапы используют учетные записи SIP, чтобы избежать первоначальных покупок и установки оборудования, необходимых для проводных телефонных линий.
Структура SIP-адреса
SIP-адрес напоминает адрес электронной почты. Структура которого:
Например, это SIP-адрес, полученный при регистрации в Ekiga:
- sip:host-adm@virtual-sim.ru
- В этом примере sip обозначает протокол и не изменяется. Он запускает каждый SIP-адрес. Некоторые SIP-адреса передаются без sip-части, так как это понимается как формат.
Имя пользователя – это та часть, которую вы выбираете при регистрации на SIP-адресе. Это может быть строка из цифр или букв. В этом примере пользовательской частью является host-adm . В других адресах это может быть номер телефона (который используется для систем УАТС ) или любая другая комбинация букв и цифр. - Знак @ является обязательным между пользователем и доменом, как и в случае с адресом электронной почты.
- Доменное имя службы, с которой вы регистрируетесь, отображается сразу после @. Это может быть полностью определенный домен или просто IP-адрес. В этом примере доменом является virtual-sim.ru. Другими примерами являются sip.mydomain.com и 154.18.10.203 . Пользователь не может изменять доменное имя.
- Порт не является обязательным и в большинстве случаев отсутствует в SIP-адресах. Во многих случаях нет технических причин для явного присутствия порта. Если появляется порт, он обеспечивает доступа с помощью прокси-сервера.
Примеры SIP-адресов:
- sip: 500@virtual-sim.ru
- sip: 236236@001.virtual-sim.ru
- sip:12345@144.18.10.203:4060
SIP-адрес отличается от номера телефона и адреса электронной почты тем, что он привязан к пользователю, а не к поставщику услуг, провайдеру или оператору.
Как использовать SIP-адрес
Используйте свой SIP-адрес для настройки SIP-клиента. Если вы занимаетесь бизнесом, вам понадобится служба для настройки системы и предоставления SIP-адреса для каждого сотрудника. Затем раздайте SIP-адреса своим друзьям и клиентам, чтобы между вами и ними была бесплатная голосовая и видеосвязь.
Вы можете использовать свой SIP-адрес для связи с людьми, которые не используют SIP на своих стационарных или мобильных телефонах. Для совершения вызова из IP-сети в телефонную сеть услуга платная. Люди, использующие обычные телефоны и стандартные сети, могут также позвонить вам по вашему SIP-адресу. В этом случае нужно прикрепить номер телефона к своему SIP-адресу
Для связи через Интернет SIP интересен множеством функций, связанных с голосовыми и видеозвонками, часто с участием нескольких сторон. Для этого выберите хороший SIP-клиент и наслаждайтесь.
SIP-клиен
VoIP – это широкая и расширяющаяся отрасль. SIP является частью этого, строительным блоком (важным) в структуре VoIP. Но наряду с SIP существует ряд других протоколов, используемых для голосовой и видеосвязи в IP- сетях. Например, Skype использует свою собственную архитектуру P2P.
Но, к счастью, большинство VoIP-провайдеров поддерживают SIP как в своих службах (то есть они дают вам SIP-адреса), так и в клиентских приложениях VoIP. Поскольку то, что предлагает Skype, является платным и предназначено для бизнеса вы захотите попробовать другие службы и клиенты для SIP. Существует множество поставщиков SIP-адресов и SIP-клиентов, которые предоставляют услугу связи бесплатно.
OnSIP
OnSIP – это платная услуга VoIP, предлагаемая Junction Networks. Компания также предлагает бесплатный план OnSIP людям, которые хотят создать бесплатный SIP-адрес.
Бесплатный план OnSIP предоставляет решение для голосовой связи среди группы, передачи видео и обмена сообщениями. Особенности включают в себя:
- До 100 пользователей.
- Интегрируется со Slack и Zendesk.
- Возможность использования в качестве расширения в Google Chrome.
- Бесплатные звонки SIP-to-SIP.
- Пользовательские ссылки на веб-вызовы и кнопки HTML.
Бесплатный план OnSIP заменяет программу GetOnSIP компании.
Преимущества |
Недостатки |
|
|
IPtel
IPTel.org предоставляет телекоммуникационные услуги IP и размещает несколько проектов, таких как SIP Express Router, SIP Express Media Server и SIP Express Router Web. IPTel также предоставляет обширную информацию о SIP-коммуникациях на своем веб-сайте. Бесплатный SIP-аккаунт, который предлагает IPTel, хорошего качества и доступен при простой регистрации.
Вам назначена пожизненная SIP-учетная запись, которую вы можете использовать для аудио- и видеозвонков с пользователями IPTel.org и других доменов. Вы можете получить доступ к службам VoIP-телефонии через веб-браузеры, не нуждаясь в специальном оборудовании, SIP-совместимом телефоне, программном телефоне или приложении для смартфона.
Чтобы воспользоваться услугой iptel.org, вам необходимо SIP-совместимое (RFC3261) оборудование или просто приложение для смартфона. В качестве альтернативы вы можете использовать WebRTC-совместимый браузер.
Доступ к сервису iptel.org предоставляется на условиях «КАК ЕСТЬ» и «КАК ДОСТУПНО». iptel.org не делает никаких заявлений и не дает никаких гарантий в отношении доступа пользователя к сервису, и что сервис будет доступен в любое время, без ошибок, дефектов, упущений, сбоев или задержек в доставке данных.
Преимущества |
Недостатки |
|
|
SIP2SIP
SIP2SIP – это простой SIP-сервис, предлагаемый AG Projects. Это бесплатный SIP-сервис, основанный на политике добросовестного использования. Регистрация и управление аккаунтом просты. AG Projects предлагает эту бесплатную услугу SIP в качестве одного из способов тестирования пользователями функций, присутствующих в ее продуктах. Используя любое из совместимых приложений или клиентов, вы можете:
- Аудио и видео звонки.
- Чат и передача файлов.
- Сделать конференц-звонки.
Достоинства |
Недостатки |
|
|
AntiSIP
Сервис Antisip предлагает набор сервисов на основе SIP. Среди них – бесплатный SIP-аккаунт, который предоставляет услуги VoIP-to-VoIP. Компания рекомендует загрузить приложение Antisip для мобильных устройств Android, но учетная запись SIP работает с другими устройствами.
Ссылки на учебные материалы YouTube доступны на веб-сайте для пользователей, впервые знакомых с SIP.
Достоинства |
Недостатки |
|
|
Как получить SIP-аккаунт
- Выберите SIP-провайдера
- Перейти на страницу регистрации
- Выберите имя пользователя
- Выберите пароль
- Далее каждый SIP-провайдер может предложить получение дополнительной информации о пользователе.
Вы должны понимать, что некоторая информация важна для SIP-серверов. К ним относятся часовой пояс и действующий адрес электронной почты. Кроме того, чтобы убедиться, что вы не робот (или программа, используемая хакерами), есть существует капча.
Обратите внимание, что действительный адрес электронной почты важен, так как на него будут отправлены полные учетные данные SIP. Существует много сервисов SIP, которые требуют от вас, как они это называют, «реального» адреса электронной почты.
Проверьте свою электронную почту
В большинстве случаев полные учетные данные, необходимые для настройки SIP, будут отправлены по электронной почте. Это электронное письмо важно и несет информацию о учетной записи, которую необходимо сохранить:
SIP-адрес, например, memyself@thatsipservice.info Пароль Имя пользователя: например, memyself Домен / Область: например, thatsipservice.info Исходящий прокси-сервер: например, proxy.proksi.com Корень XCAP: https : //xcap.proksi.com/xcap-root
В электронном письме также может содержаться полезная информация о том, как получить доступ к своей учетной записи и что там изменить, как настроить программное обеспечение SIP или аппаратный телефон, а также другую техническую информацию.
Похожие публикации
Дата публикации: 16.02.2019
Оценка статьи:
Загрузка…
Большинство пользователей глобальной сети знают и даже активно используют способ передачи мультимедийных данных через Интернет – межсетевой протокол IP (Internet Protocol). Если говорить просто, то для обмена информацией, включая аудиосообщения, требуется установить IP-соединение между устройствами.
Но что такое SIP-телефония? Это один из протоколов передачи голосовой информации, который базируется на принципах IP-телефонии. Расшифровывается SIP как Session Initiation Protocol – «Протокол Установления Сеанса». Используется для множества целей – аудио и видеоконференции, телефония, онлайн-игры и другое. Протокол SIP работает по схеме «клиент-сервер-клиент», чередуя запросы и ответы.
Далее подробно остановимся на алгоритме работы, отличиях от IP и VoIP и преимуществах SIP-телефонии.
Как работает
Что такое звонок через SIP? Обмен голосовыми сообщениями выполняется по следующему алгоритму:
- Первый абонент передает голосовое сообщение, которое записывается и сжимается с помощью специальных кодеков, встроенных в программные модули. Пользователь не замечает работу этих скриптов, однако, благодаря сжатию аудиоданных снижается нагрузка на Интернет-соединение. Качество при этом остается высоким за счет преобразования аналогового сигнала в цифровой.
- Цифровой сигнал поступает на принимающего устройство второго абонента – СИП-телефон, компьютер, смартфон.
- Между устройствами устанавливается связь, то есть сначала они находят друг друга по IP-адресу, а затем подключаются по SIP-протоколу и начинают сеанс.
- После соединения со вторым устройством цифровой сигнал преобразуется в аналоговый, и абонент слышит в трубке или гарнитуре голос собеседника.
Детально схема соединения выглядит так: голос первого абонента передается в SIP-оператор, сжимается в цифровой сигнал и направляется через интернет на SIP-оператор второго абонента, где он преобразуется в аналоговый сигнал и подается на приемное устройство.
Что нужно для отправки и приема звонка через Интернет?
Пользователям предлагается несколько вариантов применения SIP-протокола:
- С помощью ноутбука или стационарного ПК. На устройство следует установить программный клиент и оснастить его гарнитурой – обычно это наушники и микрофон.
- Используя смартфон, планшет или другой гаджет с наличием операционной системы и возможностью подключения к сети Интернет. На гаджет устанавливается специальный модуль, выполняется подключение и регистрация по инструкции к программному обеспечению. Звонок по SIP-каналу можно выполнить через мобильные сети 3G и 4G, а также через Wi-Fi.
- Посредством стационарного SIP-телефона, который подключается к роутеру.
- Применяя VoIP-шлюз с подключенным проводным телефоном. Шлюз подключается к роутеру.
Разберем на примере, что такое SIP.
Владислав планирует перелет самолетом из Пхукета в Москву на определенное время. На смартфоне у него SIP-клиент. Российская авиакомпания также имеет виртуальную АТС с поддержкой этого протокола. Владислав набирает номер компании, через сервер смартфона выполняется поиск IP-адреса авиаперевозчика. При отклике абоненты соединяются для обмена информацией.
Голосовые сообщения Владислава сжимаются и оцифровываются, после чего передаются на сервер собеседника. СИП-модуль виртуальной АТС дешифрует сигнал и передает его на устройство уже в аналоговом качестве – абонент слышит голос.
Для связи с мобильным телефоном через SIP-клиент алгоритм немного другой. Сначала сервер пытается найти IP-адрес абонента, если не может найти, то выполняется соединение с устройством напрямую стандартными технологиями. При этом сохраняется сжатие и оцифровка аналогового сигнала.
Из примера видим, что для работы SIP-телефонии необходимо интернет-соединение, а также наличие виртуального или физического телефона. Возникают вопросы, что такое SIP-номер и как его получить.
Обычно поставщик услуги предоставляет пользователям цифровую комбинацию – ID, с её помощью можно осуществлять бесплатные звонки внутри сети. Для соединения с абонентами других сетей требуется знать URI – комбинация ID и адреса провайдера.
Также клиентам выдаются стандартные телефонные номера:
- Виртуальные. Обычно – это комбинации с какой-то добавочной информацией, которая позволяет идентифицировать номер. Пользователи соединяются сначала с сервером поставщика услуги, а после по «цифровому хвосту» номера связываются непосредственно с абонентом.
- Прямые. Это привычные комбинации цифр, которые используются для городских и междугородних номеров. Звонки на такие линии выполняются без отличия от вызовов через обычные АТС. Главное преимущество – качество сигнала выше, за счет цифровой обработки на стороне SIP-оператора.
- Бесплатные. Номера вида 8-800 используются сервисами, службами поддержки и работы с клиентами по России. На них также можно звонить, используя SIP-протокол.
Ввод комбинаций номера в SIP-телефонии аналогичен с сотовой связью, то есть используется код страны. Например, для России – (+7).
Чем отличается SIP-телефония от VoIP и IP
Если СИП-протокол – это стандарт для звонков через Интернет, тогда возникает вопрос: для каких целей применяют IP-телефонию и VoIP? Например, подключаясь к виртуальной АТС, эти технологии используются совместно, что несколько запутывает неопытных пользователей. Давайте разберемся в понятиях.
Начнем с фундамента – это Internet Protocol или IP, что означает межсетевой протокол. По нему все сетевые устройства в мире связываются в глобальную сеть. Соответственно у каждого компьютера, гаджета, сервера или прибора подключенного к интернету есть уникальный IP-адрес. С его помощью пользователи обмениваются любыми данными и информацией.
Чтобы передавать аудиоданные по сети была придумана собственная технология, ответвление Internet Protocol – VoIP, то есть Voice over IP. Переводится как «голос по IP» или проще «голос по Интернету». С помощью этой технологии пользователи могут обмениваться данными, где в каком-либо виде присутствует голос. Например, вебинары и трансляции через Интернет, звонки в сети, онлайн-игры, видеонаблюдение с оповещением и другое.
SIP-телефония представляет собой более узкое понятие, то есть разновидность IP-телефонии, выделенный протокол связи. Основное отличие в том, что соединение между абонентами осуществляется только по этому каналу, не используя другие технологии. Это позволяет привязать номер к конкретному пользователю, а не к общей локации. Например, SIP-протокол применяется в Skype, а также в сервисах отслеживания звонков call tracking.
Преимущества технологии
Звонить и поддерживать связь через Интернет сегодня намного выгоднее и практичнее, чем пользоваться традиционной телефонией. Например, SIP-технология позволяет быстро и недорого обеспечить компанию связью. Рассмотрим преимущества для бизнеса и не только:
- Экономия бюджета. Подключить этот протокол гораздо дешевле, чем обеспечить офис аналоговой АТС. К тому же в вашем распоряжении многоканальный номер, отличная скорость и качество соединения. Вы можете легко увеличить число операторов в вашей сети при минимальных затратах времени и средств. Попробуйте сделать такое в аналоговой АТС.
- Телефонизация компании на «раз-два». SIP-телефонию можно описать одной фразой: «подключись и работай». Например, вы только въехали в новый офис, ещё не успели обустроиться, но связь с клиентами хотите поддерживать. Как это сделать быстро и без забот, если у вас есть ноутбук с гарнитурой, компьютер или гаджет? Только с помощью технологии SIP. Для стабильного соединения подойдет даже мобильный интернет 3G или 4G.
- Оплата осуществляется только по базовым тарифам за услуги телефонной связи, независимо от местонахождения абонента. Это очень удобно для крупных компаний с разветвленной сетью представительств, филиалов, отделов в разных городах.
- Интеграция телефонии с системами аналитики, 1С, CRM. Например, используя этот протокол в сервисе коллтрекинга можно проверять различные метрики: эффективность работы операторов, отдела продаж, отслеживать рекламные каналы, по которым приходят клиенты и многое другое. Все это повышает эффективность рекламных кампаний и уровень обслуживания.
- SIP-соединение хорошо защищено от внешнего прослушивания, чего не скажешь о аналоговых линиях связи.
- Технология позволяет создать удаленный колл-центр, не тратя деньги на закупку стационарного оборудования и аренду офиса.
- Множество опций – голосовая почта, переадресация между сотрудниками и отделами, автоответчик, голосовое меню. Также СИП-технология позволяет проставлять очередность звонков, ориентируясь на загрузку менеджеров, записывать разговоры.
- Протокол отлично работает с модулями обратного звонка, пропущенных вызовов на сайте. В связке они увеличивают показатели конверсии звонков в заявку в среднем на 60%.
- Наличие программного обеспечения для любых операционных систем, мобильных устройств, смартфонов.
Мы ответили на вопрос, SIP-телефония: что это и как работает. Рассмотрим, где эта технология активнее всего применяется.
СИП-телефония применяется коммерческими и государственными корпорациями, малым и средним бизнесом для создания скоростной сети внутрикорпоративного общения, а также для связи с партнерами и клиентами. Например, крупные колл-центры, торговые павильоны и мега-маркеты используют этот IP-протокол.
Обычные пользователи также применяют программы и оборудование для интернет-звонков. Технология СИП существенно сокращает расходы на телефонию.
Резюме
Мы изучили, что такое SIP. Узнали отличия этого вида интернет-телефонии от IP-связи и VoIP. Рассмотрели принцип работы, преимущества, программное обеспечение и сферу применения технологии.
СИП-телефония – эффективное и экономичное решение для стартапа, а также практичный вариант организации бизнес-процессов в корпорации, на крупных предприятиях и госорганизациях. Технология помогает вести аналитику звонков, повышать качество обслуживания клиентов и доходы компании.