- Manuals
- Brands
- Deutz Manuals
- Engine
- TCD 2012 Series
- Installation manual
-
Contents
-
Table of Contents
-
Bookmarks
Quick Links
Installation Manual
Series
Directions for the installation of
Liquid-cooled high-speed
Diesel engines
Responsible for contents:
TD/TCD 2012
TD/TCD 2013
DEUTZ AG
Applikations-/ System solutions
Deutz-Mülheimer-Str.147/149
Tel.: (0221) 822 2559
Fax.: (0221) 822 3198
st
1
. Edition 05.2006
Order-No. 0399 1969 en
Related Manuals for Deutz TCD 2012 Series
Summary of Contents for Deutz TCD 2012 Series
-
Page 1: Diesel Engines
Installation Manual Series TD/TCD 2012 TD/TCD 2013 Directions for the installation of Liquid-cooled high-speed Diesel engines DEUTZ AG Responsible for contents: Applikations-/ System solutions Deutz-Mülheimer-Str.147/149 Tel.: (0221) 822 2559 Fax.: (0221) 822 3198 . Edition 05.2006 Order-No. 0399 1969 en…
-
Page 2
INSTALLATION MANUAL TD/TCD 2012 / 2013 These guidelines are not meant to serve as operating instructions for the end user of machinery but refer to all equipment manufacturers using a DEUTZ diesel engine as prime mover in their products. The guidelines are therefore no user information according to DIN Standard 8418;… -
Page 3
INSTALLATION MANUAL TD/TCD 2012 / 2013 List of Modification Modification Date Chapter Request of change / modification Index 2006-06-07 P/N changed from 0399 1965 to 0399 1969 EDITION 05.2006 Modifikation Index 01 00 — 3… -
Page 4: Table Of Contents
INSTALLATION MANUAL TD/TCD 2012 / 2013 Table of Contents Page Engine Cooling System……………. 01 — 1 Arrangement of cooling system………….. 01 — 1 Circuit of engine coolant……………………01 — 1 Layout of fan and cooler…………………..01 — 3 1.3.1 Fan- Layout……………………….
-
Page 5
INSTALLATION MANUAL TD/TCD 2012 / 2013 2.9.2 Rotating screens………………02 — 6 2.9.3 Cooling air cyclone………………. 02 — 6 2.9.4 Cooling air filter mats……………….02 — 7 Combustion air system…………………………………………………….. 03 — 1 General……………………… 03 — 1 Intake vacuum pressure…………….03 — 1 3.2.1 Maximally admissible intake vacuum pressure…….. -
Page 6
INSTALLATION MANUAL TD/TCD 2012 / 2013 4.14 Heat insulation………………04 — 9 4.15 Particulate traps………………04 — 10 4.16 SCR System………………… 04 — 11 4.17 Exhaust gas recirculation………………………… 04 — 11 Fuel system……………………05 — 1 General……………………… 05 — 1 Fuel conveyance (System-Tank-Supply Pump-Tank)…………. -
Page 7
INSTALLATION MANUAL TD/TCD 2012 / 2013 8.3.3.1 Radial power take-off, flywheel side………….………..08 — 8 8.3.3.2 Radial power take-off, damper side (opposite side to clutch)………..08 — 9 Installation references……….………08 — 18 Compressor……………………09 — 1 Place of installation……………… 09 — 1 Compressor / sizes……………………. -
Page 8
INSTALLATION MANUAL TD/TCD 2012 / 2013 15.10.1 Three-phase generators (charging balance)……..15 — 14 15.10.2 Dimensioning of B+ line from the generator ………………….15 — 15 15.10.3 Application and operating conditions for BOSCH compact generators…….……………………………………….. 5 — 18 15.11 Electronic engine equipment…………………………..………..15 — 18 15.11.1 General…………………… -
Page 9: Engine Cooling System
(indirect cooling system). All cooling circuits of the Deutz diesel engines described below are closed circuits (forced circulating cooling system); open-circuit cooling of the diesel engines is not permitted.
-
Page 10
INSTALLATION MANUAL TD/TCD 2012 / 2013 The highest permissible permanent temperature for the TD/TCD engines is 110°C, (exception TCD 2013 L06 2V, performance group II and higher as well as Pgr. 1 above 2100 rpm = 105°C) The engine temperature is monitored by the control unit of the electronic engine control (ECU 3) and, depending on the selected scope of performance, exceeding of the temperature leads in steps to warning, power reduction, adjustment of start of injection and shutdown. -
Page 11: Layout Of Fan And Cooler
— Fan fitted to engine on mounting bracket and one cooler, each, mounted upstream. With these cooling systems, it is up to the customer to choose a system solution from DEUTZ (Gen-set only) or to procure a relevant system himself.
-
Page 12
INSTALLATION MANUAL TD/TCD 2012 / 2013 Performance of the coolant pump: TCD2012L04/06 2V 180** l/min, 2400/min TCD2013L04/06 2V 200** l/min 2300/min The heating circuit must be closed for checking the measurement. TCD2012L04/06 4V 185** l/min, 2400/min TCD2013L04/06 4V 295** l/min, 2300/min 0.35bar ** Maximum permissible pumping resistance for the coolant pump through liquid cooler and… -
Page 13: Cooling Constant
INSTALLATION MANUAL TD/TCD 2012 / 2013 Cooling constant (inlet temperature difference ETD) 1.3.3 The so-called cooling constant refers to the temperature difference t between coolant inlet temperature t and inlet temperature of the cooling air at the cooler: coolant in air in t = t –…
-
Page 14: Additional Coolers
INSTALLATION MANUAL TD/TCD 2012 / 2013 1.3.4 Additional coolers 1.3.4.1 Converter, transmission and retarder oil coolers in engine coolant circuit In view of the higher oil temperature level in the case of converters and retarders (except for hydrostatic transmissions), the temperature difference to the engine coolant temperature is high enough to justify the operation of additional coolers of that kind in the engine coolant circuit.
-
Page 15
INSTALLATION MANUAL TD/TCD 2012 / 2013 1.3.4.3 Additional cooler in the return pipe (engine outlet – inlet engine cooler) FIGURE 1-3 In the case of the OUTLET CONTROL, also an open-blocked thermostat is installed in the engine, if the maximally possible coolant flow shall be ensured. The thermal control is taken over by a pipe thermostat arranged in the return pipe between additional cooler (outlet) and engine cooler (inlet). -
Page 16: Charge Air Cooler Installation
INSTALLATION MANUAL TD/TCD 2012 / 2013 1.3.4.5 Additional cooler in the heating circuit In the case of cooler units with a lower cooling requirement, it may be reasonable to connect an additional cooler using the connectors at the engine (provided for the heating system). A forced bridging of the engine thermostat for representing the maximal flow rate is not necessary –…
-
Page 17: Design Of The Compensation Tank, Compensation And Venting Lines, Water Level Check
— in the additional heat exchanger (heating) — in the additional pipes — in the additional heat exchanger (gear oil) The following specifications apply for the coolant volumes in the DEUTZ engines (without cooling system): TD/TCD L04 2012 5.6 Itr TD/TCD L04 2013 7.4 Itr…
-
Page 18
INSTALLATION MANUAL TD/TCD 2012 / 2013 Insert this in the tank up to the «Max» level Filler neck: and drill a hole of 3mm. Install level monitor on the ABH Level monitoring: N.B.: Pipe connections on the compensation tank: — Centrally at the lowest point so that a. -
Page 19: Pipe Connection For External Expansion Tank
INSTALLATION MANUAL TD/TCD 2012 / 2013 1.4.1 Pipe connections for external expansion tank FIGURE 1-6 1.4.2 Pipe connections for expansion tank in the radiator end box: FIGURE 1-7 EDITION 05.2006 Modification Index 00 01 — 11…
-
Page 20: Water Level Control In The Expansion Tank
(lifting solenoid) is the only really effective monitoring method to protect the engine against damage due to lack of water. DEUTZ offers an inductive level sensor made by BEDIA for the engine series TCD 2012 / 2013 in the «normally open» function.
-
Page 21: Heating System
INSTALLATION MANUAL TD/TCD 2012 / 2013 Heating system With the liquid-cooled DEUTZ diesel engines, the heat contained in the coolant is used for heating driver cabs and passenger compartments. In this case, the engine coolant is ducted directly to the system heat exchanger and the heat is dissipated directly to the environment (direct heating system).
-
Page 22
INSTALLATION MANUAL TD/TCD 2012 / 2013 The engine coolant volume flow rates listed below are available for the heating units, always at maximal rated speed. The specified engine coolant volumes for the heating system must not be exceeded as, otherwise, the coolant supply to the engine is affected. If maximum water flow volume is exceeded an additional restrictor has to be installed in the heater circuit. -
Page 23: Design Of Heating Exchangers
1.5.5 Heating rod The electrically operated heating rod (the so-called socket heating) as per DEUTZ scope of supply (PN 0419 8898 KZ 0130-63, 230V, 820W)) is predominantly provided for keeping the cooling water warm and is installed at the lube oil cooler housing.
-
Page 24: Piping And Fittings
INSTALLATION MANUAL TD/TCD 2012 / 2013 1.6. Pipings and fittings 1.6.1 General The delivery rate and delivery height of the engine-mounted coolant pump (centrifugal pump, is also dependent on the flow resistance of piping and fittings (cocks, valves). The pipe resistances and the type of pipe laying (number and type of pipe bends) must therefore be determined with utmost care.
-
Page 25
INSTALLATION MANUAL TD/TCD 2012 / 2013 From the table (following picture), the equivalent pipe lengths in metres for fittings and shaped pipe elements may be taken. FIGURE 1-12 If the sum of resistances from pipes, fittings and coolant heat exchanger exceeds the available pump delivery head, the pipe diameters must be enlarged. -
Page 26: Pipe Layouts
INSTALLATION MANUAL TD/TCD 2012 / 2013 1.6.3 Pipe layouts Commercial steel pipes (seamless, non-galvanized) are to be used for the engine coolant, which must be descaled at the inside after bending or welding work (pickling, flushing). The pipe ends are to be provided with sealing crimps (as per DIN 71550), in order to ensure a permanent and tight rubber sleeve joint.
-
Page 27: Fastening By Clips
INSTALLATION MANUAL TD/TCD 2012 / 2013 The material for rubber sleeves, moulded parts and corrugated hose pipes (without internal wire coil!) for coolant-carrying pipes must be resistant to corrosion inhibiting oil, engine oil, antifreeze, diesel fuel and be permanently resistant to temperatures between -40°C and +125°C (also see DIN 73411 Part 1 u.2).
-
Page 28: Fan Arrangement
INSTALLATION MANUAL TD/TCD 2012 / 2013 Fan arrangement DEUTZ offer fans adapted to the engine scope of supply. Please contact the head office for air volume flow rate as a function of delivery resistance and fan speed. If the fans are procured from specialist companies, the layout-specific technical data should be clarified with the cooler manufacturer or with DEUTZ.
-
Page 29: Fan Arrangement And Mounting Configurations
INSTALLATION MANUAL TD/TCD 2012 / 2013 Fan arrangements and mounting configurations The following possibilities are provided for mounting the fan to the engine with separately mounted cooler (external cooling system): Fan mounted to coolant pump Fan mounted via mounting bracket at face of engine ( with variable fan mounting heights –…
-
Page 30: Fan Mounted To Coolant Pump
INSTALLATION MANUAL TD/TCD 2012 / 2013 1.8.1 Fan mounted to coolant pump When mounting the fan to the V-belt pulley of the coolant pump, the bearing of the coolant pump is exposed to additional stress loads for the shaft bearing of the coolant pump as a result of increased belt forces and additional axial thrusts or axial pressures (suction or pusher-type fans).
-
Page 31
INSTALLATION MANUAL TD/TCD 2012 / 2013 FIGURE 1-17 Upon reduced speed, the limit values for unbalance- and axial forces can be extended relative to speed: — Extended unbalance limit = (rated engine speed / red. speed) x unbalance — Extended axial force limit = (rated engine speed / red. speed) x axial force All figures in the table apply to a 1-belt drive {coolant pump, crankshaft, fuel pump) Rated engine speed for TCD 2012: n = 2400min… -
Page 32: Fan Mounted By Means Of Bearing Bracket
Fan mounted by means of bearing bracket For increased fan capacities in respect of the air volume flow rate for the supply of additional coolers in addition to the radiator, DEUTZ supplies an engine-mounted bracket for installation of the fan.
-
Page 33
INSTALLATION MANUAL TD/TCD 2012 / 2013 FIGURE 1-19 Upon reduced speed, the limit values for unbalance- and axial forces can be extended relative to speed: — Extended unbalance limit = (rated engine speed / red. speed) x unbalance — Extended axial force limit = (rated engine speed / red. speed) x axial force All figures in the table apply to a 1-belt drive {coolant pump, crankshaft, fuel pump) Rated engine speed for TCD 2012: n = 2400min… -
Page 34: Fan Mounted At Front Crankshaft End
INSTALLATION MANUAL TD/TCD 2012 / 2013 1.8.3 Fan mounted at front crankshaft end When mounting the fan at front crankshaft end, torsional vibration characteristics have to be taken into account. Special attention should be paid to fan assembly and configuration as the fan is exposed to high stress loads due to the tumbling movement at front crankshaft end and the torsional irregularities.
-
Page 35: Cooler / Fan Connections
INSTALLATION MANUAL TD/TCD 2012 / 2013 The specialist companies should be consulted in respect of positioning and configuration of the radiator mounting elements. The following illustration shows the possible composition of a radiator mounting element. FIGURE 1-20 The piping connection to the radiator must also be flexible so as to prevent any forces from being transmitted through the piping.
-
Page 36: Cooler/Fan Connections With Engine-Mounted Fan Ring
INSTALLATION MANUAL TD/TCD 2012 / 2013 1.10.2 Cooler/fan connections with engine-mounted fan ring It is decisive for the delivery rate of the fan to what extent the radial clearance SP between fan outer diameter and cooling duct can be minimised. The smaller, the better the fan delivery rate Für die Förderleistung des Lüfters ist entscheidend, wie klein das Radialspaltmaß…
-
Page 37: Axial Position Of The Fan In The Scoop
INSTALLATION MANUAL TD/TCD 2012 / 2013 1.10.4 Axial position of the fan in the scoop Limited installation space usually necessitates a short configuration of the power train, i.e. fan and cooler must be arranged as close as possible to the engine face. The result is a relatively high resistance at the discharge end.
-
Page 38: Cooling Air System
2.1 General The following two major rules must be observed to ensure that the engine-integrated cooling system of the DEUTZ diesel engines as well as the external cooling systems consisting of fan and cooler can feature their cooling capacity: Only fresh air is suitable for cooling and combustion purposes, the engine should never…
-
Page 39: Connection Of Air Intake And Discharge Ducts
INSTALLATION MANUAL TD/TCD 2012 / 2013 2.3 Connection of air intake and discharge ducts In most installation cases, there will be a «flexible» connection between the fan at the engine and the external cooler. Therefore, the air intake or discharge duct (suction- or pusher-type cooling) will be connected to the cooler.
-
Page 40: Mounting Of Charge Air Coolers
INSTALLATION MANUAL TD/TCD 2012 / 2013 2.5 Mounting of charge air coolers The TCD 2012 / 2013 engines are charge air-cooled. As regards the arrangement of the charge air coolers, they may be arranged side-by side or in-line with the radiator. FIGURE 2-3 In practice frequently in-line arrangement is realized.
-
Page 41: Arrangement Of Auxiliary Coolers
INSTALLATION MANUAL TD/TCD 2012 / 2013 2.6 Arrangement of auxiliary coolers Auxiliary coolers, e.g. hydraulic oil -, transmission coolers are to be arranged parallel to the engine liquid radiator because of their usually increased cooling air heating. It is necessary to adapt the fans (speed, diameter) accordingly to supply the higher additional cooling air volume.
-
Page 42: Heating Up Of Cooling Air
INSTALLATION MANUAL TD/TCD 2012 / 2013 2.8 Heating up of cooling air With the liquid-cooled engines, heating up of the cooling air reduces the cooling capacity of the cooler. This will lower the ambient temperature-operating limit of the engine without confining, however, the engine’s ability to run continuously under full-load conditions.
-
Page 43: Filtration Of Cooling Air
INSTALLATION MANUAL TD/TCD 2012 / 2013 2.9 Filtration of cooling air For special applications of the engines, filtering of the cooling air might become necessary in view of the high dust development, e.g. combine harvesting, beet and fish meal handling, slag and dump sites, etc.).
-
Page 44: Cooling Air Filter Mats
Some well-known manufacturers of combustion air filters offer such packages. Depending on the cooling air volume flow rate, it is urgently recommended to have DEUTZ investigate and evaluate the systems. 2.9.4 Cooling air filter mats Beyond filtering proper, filtering of the cooling air via so-called filter mats offers the advantage of a certain noise reduction on the intake air side.
-
Page 45: Combustion Air System
INSTALLATION MANUAL TD/TCD 2012 / 2013 COMBUSTION AIR SYSTEM 3.1 General Experience has shown that in more than 75% of all cases premature engine wear is attributable to the influence of dust. To avoid this problem, great importance should be attached to filtration of the combustion air and to proper layout of the air cleaners and clean air piping.
-
Page 46: Maximally Admissible Intake Vacuum Pressure
INSTALLATION MANUAL TD/TCD 2012 / 2013 Maximally admissible intake vacuum pressure 3.2.1 The total intake vacuum pressure for engines for «general applications» and engines for «power generating sets» referred to in the following tables 1, 2 are values which, when measured on the engine, must not be exceeded.
-
Page 47: Measuring The Intake Vacuum Pressure
INSTALLATION MANUAL TD/TCD 2012 / 2013 To ensure an adequate service life of the filter elements under normal dust conditions, the following intake vacuum pressure at the clean air socket of the filter (without raw air pipe upstream of the filter) should not exceed the following values in new condition: from 4-cylinder engines 25 mbar, 250 mmWS…
-
Page 48: Monitoring The Intake Vacuum Pressure
INSTALLATION MANUAL TD/TCD 2012 / 2013 FIGURE 3-2 Alternative positions of measuring points in front of turbocharger 3.2.3 Monitoring the intake vacuum pressure Contrary to the oil-bath air cleaners, the flow resistance of the dry-type air cleaner considerably rises with increasing contamination of the paper cartridge; therefore a servicing indicator for monitoring the intake vacuum pressure must be fitted when installing dry-type air cleaners.
-
Page 49: Air Cleaner Systems
Here, the oil-bath air cleaner acts as an excellent preliminary filter. If required, contact the head office of DEUTZ, as systems of that kind are not available by series. EDITION 05.2006…
-
Page 50: Wet-Type Air Cleaners
The combustion air filter versions supplied by DEUTZ are described in detail in the sales documentation of the individual engine series. If an air cleaner especially requested by the customer is not part of the DEUTZ scope of supply, the OEM is fully responsible for the correct layout and execution. If the engine should be damaged as a consequence of mistakes in the cleaner system, DEUTZ refuses any claims under engine warranty.
-
Page 51: Calculation Data For Combustion Air Volume Flow Rate
INSTALLATION MANUAL TD/TCD 2012 / 2013 Calculation data for combustion air volume flow rate Calculation of the combustion air flow rate «Q » Turbocharged engines whose exhaust gas qualities must meet the higher requirements of the recent national and international exhaust gas regulations partly require a higher combustion air volume flow rate.
-
Page 52
INSTALLATION MANUAL TD/TCD 2012 / 2013 Determining the practical service life an air cleaner Before determining the filter size, the dust concentration must be estimated expected for the respective engine application. The table of the reference examples is a selection aid for dimensioning the dry-type air cleaner. -
Page 53
INSTALLATION MANUAL TD/TCD 2012 / 2013 Reference examples for dimensioning the dry-type air cleaners including preliminary filter Table 3 Mean dust Lab test life in Lab test life in hours as Group Engine application concentration in hours as per SAE per ISO at 1000 mg/m mg/m³… -
Page 54: Combustion Air Piping
INSTALLATION MANUAL TD/TCD 2012 / 2013 Combustion air pipings 3.6.1 General remarks to the pipings Combustion air pipings between air cleaner and engine («clean air piping») must be absolutely air-tight and resist the mechanical stresses caused by engine vibrations and pressure pulsations.
-
Page 55: Ribbed Hoses
In this connection, the detailed installation instructions of the hose manufacturers are referred to. Ribbed hoses as per DEUTZ specification * H3482 — 2 have proved in service. Among other items, the DEUTZ specification is as follows: Hose to be composed of two rubber layers with textile reinforcement.
-
Page 56: Rubber Sleeves
Rubber sleeves for charge air lines, hot (between turbocharger and intercooler) The rubber sleeves in this pipe area must meet the requirements of the DEUTZ Works Standard H 3407 – 8. In particular, these sleeves must have an inner locking layer against oil penetration.
-
Page 57: Shapped Rubber Elements
DEUTZ specifications for materials – depending on their position in the pipe system for the combustion air. Shaped rubber elements in air intake lines (vacuum pressure) must comply with the DEUTZ delivery instructions 0161 0093 US 8093-35 which, among others, specify the following:…
-
Page 58: Hose Clamps
INSTALLATION MANUAL TD/TCD 2012 / 2013 3.6.5 Hose clamps The ribbed hoses, rubber sleeves and shaped rubber elements, if any, are fastened to the pipe ends with hose clamps. Admissible are hose clamps with clamping jaws and screw-nut union: Width of the clamp strap at least 15 mm. Hose outer diameter and hose clamp inner diameter must correspond, as the clamping range of the clamping jaw clips is small.
-
Page 59: Installation Manual Td/Tcd
INSTALLATION MANUAL TD/TCD 2012 / 2013 To ensure proper seating of the rubber sleeves or ribbed hoses, observe the following: The connecting ends of sheet metal pipes are to be provided with a sealing crimp a per DIN 71550 (plug-on length of the rubber element 35 mm, hose clamp arranged behind sealing crimp). Cast iron or steel pipings with a wall thickness of more than 2 mm do not require a sealing crimp, if the seat for the rubber sleeves is machined (cast tube) or drawn seamlessly (steel pipe) and the surface quality corresponds to Rt = 40.
-
Page 60: Edition 05.2006 Modification Index
Note: Because of the high pressures and the high temperatures in the charge air system of the TCD engines, DEUTZ recommends only using the double clamping jaw clip in addition to the V-band clamp. Clamps and hose material must be carefully matched. The user is responsible for a durable and tight connection.
-
Page 61
INSTALLATION MANUAL TD/TCD 2012 / 2013 FIGURE 3-4 EDITION 05.2006 Modification index 00 03 — 17… -
Page 62: Passages Of Clean Air Pipes
INSTALLATION MANUAL TD/TCD 2012 / 2013 3.6.6 Passages of clean air pipes The passages of clean air pipes through engine cowlings or sound insulating walls must be executed such that the pipes cannot chafe through. Check for reciprocal vibrations; if necessary, increase the passages for the piping and fill the annular gap towards the pipe with foam rubber or a similar material.
-
Page 63: Charge Air Cooling System
Combustion air outlet to the CAC Inlet always at the bottom if possible Other design data such as: Consult DEUTZ Technical Support air throughput, volume of heat to be dissipated – engine performance-related, etc. * 46°C for the engine TCD 2013L06 4V, power variant 261kW / 2200 rpm **The specification refers to the engine full load operation at nominal speed.
-
Page 64: Intercooler (Air-Air Cooler)
INSTALLATION MANUAL TD/TCD 2012 / 2013 3.10.3 Intercooler (air-air cooler) The coolers used for cooling the charge air are so-called air-air coolers, i.e. the charge air is back-cooled with the cooling air. FIGURE 3-5 3.10.4 Intercooler (air-water cooler) Cooling of the charge air with Engine coolant from the engine coolant circuit or with raw water via separate raw water pump, e.g.
-
Page 65: Pre-Loading Of Hydraulic Oil Tanks
INSTALLATION MANUAL TD/TCD 2012 / 2013 3.11Pre-loading of hydraulic oil tanks To reduce to the tendency of hydraulic systems to form cavitations, closed circuits are used, where the hydraulic oil is pressurized in the hydraulic oil tank (pre-loaded oil). To that end, normally an air compressor is required.
-
Page 66: Exhaust Gas System
TD/TCD 2012 * In individual cases a higher exhaust back-pressure can have been certified. Information for this can be inquired at the technical support DEUTZ. Table 3: BHKW If the engines are used as genset engines in block-type thermal power stations (BHKW),…
-
Page 67: Measuring The Exhaust Gas Back Pressure
(within the area of the pressure pick-up point) as well as the combustion air temperature at (the inlet of the intake pipe). Technical support DEUTZ will assess, whether the measured exhaust gas back pressure is permissible.
-
Page 68: Dimensioning Of Exhaust Gas Pipes And Determination Of The Piping Resistance
INSTALLATION MANUAL TD/TCD 2012 / 2013 Exhaust gas pick-up point (measuring point): See the following sketch FIGURE 4-2 Measures in mm Dimensioning of exhaust gas pipes and determination of the piping resistance The reference value for laying out the exhaust gas piping is the internal diameter of the engine exhaust gas pipe;…
-
Page 69: Silencer And End Pipe Lengths
INSTALLATION MANUAL TD/TCD 2012 / 2013 Examples for determining the piping resistances may be taken from the graphs. For given lengths and resistances, the necessary pipe diameters can be similarly determined with the aid of the graphs. Silencer and end pipe lengths The silencers offered in the respective scope of supply are matched to our engines in respect of noise and resistance.
-
Page 70: Exhaust Brake
This is controlled by the electronic engine control unit (ECU). Therefore the engine brake actuator must be connected accordingly to the engine control unit . See the valid DEUTZ connection diagrams of the engine control units. EDITION 05.2006 Modification index 00…
-
Page 71
The integrated air cylinder for actuating the brake flap is exposed to high thermal stresses. As exhaust flaps are matched to the relevant engine design, it is recommended to only use such flaps which are included in the DEUTZ scope of supply. Installation conditions:… -
Page 72: Nomographs For Determining The Exhaust Gas Pipe Resistance
INSTALLATION MANUAL TD/TCD 2012 / 2013 Nomographs for determining the exhaust gas pipe resistance FIGURE 4-5 EDITION 05.2006 Modification index 00 04 — 7…
-
Page 73: Water Scrubbers
INSTALLATION MANUAL TD/TCD 2012 / 2013 Water scrubbers In the case of water scrubbers, the exhaust gas is directed through a water bath in which the exhaust gas is cooled and some particles are washed out. Water scrubbers are water tanks with several inner baffle plates and separating facilities connected behind, which feature a considerable flow resistance even without water filling.
-
Page 74: Exhaust Gas End Pipe/Water Penetration Guard
A heat insulation of the surfaces of exhaust gas manifolds at the engine and the following exhaust gas turbochargers is generally not permitted and always require a consultation with DEUTZ. Partial insulation especially at a low engine output setting may be permissible but DEUTZ Technical Support must always be consulted first . EDITION 05.2006…
-
Page 75: Particulate Traps
The insulation of the exhaust gas manifold and the turbochargers must always be seen as a function of the engine application and the blocked engine power. Therefore, in the individual case, always technical support DEUTZ must be consulted. 4.15 Particulate traps The exhaust gas emission of a diesel engine contains solid matter –…
-
Page 76: Scr System
Details and installation instructions for this system are shown in a separate installation regulation. 4.17 Exhaust gas recirculation To achieve the exhaust gas emission values, the DEUTZ engines TD / TCD 2012 /2013 are equipped with exhaust gas recirculation systems. The following systems are used:…
-
Page 77: Fuel System
An adequate supply of the injection pump with fuel at all times is a pre condition for proper starting behaviour and satisfactory performance of diesel engines. DEUTZ diesel engines are laid out for the diesel fuels as per DIN EN 590. Release is granted for: Diesel fuel with additives according to EN 590, added by the oil company, as far as the EN 590 /2004 will be complied.
-
Page 78: Fuel Conveyance (System-Tank-Supply Pump-Tank)
INSTALLATION MANUAL TD/TCD 2012 / 2013 Fuel conveyance (System Tank – Supply Pump — Tank) 5.2.1 Permissible resistances The engine integrated fuel supply pumps are gear pumps which are driven, depending on the engine type, by V-belts, poly V-belts or toothed gears. Due to the different drive types, deviations in the transmission ratios occur with slight effects on the supply volumes.
-
Page 79: Permissible Temperatures
INSTALLATION MANUAL TD/TCD 2012 / 2013 5.2.2 Permissible temperatures Component, medium, environment Permanent Brief temperature temperature °C °C Fuel in normal operation » in case of fault briefly in the return up to The fuel temperature may never exceed 90°C in the lead Fuel pipes -40 / 100 Ambient…
-
Page 80
The standard equipment is the 2 x 1.4 ltr. exchange filter. For TIER III engines, there are greater demands on the fuel main filter. Only filters released by DEUTZ may be used. The distance «a» between the return and suction pipe in the tank must be chosen as great as possible. -
Page 81: Tank Arrangement In Relation To The Engine
INSTALLATION MANUAL TD/TCD 2012 / 2013 5.2.4 Tank arrangement in relation to the engine Tank underneath engine At greater suction heights a higher operating tank can be used which can be filled for example with a vane pump or an electric tank supply pump from the main tank. An overflow pipe can be laid between the high tank and the main tank or the tank supply pump of the main tank is switched on intermittently after float contact in the high tank.
-
Page 82: Laying And Dimensioning Of The Fuel Pipes
Deutz scope of delivery must be used. When using standard-compliant pipes, makes sure you select pipes which do not exceed the required inside pipe diameter.
-
Page 83: Pipes In The Low Pressure System
INSTALLATION MANUAL TD/TCD 2012 / 2013 All pipe connections must be made air-tight. The suction opening of the suction pipe in the fuel tank must be about 40 mm away from the bottom of the tank so that no residue water or sludge can be sucked in. 5.3.2 Pipes in the low pressure system The hoses between the supply pump –…
-
Page 84: Fuel Heater, Fuel Cooler
INSTALLATION MANUAL TD/TCD 2012 / 2013 Fuel heater, fuel cooler As a maximum permissible permanent fuel temperature before entering the engine-internal fuel supply pump, 70 °C are permissible. On exceeding the permissible temperature, components of the fuel injection system may be damaged which can be proved to have been caused by non- compliance with the installation regulation.
-
Page 85
INSTALLATION MANUAL TD/TCD 2012 / 2013 Figure: Representation of arrangement of suction and return pipe in the tank When using plastic fuel tanks, consult the fuel tank manufacturer concerning the permissibility of the used plastic with regard to the fuel and temperature. EDITION 05.2006 Modification index 00 05 — 9… -
Page 86: Fuel Filtering / Water Trapping
INSTALLATION MANUAL TD/TCD 2012 / 2013 Fuel filtering / water trapping 5.6.1 Main filtering: The following main filter variants are available for the engine series: FIGURE 5-2 Bowl filter FIGURE 5-3 Mounted main filter EDITION 05.2006 Modification index 00 05 — 10…
-
Page 87: Pre-Filtering
The above mentioned filter exists in the DEUTZ scope of delivery and is prescribed bindingly for engine applications: According to the DEUTZ scope of delivery the filter version has a water collecting vessel with an electric water level monitor to initiate timely disposal of water.
-
Page 88
INSTALLATION MANUAL TD/TCD 2012 / 2013 Installation instructions: Always make sure this fuel pre-filter is installed where it can be easily maintained, i.e. easily visible and accessible for the operator as well as sufficient room for assembly work. Installation position of this fuel pre-filter always standing vertically, water drainage from bottom. -
Page 89: Fuel Filtering In Extreme Applications
INSTALLATION MANUAL TD/TCD 2012 / 2013 FIGURE 5-5 Fuel pre-filter for TIER III engines, TYP RACOR 5.6.3 Fuel filtering in extreme applications In engine and equipment applications under very difficult conditions such as poor fuel quality, i.e. increased soiling of the fuel, large amount of dust in the atmosphere or when refuelling, high workload of the engines, the filter change intervals must be reduced to a max.
-
Page 90: Representation Of Fuel Connections With Regard To Air Tightness
INSTALLATION MANUAL TD/TCD 2012 / 2013 Representation of fuel connections with regard to air tightness When screwing the pipes of the LP system, always make sure that the connections guarantee air tightness during the engine operation. FIGURE 5-6 gives constructional hints which must be observed when fastening.
-
Page 91: Connecting Elements In The Suction Pipe
In fig. 5-7 examples of the connecting elements are shown which are necessary for setting up a low resistance suction pipe system – such elements belong to the DEUTZ scope of delivery for inside pipe diameter 12 mm and 14 mm and can therefore be used up to a pipe length of 6m or 15m as a rule.
-
Page 92: Assembly Instructions For Working On The Low Pressure System
The heating cartridge cannot be screwed in later but the complete filter head must be changed. This is not offered by DEUTZ and can be ordered from the following address if required : See next page: EDITION 05.2006…
-
Page 93
This filter is available at the moment under the following part number: MD 5790R-DTZ-02. Heating power: 300W in 28V systems, 225W in 14V systems. Changes are not tracked by DEUTZ. Agreement with Parker Hannifin may be necessary. DEUTZ Technical Support offers help with application questions. -
Page 94: Lube Oil System
INSTALLATION MANUAL TD/TCD 2012 / 2013 LUBE OIL SYSTEM DEUTZ engines are laid out for forced-feed oil lubrication. Oil pressure and oil volume flow rate ensure lubrication of the engine and also, to a considerable extent, cooling of the engine.
-
Page 95: Layout Of The Pipe Diameter
INSTALLATION MANUAL TD/TCD 2012 / 2013 TDC 2013 L06 4V Industrial engine TDC 2013 L06 4V Agripower TDC 2013 L04 4V Automotive engine TDC 2013 L06 4V Automotive engine 6.1.2 Layout of the pipe diameter When considering the reference value of approx. 5 (m/s) for the maximum volume flow rate in the system elements (piping, banjo bolts etc.), the theoretical design diameter will be: If possible, the actually existing diameters „D «…
-
Page 96
If for the external lube oil filter system the same design is used as for the engine main filter, the filter element resistance may be neglected when determining the external system resistance. For determining the filter element resistance, please consult the technical support DEUTZ. EDITION 05.2006… -
Page 97: Installation Instructions
INSTALLATION MANUAL TD/TCD 2012 / 2013 Example: System resistance of external filter assembly Engine TCD 2012 L04 2V bei n = 2300 min Lube oil filter bracket: Q = 33.3 ltr/min Equipment Distance: LR = 700 mm ; p = 0.09 bar 2300 0,9 22 45,5 ltr/min…
-
Page 98: External Oil Tank
The engine warranty can only be maintained, if such retrofitting are carried out in consultation with the technical support DEUTZ. External oil tank Engines with extremely flat oil pans (so-called dry sump oil pans) will be equipped with separate oil tanks to accommodate the necessary oil volume.
-
Page 99: Engine Mounting
INSTALLATION MANUAL TD/TCD 2012 / 2013 ENGINE MOUNTING General Basically, a properly designed flexible mounting is preferable to other mounting configurations. A flexible mounting is optimally designed, if the natural frequency of the vibrating system comprising the engine mass and the elasticity of the mounting is at least 40% lower than the lowest exciting frequency of the engine.
-
Page 100
INSTALLATION MANUAL TD/TCD 2012 / 2013 When flexible elements are properly dimensioned, coupling, torque converter, transmission etc. can be flanged to the engine. These attachments can be mounted to the engine in an overhung position, if the following limits for the reversed bending moment between engine crankcase and flywheel housing (SAE housing) are not exceeded: FIGURE 7-1 Table 1… -
Page 101
INSTALLATION MANUAL TD/TCD 2012 / 2013 When installing the engine or the engine/transmission driveline with the fitted mounting elements, it must be ensured that the base is plane parallel and even and the connecting surface is not painted. The bore pattern must be within the specified tolerances of longitudinally ± 2 mm and transversely ±… -
Page 102
INSTALLATION MANUAL TD/TCD 2012 / 2013 Uniform loading of mounting elements. When arranging the mounting elements, ensure uniform loading. This can be achieved by balanced distribution of forces acting on the mounting elements, by changing the distances between the mounts or by changing the number of mounts. The variation in the number of mounts is in most cases the more appropriate approach. -
Page 103
INSTALLATION MANUAL TD/TCD 2012 / 2013 Elastic mounting versions: The DEUTZ scope of delivery offers a “hard” and “soft” version of the engine mounting for the different engine variants which are distinguished by low assembly effort and space requirements. The material is identical, the hardness is determined by the form. Flywheel-side double bearings can be arranged especially depending on the load. -
Page 104: Rigid Mounting
INSTALLATION MANUAL TD/TCD 2012 / 2013 Table 2: Admissible mount loads Fig. Design Material Engine type Load per Max. mounting admissible bracket temperature [°C] Strong Natural rubber TD/TCD 2012 / 2013 2200 -40 / +120 cast mounting 56°+/-3° Shore Soft cast Natural rubber TD7TCD 2012 / 2013…
-
Page 105: Bending Moment On The Sae-Housing
If the customer provides the engine mounting, the distance from its centre to the SAE housing or engine block may not exceed the distances of the corresponding DEUTZ engine series, i.e. DEUTZ track width must also be observed by engine mountings provided by the customer.
-
Page 106: Power Transmission
For details, see VDI-regulation 3840. The engine-related data for a torsional vibration calculation can be made available by DEUTZ – please contact the purchase department or the technical support of the head office. 8.1 Clutches / couplings The design of the clutch/coupling for transmitting the engine power to a drive element, e.g.
-
Page 107: Power Take-Offs
1°. Power take-offs 8.3.1 Auxiliary power take-offs at the engine For the DEUTZ diesel engines TD/TCD2012 and TD/TCD2013, beyond the normal power take- offs such as axial and radial power take-offs at the flywheel axial and radial power take-offs at the front crankshaft end,…
-
Page 108
INSTALLATION MANUAL TD/TCD 2012 / 2013 The admissible power take-offs at the auxiliary drives A, B and C are explained in the following pictures: FIGURE 8-2 All auxiliary drives are geared up EDITION 05.2006 Modification index 00 08 — 3… -
Page 109
INSTALLATION MANUAL TD/TCD 2012 / 2013 FIGURE 8-3 All auxiliary drives are geared up Number of teeth for auxiliary drive C of TC/TCD 2013: Crankshaft = 48 Auxiliary drive C = 37 EDITION 05.2006 Modification index 00 08 — 4… -
Page 110: Axial Power Take-Off At Crankshaft
DIN 5482 B 17×4 (for 30 kW) All items a, b, c with pre-bearing d) Bosch through-bolt version DEUTZ, pilot dia. 50 , cone 1:5 with adapter (max. 20 kW) Air compressors are normally connected to auxiliary PTO A, e.g. 225 m compressor, also with straight drive shaft for steering booster pump.
-
Page 111
INSTALLATION MANUAL TD/TCD 2012 / 2013 FIGURE 8 — 4 EDITION 05.2006 Modification index 00 08 — 6… -
Page 112
INSTALLATION MANUAL TD/TCD 2012 / 2013 FIGURE 8-5 EDITION 05.2006 Modification index 00 08 — 7… -
Page 113: Radial Power Takeoff On The Crankshaft
Radial power takeoff without flange-on outer bearing is not permissible on the flywheel side, see FIG. 8-4 / FIG. 8-5. For the assessment of such drives / constructions, always consult the technical support of the DEUTZ head office. EDITION 05.2006 Modification index 00…
-
Page 114: Radial Power Take-Off, Damper Side (Opposite Side To Clutch)
INSTALLATION MANUAL TD/TCD 2012 / 2013 8.3.3.2 Radial power take-off, damper side (opposite side to clutch) Radial power takeoffs produce an oscillating bending stress of the crankshaft as well as an additional load on the crankshaft mounting by the effective cross force. The following charts are showing the calculation program.
-
Page 115
INSTALLATION MANUAL TD/TCD 2012 / 2013 FIGURE 8-7a Example EDITION 05.2006 Modification index 00 08 — 10… -
Page 116
INSTALLATION MANUAL TD/TCD 2012 / 2013 FIGURE 8-7b Example EDITION 05.2006 Modification index 00 08 — 11… -
Page 117
INSTALLATION MANUAL TD/TCD 2012 / 2013 FIGURE 8-8 Table «A» TD/TCD 2012 2V TCD 2013 L06 2V * Containing all additionally torsion-proof front end-mounted masses mass inertia of flywheel and accessories <= 2,5kgm² EDITION 05.2006 Modification index 00 08 — 12… -
Page 118
INSTALLATION MANUAL TD/TCD 2012 / 2013 FIGURE 8-9, DIAGRAMM 2012 EDITION 05.2006 Modification index 00 08 — 13… -
Page 119
INSTALLATION MANUAL TD/TCD 2012 / 2013 FIGURE 8-10 2013 DIAGRAMM 1-7 Lettering for the following diagrams 2-7 see diagram 1 EDITION 05.2006 Modification index 00 08 — 14… -
Page 120
INSTALLATION MANUAL TD/TCD 2012 / 2013 EDITION 05.2006 Modification index 00 08 — 15… -
Page 121
INSTALLATION MANUAL TD/TCD 2012 / 2013 EDITION 05.2006 Modification index 00 08 — 16… -
Page 122
INSTALLATION MANUAL TD/TCD 2012 / 2013 EDITION 05.2006 Modification index 00 08 — 17… -
Page 123: Installation References
2012/2013 were not yet completely available. Therefore, please contact our purchase department or the technical support of the DEUTZ head office. Due to technical changes and further developments, it is generally recommended to always check the validity of the technical data given here in connection with power take-off by consulting our purchase department.
-
Page 124: Compressor
Two-cylinder compressor (720cm³ stroke) The compressors offer the possibility of a hydraulic pump assembly on the powertrain, design details can be found in the electronic pocket book ELTAB or agreed with DEUTZ Technical Support. 9.3 Pipe connections / pipe design All pipes connected to the compressor must be connected in a permanently sealing and air-tight manner;…
-
Page 125
INSTALLATION MANUAL TD/TCD 2012 / 2013 crankcase breathing (as distant as possible) (seen in the direction of flow of the combustion air) to avoid that oil is sucked in by the compressor. (The TIER III engines are supplied with open crankcase breathing system, so that this point is not relevant for the moment. -
Page 126: Pressure Regulation
INSTALLATION MANUAL TD/TCD 2012 / 2013 Table 2: Sizes pressure pipe Pipe length between compressor and following Diameter Compressor size / kind of cooling system (pressure governor) [ mm ] [ cm³ ] Recommendation: maximally up to 4 [m] 225 + 360 + 720 however see note below water cooled (pipe 18×1,5)
-
Page 127: Energy Saving System (Ess) — Not In The 225Cm³ Compressor
INSTALLATION MANUAL TD/TCD 2012 / 2013 9.4.3 Energy saving system ( ESS ) – not in the 225cm³ compressor During the pumping phase the valve piston (1) closes the valve seat (2). The compressor cylinder sucks the air to be compressed through the suction holes (3). The compressor then operates like a compressor of the earlier type without ESS.
-
Page 128: Engine Cooling System
INSTALLATION MANUAL TD/TCD 2012 / 2013 FIGURE 9-3 Control line (connection 4 at cylinder head – see circuit diagram compressor) The control line for the compressor with ESS (energy saving system) must laid by the customer with a continuous inclination between the cylinder of the compressor and the pressure governor or the air drier (connection 4).
-
Page 129: Compressor Design
Optionally, individual compressors are equipped with a power take-off for connecting e.g. auxiliary steering pumps to the compressor crankshaft. Generally, the power take-off is suitable for a take-off of 82Nm. Auxiliary steering pump as per DEUTZ scope of supply (Presently available only for the 225cm³ variant): Vane cell pumps of ZF 21 cm³/min (max 16.l/min delivery, controlled) up to 150 [bar] pressure…
-
Page 130: Coolant Preheating
(to avoid heat losses upon preheating) and internal engine or component preheating. The details for a certain application are to be clarified with the technical support DEUTZ 10.1 Coolant preheating The liquid-cooled DEUTZ diesel engines BF M 1012/1013 and BF M 2012/2013 are equipped for the subsequent installation of a coolant heating system via heating rod (socket heating), PN 0419 8898 KZ 0130-63, having a heating capacity of abt.
-
Page 131: Radiator Cover (Winter Cover)
INSTALLATION MANUAL TD/TCD 2012 / 2013 10.2 Radiator cover (winter cover) When liquid-cooled engines are operated in winter, relevant functions of thermostat and/or viscous fan clutches keep the coolant temperature at optimal level. As a result of installation conditions and equipment applications, additional measures may be required to keep the engine and the engine compartment «warm».
-
Page 132: Vibration Damper
INSTALLATION MANUAL TD/TCD 2012 / 2013 VIBRATION DAMPER 11.1 Cooling system The torsional vibration damper fitted to the free crankshaft end of the engine must emit vibration energy to the environment in the form of heat. To prevent damage to the vibration damper, it must be made sure that the heat energy generated in the vibration damper is dissipated by cooling.
-
Page 133: Sound Insulation / Sound Absorption
INSTALLATION MANUAL TD/TCD 2012 / 2013 SOUND INSULATION / SOUND ABSORPTION 12.1 General The nose of a diesel engine originates from many individual noise sources, e.g. intake and exhaust noise, injection-, combustion- noise, noise generated by the operation of valves, gears, bearings and the blower.
-
Page 134: Sound Insulation And Absorption Materials
INSTALLATION MANUAL TD/TCD 2012 / 2013 In rooms or capsules the active noise level can be increased by unhindered reflections from the walls which could cause additional efforts for insulation measures. To suppress vibrations and thus the noise emissions from walls or body parts, these must be subjected to appropriate damping measures.
-
Page 135: Figure
INSTALLATION MANUAL TD/TCD 2012 / 2013 FIGURE 12 – 1 Material examples EDITION 05.2006 Modification Index 00 12 — 3…
-
Page 136: Additional Measures Required For Engine Enclosures
INSTALLATION MANUAL TD/TCD 2012 / 2013 12.4 Additional measures required for engine enclosures The sound insulation features a high thermal insulation which must be considered for the heat dissipation. The temperatures inside an engine enclosure can considerably increased; therefore, attention must be paid to the temperature resistance of the engine components and used construction elements.
-
Page 137: Heating Of Engine Compartment
INSTALLATION MANUAL TD/TCD 2012 / 2013 13. HEATING OF ENGINE COMPARTMENT 13.1. Radiation heat The air in the engine compartment is heated up by the radiation heat of the engine, the exhaust gas system, the power take-off units at the engine (e.g. generators, transmissions, hydraulic pumps, compressors etc.) as well as of possible auxiliary systems (heating, hot water boiler etc.).
-
Page 138: Air Volume For Ventilating The Engine Compartment
The DEUTZ engines TC/TCD 2012/2013 are provided without re-circulating crankcase breathing systems. If installation assistance is required, please ask the technical support DEUTZ EDITION 05.2006 Modification index 00 13 — 2…
-
Page 139: Installation Survey By Measurement
INSTALLATION MANUAL TD/TCD 2012 / 2013 INSTALLATION SURVEY BY MEASUREMENT For a final assessment of an engine installation, the following examinations must be made by measurement. 14.1 Temperature test: In installed condition (in the equipment), an engine must operate at its full power- without restrictions.
-
Page 140: Pressure Measurement
INSTALLATION MANUAL TD/TCD 2012 / 2013 Temperature at the starter motor / starter solenoid (ambient, housing) Fuel temperature (in tank, if necessary, in front of delivery pump inlet and in the return line) Temperature at the vibration damper (ambient / housing) To complete the temperature examinations, the „Hot-Shut-Down“…
-
Page 141: Temperature Limit Values
INSTALLATION MANUAL TD/TCD 2012 / 2013 Measuring point connections: for pressures: Threaded nipple M12x1,5 or threaded bore M10x1 (P1,P2,P3,P5,P6) Threaded nipple M10x1 (P4) for temperature: Threaded bore M8x1 or M14x1,5 (6,7,8,9,10) 14.3. Temperature limit values The engine installation must be such that, during continuous operation of the engine under nominal load (or at max.
-
Page 142
Fuel main filter: Fuel pre-filter (Racor): Ambient temperature – crankcase bleeding valve Ambient temperature – compressor water-cooled, not a Deutz part Vibration damper Ambient temperature: measured, 100mm axially from damper Component temperature: measured on upper ring Engine mounting (DEUTZ BS) Ambient temperature –… -
Page 143: Diagram Of Measuring Points
INSTALLATION MANUAL TD/TCD 2012 / 2013 14.4 Diagram of measuring points FIGURE 14-1 EDITION 05.2006 Modification index 00 14 — 5…
-
Page 144: Electrics
INSTALLATION MANUAL TD/TCD 2012 / 2013 ELECTRICS 15.1 Starter and battery capacities, Battery switch / master controller / starter switch In view of its short-term high current consumption, the starter is decisive for dimensioning the battery. The starter converts the electrical energy stored in the battery into mechanical energy. It can develop its capacity only, if a battery of sufficient capacity is available.
-
Page 145
INSTALLATION MANUAL TD/TCD 2012 / 2013 The admissible tightening torques for nuts and screws at terminals 30, 50 may be taken form the starter drawings. No additional consumer may be connected at terminal 50, these must be connected to terminal 45. The cables must be fixed after about 30 cm. -
Page 146
INSTALLATION MANUAL TD/TCD 2012 / 2013 If a battery with a larger cold-start test current than recommended is used, the starter can become mechanically and thermally overloaded. If the cold-start test currents are too small, the cold starting behaviour deteriorates; the starting function is no more ensured. -
Page 147
INSTALLATION MANUAL TD/TCD 2012 / 2013 Starter- Rated Admiss. Battery cold- Starter short- Circuit Min. / max. capacity voltage battery start test circuit current diagram of admissible [kW] capacity[Ah] current total [A] (+20°C) [Volt] batteries resistance (27°C) at supply cable l kp [A](-18°C) resistance Batt… -
Page 148: Dimensioning Of The Starter Main Cable
INSTALLATION MANUAL TD/TCD 2012 / 2013 *** This battery capacity is absolutely required, if the max. cold-start limit temperature of the engine (assignment starter – engine type as per pocket book) must be reached. The minimal supply cable resistance of the starter main cable (advance/reverse) with 1 Milliohm (MELCO starter 2mOhm) must be observed.
-
Page 149
4800 0,687 / I iBatt +20°C Attention: The formula only applies in connection with a BOSCH starter system! For MELCO starter systems it is necessary to consult DEUTZ Technical Support at the moment. EDITION 05.2006 Modification Index 00 15 — 6… -
Page 150: Dimensioning Of Control Line To The Starter
(instead of the picking up relay). Required rated cross section of the control cable for engines without cable harness as per DEUTZ scope of supply The rated cross section of the control cable is determined by determining the supply line resistance of the control cable between battery plus pole via starter switch up to terminal 50 (switch relay starter).
-
Page 151
Required cross section of the control cable for engines with cable harness as per DEUTZ scope of supply The portion of the control cable in the cable harness has a line resistance, which must be considered when determining the cross section of the residual length of the control cable. -
Page 152: Triggering Protection Terminal 50
This means that between terminal 50 of the starter solenoid switch and the output of the starter key (terminal 50) no additional consumers are permitted to be connected as this can lead to starter defects due to a hindered reeling out – unless a start lock relay e.g. DEUTZ No. 0421 3663 is connected.
-
Page 153
INSTALLATION MANUAL TD/TCD 2012 / 2013 15.6 Start lock relay — see TPI 0199-99-0217c The start lock relay avoids reeling in of the starter pinion with running engine and, in this way, protects the starter pinion and the girth gear against destruction. The start lock function can be represented by a separate start lock relay or integrated in the electronic engine control (EMR III). -
Page 154
INSTALLATION MANUAL TD/TCD 2012 / 2013 Actual line cross section A [mm²] : The line cross section A determined by calculation must be rounded to the next higher value Aw according to table «copper line cross sections». Cross sections below 1.5 mm² are not admissible! Actual voltage drop U [V] : VList… -
Page 155: Admissible Voltage Drops
DIN VDE 0298, Part 4. Remark 5: smaller outer diameters can be represented with other insulation material (values in brackets for material TPE-E, line 13Y as per DEUTZ works standard 823 600-2, temp.-resistant from -40°C…+150°C, e.g. for engine cable harness). EDITION 05.2006…
-
Page 156: Generators And Regulators
However, this room must not be under vacuum pressure. The availability is to be inquired over the technical support DEUTZ Internal width of the hose line: Upon sucking from free space: 60 mm for 55, 80 Amp.
-
Page 157: Three-Phase Generators (Charging Balance)
All generators with attached governors included in the DEUTZ scope of supply are protected against overvoltage from the on-board mains. Increasingly, however, electronic components are connected to the mains. These electronic components are very sensitive to voltage peaks generated by the generator or during switching operations in the mains.
-
Page 158
INSTALLATION MANUAL TD/TCD 2012 / 2013 15.10.2 Dimensioning of the B+ line from the generator (charging line) Dimensioning of the B+ line (from generator B to battery plus-pole) depends on the maximally admissible voltage loss. Max. admiss. voltage loss = 0,65 V 24V-systems with ground connection total. -
Page 159: Application And Operating Conditions For Bosch Compact Generators
DEUTZ is unable to test all the requirements according to the BOSCH customer document in the course of an engine installation inspection. The equipment manufacturer is therefore jointly responsible for meeting the requirements of this customer document.
-
Page 160
INSTALLATION MANUAL TD/TCD 2012 / 2013 Attention: Disassembly of the battery cable can loosen the generator-side B+nut below it. It is essential to re-tighten the nut in this case. The equipper must ensure that third persons concerned (car repair shops, end customers…) are informed of this in an appropriate manner. (2.5) Generator drive The generator is driven by a V-belt or poly V-belt. -
Page 161: Electronic Engine Equipment
Order no. 0399 1990/5 (German) or 0399 1991/5 (English) 15.11.3 Engine monitoring The engine is monitored by the electronic engine control. Sensors and cable harness up to the engine control unit are delivered by DEUTZ. See the aforementioned installation regulation for installation instructions. EDITION 05.2006…
-
Page 162: Cold Start Aid
INSTALLATION MANUAL TD/TCD 2012 / 2013 15.11.4 Cold start aid The engines are equipped with heating plugs as a standard cold start aid. By pre-heating of the heating plugs in the combustion chamber of the diesel engine, these guarantee a reliable cold start on the one hand and, on the other hand, the emissions of the still “cold running”…
-
Page 163: Accessibility For Servicing And Maintenance Jobs Start-Up Procedure
INSTALLATION MANUAL TD/TCD 2012 / 2013 16. ACCESSIBILITY FOR SERVICING AND MAINTENANCE JOBS, START-UP PROCEDURE 16.1 General A correct installation must not only meet the technical requirements but also ensure an easy access to parts requiring maintenance work. If this accessibility is not given, there is always the risk that the necessary maintenance jobs are not carried out at all or not at the specified intervals.
-
Page 164: Maintenance Jobs Not Requiring Easy Access
INSTALLATION MANUAL TD/TCD 2012 / 2013 Example of a maintenance sticker FIGURE 16 — 1 Maintenance interval dependent on the filter size, with double-filter according to standard 2 x 1,4ltr. = 1000Bh 16.3 Maintenance jobs not requiring easy access Maintenance jobs which should be carried out with direct access wherever practicable, i.e. without having to remove parts or plates and without having to overcome other kinds of access problems: Checking alternators and regulators…
-
Page 165: Engine Commissioning
INSTALLATION MANUAL TD/TCD 2012 / 2013 16.4 Engine commissioning: Venting the fuel system: On long fuel suction pipe, wet the inner parts of the fuel hand supply pump with fuel to guarantee an immediate suction effect of the manual supply pump. Unlock the bayonet connection of the hand supply pump by turning to the left.
-
Page 166: Annex
INSTALLATION MANUAL TD/TCD 2012 / 2013 ANNEX 17.1 Calculation formulae for internal combustion engines Exhaust gas volume flow rate: In the pocket book, the exhaust gas volume flow rate M [kg/h] is indicated related to 25 °C. To determine the actual volume flow rate V , the first «cold»…
-
Page 167: Formal Connections Concerning Fans And Coolant Pumps
[Nm] 18.2 Formal connections concerning fans and coolant pumps The centrifugal pumps used as coolant pumps on DEUTZ diesel engines and the fans are fluid flow engines and, as such, are subject to the same physical laws. For the calculation of the volume flow rates, pressures and the power requirement at different speeds, the following equations apply.
-
Page 168: Checklist For Inspection Of Starter Motor System
INSTALLATION MANUAL TD/TCD 2012 / 2013 17.3 Checklist for inspection of starter motor system Cable laying, cable dimensioning, cable connection: Main cable (to terminal 30) and control cable (to terminal 50) have to be routed in that way that they do not come into contact (prevent short circuit) The cables have to be fixed approx.
-
Page 169: Engine Coolant (Tr 0199 — 99 — 1115)
INSTALLATION MANUAL TD/TCD 2012 / 2013 17.4 Engine coolant Technical Circular 0199-99-1115 Delivery specification coolants H-LV 0161 0188 US 8039-40 17.5 Engine lube oil Technical circular 0199 – 99 – 1119 Technical circular 0199 – 99 – 3002 17.6 Fuel Technical circular 0199 –…
- Manuals
- Brands
- Deutz Manuals
- Engine
- TCD 2012 L04/06 V2
- Operation manual
-
Contents
-
Table of Contents
-
Bookmarks
Quick Links
Operation Manual
TCD 2012 L04/06 V2
TCD 2013 L04/06 V2
Related Manuals for Deutz TCD 2012 L04/06 V2
Summary of Contents for Deutz TCD 2012 L04/06 V2
-
Page 1
Operation Manual TCD 2012 L04/06 V2 TCD 2013 L04/06 V2… -
Page 2
Only DEUTZ original parts may be used when repairs — Danger to life. manufacturer. The engine may only be used, carrying out maintenance/repair work on the maintained and repaired by persons who are engine. -
Page 3
Operation Manual TCD 2012 L04/06 V2 TCD 2013 L04/06 V2 312 1890 en Engine number: Please enter the engine number here. This will simplify the handling of customer service, repair and spare parts queries (see Section 2.1). Illustrations and data in this instruction manual are subject to technical changes in the course of improvements to the engines. -
Page 4
Foreword Dear customer, The liquid-cooled engines made by DEUTZ are developed for a wide variety of applications. An extensive range of variants ensures that the respective special requirements are met. Your engine is equipped according to the installation, i.e. not all the parts and components described in this instruction manual are installed on your engine. -
Page 5: Table Of Contents
Contents Operation General Care and maintenance Initial commissioning Engine description work 3.1.1 Filling engine oil Engine type Lubrication system 3.1.2 Filling fuel 2.1.1 Company plate 6.1.1 Oil change intervals 3.1.3 Filling / bleeding cooling system 2.1.2 Location of company plate 6.1.2 Checking oil level, changing engine oil 3.1.4…
-
Page 6
Contents Add-on parts 6.7.1 Battery 6.7.2 Three-phase current generator 6.7.3 Transportation suspension Faults, causes and remedies Fault table Engine management 7.2.1 Engine protection function of the electronic engine controller EMR3 7.2.2 Using the diagnosis button 7.2.3 Table of fault blink codes Engine corrosion protection Corrosion protection Technical data… -
Page 7: General
It goes without saying that DEUTZ Diesel conscientiously. Special care should be taken parts. Original parts from DEUTZ AG are Engines meet the highest standards for en-…
-
Page 8: Engine Description
Engine description 2.1 Engine type 2.2 Engine diagrams 2.3 Lube oil circuit 2.4 Fuel circuit 2.5 Coolant circuit 2.6 Electrics…
-
Page 9: Location Of Company Plate
Engine description 2.1 Engine type 2.1.1 Company plate 2.1.2 Location of company plate © 35 985 0 © 38 987 1 © 43 834 0 The company plate C is fixed to the cylinder The engine type A, engine number B and the head cover crankcase.
-
Page 10
Engine description 2.1 Engine type 2.1.3 Engine number 2.1.4 Cylinder numbering © 43 833 0 © 38989 0 The engine number is stamped on the crankcase The cylinders are counted consecutively, starting (arrow) and on the company plate. from the flywheel. -
Page 11
Engine description 2.2 Engine diagrams 2.2.1 Operation side TCD 2012 L04 2V Oil filler Combustion air inlet Cover Generator Fuel pump Tension pulley with torsion spring Oil cooler Exchangeable fuel filter 10 Exchangeable lube oil filter 11 Oil tray 12 Hydraulic pump or compressor mounting possibility 13 Flywheel 14 Crankcase bleeding valve… -
Page 12
Engine description 2.2 Engine diagrams 2.2.2 Starter side TCD 2012 L04 2V 18 Exhaust manifold 19 Turbocharger 20 Oil filler (optional) 21 Engine mounting 22 Oil return line from turbocharger 23 Relay (starter) 24 V-rib belt 25 Coolant inlet 26 Coolant outlet 27 Coolant pump 28 Connection cabin heater or compensation line… -
Page 13
Engine description 2.2 Engine diagrams 2.2.3 Operation side TCD 2012 L06 2V Oil filler Combustion air inlet Transport eyes Generator Fan hub Fuel pump V-rib belt drive on crankshaft V-rib belt Tension pulley with torsion spring 10 Coolant pump 11 Exchangeable lube oil filter (1x optional) 12 Oil drain screw 13 Oil dipstick 14 Lube oil cooler… -
Page 14
Engine description 2.2 Engine diagrams 2.2.4 Starter side TCD 2012 L06 2V 23 Crankcase bleeding valve 24 Charge air pipe 25 Solenoid valve for exhaust gas recirculation 26 SAE housing 27 Oil tray 28 Starter cover 29 Oil return line from turbocharger 30 Exhaust turbocharger 31 Charge air connection to charge air cooler 32 Coolant inlet… -
Page 15
Engine description 2.2 Engine diagrams 2.2.5 Operation side TCD 2013 L04 2V Combustion air inlet (heating flange installation facility, optional) Connection cabin heater or compensation line Fan (drive coolant pump) Generator Belt pulley on crankshaft V-belt Fuel pump drive Exchangeable fuel filter Exchangeable lube oil filter 10 Oil cooler 11 Drive facility (e.g. -
Page 16
Engine description 2.2 Engine diagrams 2.2.6 Starter side TCD 2013 L04 2V 19 Oil filler (optional) 20 SAE housing 21 Engine mounting 22 Oil drain screw 23 Oil tray 24 Starter 25 Lube oil return from turbocharger 26 Turbocharger 27 Coolant inlet 28 Charge air connection to cooler 29 Coolant outlet 30 Exhaust manifold… -
Page 17
Engine description 2.2 Engine diagrams 2.2.7 Operation side TCD 2013 L06 2V Combustion air inlet Oil filler Transport eyes Generator Coolant pump Exchangeable lube oil filter Exchangeable fuel filter Oil tray Oil dipstick 10 Oil drain screw 11 Oil return line crankcase bleeding 12 Engine mounting 13 SAE housing 14 Plug to control unit… -
Page 18
Engine description 2.2 Engine diagrams 2.2.8 Starter side TCD 2013 L06 2V 19 Turbocharger 20 Exhaust manifold 21 Starter 22 Lube oil line to turbocharger 23 Coolant drain screw 24 Coolant inlet 25 V-rib belt 26 Fan 27 Tension pulley with torsion spring 28 Connection compensation line 29 Ventilation line to compensation tank 30 Coolant outlet from engine to cooler… -
Page 19: Lube Oil
Engine description 2.3 Lube oil circuit 2.3.1 Lube oil diagram (example) Oil tray Intake pipe Lube oil pump 3.1 Safety valve Lube oil cooler 4.1 Return shutoff valve (only in 2012) 4.2 By-pass valve 4.3 By-pass valve oil filter 4.4 Pressure control valve Exchangeable lube oil filter Main oil pipe 6a Internal exhaust gas recirculation…
-
Page 20
Engine description 2.4 Fuel circuit 2.4.1 Fuel diagram Fuel container Fuel pre-filter with pre-pressure pump possibility for filling the low pressure area (to be provided by the customer) Line to fuel pump Fuel pump Fuel filter Fuel supply line to fuel control unit Rail High-pressure pump Fuel line to injector… -
Page 21
2.5 Coolant circuit Engine description 2.5.1 Coolant diagram (example) © 43 897 4… -
Page 22: Coolant
2.5 Coolant circuit Engine description Coolant outlet at the cooler Thermostat Coolant feed line to pump Coolant pump Lube oil cooler Cylinder cooling Cylinder head cooling Coolant inlet to heating Heating 10 Coolant to thermostat 11 Heating connection 12 Compensation line 13 Ventilation line to compensation tank 14 Coolant outlet to cooler 15 Compensation tank…
-
Page 23: Electrical Cable Connections For
Engine description 2.6 Electrics 2.6.1 Electrical cable connections for monitoring Solenoid valve EGR (optional) Coolant temperature Charge air pressure/temperature transmitter Connection facility example: Control unit not mounted on the engine Engine control unit Speed governor via crankshaft Rail pressure, on side of rail Oil level transmitter (optional) Oil pressure transmitter 10 Fuel pressure…
-
Page 24
Engine description 2.6 Electrics Other application-side components (depending on the application) Water trap fuel filter, see chap. 6.2.3 Override key, see chap. 3.3.1 (for temporary bypassing of the engine protection functions) Coolant level transmitter Separate engine stop switch Fan control Switch for brake contact, engine brake, clutch Drive speed sensor, drive speed control unit (+ — keys, for speed increase reduction) -
Page 25: Initial Commissioning
Operation 3.1 Initial commissioning 3.2 Starting 3.3 Operation monitoring 3.4 Shutting down 3.5 Operating conditions…
-
Page 26: Filling Engine Oil
Operation 3.1 Initial commissioning 3.1.2 Filling fuel 3.1.1 Filling engine oil © 43 838 2 © 43 843 2 The engines are generally supplied without oil Only use clean, standard, branded diesel fuel. For filling. fuel quality see 4.2. Fill engine with lube oil through the oil filler (1) Depending on the outdoor temperature, use on the cylinder head cover.
-
Page 27: Filling / Bleeding Cooling System
Operation 3.1 Initial commissioning 3.1.3 Filling / bleeding 3.1.4 Other preparations cooling system Check battery and cable connections, see 6.7.1. Trial run — After preparations carry out a short trial run of approx. 10 min. Do not fully load the engine. During and after the trial run — Check engine for tightness.
-
Page 28: Electrical Starting
Operation 3.2 Starting 3.2.1 Electrical starting without cold start aid Before starting make sure that Insert key there is nobody in the engine/ — Step 0 = no operating voltage. work machine danger area. Turn key to the right After repairs: Check that all — Step 1 = operating voltage, protective equipment is — Warning lights light up.
-
Page 29
Operation 3.2 Starting with cold start aid Heating plug/heating flange © 26 411 0 Insert key. — Step 0 = no operating voltage. Turn key to the right. — Step 1 = operating voltage, — Warning lights 1+2+3 light up. — Pre-heat until heating indicator goes out. -
Page 30: Operation Monitoring
Operation 3.3 Operation monitoring 3.3.1 Engine oil pressure The EMR3 system monitors the engine condition and itself. Oil pressure light Oil pressure gauge The states are indicated by the diagnostic lamp. Lamp test: The diagnostic lamp lights for about 2s after ignition (ignition lock stage 1).
-
Page 31: Coolant Temperature
Operation 3.3 Operation monitoring 3.3.2 Coolant temperature 3.3.3 Coolant level © 26 246 0 © 26 291 1 The needle of the temperature display should Light on coolant level display comes on (contact always be in the green area, and only as an is via float switch/ level probe if coolant level exception in the yellow/green area.
-
Page 32: Electrical Shutdown
Operation 3.4 Shutting down 3.4.1 Electrical shutdown © 26 411 0 Turn the key to the left (to step 0) and remove. Warning lights go out. Note: The control unit remains active for about another 40 seconds to save the system data (lag) and then switches itself off.
-
Page 33: Operating Conditions
Operation 3.5 Operating conditions 3.5.1 Winter operation Lube oil viscosity Battery — A well-charged battery is a — Select the viscosity (SAE class) prerequisite for a good cold start, according to the ambient temperature see 6.7.1. before starting the engine, see 4.1.2. — Heating the battery to approx.
-
Page 34: High Ambient Temperature
Operation 3.5 Operating conditions 3.5.2 High ambient temperature, high altitude When the altitude or ambient temperature increases, the air density decreases. This impairs the maximum engine performance, exhaust quality, temperature level and, in extreme cases, the starting performance. For transient operation, usage up to 1500 m altitude and a temperature of 30 °C is permissible, for stationary operation 1000 m altitude and a temperature of 40 °C is…
-
Page 35: Operating Substances
Operating substances 4.1 Lube oil 4.2 Fuel 4.3 Coolant…
-
Page 36
Biodegradable lube oils may be used in dominant. Basically all engine oils are mixable so DEUTZ engines if they meet the requirements of that a complete lube oil change from one oil type this operating manual. -
Page 37
Operating substances 4.1 Lube oil 4.1.1 Quality Lube oils are classified by DEUTZ according to DEUTZ lube oil quality classes DQC I — 02 DQC II — 05 DQC III — 05 DQC IV — 05 their performance and quality class (DQC : Deutz… -
Page 38
Salzbergen Wintershall TFG 10W-40 Europe Texaco Ursa Super TDX 10W-40 Europe Ursa Premium FE 5W-30 Europe TOTAL TOTAL RUBIA TIR 8600 10W-40 worldwide EXPERTY 10W-40 worldwide T 4-1-3 Release list for DEUTZ lube oil quality class DQC III — 05… -
Page 39
Fuchs Titan Cargo SL 5W-30 worldwide FUCHS EUROPE SHELL International Shell Rimula Ultra 5W-30 Europe, code country-specific, varies Shell Rimula Ultra 10W-40 Europe, code country-specific, varies T 4-1-4 Release list for DEUTZ lube oil quality class DQC IV — 05… -
Page 40
Operating substances 4.1 Lube oil 4.1.2 Quality The ambient temperature at the installation site or area of application of the engine is decisive for the choice of the right viscosity class. Too high a viscosity can lead to starting difficulties, too low a viscosity can endanger the lubrication effect and cause high lube oil consumption. -
Page 41
For questions regarding this please contact Paraffin mixing proportion your DEUTZ partner. fuels defined by law. These correspond to the diesel fuels according to EN 590 and ASTM D 975 Only carry out mixing in the tank! described in this operating manual. -
Page 42
(city water). carbonate hardness proportion of total hardness min 3 dGH. Water quality data are obtainable from the local waterworks. A test case can be requested from DEUTZ Service (order no. 1213 0382) for checking your water quality. -
Page 43: Coolant Preparation
The inspection of the concentration of cooling system preservative can be carried out with The best results are achieved with DEUTZ cooling standard testing devices (e.g. refractometer). system preservatives: Container Order no.
-
Page 44: Maintenance
Maintenance 5.1 Maintenance schedule 5.2 Maintenance diagram 5.3 Maintenance work carried out…
-
Page 45
Maintenance 5.1 Maintenance schedule check= set= clean=L renew= Industrial engines ⇓ check 2x daily before or during the 1st trial run, during the running-in phase or The engine maintenance times given are maximum permissible job when commissioning new and overhauled engines times. -
Page 46
Maintenance 5.1 Maintenance schedule clean= L check= set= renew= Enhancements or modifications max. permissible job times in operating hours (oh) every for engines with EPA acceptance ⇓ check 2x daily before or during the 1st trial run, during the running-in phase or The engine maintenance times given are maximum permissible job times. -
Page 47
6 000 oh E 60 extended partial overhaul authorised specialists 12 000 oh E 70 general overhaul authorised specialists *) approximate value, depends on the type of engine application and/or regular engine maintenance. Please contact your responsible DEUTZ Service partner. -
Page 48
Maintenance 5.2 Maintenance diagram The maintenance diagram shown on this page is supplied with every engine in self- adhesive form. It should be stuck onto a well visible location on the engine or equipment. Check that this is the case! If not, request a replacement from your engine or equipment supplier! The maintenance schedule is decisive for… -
Page 49
Maintenance 5.3 Maintenance work carried out Signature / stamp Op. hrs. Date Signature / stamp Op. hrs. Date 50-150 1000 1250 1125 1500 1375 1750 1625 2000 1875 2250 2115 2500 2375 2750 * after commissioning new and overhauled engines The maintenance work carried out methodically can be recorded in the table and confirmed. -
Page 50
Maintenance 5.3 Maintenance work carried out Op. hrs. Date Signature / stamp Op. hrs. Date Signature / stamp 2875 3000 3125 3250 3375 3500 3625 3750 3875 4000 4125 4250 4375 4500 4625 4750 4875 5000 5125 5250 5375 5500 5625 5750 The maintenance work carried out methodically can be recorded in the table and confirmed. -
Page 51
Maintenance 5.3 Maintenance work carried out Signature / stamp Op. hrs. Date Signature / stamp Op. hrs. Date 6000 5875 6250 6125 6375 6500 6625 6750 6875 7000 7125 7250 7375 7500 7625 7750 7825 8000 8125 8250 8375 8500 8625 8750 The maintenance work carried out methodically can be recorded in the table and confirmed. -
Page 52
Maintenance 5.3 Maintenance work carried out Op. hrs. Date Signature / stamp Op. hrs. Date Signature / stamp 8875 9000 9250 9125 9500 9375 9750 9625 10000 9875 10250 10125 10500 10375 10750 10625 11000 10875 11250 11125 11500 11375 11750 11625 The maintenance work carried out methodically can be recorded in the table and confirmed. -
Page 53: Add-On Parts
Care and maintenance work 6.1Lubrication system 6.2Fuel system 6.3Cooling system 6.4Combustion air filter 6.5Belt drive 6.6Setting work 6.7Add-on parts…
-
Page 54
Care and maintenance work 6.1 Lubrication system 6.1.1 Oil change intervals If the lube oil change intervals are planned The oil change times depend on the engine in terms of operating hours, the lube oil application and the quality of the lube oil. change intervals for installed engines 6.1.1.1 apply. -
Page 55
Care and maintenance work 6.1 Lubrication system 6.1.1.1 Lube oil change intervals for installed engines Lube oil quality Deutz lube oil quality class DQC I-02 DQC II-05 DQC III-05 DQC iV-05 ACEA specification E2-96 E3-96/E5-02/E07-04 E4-99/E6-04 E4-99/E6-04 see chap 6.1.1.3 only fully synthetic… -
Page 56
Care and maintenance work 6.1 Lubrication system 6.1.2 Checking oil level, changing engine oil 6.1.2.1 Checking oil level 6.1.2.2Changing engine oil © 26 023 0 © 26 022 0 © 25 729 0 Position the engine or vehicle so as to be level. Warm up the engine. -
Page 57
Care and maintenance work 6.1 Lubrication system 6.1.3 Changing oil filter © 25 882 0 © 25 880 0 © 25 881 0 When anti-rotation lock is installed: Clean the sealing surface of the filter support Tighten the lube oil filter cartridge with a three- Loosen clamping screws and remove for any dirt there may be. -
Page 58
Care and maintenance work 6.1 Lubrication system 6.1.4 Cleaning / changing oil filter (cup) © 30 0 74 1 © 43 937 0 © 300 74 0 Change the round sealing ring 2 and lightly oil. Switch off engine. Collect any lube oil which may run out. Press new paper filter cartridge 5 into the clip Loosen lube oil filter cover 1 with two or three Crease the paper filter cartridge 5 in the… -
Page 59
Care and maintenance work 6.1 Lubrication system… -
Page 60
Care and maintenance work 6.2 Fuel system Additional regulations for DEUTZ Common Cleanliness hints and measures for Regulations for working on the fuel system handling DEUTZ Common Rail Systems Rail Systems Engine must be switched off! Danger to life! Never work on… -
Page 61
Care and maintenance work 6.2 Fuel system 6.2.1 Changing fuel filter © 25 882 0 © 25 880 0 © 25 881 0 Close fuel stopcock. Lightly oil the fuel filter cartridge or wet with Tighten the fuel filter cartridge with a three- Loosen fuel filter cartridge with standard tool diesel fuel. -
Page 62
Care and maintenance work 6.2 Fuel system 6.2.2 Cleaning / changing fuel filter (cup) © 43 938 0 © 30 074 0 © 43 937 0 Switch off engine. Collect any fuel which may run out. Change the round sealing ring 2 and lightly oil. Loosen fuel filter cover 1 with two or three Slightly bend paper filter cartridge 5 sideways Press new paper filter cartridge 5 into the clip… -
Page 63
Care and maintenance work 6.2 Fuel system 6.2.3 Fuel pre-filter, changing / bleeding filter insert 1 Fuel supply to pump Clean any dirt from the sealing surface of the 2 Fuel return from control block FCU new filter cartridge (5) and the reverse side (Fuel Control Unit) of the filter head 3 Fuel hand pump with bayonet… -
Page 64
Care and maintenance work 6.3 Cooling system 6.3.1 Cleaning intervals 6.3.2 Cleaning cooling system The cooling system soiling depends on thetype of engine application. The risk of soiling is increased by oil and fuel residues on the engine. Therefore pay particular attention to tightness when operating under high dust exposure. -
Page 65
Care and maintenance work 6.3 Cooling system © 43 903 0 Cleaning with steam or hot water Remove oil and greasy residues with a gentle jet setting (do not spray directly on sensitive engine parts, e.g. generator, wiring, electrical- components, fan drive). Warm up the engine so that the water residues evaporate. -
Page 66
Care and maintenance work 6.3 Cooling system 6.3.4 Filling / bleeding 6.3.3 Emptying cooling system cooling system © 43 839 0 © 39 850 1 Open cooler cover. Open cooler cover. The cooling system (if constructed under Position collecting dish underneath locking Loosen locking screw item 1 (chap.6.3.3). -
Page 67
Care and maintenance work 6.4 Combustion air filter 6.4.1 Cleaning intervals The soiling of the combustion air filter de- pends on the dust content of the air and the selected filter size. If a high dust exposure is to be expected, a cyclone separator can be connected to the combustion air filter. -
Page 68
Care and maintenance work 6.4 Combustion air filter 6.4.2 Emptying cyclone pre- 6.4.3 Cleaning oil bath air filter separator © 25 886 0 © 25 887 1 Loosen wing nut 1 and lift housing cover 2. Turn off the engine and wait approx. 10 min In the event of heavy soiling, clean filter hou- Remove the dust container 3 from the base of until the oil has run out of the filter housing 1. -
Page 69
Care and maintenance work 6.4 Combustion air filter 6.4.4 Dry air filter Dust discharge valve Filter cartridge © 25 888 1 © 25 889 0 Empty the dust discharge valve 1 by squee- Check filter cartridge for damage to the filter Open clamping bracket 1. -
Page 70
Care and maintenance work 6.5 Belt drive 6.5.1 Checking V-belt 2013 example © 43 894 0 © 26 261 1 Visual inspection of entire length of V-belt for To check the V-belt tension — Carefully lift the measuring device, without damages. -
Page 71
Care and maintenance work 6.5 Belt drive 6.5.2 Changing V-rib belt 6.5.3 Checking wear limit of V-rib belt © 43 851 0 © 31 814 4 The wear limit of the V-rib belt is checked as Push tension roller 1 with ratchet 3 in direction follows: of arrow until locking pin 4 can be fixed in the Check the distance between the projection… -
Page 72
Care and maintenance work 6.6 Setting work 6.6.1 Checking valve clearance, setting if necessary © 43 849 0 © 43 831 1 Loosen lock nut 1 Hold rotation angle disc 3 tight against Before setting the valve clearance allow the twisting. -
Page 73
Care and maintenance work 6.6 Setting work © 44 304 0 © 44 305 0 Valve clearance setting inlet valve Hold rotation angle disc 3 tight against twisting. in exhaust gas return line (EGR): Tighten the lock nut 6. Loosen lock nut 6. Perform the setting on every inlet valve (see Place rotation angle disc 3 with crow’s foot chap. -
Page 74
Care and maintenance work 6.6 Setting work 6.6.2 Setting control piston clearance in exhaust gas recirculation (EGR) © 43 830 1 © 43 832 0 Loosen lock nut 1. After setting the valve clearance, the control Place the rotation angle disc and socket wrench piston clearance should be set as follows: insert on the setting screw 2 Place the turning device over the fastening… -
Page 75
Care and maintenance work 6.6 Setting work 6.6.3 Diagram for setting valve / control piston clearance Engine TCD 2012/2013 L04 2V Engine TCD 2012/2013 L06 2V Ignition sequence: 1–3–4–2 Ignition sequence: 1–5–3–6–2–4 Valves Cylinder Valves Cylinder overlap overlap set to set to Valve operlap: Outlet valve not yet closed, inlet Valve operlap: Outlet valve not yet closed, inlet… -
Page 76: Battery
Care and maintenance work 6.7 Add-on parts 6.7.1 Battery 6.7.1.1 Checking battery and cable 6.7.1.3 Checking acid density 6.7.1.2 Checking the acid level connections © 25 895 0 © 24 232 3 © 25 896 0 Remove sealing caps 1. Keep the battery clean and dry.
-
Page 77
Care and maintenance work 6.7 Add-on parts Acid density in [kg/ l] Charge level Normal Tropics 1.28 1.23 well charged 1.20 1.12 half charged, re-charge 1.12 1.08 discharged, charge immediately The gases released by the battery are explosive! Avoid sparks and open fire in the vicinity of the battery! Do not allow acid to get on skin or clothes! -
Page 78: Transportation Suspension
Care and maintenance work 6.7 Add-on parts 6.7.2 Three-phase current 6.7.3 Transportation suspension generator Notes on three-phase current system: Do not interrupt the connections between the battery, generator and governor when the engine is running. If, however, an engine must be started and operated without battery, the connection go- vernor / generator is to be separated before starting.
-
Page 80: Faults, Causes And Remedies
Faults, causes and remedies 7.1 Fault table 7.2 Engine management…
-
Page 81
A corresponding fault table can be found overleaf. If you cannot recognise the cause of a fault or cannot remedy a fault yourself, please contact your DEUTZ Service. Before starting make sure that there is nobody in the engine/ work machine danger area. -
Page 82
7.1 Fault table Faults, causes and remedies Faults Action Engine doesn’t start up, or starts up with difficulty Engine doesn’t start up and diagnosis light is blinking Check Engines starts up, but runs irregularly or misfires Engine gets too hot. Temperature warning system is activated Change Engine lacks power Engine lacks power and diagnosis light is lit up… -
Page 83
7.1 Fault table Faults, causes and remedies Faults Action Engine doesn’t start up, or starts up with difficulty Check Engine doesn’t start up and diagnosis light is blinking Engines starts up, but runs irregularly or misfires Change Engine gets too hot. Temperature warning system is activated Clean Engine lacks power Fill up… -
Page 84: Engine Protection Function Of The
7.2 Engine management Faults, causes and remedies 7.2.3 Table of fault blink codes 7.2.1 Engine protection function of 7.2.2 Using the diagnosis button the electronic engine controller EMR3 Depending on the design of the monitoring With the diagnosis button (1) the fault at hand can functions, the EMR3 can protect the engine be read out as a blink code.
-
Page 85
7.2 Engine management Faults, causes and remedies Blinkcode Function / Component Error Short Long Short 0.4s 0.8s 0.4s Output to coolant temperature light Signal faulty, Overtemperature control unit Hand accelerator Signal faulty / implausible Suction air temperature sensor Signal faulty Gear oil temperature sensor Signal faulty Monitoring rail pressure… -
Page 86
7.2 Engine management Faults, causes and remedies Blinkcode Function / Component Error Short Long Short 0.4s 0.8s 0.4s Monitoring camshaft/crankshaft No camshaft signal, no crankshaft signal Monitoring camshaft/crankshaft Deviation between the camshaft and crankshaft signal Engine protection: Overspeed/override status implausible Fuel low pressure sensor Signal faulty Monitoring fuel low pressure… -
Page 87
7.2 Engine management Faults, causes and remedies Blinkcode Function / Component Error Short Long Short 0.4s 0.8s 0.4s Monitoring oil pressure Pressure outside the nominal range Monitoring coolant temperature Temperature above the nominal range Monitoring suction intake air temperature Temperature above the nominal range Monitoring coolant state Level below the nominal range Monitoring fuel temperature… -
Page 88
7.2 Engine management Faults, causes and remedies Blinkcode Function / Component Error Short Long Short 0.4s 0.8s 0.4s Hydraulic oil temperature sensor Signal faulty Monitoring hydraulic oil temperature Temperature outside the nominal range Monitoring battery Voltage outside the nominal range Output to cold start aid indicator lamp Signal faulty, overtemperature control unit Output to external EGR actuator… -
Page 89
7.2 Engine management Faults, causes and remedies Blink code Function / Component Error Short Long Short 0,4s 0,8s 0,4s Output to start relay Signal faulty, overtemperature control unit Output to error lamp Signal faulty, overtemperature control unit Monitoring terminal 15 No signal detected Monitoring terminal 50 Permanent signal detected… -
Page 90: Engine Corrosion Protection
Engine corrosion protection 8.1 Corrosion protection…
-
Page 91
Engine corrosion protection 8.1Corrosion protection Corrosion protection If the engine should be shut down for a long period of time, corrosion protection will be necessary in order to prevent rust formation. The measures described here apply for a shutdown period of up to approx. 6 months. Before the engine is commissioned again the corrosion protection should be removed. -
Page 92: Technical Data
Technical data 9.1 Engine and setting data 9.2 Screw tightening torques 9.3 Tools…
-
Page 93
[°C] ————————————————————- 50 ———————————————————— Direction of rotation —————————————————— rotation to left —————————————————- Injection system Deutz Common Rail (DCR) ——————————— DCR + PLD —————————— DCR ———————————— Pump Line Nozzle (PLD) Weight TDC 2012 without cooling system according to DIN 70020-A [approx.kg] ————————————— 410 ———————————— 530 ————————————-… -
Page 94
Technical data 9.1 Engine and setting data Engine type —————————— TDC 2012 L04 2V —————— TDC 2012 L06 2V ————————— Cooling —————————————— Liquid-cooled / cooling system protection ————————— Coolant quantity (only engine content without cooler)[approx.ltr.] ————————————— 5.6 ————————————- 7.3 ————————————- Permissible continuous coolant temperature engine outlet [°C] ————————————————————— max.110 ——————————————————- Temperature difference between Coolant inlet/outlet… -
Page 95
[°C] ————————————————————- 50 ———————————————————— Direction of rotation —————————————————— rotation to left —————————————————- Injection system Deutz Common Rail (DCR) [bar] ———————————- DCR+PLD ——————————- DCR ———————————— Pump Line Nozzle (PLD) Weight TDC 2013 without cooling system according to DIN 70020-A [approx.kg] ————————————— 450 ———————————— 590 ————————————-… -
Page 96
Technical data 9.1 Engine and setting data Engine type —————————— TDC 2013 L04 2V —————— TDC 2013 L06 2V ————————— Cooling —————————————— Liquid-cooled / cooling system protection ————————— Coolant quantity (only engine content without cooler)[approx.ltr.] ————————————— 7.2 ————————————- 9.8 ————————————- Permissible continuous coolant temperature engine outlet [°C] ————————————————————— max.105 ——————————————————- Temperature difference between Coolant inlet/outlet… -
Page 97
Technical data 9.2 Screw tightening torques Installation Pre-tightening Re-tightening Total Comments [Nm] 1st step 2nd step 3rd step 4th step Cylinder head cover – – – – – 9 ± 1 Nm Lock nut Valves – – – – – 20 ±… -
Page 98
The special tools listed in this chapter must be ordered from: FA.WILBÄR Postfach 14 05 80 D-42826 Remscheid http://www.deutz-tools.com 25899 0 ©26 002 0 Order No. 8189 Order No. 8115 For engines of series 2012/2013, the TORX Measuring device for checking the prescribed screw system BN. -
Page 99
Technical data 9.3 Tools Rotation angle disc Socket wrench insert Crow’s foot wrench © 44 306 0 © 44 307 0 © 43 202 1 Order No. 8190 Order No. 8193 (5 mm) valve clearance Order No. 8199 Rotation angle disc for setting the valve/ Order No. -
Page 100
Technical data 9.3 Tools Turning gear © 35 423 1 Order No. 100 330 For turning over the engine (as add-on on the torsional vibration damper). -
Page 101: Service
Service Service For many years DEUTZ has stood for pioneering Thus, DEUTZ is not just a name for innovative Deutz-Mülheimer Str. 147-149 development in engine construction. As an inde- engines. But also for a complete service package D-51063 Cologne pendent manufacturer we offer a complete…
-
Page 102
DEUTZ AG Service-Information Systems Deutz-Mülheimer Str. 147-149 D-51057 Köln Tel.: ++49 (0)2 21-8 22-0 Fax: ++49 (0)2 21-8 22-53 58 Internet: www.deutz.de Printed in Germany All rights reserved 1st Edition, © 01/06 the engine company Order No.: 0312 1890…

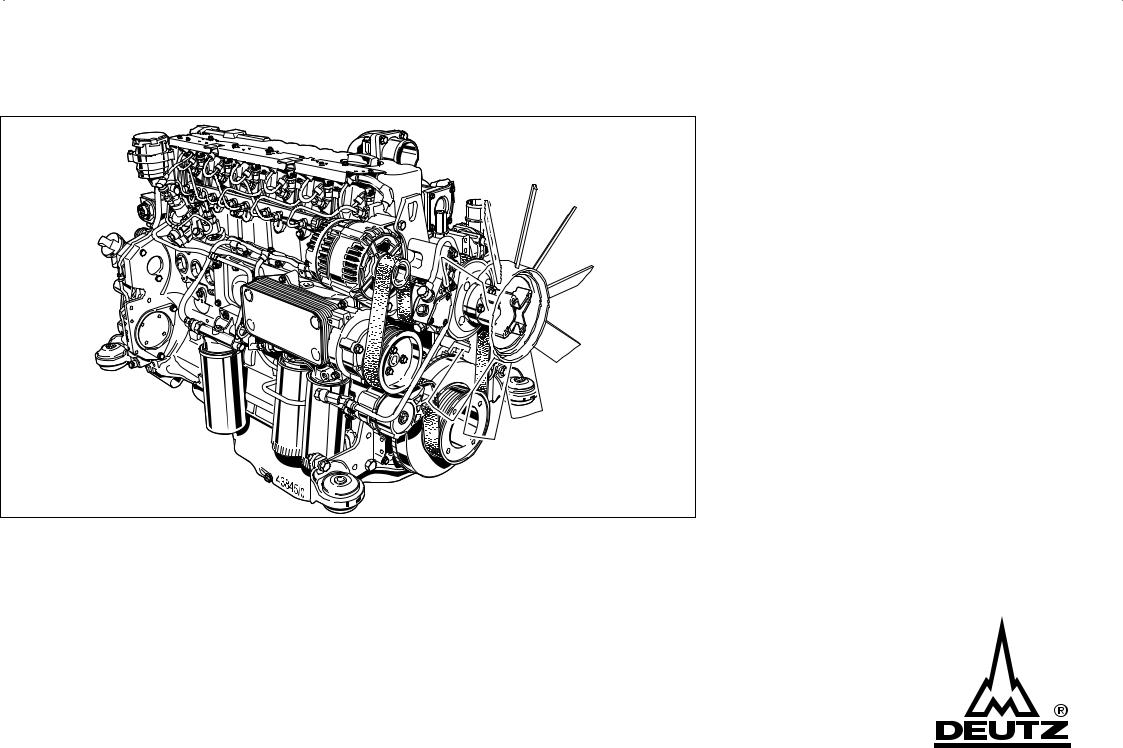
Operation Manual
TCD2012L04/06V2 TCD 2013 L04/06 V2

zRead and observe the information in this instruction manual. You will avoid accidents, retain the manufacturer’s warranty and have a fully functional, ready to use engine at your disposal.
zThis engine is exclusively for the purpose according to the scope of delivery — defined and built by the equipment manufacturer (use for the intended purpose). Any use above and beyond this is considered improper use. The manufacturer will not be liable for damages resulting from this. The user will bear the sole risk in this case.
zUse for the intended purpose also includes observance of the operating, maintenance and repair instructions specified by the manufacturer. The engine may only be used, maintained and repaired by persons who are familiar with it and instructed in the dangers.
zThe pertinent rules for the prevention of accidents and other generally recognised safety and industrial medicine rules must be observed.
zWhen the engine is running there is a danger of injury caused by:
—rotating / hot components
—engines with extraneous ignition
—ignition systems (high electrical voltage) Contact must be avoided!
zThemanufacturerwillnotbeliablefordamages resultingfromunauthorisedmodificationtothe engine.
Equally,manipulationstotheinjectionandcontrol system can affect the engine’s performance and the exhaust characteristics. Compliance with environmental regulations will no longer be guaranteed in this case.
zDo not alter, obstruct or block the area of the cool air supply to the fan.
The manufacturer will accept no liability for damages resulting from this.
zOnly DEUTZ original parts may be used when carrying out maintenance/repair work on the engine. These have been designed especially for your engine and ensure a trouble-free operation.
Failuretoobservethiswillleadtovoidingofthe warranty!
zMaintenance/cleaning work on the engine may only be carried out when the engine is not running and has cooled down.
When doing this, make sure that the electrical system is switched off (remove ignition key). The specifications for accident prevention with electrical systems (e.g. VDE-0100/-0101/ -0104/-0105 Electrical protective measures against dangerous touch voltages) must be observed.
Cover all electrical components tightly when cleaning with liquids.
zDo not work on the fuel system while the engine is running — Danger to life.
Wait (1 minute) for the engine to come to a standstill (pressure release), as system is under high pressure: there is a — Danger to life.
During the first trial run do not stand in the danger area of the engine (danger due to high pressure of leaks) — Danger to life.
—In case of leaks immediately contact the workshop.
—When working on the fuel system ensure that theengineisnotunintentionallystartedduring repairs — Danger to life.

Operation Manual
TCD 2012 L04/06 V2
TCD 2013 L04/06 V2
312 1890 en
Enginenumber:
Please enter the engine number here. This will simplify the handling of customer service, repair and spare parts queries (see Section 2.1).
Illustrationsanddatainthisinstructionmanualare subject to technical changes in the course of improvements to the engines. Reprinting and reproductions of any kind, even in part, require our written permission.

Foreword
Dear customer,
Theliquid-cooledenginesmade by DEUTZ are developed for a wide variety of applications. An extensive range of variants ensures that the respective special requirements are met.
Your engine is equipped according to the installation, i.e. not all the parts and components described in this instruction manual are installed on your engine.
We have done our best to clearly identify the differences, so that you can easily find the operating, maintenance and repair instructions relevant to your engine.
Please read these instructions before you start your engine and observe the operating and maintenance instructions.
We are at your service for any questions you may have in this matter.
Your
DEUTZAG
© 2005

1.General
2.Enginedescription
2.1Engine type
2.1.1Companyplate
2.1.2Location of company plate
2.1.3Enginenumber
2.1.4Cylindernumbering
2.2Engine diagrams
2.2.1Operation side TCD 2012 L04 2V
2.2.2Starter side
TCD 2012 L04 2V
2.2.3Operation side TCD 2012 L06 2V
2.2.4Starter side
TCD 2012 L06 2V
2.2.5Operation side TCD 2013 L04 2V
2.2.6Starter side
TCD 2013 L04 2V
2.2.7Operation side TCD 2013 L06 2V
2.2.8Starter side
TCD 2013 L06 2V
2.3Lube oil circuit
2.3.1Lube oil diagram (example)
2.4Fuel circuit
2.4.1Fueldiagram
2.5Coolant circuit
2.5.1Coolant diagram (example)
2.6Electrics
2.6.1Electrical cable connections for monitoring
3.Operation
3.1Initialcommissioning
3.1.1Fillingengineoil
3.1.2Fillingfuel
3.1.3Filling / bleeding cooling system
3.1.4Other preparations
3.2Starting
3.2.1Electrical starting
3.3Operation monitoring
3.3.1Engine oil pressure
3.3.2Coolant temperature
3.3.3Coolantlevel
3.4Shutting down
3.4.1Electrical shutdown
3.5Operating conditions
3.5.1Winter operation
3.5.2High ambient temperature, highaltitude
4.Operatingsubstances
4.1Lube oil
4.1.1Quality
4.1.2Viscosity
4.2Fuel
4.2.1Quality
4.2.2Winter fuel
4.3Coolant
4.3.1General
4.3.2Coolant preparation
5.Maintenance
5.1Maintenance schedule
5.2Maintenance diagram
5.3Maintenance work carried out
Contents
6.Care and maintenance
work
6.1Lubrication system
6.1.1Oil change intervals
6.1.2Checking oil level, changing engine oil
6.1.3Changing oil filter
6.1.4Cleaning / changing oil filter (cup)
6.2Fuel system
6.2.1Changing fuel filter
6.2.3Fuel pre-filter, changing / bleeding
filter insert
6.3Cooling system
6.3.1Cleaning intervals
6.3.2Cleaning cooling system
6.3.3Emptying cooling system
6.3.4Filling / bleeding cooling system
6.4Combustion air filter
6.4.1Cleaning intervals
6.4.2Emptying cyclone pre-separator
6.4.3Cleaning oil bath air filter
6.4.4Dry air filter
6.5Belt drive
6.5.1Checking V-belt
6.5.2Changing V-rib belt
6.5.3Checking wear limit of V-rib belt
6.6Setting work
6.6.1 Checking valve clearance, setting if necessary
6.6.2 Setting control piston clearance in exhaust gas recirculation (EGR)
|
6.6.3 Diagram for setting valve / control |
2005 |
|
piston clearance |
|
|
© |

Contents
6.7Add-on parts
6.7.1Battery
6.7.2Three-phase current generator
6.7.3Transportation suspension
7.Faults, causes and remedies
7.1Faulttable
7.2Enginemanagement
7.2.1Engine protection function of the electronic engine controller EMR3
7.2.2Using the diagnosis button
7.2.3Table of fault blink codes
8.Enginecorrosionprotection
8.1Corrosion protection
9.Technical data
9.1Engine and setting data
9.2Screw tightening torques
9.3Tools
10. Service
© 2005
General
|
DEUTZ Diesel Engines |
Care and Maintenance |
Service |
1 |
|
are the product of many years of research and development. The resulting know-how, coupled with stringent quality standards, guarantee their long service life, high reliability and low fuel consumption.
It goes without saying that DEUTZ Diesel Engines meet the highest standards for environmental protection.
Sound care and maintenance practices will ensure that the engine continues to meet the requirements placed on it. Recommended service intervals must be observed and service and maintenance work carried out conscientiously. Special care should be taken under abnormally demanding operating conditions.
Please contact one of our authorized service representatives in the event of breakdowns or for spare parts inquiries. Our trained specialists will carry out repairs quickly and professionally, using only genuine spare parts. Original parts from DEUTZ AG are always produced in accordance with state- of-the-art technology.
The Technical Circulars listed in the instruction manual are obtainable from your DEUTZ partner.
Please turn to the end of this manual for further service information.
|
Beware of Running Engine |
Safety |
Asbestos |
Shut the engine down before carrying out maintenance or repair work. Ensure that the engine cannot be accidentally started. Risk of accidents!
When working on the running engine, work clothing must be close fitting.
Observe industrial safety regulations when running the engine in an enclosed space or underground.
When the work is complete, be sure to refit any panels and guards that may have been removed.Never fill the fuel tank while the engine is running.
This symbol is used for all safety warnings which, if not observed, present a direct danger to life and limb for the person involved. Please follow
them carefully. The attention of operating personnel should be drawn to these safety instructions. General safety and accident prevention regulations laid down by law must also be observed.
DEUTZ original parts are asbestos-free.
© 2005

Engine description
2
2.1Engine type
2.2Engine diagrams
2.3Lube oil circuit
2.4Fuel circuit
2.5Coolant circuit
2.6Electrics
© 2005
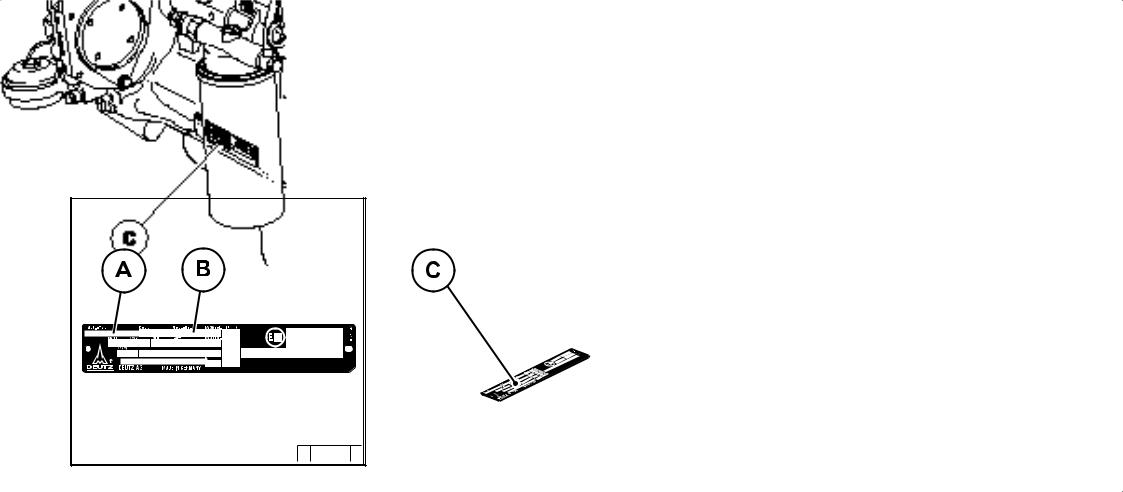
|
Engine description |
2.1 Engine type |
|
2 |
2.1.1 Company plate |
2.1.2 Location of company plate |
|
The engine type A, engine number B and the power data are stamped on the company plate. The engine type and number must be stated when purchasing spare parts.
|
© |
38 987 |
1 |
© |
43 834 |
0 |
|||
The company plate C is fixed to the cylinder head cover or the crankcase.
© 2005
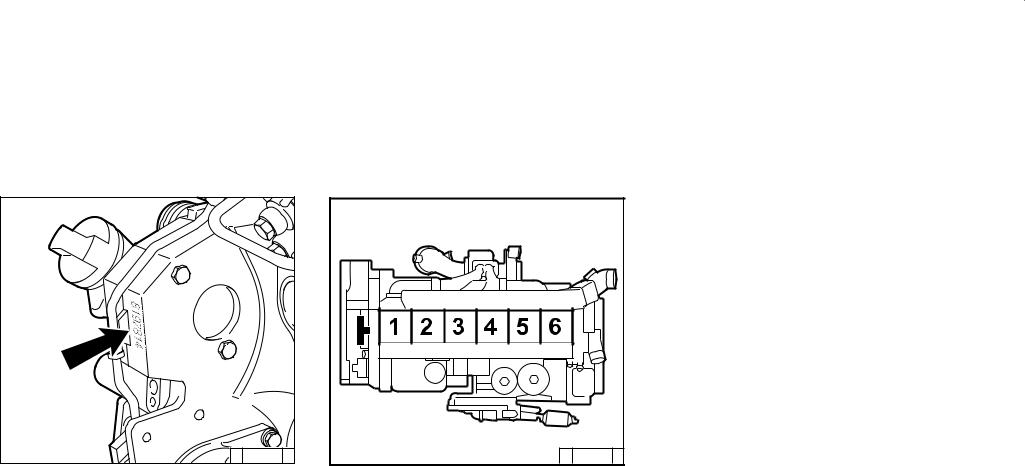
|
2.1 Engine type |
Engine description |
|
2.1.3 Engine number |
2.1.4 Cylinder numbering |
2 |
|
Theenginenumberisstampedonthecrankcase (arrow) and on the company plate.
The cylinders are counted consecutively, starting from the flywheel.
© 2005

|
Engine description |
2.2 Engine diagrams |
|
2 |
2.2.1 |
Operation side |
||
|
TCD2012L042V |
||||
|
1 |
Oil filler |
|||
|
2 |
Combustion air inlet |
|||
|
3 |
Cover |
|||
|
4 |
Fan |
|||
|
5 |
Generator |
|||
|
6 |
Fuel pump |
|||
|
7 |
Tension pulley with torsion spring |
|||
|
8 |
Oil cooler |
|||
|
9 |
Exchangeable fuel filter |
|||
|
10 |
Exchangeable lube oil filter |
|||
|
11 |
Oil tray |
|||
|
12 |
Hydraulic pump or compressor mounting |
|||
|
possibility |
||||
|
13 |
Flywheel |
|||
|
14 |
Crankcase bleeding valve |
|||
|
15 |
Transport eyes |
|||
|
16 |
Charge air pipe |
|||
|
17 |
Fuel control unit |
|||
|
© 2005 |
© 43 302 |
0 |
||
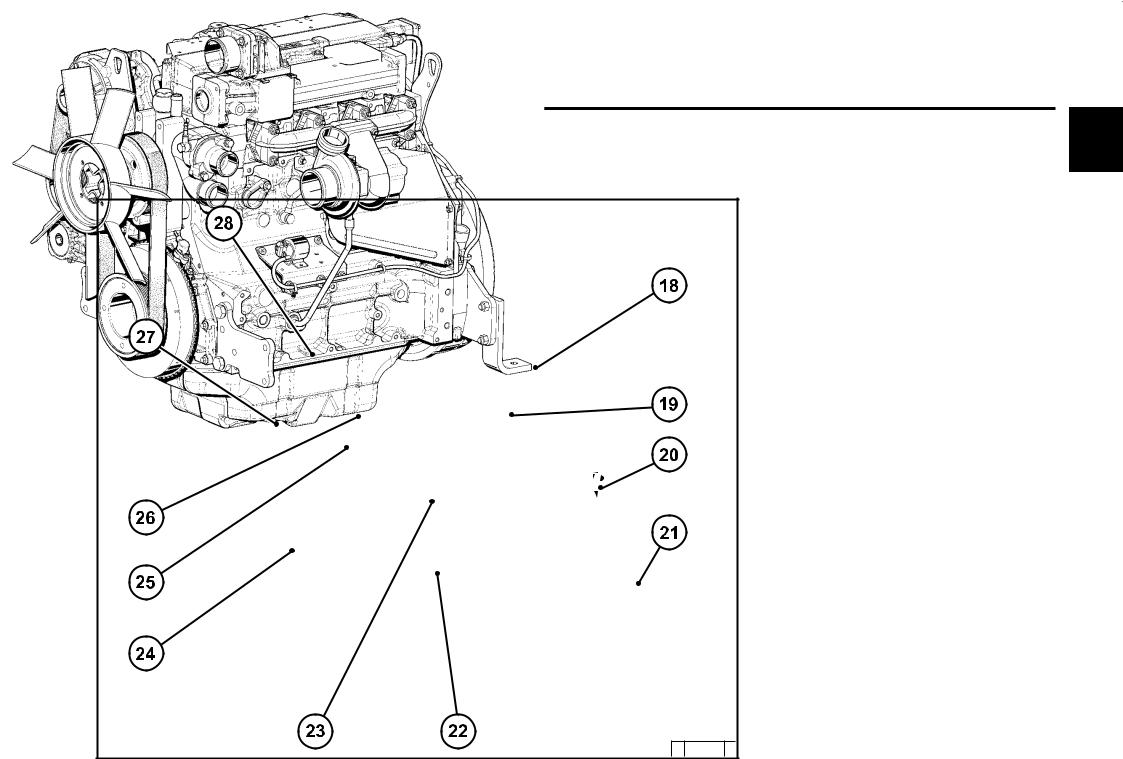
|
2.2 Engine diagrams |
Engine description |
|
2.2.2 |
Starter side |
|
|
TCD2012L042V |
||
|
© 44 303 |
0 |
2
18Exhaust manifold
19Turbocharger
20Oil filler (optional)
21Engine mounting
22Oil return line from turbocharger
23Relay (starter)
24V-rib belt
25Coolant inlet
26Coolant outlet
27Coolant pump
28Connection cabin heater or compensation line
© 2005
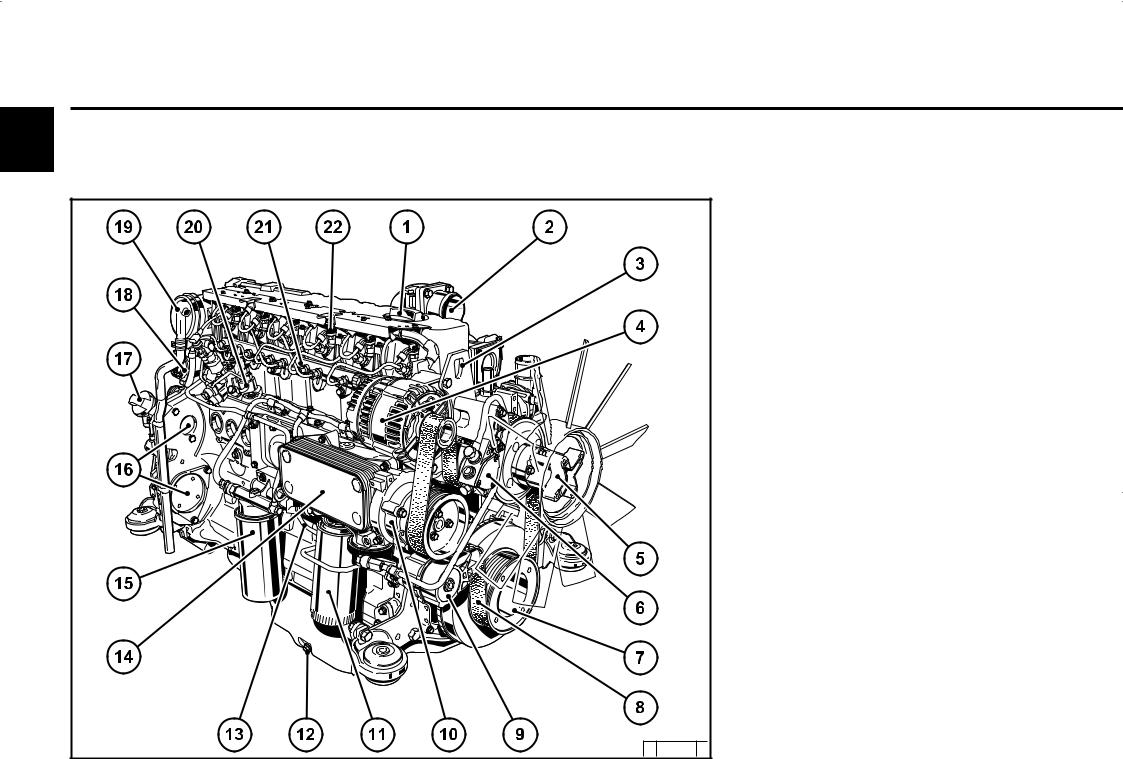
|
Engine description |
2.2 Engine diagrams |
|
2 |
2.2.3 |
Operation side |
||
|
TCD2012L062V |
||||
|
1 |
Oil filler |
|||
|
2 |
Combustion air inlet |
|||
|
3 |
Transport eyes |
|||
|
4 |
Generator |
|||
|
5 |
Fan hub |
|||
|
6 |
Fuelpump |
|||
|
7 |
V-rib belt drive on crankshaft |
|||
|
8 |
V-rib belt |
|||
|
9 |
Tension pulley with torsion spring |
|||
|
10 |
Coolantpump |
|||
|
11 |
Exchangeable lube oil filter (1x optional) |
|||
|
12 |
Oil drain screw |
|||
|
13 |
Oil dipstick |
|||
|
14 |
Lube oil cooler |
|||
|
15 |
Exchangeable fuel filter |
|||
|
16 |
Hydraulic pump or compressor installation |
|||
|
(optional) |
||||
|
17 |
Oil filler (optional) |
|||
|
18 |
Plug to control unit |
|||
|
19 |
Crankcase bleeding valve |
|||
|
20 |
High-pressure pump (2) |
|||
|
21 |
Rail |
|||
|
22 |
Injector |
|||
|
© 2005 |
© 43 828 |
1 |
||
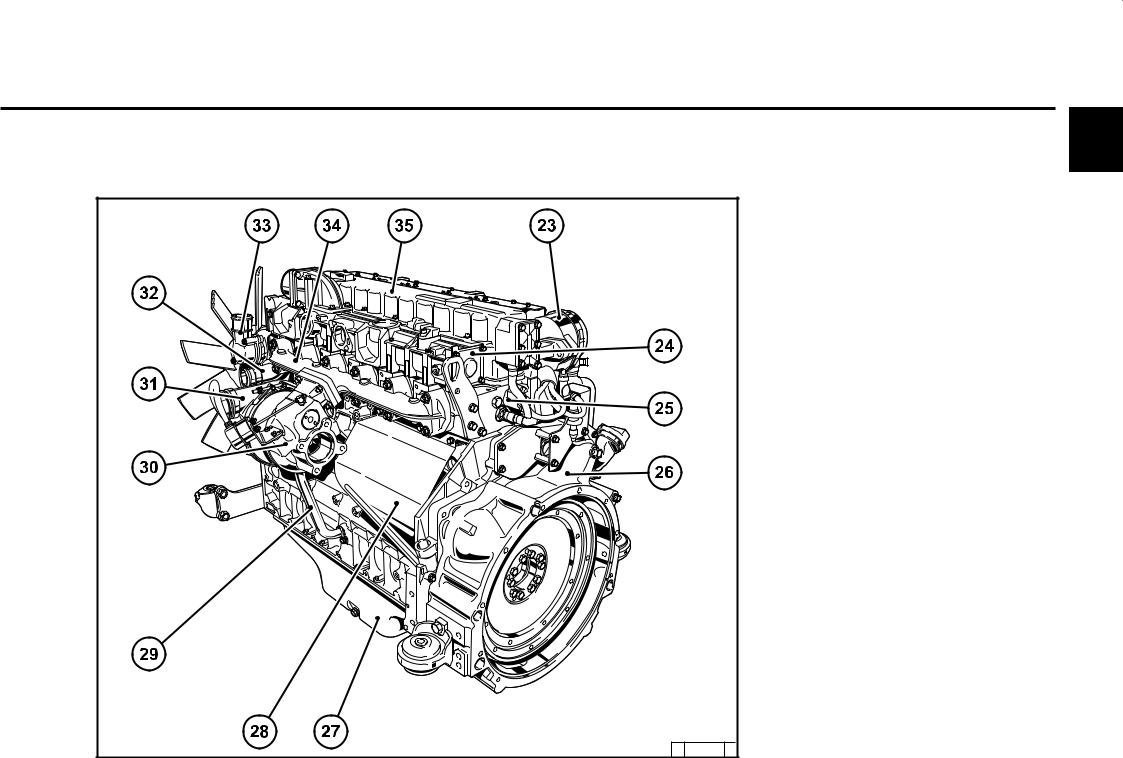
|
2.2 Engine diagrams |
Engine description |
|
2.2.4 |
Starter side |
|
|
TCD2012L062V |
||
|
© 43829 |
2 |
2
23Crankcase bleeding valve
24Charge air pipe
25Solenoid valve for exhaust gas recirculation
26SAE housing
27Oil tray
28Starter cover
29Oil return line from turbocharger
30Exhaust turbocharger
31Charge air connection to charge air cooler
32Coolant inlet
33Coolant outlet
34Exhaust manifold
35Cylinder head cover
© 2005

|
Engine description |
2.2 Engine diagrams |
|
2 |
2.2.5 |
Operation side |
||
|
TCD2013L042V |
||||
|
1 |
Combustion air inlet |
|||
|
(heating flange installation facility, optional) |
||||
|
2 |
Connection cabin heater or compensation |
|||
|
line |
||||
|
3 |
Fan (drive coolant pump) |
|||
|
4 |
Generator |
|||
|
5 |
Belt pulley on crankshaft |
|||
|
6 |
V-belt |
|||
|
7 |
Fuel pump drive |
|||
|
8 |
Exchangeable fuel filter |
|||
|
9 |
Exchangeable lube oil filter |
|||
|
10 |
Oil cooler |
|||
|
11 |
Drive facility (e.g. hydraulic pump, |
|||
|
optional) |
||||
|
12 |
Oil return line crankcase bleeding |
|||
|
13 |
Plug to control unit |
|||
|
14 |
Fuel control unit |
|||
|
(Electronic Control Unit) |
||||
|
15 |
High-pressure pump |
|||
|
16 |
Crankcase bleeding valve |
|||
|
17 |
Injector |
|||
|
18 |
Oil filler |
|||
|
© 2005 |
© 43 899 |
1 |
||
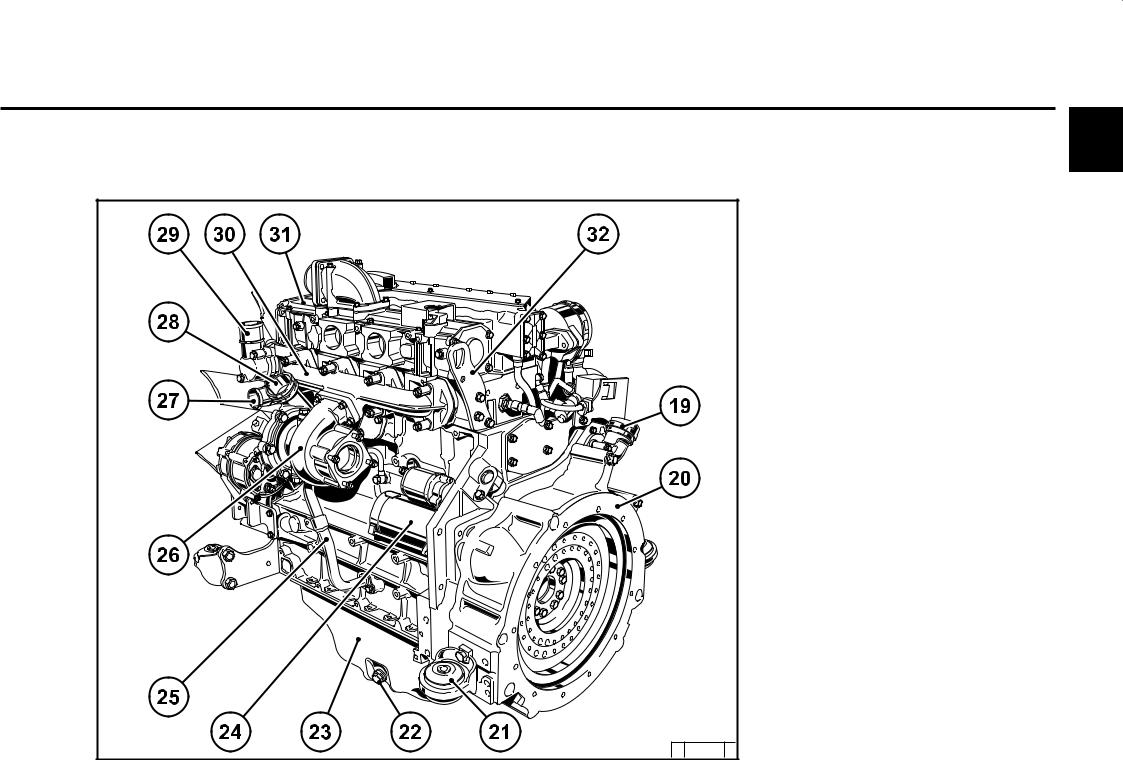
|
2.2 Engine diagrams |
Engine description |
|
2.2.6 |
Starter side |
|
|
TCD2013L042V |
||
|
© 43 900 |
3 |
2
19Oil filler (optional)
20SAE housing
21Enginemounting
22Oil drain screw
23Oil tray
24Starter
25Lube oil return from turbocharger
26Turbocharger
27Coolantinlet
28Charge air connection to cooler
29Coolant outlet
30Exhaust manifold
31Charge air pipe
32Transport eyes
© 2005
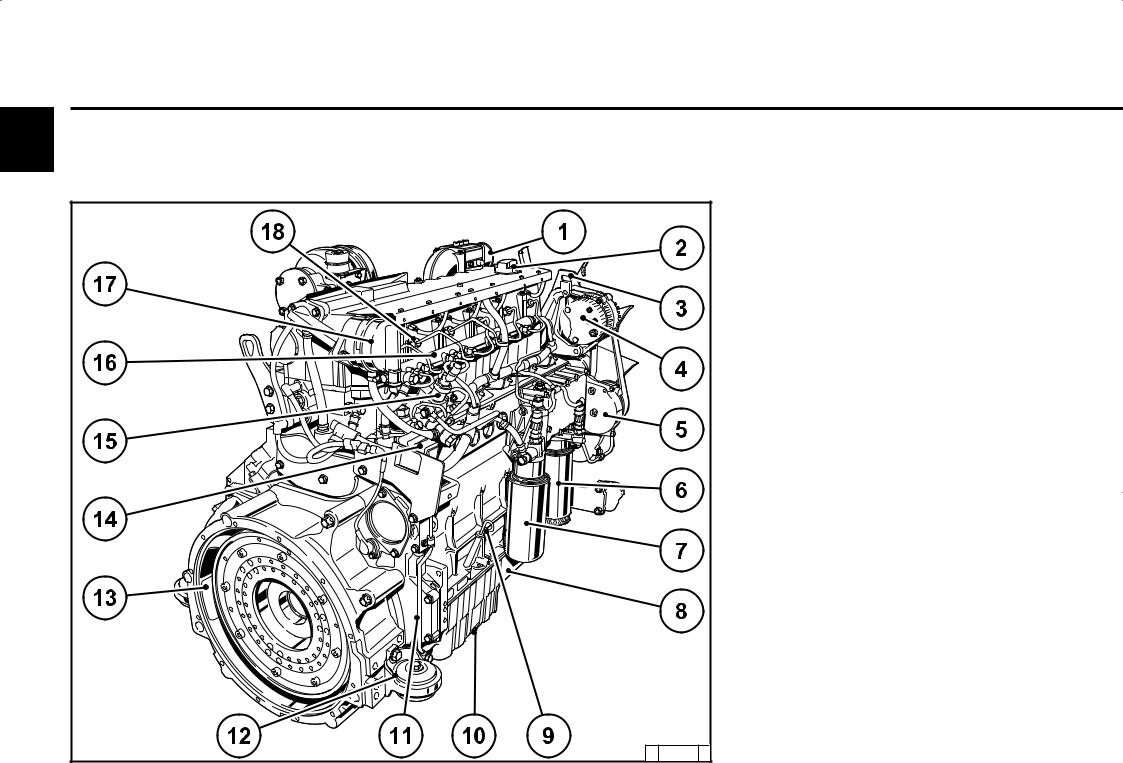
|
Engine description |
2.2 Engine diagrams |
|
2 |
2.2.7 |
Operation side |
||
|
TCD2013L062V |
||||
|
1 |
Combustion air inlet |
|||
|
2 |
Oil filler |
|||
|
3 |
Transport eyes |
|||
|
4 |
Generator |
|||
|
5 |
Coolantpump |
|||
|
6 |
Exchangeable lube oil filter |
|||
|
7 |
Exchangeable fuel filter |
|||
|
8 |
Oil tray |
|||
|
9 |
Oil dipstick |
|||
|
10 |
Oil drain screw |
|||
|
11 |
Oil return line crankcase bleeding |
|||
|
12 |
Enginemounting |
|||
|
13 |
SAE housing |
|||
|
14 |
Plug to control unit |
|||
|
15 |
High-pressure pump |
|||
|
16 |
Rail |
|||
|
17 |
Crankcase bleeding valve |
|||
|
18 |
Injector |
|||
|
© 2005 |
© 43 924 |
0 |
||
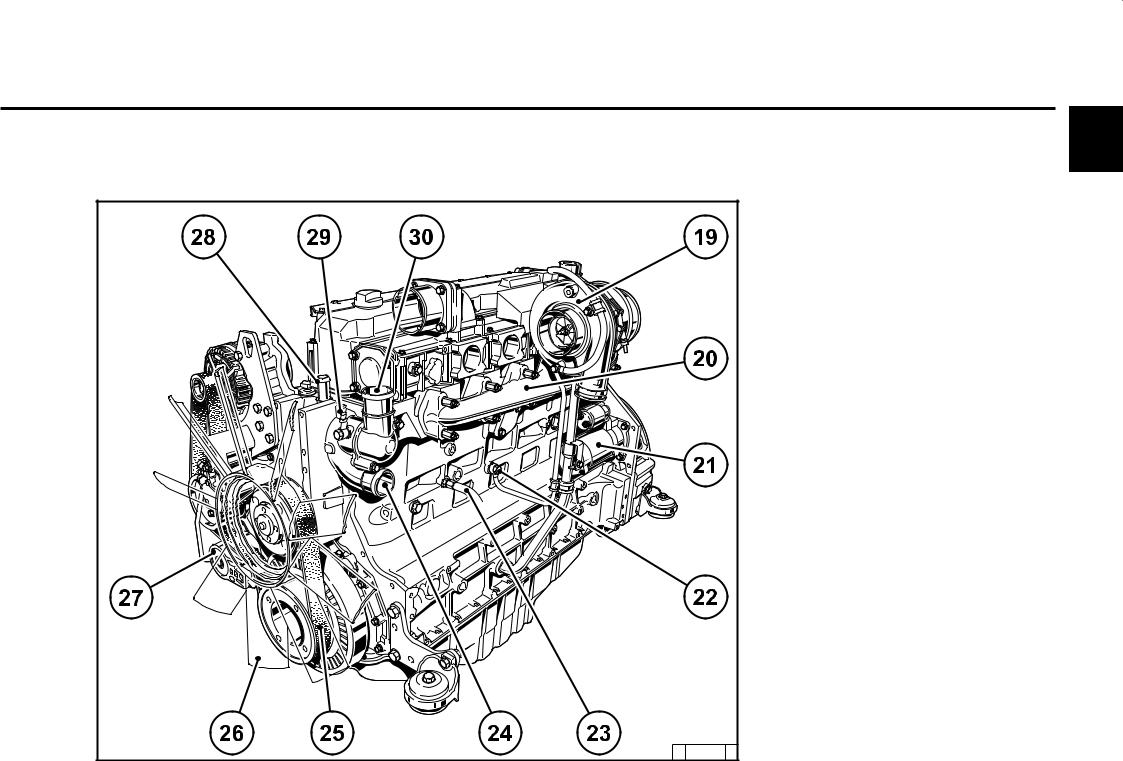
|
2.2 Engine diagrams |
Engine description |
|
2.2.8 |
Starter side |
|
TCD2013L062V |
|
|
© 43 925 1 |
2
19Turbocharger
20Exhaust manifold
21Starter
22Lube oil line to turbocharger
23Coolant drain screw
24Coolantinlet
25V-rib belt
26Fan
27Tension pulley with torsion spring
28Connection compensation line
29Ventilation line to compensation tank
30Coolant outlet from engine to cooler
© 2005
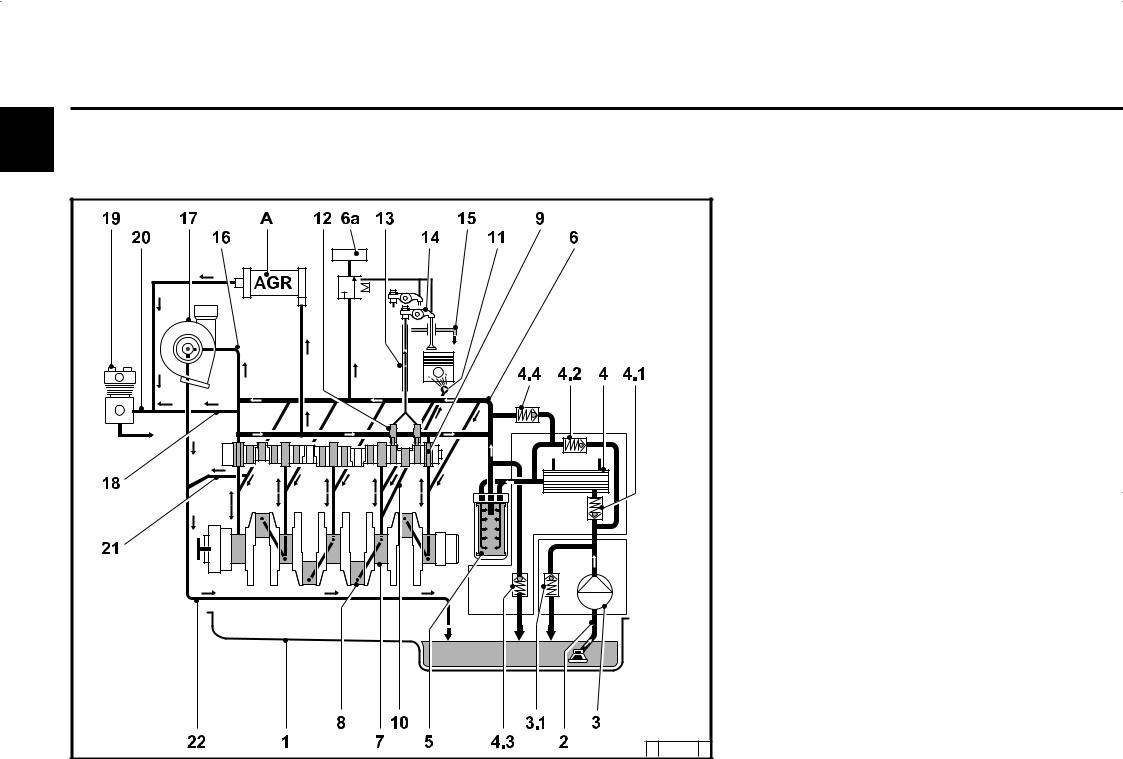
|
Engine description |
2.3 Lube oil circuit |
|
2 |
2.3.1 Lube oil diagram (example) |
|
1 |
Oil tray |
|
|
2 |
Intakepipe |
|
|
3 |
Lube oil pump |
|
|
3.1 Safety valve |
||
|
4 |
Lube oil cooler |
|
|
4.1 Return shutoff valve (only in 2012) |
||
|
4.2 By-pass valve |
||
|
4.3 By-pass valve oil filter |
||
|
5 |
4.4 Pressure control valve |
|
|
Exchangeable lube oil filter |
||
|
6 |
Mainoilpipe |
|
|
6a Internal exhaust gas recirculation |
||
|
7 |
Crankshaft bearing |
|
|
8 |
Con rod bearing |
|
|
9 |
Camshaft bearing |
|
|
10 |
Line to injection nozzle |
|
|
11 |
Injection nozzle for piston cooling |
|
|
12 |
Tappet with rocker arm pulse lubrication |
|
|
13 |
Stop rod, oil supply for rocker arm |
|
|
lubrication |
||
|
14 |
Rocker arm |
|
|
15 |
Return line to oil tray |
|
|
16 |
Lube oil line toexhaust turbocharger |
|
|
17 |
Exhaust turbocharger |
|
|
18 |
Return line from compressor 2x |
|
|
19 |
Compressor or hydraulic pump |
|
|
20 |
Oil line to compressor or hydraulic |
|
|
pump |
||
|
21 |
Return line from exhaust turbocharger |
|
|
©2005 |
20 |
|
|
© 4339 893012 |
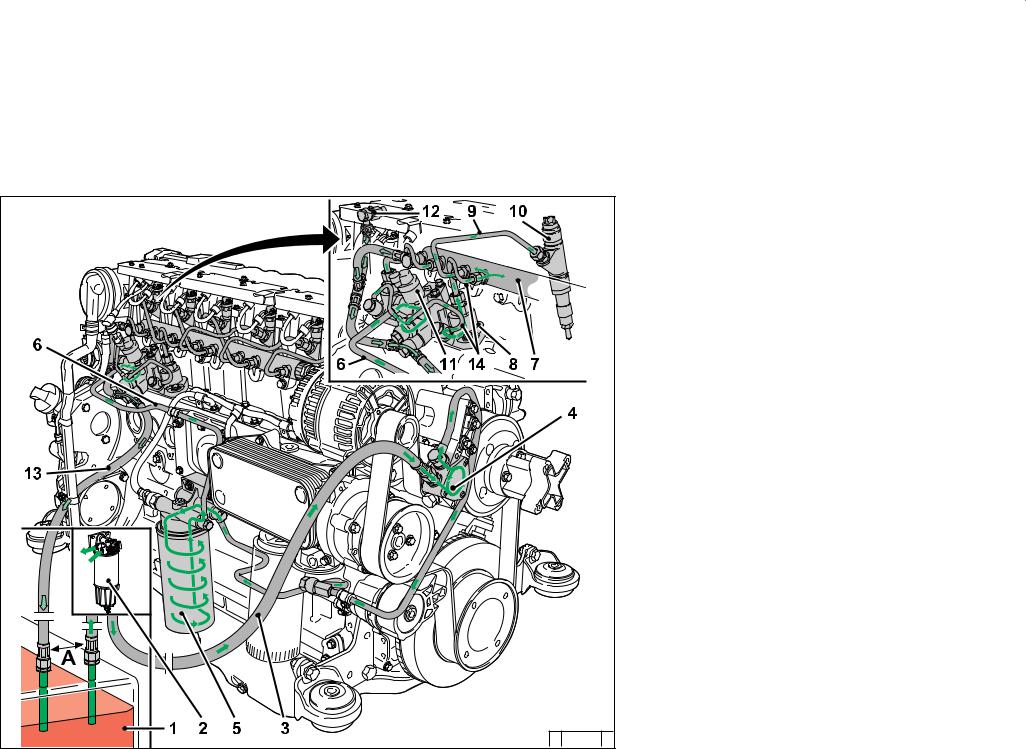
|
2.4 Fuel circuit |
Engine description |
1Fuel container
2Fuel pre-filter with pre-pressure pump possibility for filling the low pressure area (to be provided by the customer)
3Line to fuel pump
4Fuelpump
5Fuel filter
6Fuel supply line to fuel control unit
7Rail
8High-pressure pump
9Fuel line to injector
10Injectors
11Control block FCU (Fuel Control Unit)
12Fuel return at the cylinder head
13Fuel return line to the tank
14Fuel lines from the control block to the high — pressure pumps and to the rail
A min. distance 500 mm
© 2005
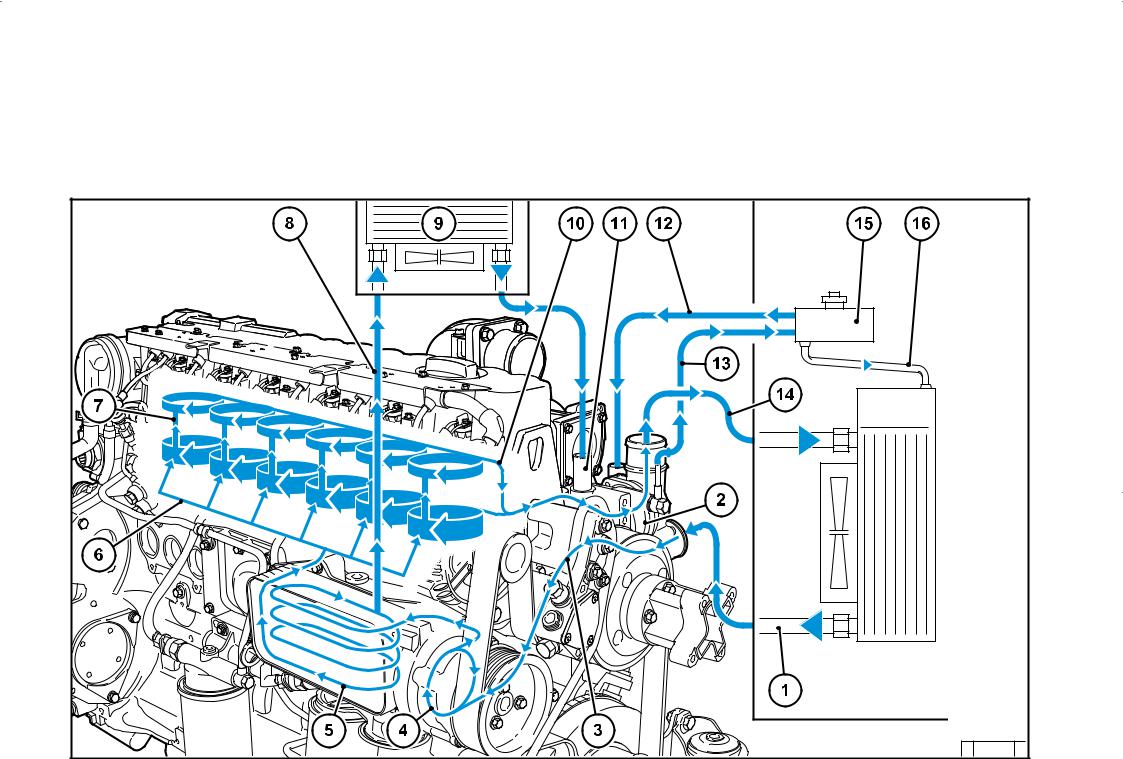
|
Engine description |
2.5 Coolant circuit |
|
2 |
2.5.1 |
Coolant diagram |
|
|
(example) |
|||

1Coolant outlet at the cooler
2Thermostat
3Coolant feed line to pump
4Coolantpump
5Lube oil cooler
6Cylinder cooling
7Cylinder head cooling
8Coolant inlet to heating
9Heating
10Coolant to thermostat
11Heating connection
12Compensation line
13Ventilation line to compensation tank
14Coolant outlet to cooler
15Compensation tank
16Compensation line to heat exchanger
© 2005

|
Engine description |
2.6 Electrics |
|
2 |
2.6.1 Electrical cable connections |
|||||||||||||||||||||
|
for monitoring |
||||||||||||||||||||||
1Solenoid valve EGR (optional)
2Coolant temperature
3Charge air pressure/temperature transmitter
4Connection facility example:
Control unit not mounted on the engine
5Engine control unit
6Speed governor via crankshaft
7Rail pressure, on side of rail
8Oil level transmitter (optional)
9Oil pressure transmitter
10Fuel pressure
11Speed governor via camshaft
12Central plug (for engine control)
13Power supply (battery)
14Multifunction displays
15Outputs (configurable, e.g. for lamps, torque (PWM), speed, engine running signal, etc.)
16Inputs (configurable) (PWM/digital/analogue)
17Accelerator pedal
18Hand throttle (optional)
19Switch functions (optional, e.g. for P factor, controller type, roof curves, fixed speeds, (etc. also multistage switches))
20Key switch Start/stop
21Diagnosis button
22Fault light with blink code
23Diagnosis interface / CAN-Bus

Other application-side components (depending on the application)
zWater trap fuel filter, see chap. 6.2.3
zOverride key, see chap. 3.3.1 (for temporary bypassing of the engine protection functions)
zCoolant level transmitter
zSeparate engine stop switch
zFan control
zSwitch for brake contact, engine brake, clutch
zDrive speed sensor, drive speed control unit (+ — keys, for speed increase reduction)
zCold start aid control lamp, see chap. 3.2.1
If there is a serious fault, e.g. the heating flange draws current although the control unit does not control it, this lamp flashes. The power supply to the heating flange must then be disconnected separately (overheating protection heating flange).
© 2005

Operation
3
3.1Initial commissioning
3.2Starting
3.3Operation monitoring
3.4Shutting down
3.5Operating conditions
© 2005
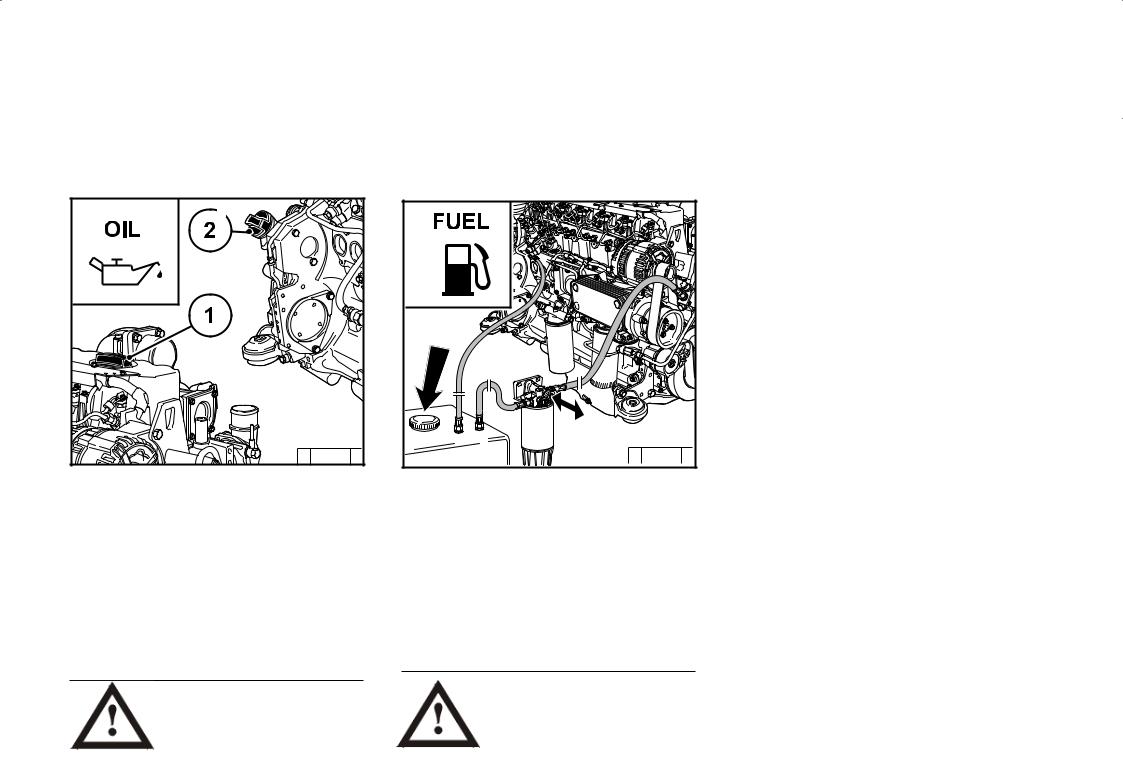
|
Operation |
3.1 Initial commissioning |
||
|
3 |
3.1.1 Filling engine oil |
3.1.2 Filling fuel |
|
© 2005
The engines are generally supplied without oil filling.
Fill engine with lube oil through the oil filler (1) on the cylinder head cover. Alternatively, you can fill on the wheel box (2) or on the side of the crankcase.
For oil filling amount see 9.1.
For quality and viscosity of oil see 4.1.
Oilmaynotbefilledintothedust collecting tank of the preseparator, if this is present.
Only use clean, standard, branded diesel fuel. For fuel quality see 4.2.
Depending on the outdoor temperature, use either summer or winter diesel fuel.
Bled the fuel low pressure system after filling, see 6.2.3.
Additional venting of the fuel system by a 5 minute trial run in idle or low load is absolutely essential.
Only re-fuel when the engine is not running!
Pay attention to cleanliness!
Do not spill any fuel!
|
3.1 Initial commissioning |
Operation |
||
|
3.1.3 Filling / bleeding |
3.1.4 Otherpreparations |
3 |
|
|
coolingsystem |
|||
zConnectconnectioncoolantoutlet1andcoolant inlet 2 to the cooling system. Connect the lead line from the compensation tank to the water pump or to the coolant inlet pipe 2.
zConnect the bleed lines from the engine and poss. from the cooler to the compensation tank.
zFill the cooling system through the compensation tank.
zClose the compensation tank with the valve.
zStart the engine and run warm until the thermostat opens (line 1 heats up).
zEngine run with open thermostat 2 — 3 minutes.
zCheck the coolant level in the compensation tank and top up the coolant if necessary.
zRepeat the process with engine start if necessary.
Never operate the engine without coolant (not even briefly).
zCheck battery and cable connections, see 6.7.1.
zTrial run
—After preparations carry out a short trial run of approx. 10 min.
Do not fully load the engine.
During and after the trial run
— Check engine for tightness.
With engine not running
—Check oil level, re-fill oil if necessary, see 6.1.2
—Check V-belt, re-tighten if necessary, see 6.5.
zRunning-in
Check the oil level twice a day during the running-in phase.
After the running-in phase, checking once a day is sufficient.
© 2005
|
3 |
3.2.1 Electricalstarting |
|
|
Before starting make sure that |
||
|
there is nobody in the engine/ |
||
|
work machine danger area. |
||
|
After repairs: Check that all |
||
|
protective equipment is |
||
|
mounted and all tools have been removed |
||
|
from the engine. |
||
|
When starting with heating plugs/heating |
||
|
flange, do not use additional start aids (e.g. |
||
|
injection with start pilot)! Danger of accidents! |
||
|
z Engine is electronically controlled by |
||
|
Example: EMR3 (electronic engine control) |
||
|
— engine is programmed and supplied with |
||
|
the necessary function configurations. |
||
|
z As far as possible separate engine from |
||
|
driven devices by disconnecting. |
||
|
z Engine connector plug must be connected |
||
|
by the customer (e.g in driver’s cab/ |
||
|
device) to at least: |
||
|
— Supply voltage |
||
|
— Torque output |
||
|
— Speed output. |
||
|
z Warm up the engine for approx. 30 seconds |
||
|
at a low idling speed. |
||
|
z Do not run up the engine immediately to |
||
|
high idling speed / full load operation from |
||
|
cold. |
||
|
If the starter is connected by a relay on |
||
|
the EMR3, |
||
|
— the maximum starting time is limited by |
||
|
the EMR3. |
||
|
2005© |
— the pause between two start attempts |
|
|
is given by the EMR3. |
||
without cold start aid
z Insert key
— Step 0 = no operating voltage. z Turn key to the right
— Step 1 = operating voltage, — Warning lights light up.
z Turn the key further to the right against the spring load.
— Step 2 = start
z Release key as soon as the engine starts up. — Warning lights go out.
© 26 411 0
—If the touch start function is programmed, a short start command with the ignition key suffices in position 2 or, if available, by a start button.
Thestartisthencontinuedautomaticallybythe EMR3.
—For special applications, the EMR3 can be programmed by data record so that the control unit performs other automatic start attempts if the engine fails to start.
Start the engine for a maximum of 20 seconds uninterrupted. If the engine does not start up, wait for one minute and then repeat the starting process. If the engine does not start up after two starting processes, determine the cause as per fault table (see 7.1).
Iftheenginedoesnotstartandthediagnosticlamp flashes, the EMR3 system has activated the start lock to protect the engine.
The start lock is released by switching off the systemwiththeignitionkeyforabout30seconds.

3.2 Starting
with cold start aid
Heating plug/heating flange
© 26 411 0
zInsert key.
—Step 0 = no operating voltage.
zTurn key to the right.
—Step 1 = operating voltage,
—Warning lights 1+2+3 light up.
—Pre-heatuntilheatingindicatorgoesout.Ifthe pre-heating indicator flashes, there is an error, e.g. pre-heating relay sticking which can fully discharge the battery at standstill.
—Engine is ready for operation.
zTurn the key further to the right against the spring load to
—Step 2 = start
zRelease key as soon as the engine starts up.
—Warning lights go out.
Caution: Engine must start within 30 seconds, if not, repeat the starting process.
© 2005
|
Operation |
3.3 Operation monitoring |
|
3 |
TheEMR3system monitors the engine condition |
|
and itself. |
|
|
The states are indicated by the diagnostic |
lamp. Lamp test:
z The diagnostic lamp lights for about 2s after ignition (ignition lock stage 1).
Steady light:
z There is an error in the system or a variable of the engine (temperature, pressure, etc.) is in the warning area. Depending on the error, the performance of the engine may be reduced by the EMR3 to protect the engine so that it is not in danger.
Fast flashing:
z Attention, the engine is in danger and must be switched off.
z Depending on the application, the control unit switches the engine off automatically.
z Thecontrolunitmayalsospecifyanidlespeed to cool the engine before shutting down.
z There may be a start lock after stopping the engine.
z Additional control lamps e.g. for oil pressure or oil temperature may be on.
z The override key can bypass the reduction in performance to avoid critical situations, as well as delay the automatic shutdown or bypass a start lock. This overwriting of the engine protection functions is logged in the control unit.
z The start lock is released by switching off the system with the ignition key for about 30 seconds.
3.3.1Engine oil pressure Oil pressure light
© 25 752 1
zThe oil pressure light comes on for about 2s after switching on the system.
zThe oil pressure light must be off when the engine is running.
Oil pressure gauge
© 25 754 0
zOilpressuregaugeshowsthelubeoilpressure (minimum lube oil pressure, see chap. 9.1).
© 2005

|
3.3 |
Operation monitoring |
Operation |
||||||||||||
|
3.3.2 |
Coolant temperature |
3.3.3 Coolant level |
3 |
|||||||||||
© 26 246 0
zThe needle of the temperature display should always be in the green area, and only as an exception in the yellow/green area. If the needle rises into the orange area the engine is getting too hot. Switch off the engine and determine the cause as per fault table (see 7.1).
min
© 26 291 1
zLightoncoolantleveldisplaycomeson(contact is via float switch/ level probe if coolant level is below minimum):
Switch off the engine and determine the cause as per fault table (see 7.1).
zFunction check of coolant level: — Coolant level OK: Light goes out
© 2005

|
Title |
File Size |
Download LInks |
|
Deutz 912 Parts Manual [PDF] |
4.3Mb |
Download |
|
Deutz 912 Technical Specifications [PDF] |
384.6kb |
Download |
|
Deutz 912-913 Repair Manual [PDF] |
5.8Mb |
Download |
|
Deutz 912-913 Service Manual [PDF] |
2.6Mb |
Download |
|
Deutz 912-913 Workshop Manual [PDF] |
34.5Mb |
Download |
|
Deutz F 3 L912 / W, F 4 L912 / W, F 5 L912 / W, B / F6 L912 / W Spare |
15.7Mb |
Download |
|
Title |
File Size |
Download LInks |
|
Deutz 2008-2009 Parts Manual [PDF] |
3.1Mb |
Download |
|
Deutz 2008-2009 Service Manual [PDF] |
4.4Mb |
Download |
|
Deutz 226B Operation Manual [PDF] |
8.5Mb |
Download |
|
Deutz 413 Parts Manual [PDF] |
4.5Mb |
Download |
|
Deutz Accessories Catalogue [PDF] |
5.2Mb |
Download |
|
Deutz BF4M1013C Spare Parts Catalogue [PDF] |
3Mb |
Download |
|
Deutz BFM 1015 Series — BF6M 1015 C, BF8M 1015, BF8M 1015 C, BF8M |
12.3Mb |
Download |
|
Deutz D 2008-2009 Workshop Manual [PDF] |
4.6Mb |
Download |
|
Deutz D 909 / 910, B / FL 1011 / F / 2011, B / FL 912 / 913 / 914 / |
7.8Mb |
Download |
|
Deutz Engine D2008 2009 Workshop Manual PDF [PDF] |
3.8Mb |
Download |
|
Deutz Engine Fire Protection — Operation Manual [PDF] |
21.2Mb |
Download |
|
Deutz Engine S-BV6-8-9M628 Operation Manual [PDF] |
10Mb |
Download |
|
Deutz FL 411 Service Manual [PDF] |
8.7Mb |
Download |
|
Deutz FL 413 Service Manual [PDF] |
8.7Mb |
Download |
|
Deutz Serie 7 Agrotron Service Manual [PDF] |
4.1Mb |
Download |
|
Gt-50dz Tow Tractor With Deutz Engine [PDF] |
36.1Mb |
Download |
|
Title |
File Size |
Download Links |
|
Deutz — Workshop Manual BFM 1008F part 1 [PDF] |
2.5Mb |
Download |
|
Deutz — Workshop Manual BFM 1008F part 2 [PDF] |
2.2Mb |
Download |
|
Deutz Engines B / FM 1008 / F Workshop Manual [PDF] |
2.7Mb |
Download |
|
Title |
File Size |
Download LInks |
|
Deutz 914 Parts Manual [PDF] |
4.3Mb |
Download |
|
Deutz 914 Service Manual [PDF] |
2.7Mb |
Download |
|
Deutz Engine 914 Operation Manual [PDF] |
3.2Mb |
Download |
Deutz — Workshop Manual BFM 1008F part 1
Deutz — Workshop Manual BFM 1008F part 1
Adobe Acrobat Document
2.5 MB
Deutz 0312 1936 2011 Workshop Manual
Deutz 0312 1936 2011 Workshop Manual.pdf
Adobe Acrobat Document
20.7 MB
Deutz 912-913 Workshop Manual
Deutz 912-913 Workshop Manual.pdf
Adobe Acrobat Document
34.6 MB
Deutz — Workshop Manual BFM 1008F part 2
Deutz — Workshop Manual BFM 1008F part 2
Adobe Acrobat Document
2.2 MB
Deutz 912-913 Service Manual
Deutz 912-913 Service Manual.pdf
Adobe Acrobat Document
2.8 MB
Deutz 914 Service Manual PDF
Deutz 914 Service Manual.pdf
Adobe Acrobat Document
2.8 MB
Deutz 1012-1013 Service Manual
Deutz 1012-1013 Service Manual.pdf
Adobe Acrobat Document
3.7 MB
Deutz 2008-2009 Service Manual
Deutz 2008-2009 Service Manual.pdf
Adobe Acrobat Document
4.5 MB
Deutz F3M 1011F, BF3M, F4M, BF4M Service Manual
Deutz F3M 1011F, BF3M, F4M, BF4M Service
Adobe Acrobat Document
1.3 MB
Deutz Serie 7 Agrotron Service Manual
Deutz Serie 7 Agrotron Service Manual.pd
Adobe Acrobat Document
4.5 MB
Deutz TCD 2015 Service Manual
Deutz TCD 2015 Service Manual.pdf
Adobe Acrobat Document
4.0 MB
Deutz 1015 Service Manual
Deutz 1015 Service Manual.pdf
Adobe Acrobat Document
2.9 MB
Deutz 2012 Service Manual
Deutz 2012 Service Manual.pdf
Adobe Acrobat Document
11.1 MB
Deutz FL 411 Service Manual
Deutz FL 411 Service Manual.pdf
Adobe Acrobat Document
8.7 MB
Deutz FL 413 Service Manual
Deutz FL 413 Service Manual.pdf
Adobe Acrobat Document
8.7 MB
Deutz TCD 2012-2013 Service Manual
Deutz TCD 2012-2013 Service Manual.pdf
Adobe Acrobat Document
3.9 MB
Deutz 413 Parts Manual
Deutz 413 Parts Manual.pdf
Adobe Acrobat Document
4.6 MB
Deutz 914 Parts Manual
Deutz 914 Parts Manual.pdf
Adobe Acrobat Document
4.4 MB
Deutz 2008-2009 Parts Manual
Deutz 2008-2009 Parts Manual.pdf
Adobe Acrobat Document
3.2 MB
Deutz 912 Parts Manual
Deutz 912 Parts Manual.pdf
Adobe Acrobat Document
4.4 MB
Deutz 1011 Parts Manual.pdf
Adobe Acrobat Document
2.0 MB
The German company Deutz AG has been producing engines for more than 130 years. Its emblem on diesel engines and gas engines is evidence of the highest quality of products, in
which the rich experience of several generations of talented German engineers and technicians is accumulated. The range of power units offered in 2001 includes dozens of basic models of motors
for various purposes with a power from 4 to 7,400 kW. The long way of Deutz AG to today’s achievements begins in the distant 1864. We will get acquainted with its main stages, especially since in
the history of the firm there were mutually beneficial contacts with our country.

So, the year 1864-th. German designer and inventor Nikolaus Otto, one of the first creators of an efficient internal combustion engine, gets acquainted with an entrepreneur from Cologne, Evgeny
Longen, a very wealthy and technically competent man, and inspires him to create a company that would manufacture industrial combustion engines-atmospheric gas engines.
Longen helps Otto to obtain a patent for the engine and conducts a «wide advertising campaign», demonstrating the motor at many exhibitions in the Old and New World. Finally, in 1867, the sample
was awarded a gold medal at an exhibition in Paris, and interest in it reached the level at which it was worth starting its production. In 1869, launched a large plant near Cologne, in the
suburbs of Doitz. The new enterprise is named after the names of its owners «Longen, Otto and Roosen». At the same time, the license for the production of the internal combustion gas engine of
the English company Crossley is being sold.
So, in the Old World a new compact energy source appeared on the market, ready to compete with bulky steam engines. In 1872 a new technical director — Gottlieb Daimler (the future inventor of the
car) was appointed to the reconstructed enterprise, and Wilhelm Maybach — the person no less legendary in the automotive industry — became the head of the design department. The company receives
the new name Gasmotoren-Fabrik Deutz AG and expands the scope of application of engines.
In 1879 Nikolaus Otto successfully completes the experiment to create the world’s first four-stroke engine with compression of the fuel-air mixture before its ignition — the prototype of most
modern gasoline engines. Encouraged by the success, the enterprise is again being reconstructed and preparing for a new round of development, despite the departure of G. Daimler and V. Maybach
from it. In 1886, Otto received his Ph.D. from the University of Wurzburg and, together with Robert Bosch, developed an electrical ignition system.

So, working engines that consumed a gasoline mixture, appeared. They are compact, fast and affordable. And all this, thanks to the pioneer of engine building, the company Deutz. In 1896, the
history of the automobile industry begins. At the same time much more powerful gasoline engines began to be installed on railroad locomotives.
However, the technical department of the company was not asleep. In 1898, a fundamentally new engine was constructed and presented to the public, having compression ignition. In honor of the
author, Rudolf Diesel, he was called a diesel engine. A new era in motor-building began.
By 1907, the design of the first sample had been worked out and patented; It was possible to start the production of diesel engines. Their consumption increased, and the size range expanded.
After the short-term production of Deutz-Bugatti cars (1907 — 1912) with the participation of the very creator, Ettore Bugatti, who worked in the company from 1907 to 1909, the management turned
its eyes to the tractors. The first machine of its own design came off the assembly line in 1924. The model was called Deutz MTN 222 and was equipped with special pulleys for driving agricultural
equipment.
At the same time, different types of engines were produced — for cars and trucks, rail cars, as well as industrial engines that were sent to other companies. Since 1921 the company was officially
called Motorenfabrik Deutz AG. In 1938 — the next transformation. Having acquired new plants, the company became known as Klockner-Humboldt-Deutz AG (KHD). In the same year, its technical
department developed another novelty — the first diesel with air cooling. However, soon everything changed abruptly. The bombing of factories by aircraft of the USSR and its allies destroys 74%
of the entire industrial potential of the concern. It was, as can be easily guessed, in late 1944 — the first half of 1945.
A new stage, called «restoration of former grandeur,» began in 1949. It was then that management decided to resurrect the production of agricultural tractors with air-cooled diesel engines. The
goods were dispersed in the market instantly. Gradually, together with the tractors, the production of trucks and buses began, which bore the brand of Magirus-Deutz and was considered one of the
best in Europe.
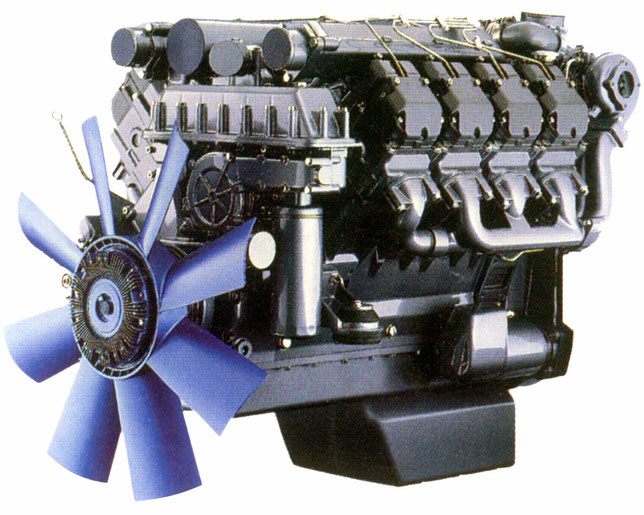
By 1964, a new Technical Center was built near Cologne, which increased the competitiveness of the structures being built. Machines with the KHD brand (dump trucks, construction chassis, diesel
engines) have been exhibited many times since 1964 at exhibitions in Moscow and have been evaluated by domestic experts. When the construction of the Baikal-Amur Mainline began, Deutz AG received
an unprecedented order for the supply in the USSR of 10,000 (!) First-class dump trucks that formed the basis of the contractors’ car fleet. Striking, but true: some of them are still on the go.
After the purchase of the USSR, the license for the right to produce Deutz diesel engines with air cooling, the specialists of the German company together with Russian engineers did a great job
of conducting full-scale tests of the motors on trucks Ural-375D, the ones for which they were intended. The design of the diesel engines was fully adapted to operation at temperatures from -40
to + 40 ° C. The work was carried out in 1966 — 1980 gg. As a result, a plant was built in Kustanai (now the Republic of Kazakhstan), designed to supply several tens of thousands of motors per
year. It was not possible to launch this enterprise before 1991, and then the Soviet Union did not. However, the experience gained in researching diesel engines under extreme conditions has
benefited both Deutz specialists and ours.
In 1975, the brand Magirus-Deutz disappeared from the automobile directories of current products. The truck and bus division was part of IVECO, a multinational concern controlled by FIAT. And the
company Deutz AG continued to engage in engine construction and tractors. In 1978, the production of a 4 millionth internal combustion engine was commemorated in the year 1867. The next such
event occurred only in 1989. And also in connection with the release of a 4 millionth diesel engine, but only with air cooling. Their production began in 1944. In 1995, the department for the
production of tractors and agricultural machines was sold to the Italian company Same Group, and the firm Deutz AG focused on where it started: the engines supplied to a wide variety of
manufacturers. «Everything has returned to normal.»
However, the history of this amazing company does not end there … There are still many interesting projects ahead of it, among them … the organization of the assembly of Deutz diesel engines
in Russia. Were you surprised? Nothing surprising. We need good diesel engines, and Russia needs Deutz AG. That’s all.









